AP Psychology: Topic 3.6 - Social-Emotional Development Across the Lifespan, AP Psychology: Topic 3.1 - Themes and Methods in Developmental Psychology, AP Psychology: Topic 3.2 - Physical Development Across the Lifespan, AP Psychology: Topic 3.4 - Co…
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
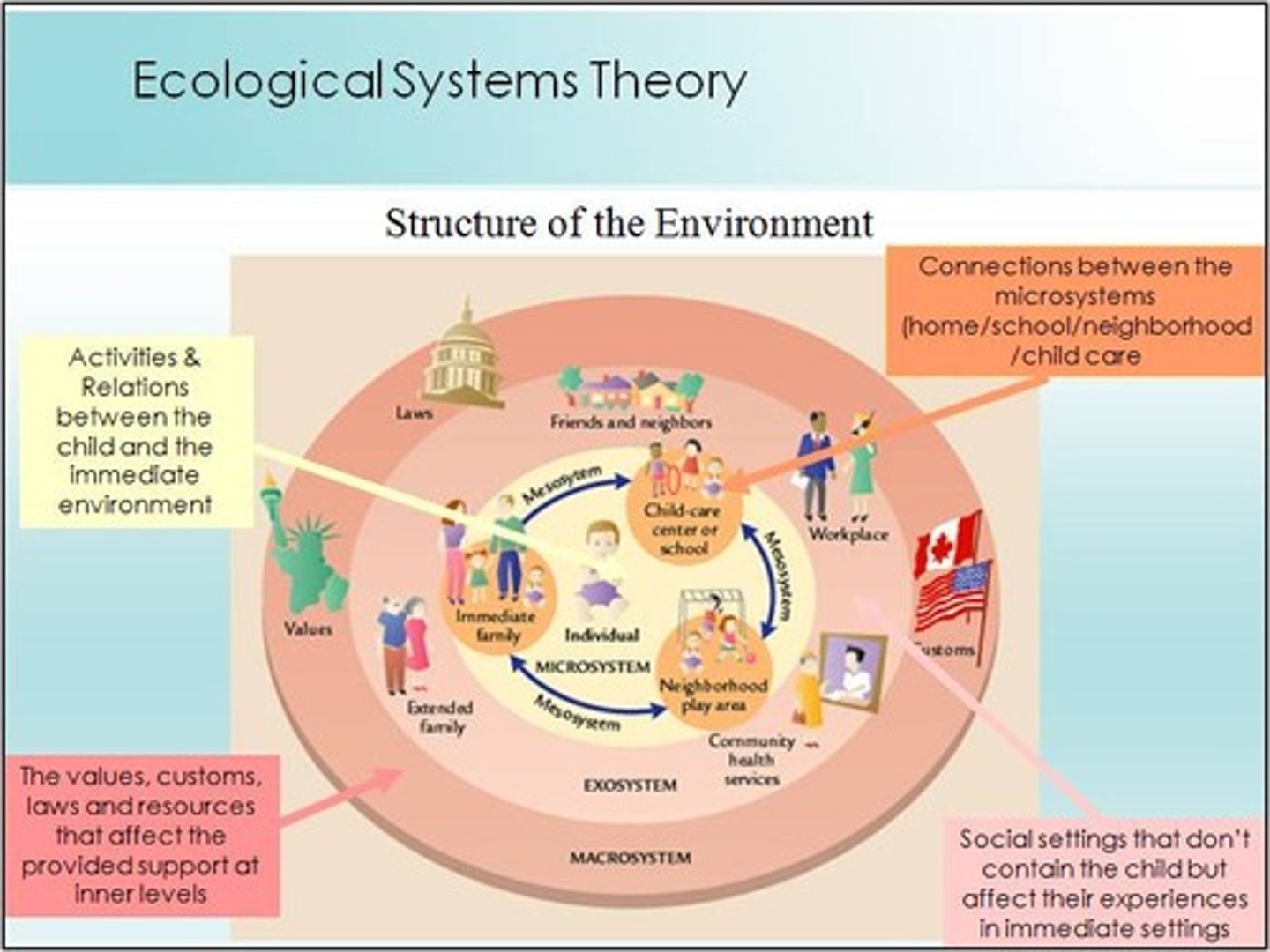
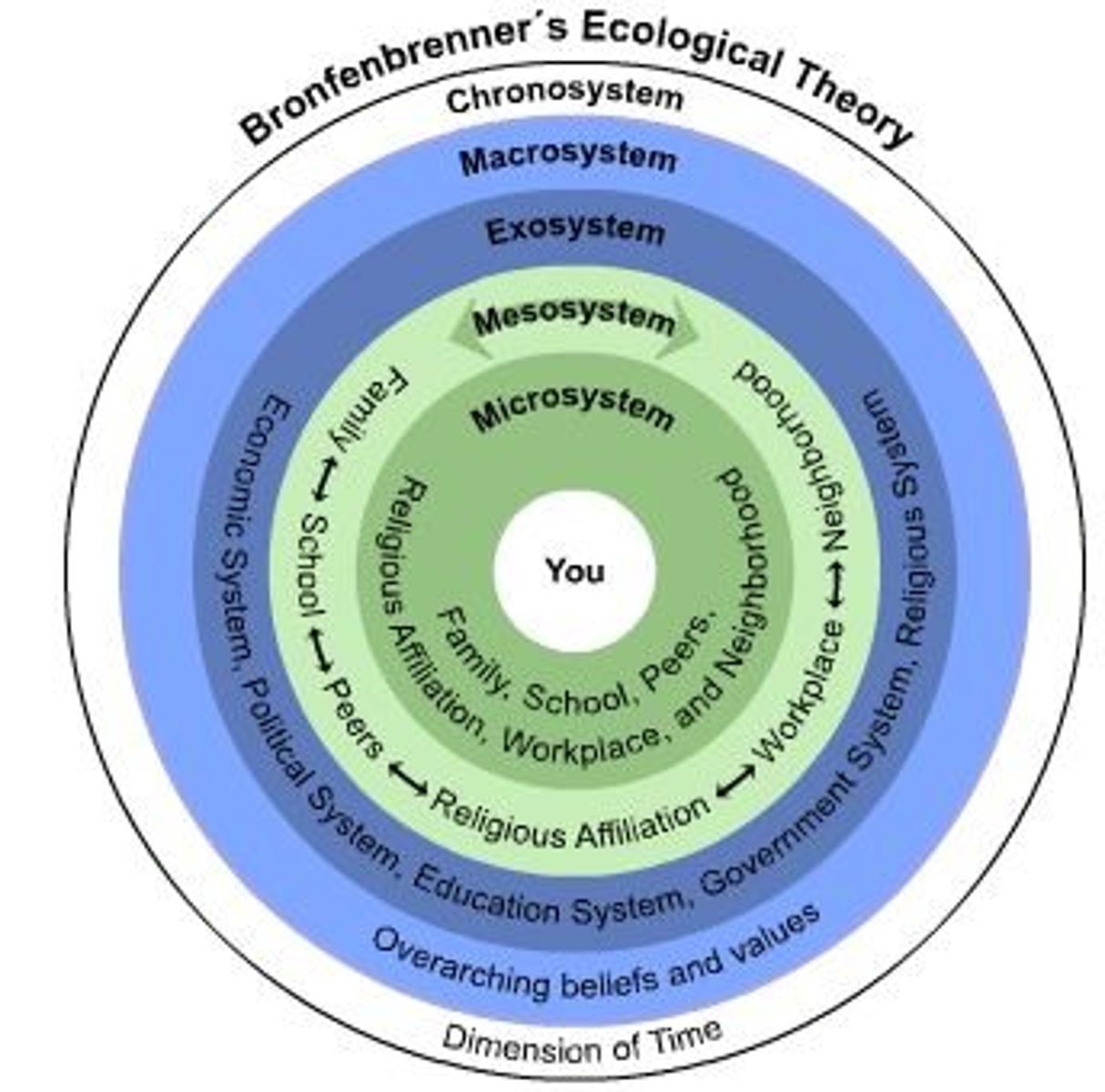
Ecological systems theory
holds that people encounter different environments throughout their lifespan that may influence behavior in varying degrees
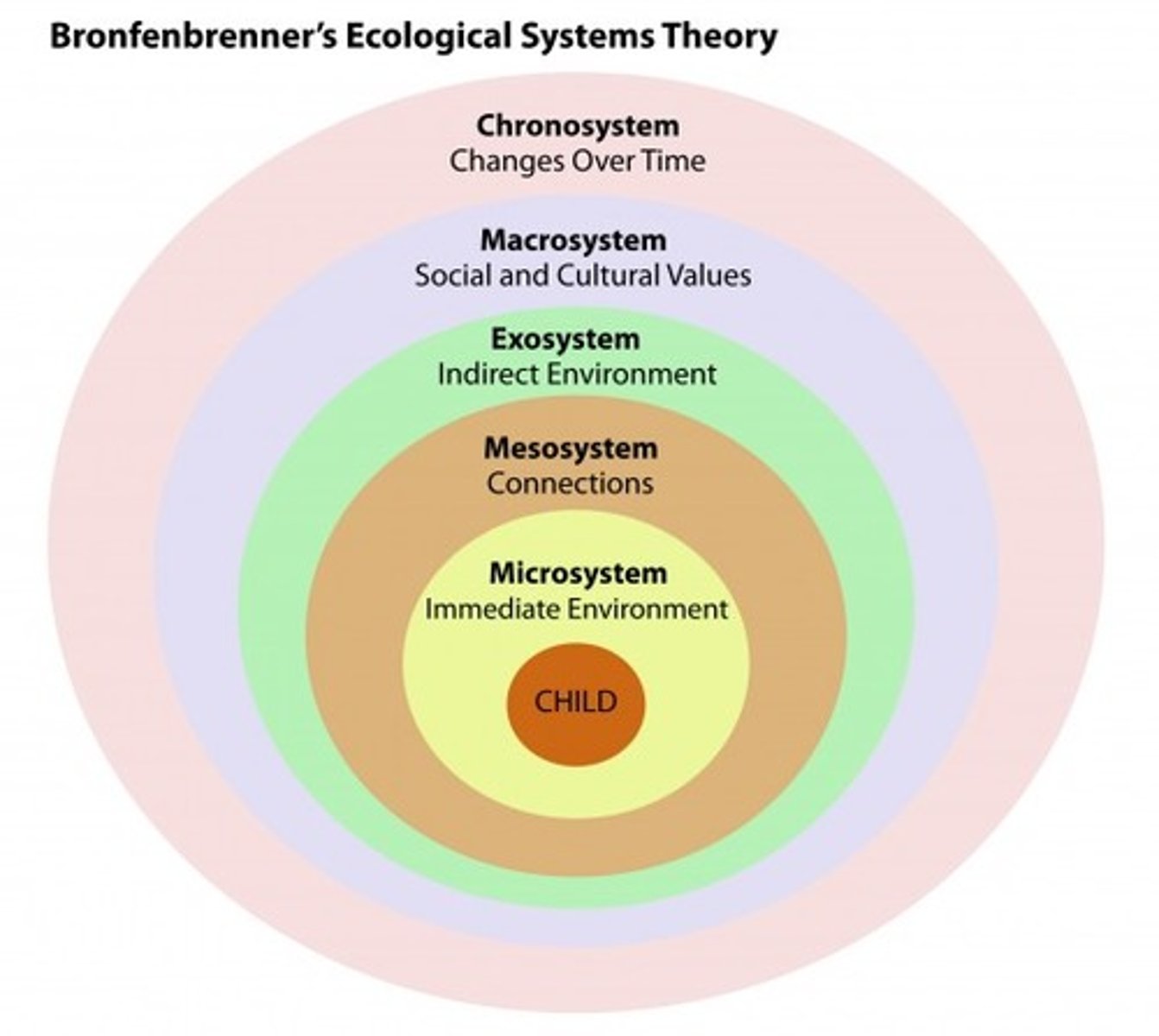
Microsystem
an individual's immediate environment which includes the people the person interacts with daily, having the most direct, immediate impact on the individual
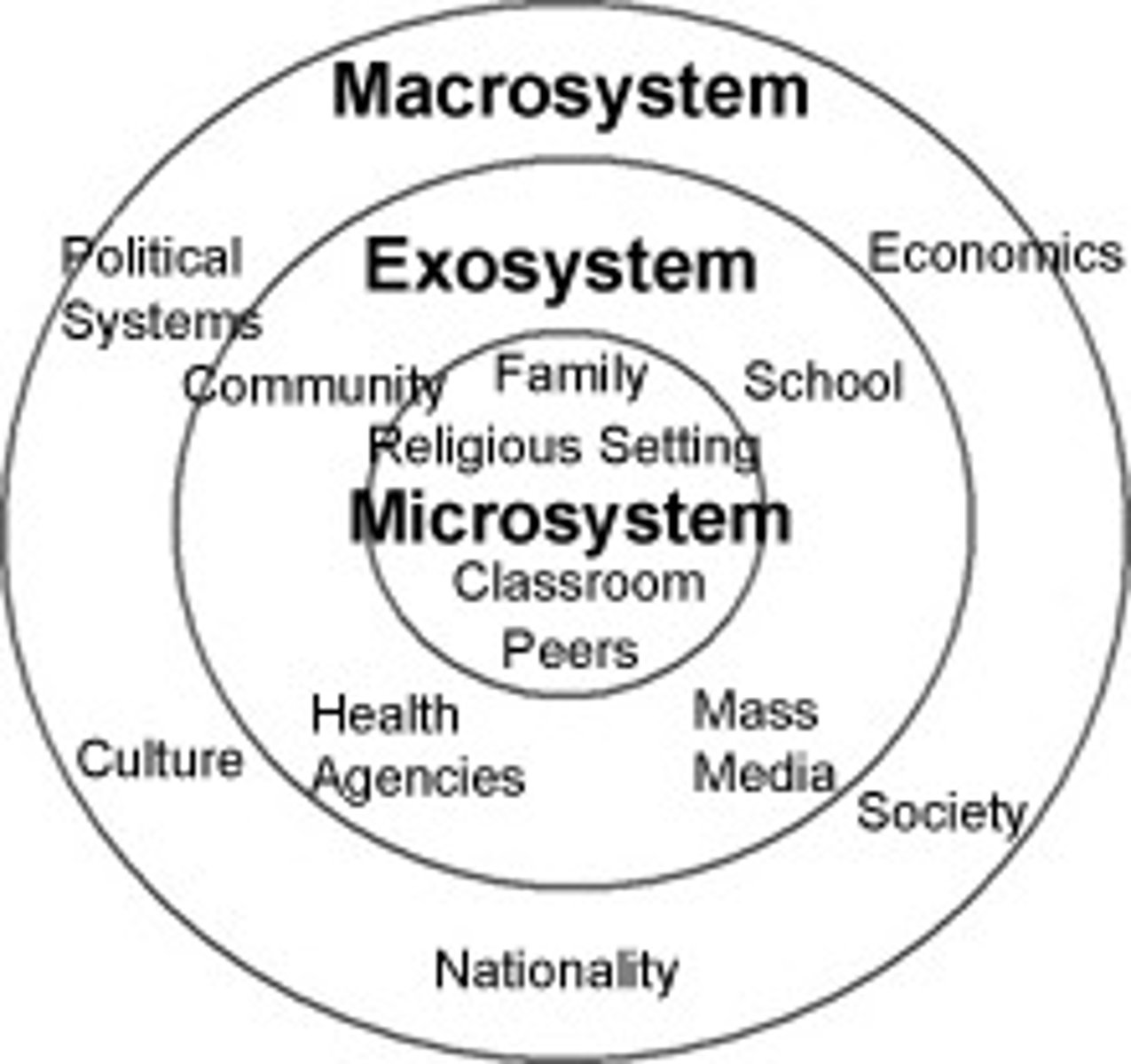
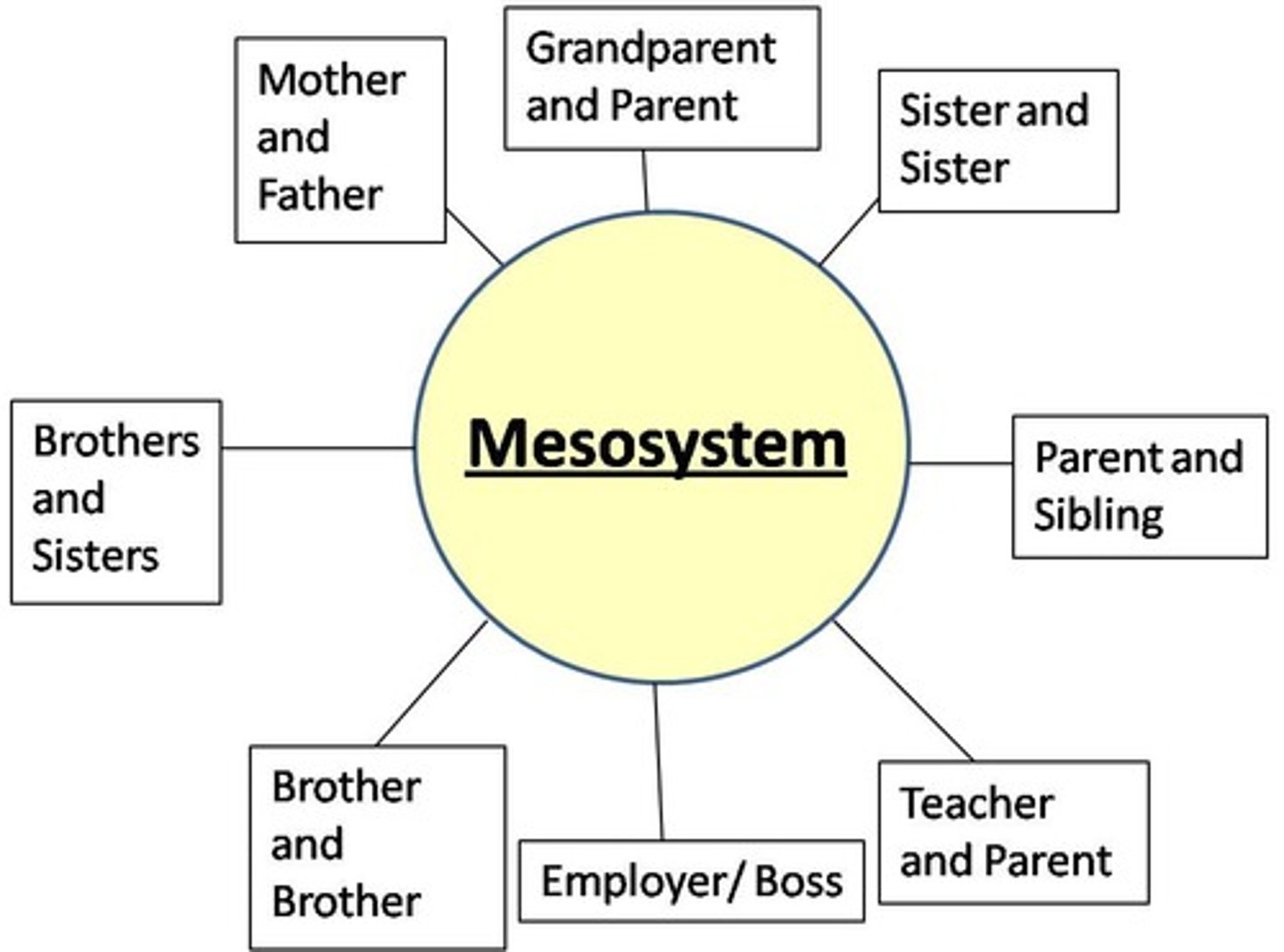
Mesosystem
a connection of two or more microsystems, such as a child's home and school
Exosystem
environments in which an individual is not an active participant, yet these still impact the person's development (e.g., mass media or government policies)
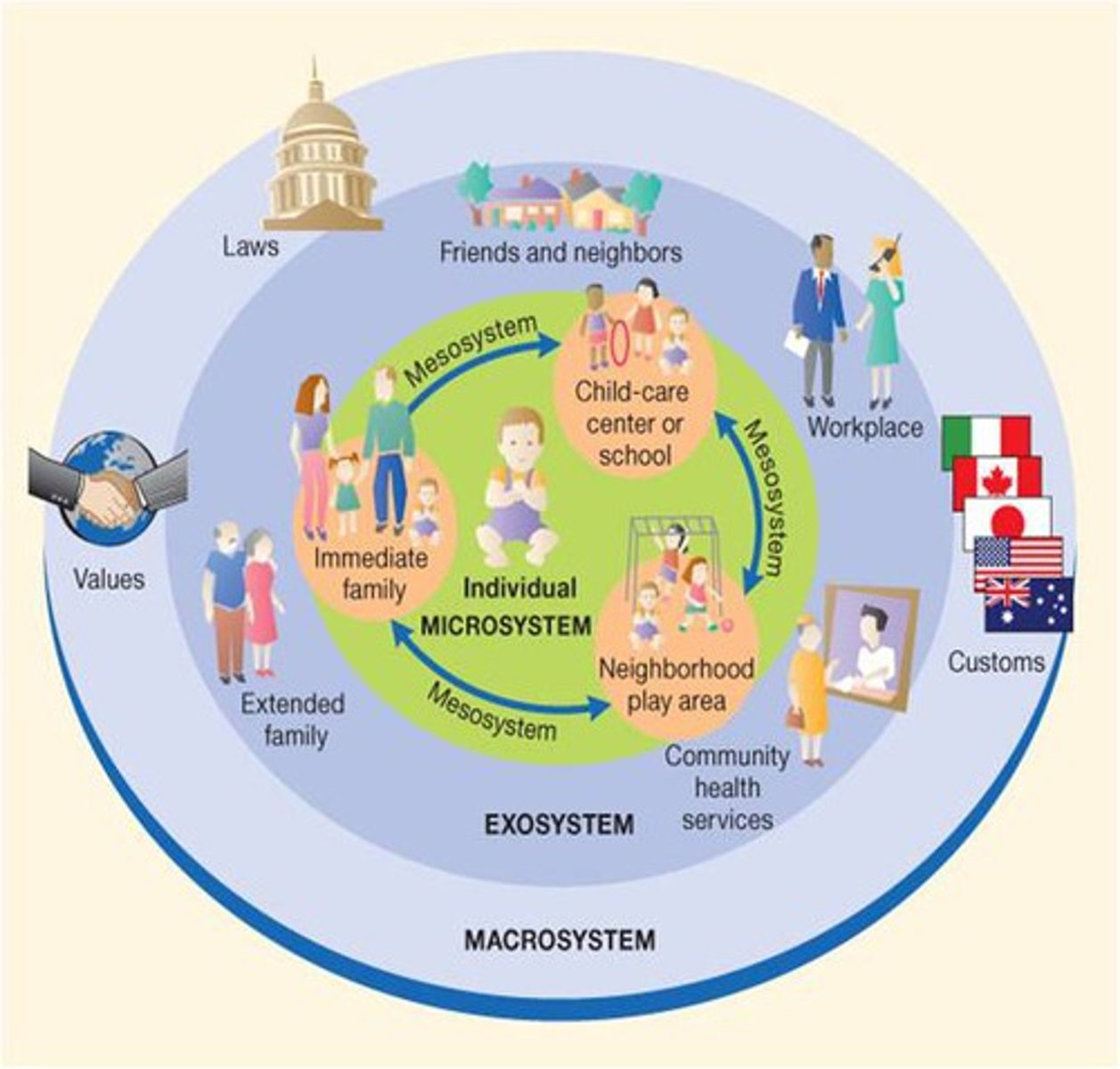
Macrosystem
the collection of broad systems that surround an individual such as cultural values, laws, and social customs
Chronosystem
all of the experiences a person has had during their lifetime, including environmental events, major life transitions, and historical events
Authoritarian parenting
a style of parenting in which a parent is rigid and overly strict, showing little warmth to the child

Authoritative parenting
a style of parenting characterized by emotional warmth, high standards for behavior, explanation and consistent enforcement of rules, and inclusion of children in decision making

Permissive parenting
a style of parenting in which few, if any, demands are made on a child's behavior

Attachment styles
a theory about the early bonds between infants and their parents/caregivers with the idea that babies need to form a close relationship with at least one primary caregiver to ensure their survival
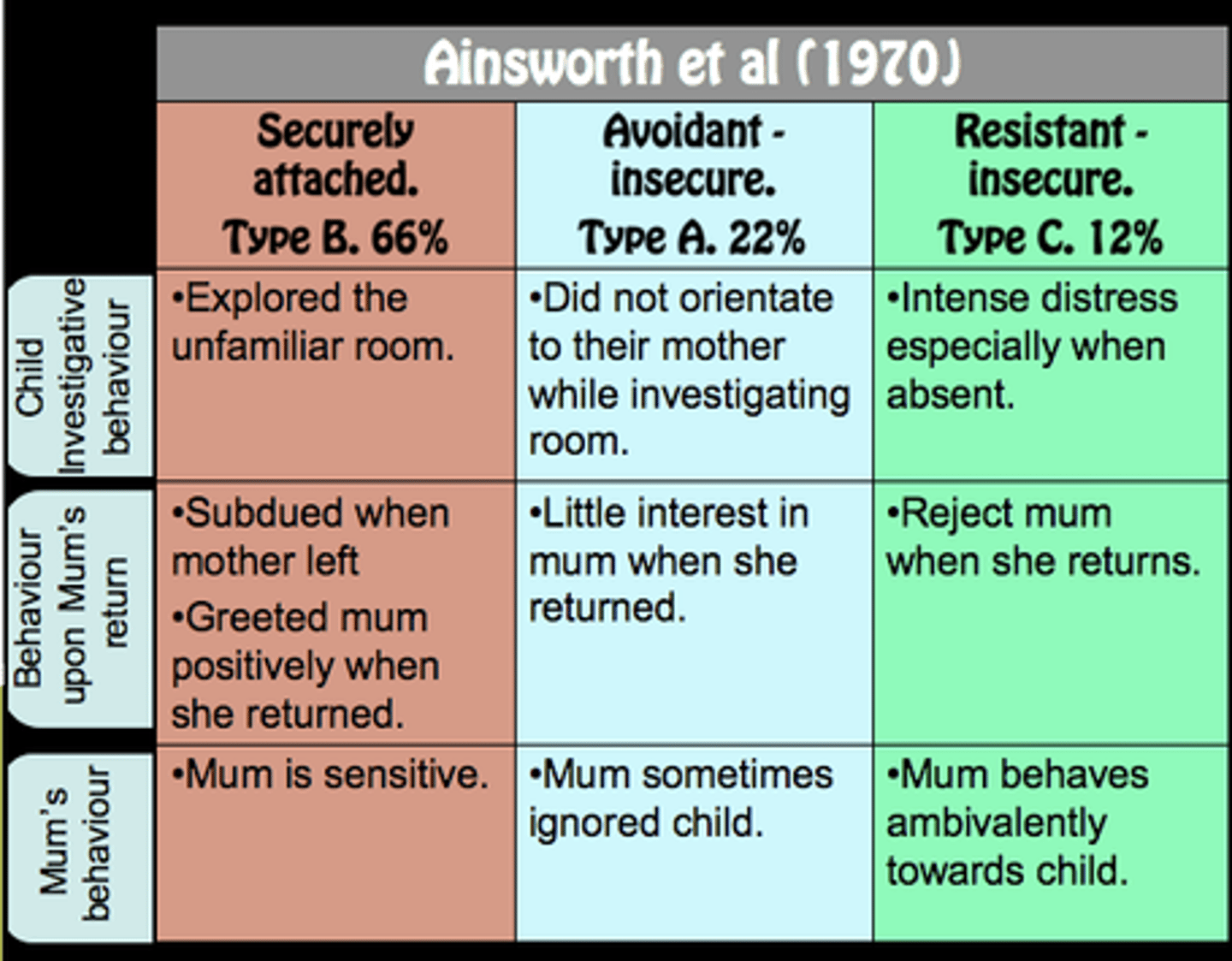
Secure attachment
a relationship in which an infant obtains both comfort and confidence from the presence of his or her caregiver

Insecure attachment
characterized by lack of trust, such as avoiding contact with the caregiver, or by alternating between approach and avoidance behaviors; results from trauma, neglect, or abuse

Avoidant attachment
characterized by physical and emotional independence from a caregiver; results from a caregiver who does not show nurturing other than providing necessities such as food and shelter

Anxious attachment
characterized by insecurity, fear of abandonment, and mistrust; results from a caregiver who fails to give attention and show affection in a dependable way

Disorganized attachment
characterized by conflicting feelings of wanting to be cared for while simultaneously being intensely afraid of such a relationship; results from a parent who repeatedly causes a state of fear in a child

Separation anxiety
excessive fear or distress about separation from a caregiver

Temperament
an individual's basic emotional style that appears early in development and is largely genetic in origin rather than learned
Parallel play
activity in which children play side by side with similar toys without interacting

Imaginary audience
a common adolescent belief that they are under constant, close observation by peers, family, and even strangers

Personal fable
a common adolescent belief that they are unique, so none of life's dangers or difficulties will affect them regardless of their behavior
Social clock
the cultural timeline set by a society on what should happen at given stages of life (e.g., marriage, parenthood, and retirement)

Emerging adulthood
a period from about age 18 to 25 when adolescents gradually rely less on parents and develop adult level commitments toward romantic relationships and work

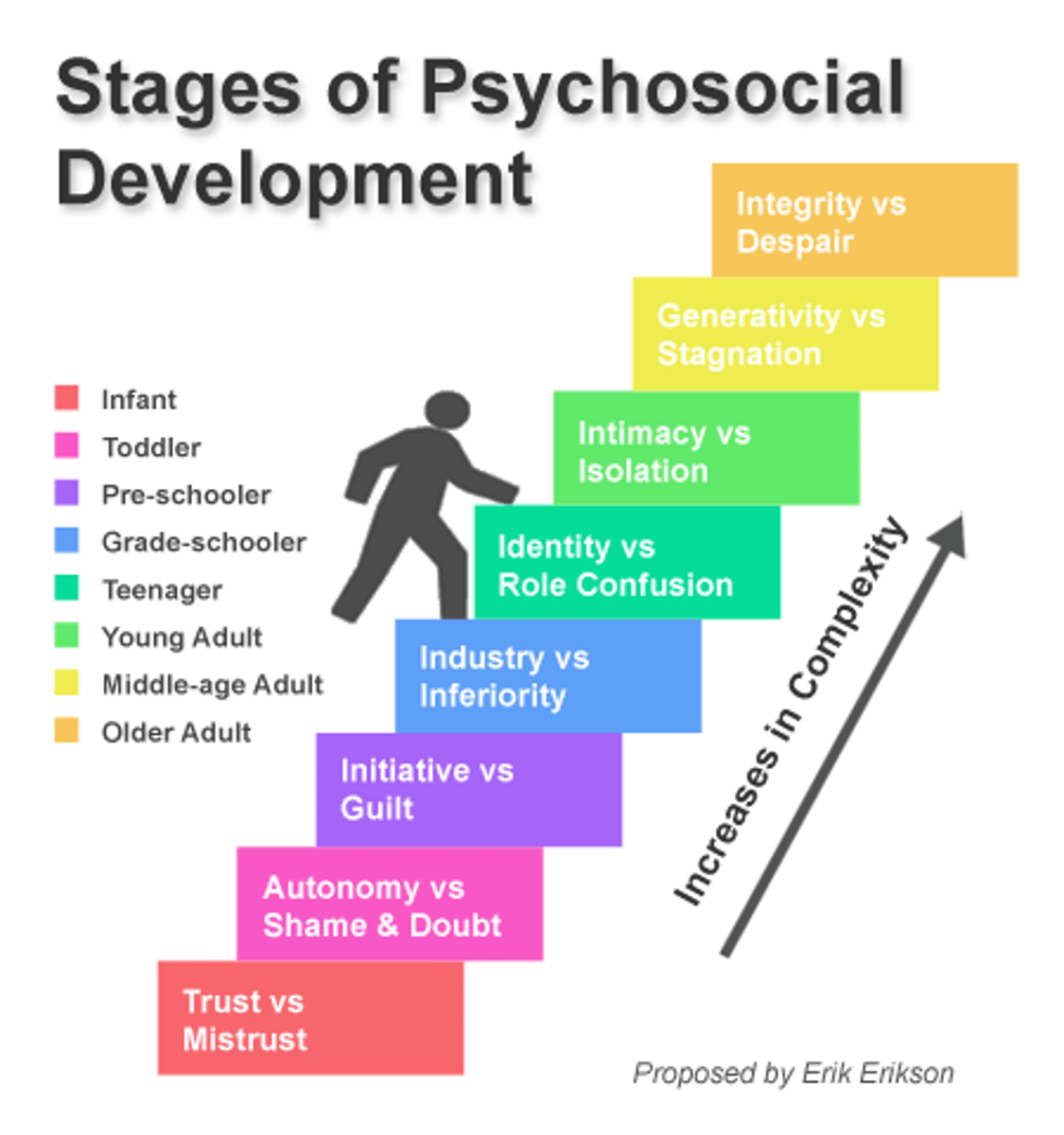
Stage theory of psychosocial development
Erikson's theory that personality is shaped in a sequence of eight stages that occur over time and through the influence of other people
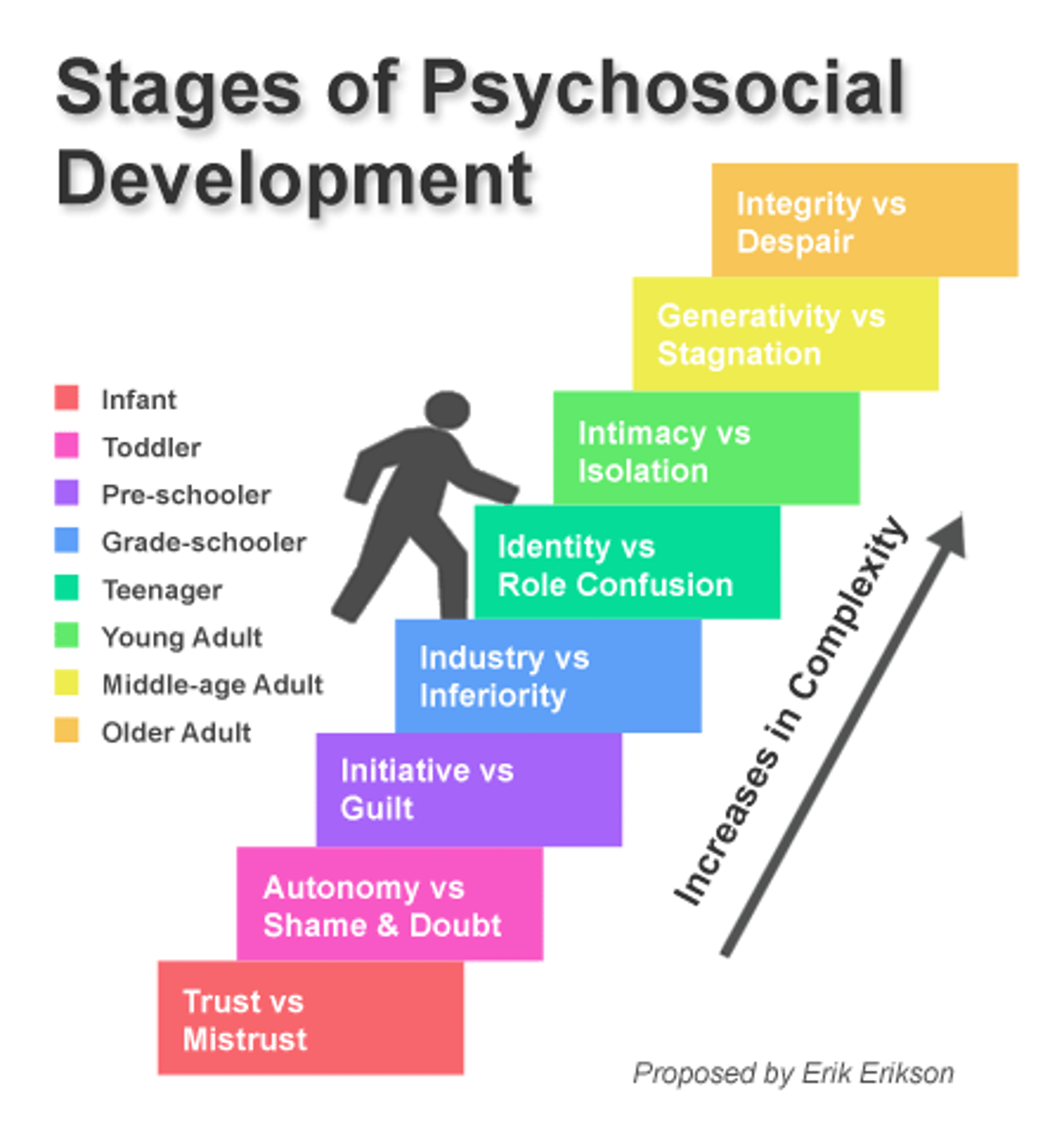
Trust vs. mistrust stage
the period during which infants develop a sense of trust or mistrust, largely depending on how well their needs are met by their caregivers

Autonomy vs. shame & doubt stage
the period during which toddlers develop independence and autonomy if they are allowed the freedom to explore, or shame and self-doubt if they are restricted and overprotected

Initiative vs. guilt stage
the period during which children experience conflict between independent actions and the sometimes negative results of their actions

Industry vs. inferiority stage
the period from age 6 to 12 when children develop confidence in their own efforts and are able to respond to feedback from adults about their efforts

Identity vs. role confusion stage
a period when adolescents explore their independence and develop a sense of self and what makes them unique
Intimacy vs. isolation stage
a period during early adulthood when individuals engage with the challenges of close relationships

Generativity vs. stagnation stage
a time of adulthood when individuals engage with the challenges of making a positive contribution to the world while dealing with being unproductive or lacking a sense of purpose

Integrity vs. despair stage
when older individuals reflect on their life and come away with a sense of fulfillment (a life well-lived) or a sense of regret (a life misspent)

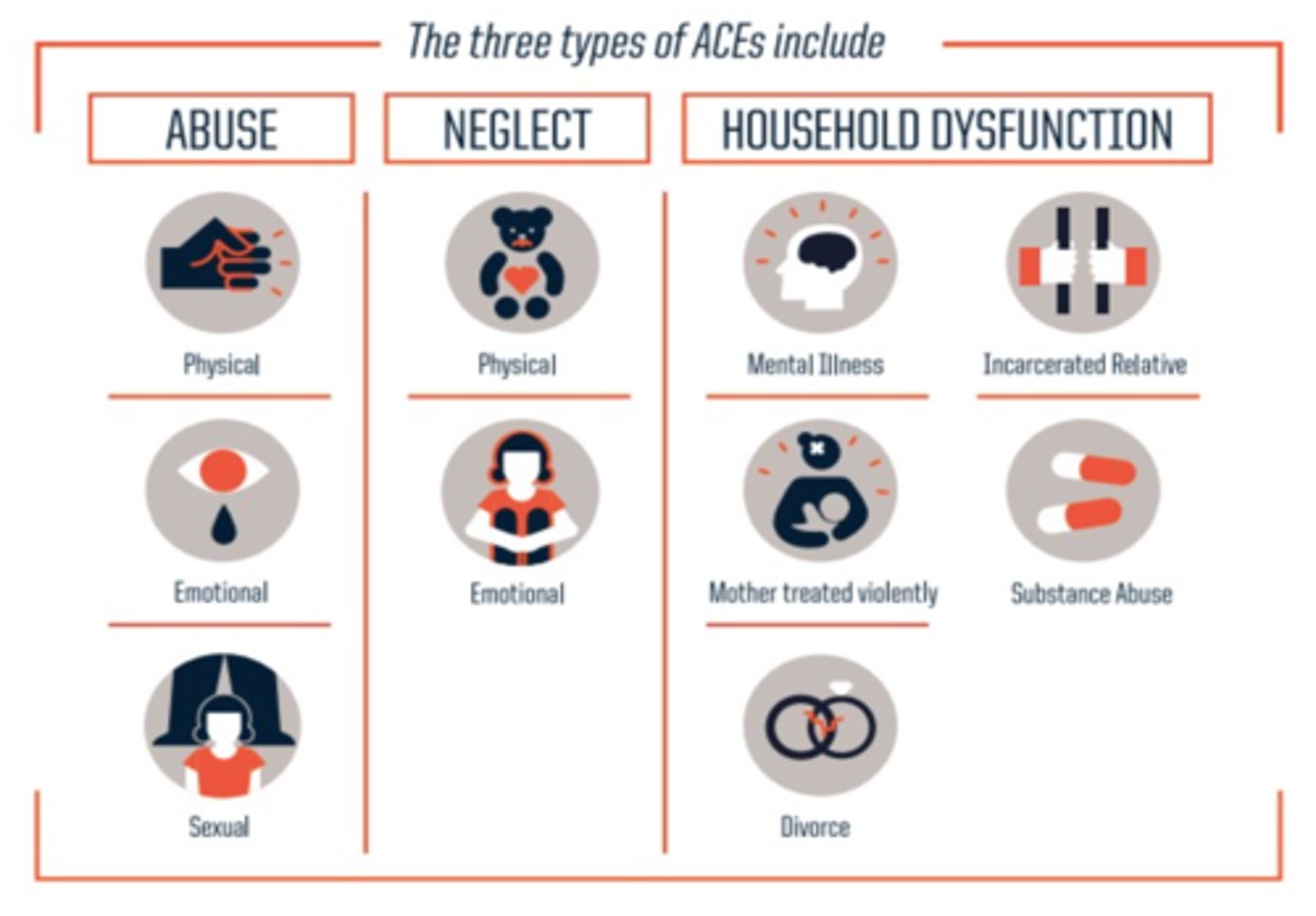
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs)
traumatic childhood experiences, such as abuse, neglect, violence exposure, or death of a parent, that are linked to mental and physical health problems later in life
Achievement
the status of adolescents who commit to a particular identity following a period of crisis during which they consider various alternatives
Diffusion
when an adolescent has not yet developed a firm identity, or their identity is in a state of crisis and they haven't committed to a resolution

Foreclosure
when an adolescent has not explored other identities, but is committed to one or more choices
Moratorium
when an adolescent is actively exploring their identity but has yet to make a commitment

Racial/ethnic identity
the sense of membership in a racial or ethnic group and the feelings that are associated with that membership

Sexual orientation
a person's sexual identity in relation to the gender to which they are attracted
Religious identity
the sense of group membership in a religion and the importance of this membership as it pertains to one's self-concept

Occupational identity
the conscious awareness of oneself as a worker and how you feel about your occupation

Familial identity
a sense of group membership in a family and the importance of this group membership as it pertains to one's self-concept

Possible selves
individuals' ideas of what they might become, what they would like to become, and what they are afraid of becoming
Chronological development
the various periods of life (e.g., infancy, adolescence, middle age, old age) and the typical years of life these happen
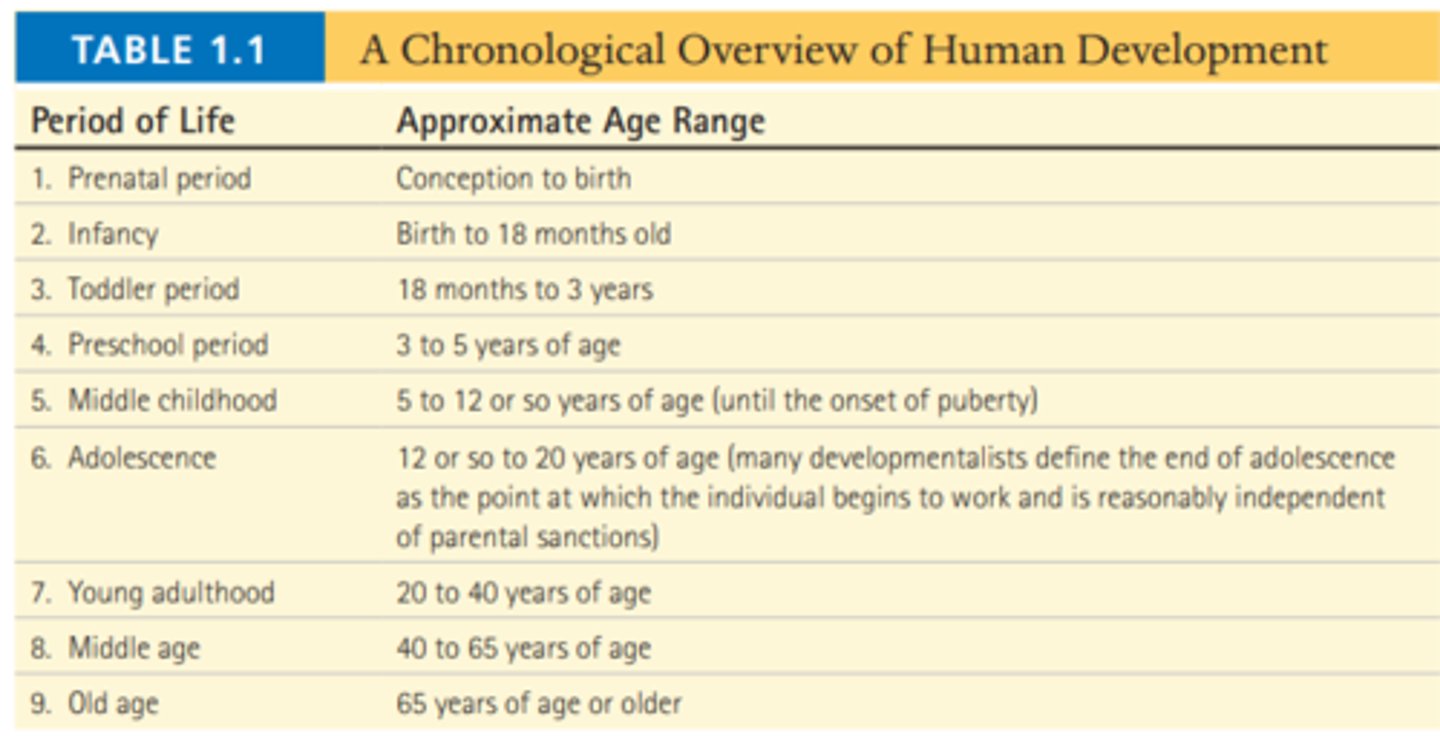
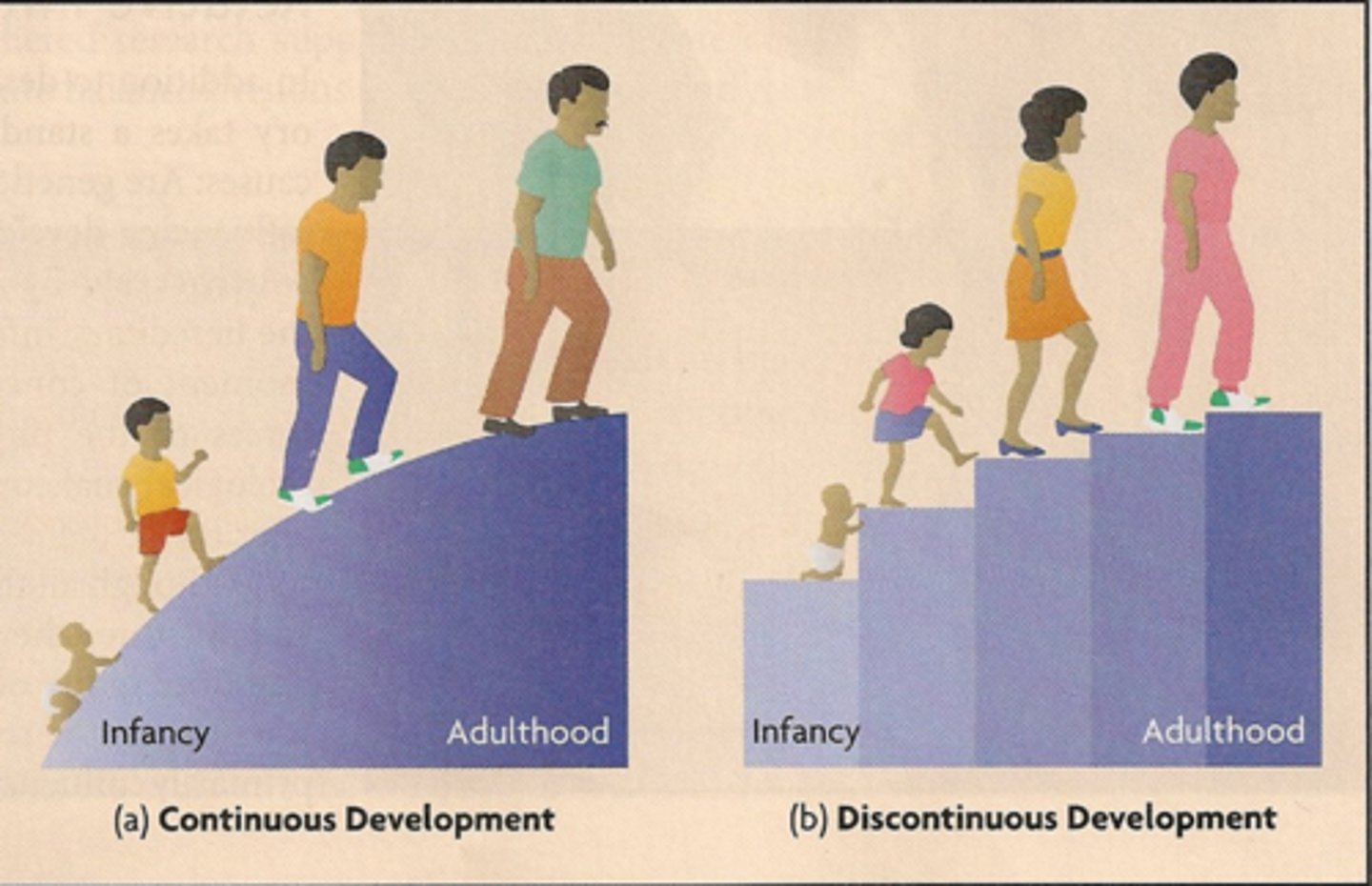
Continuous development
the idea that changes with age are cumulative and occur gradually (e.g., Vygotsky's theory)
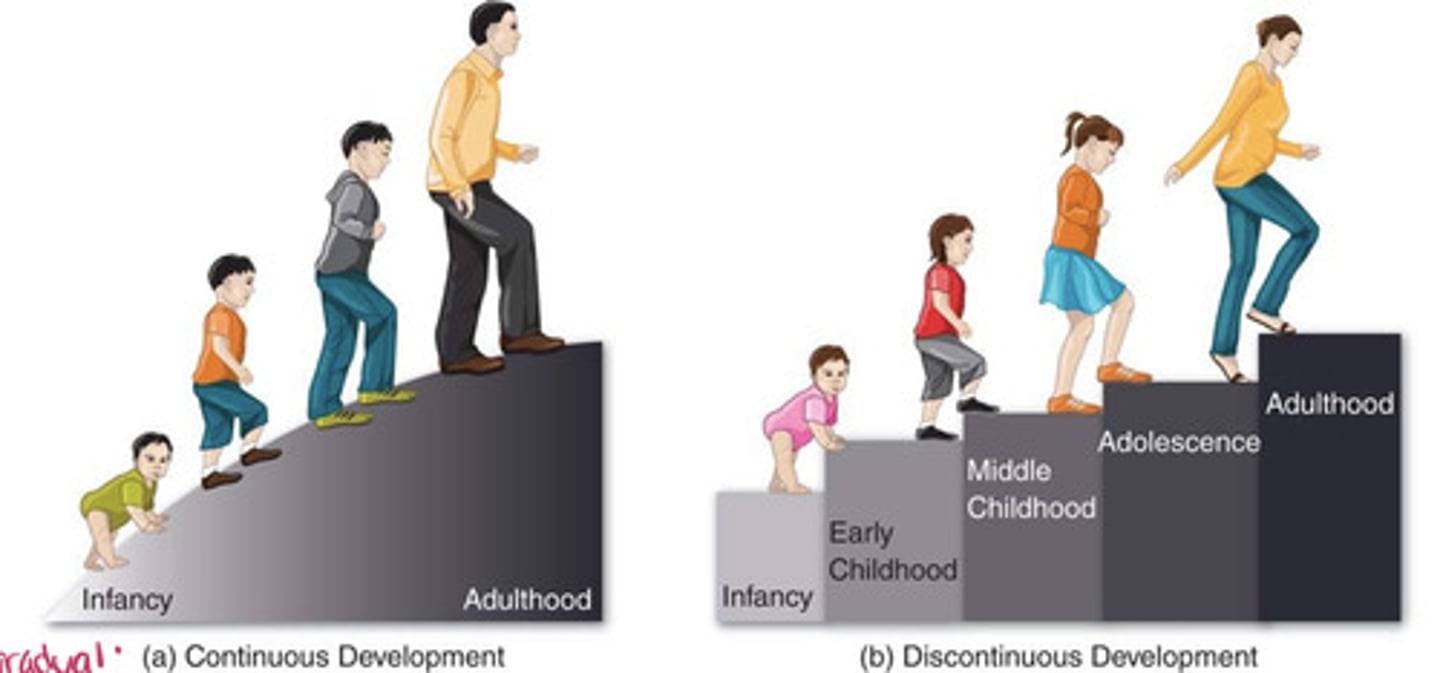
Discontinuous development
the idea that development takes place in unique stages, which happen at specific times or ages (e.g., Erikson's 8 stages of development)
Lifespan development
the study of patterns of growth, change, and stability in behavior that occur throughout the entire life span
Stability and change
stability refers to traits and behaviors that remain more or less constant throughout a person's life, while change refers to traits and behaviors that are more fluid and flexible

Nature and nurture
the debate of whether genetics or environment is primarily responsible for driving behavior

Teratogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm

Fine motor coordination
using small muscle groups for controlled movements, particularly in object manipulation

Gross motor coordination
using large muscle groups for controlled, goal-directed movements

Maturation
the emergence of psychological and behavioral characteristics over time; a process occurring in stages which are governed by genes.

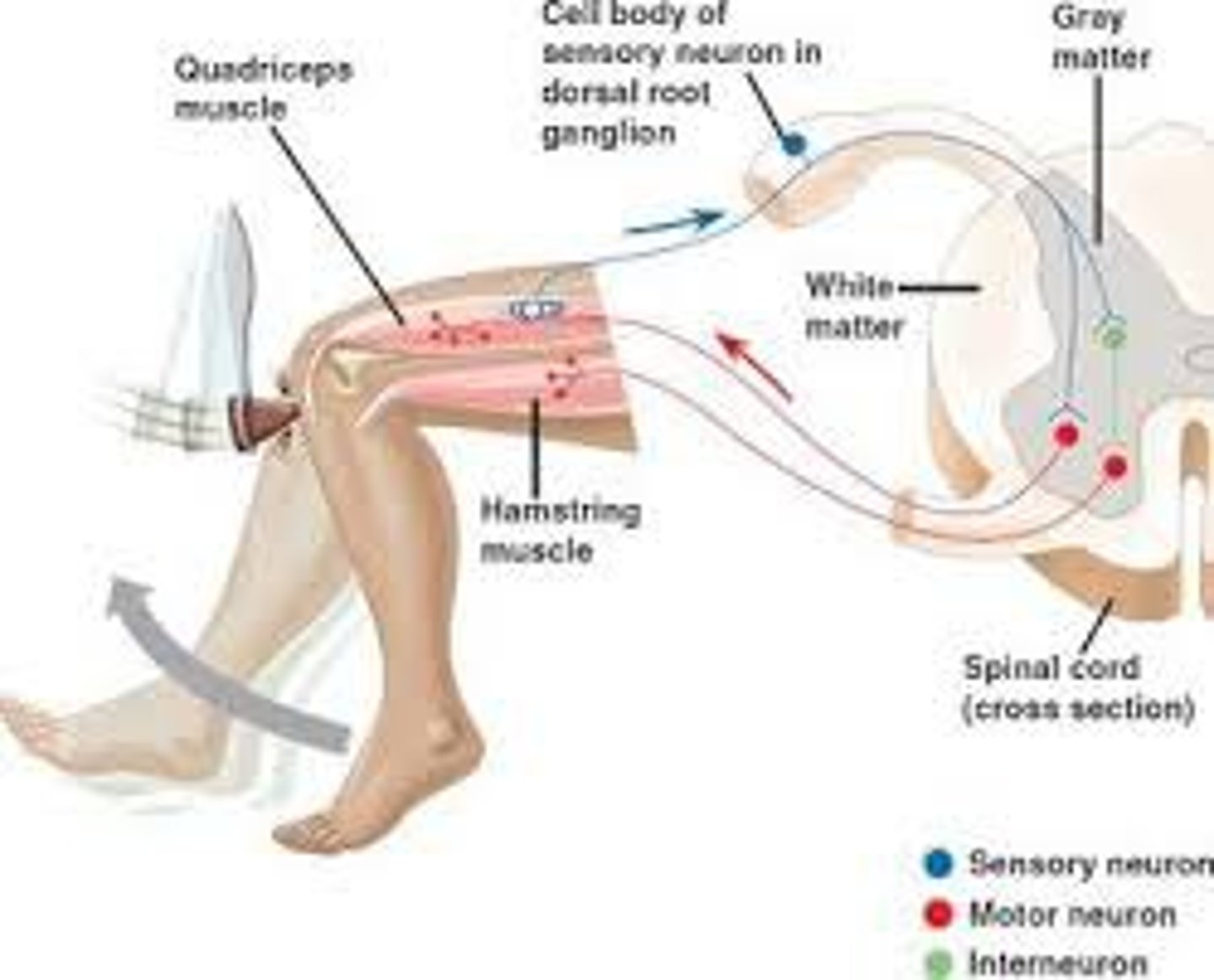
Reflexes
involuntary, automatic responses to sensory stimuli, such as the knee-jerk response
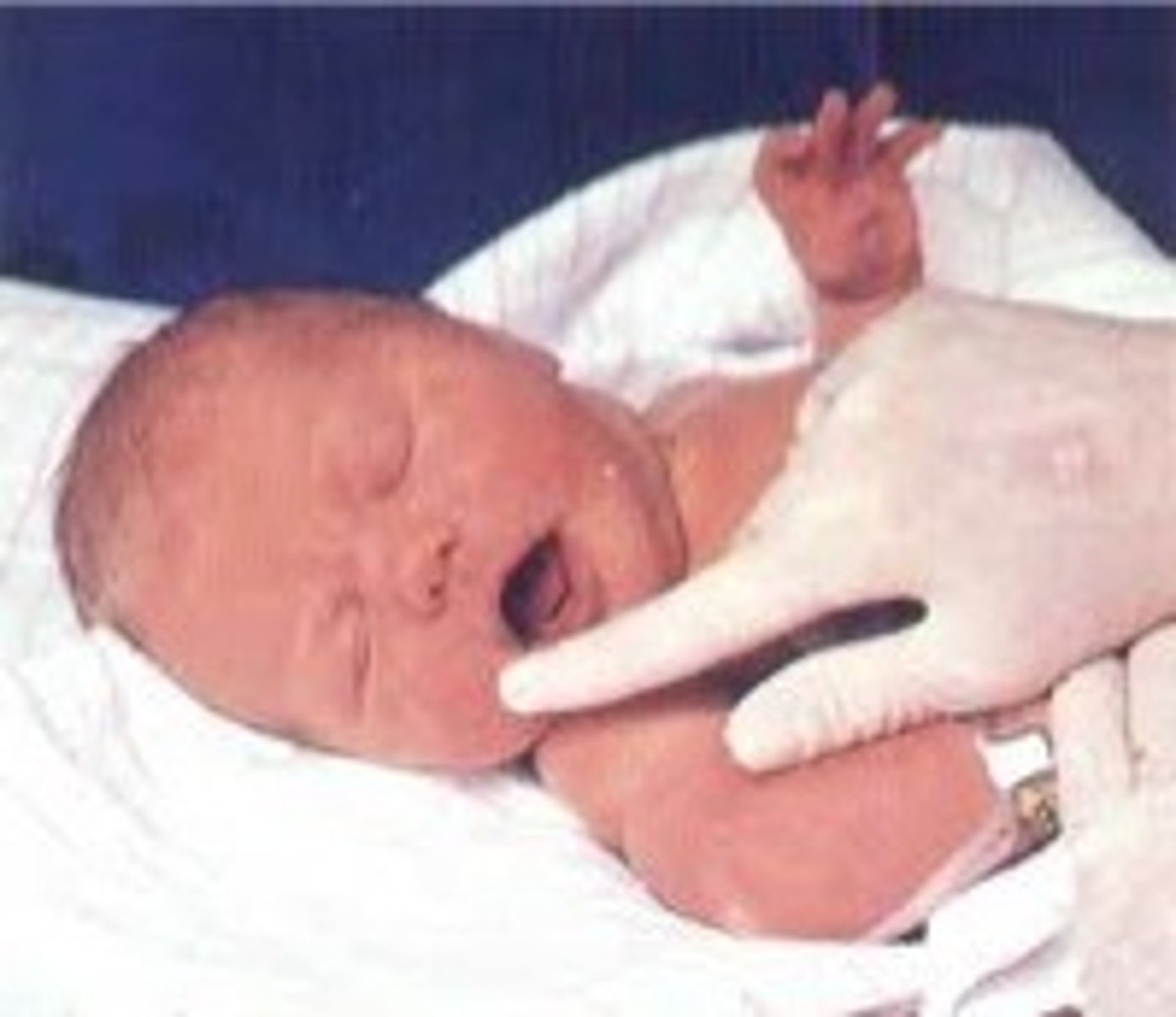
Rooting reflex
a baby's tendency, when touched on the cheek, to open the mouth and search for the nipple
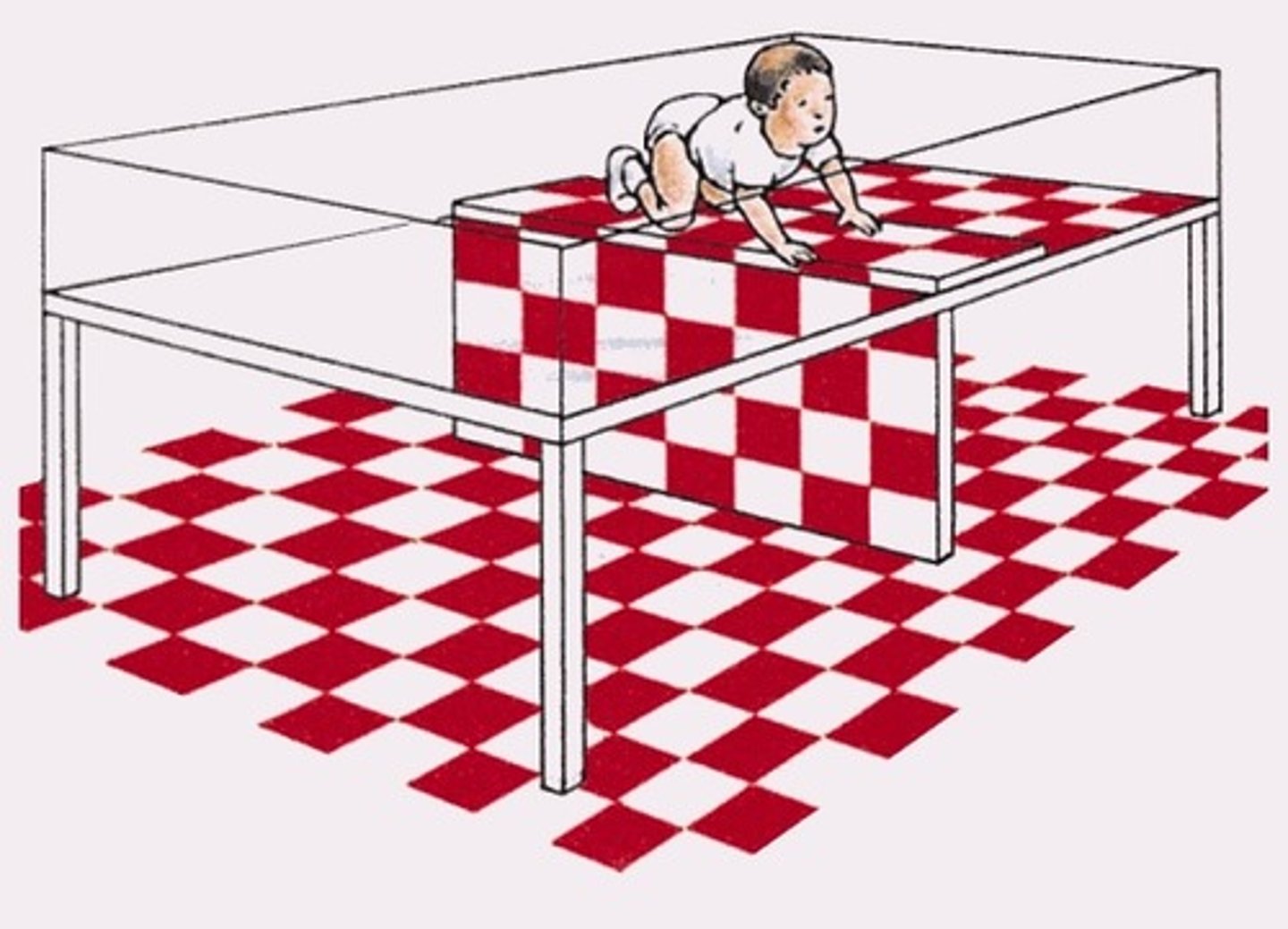
Visual cliff
a laboratory test of depth perception for infants and young animals
Critical periods
times in the developmental sequence during which a person must experience certain kinds of social or sensory experiences for the normal development of a particular behavior
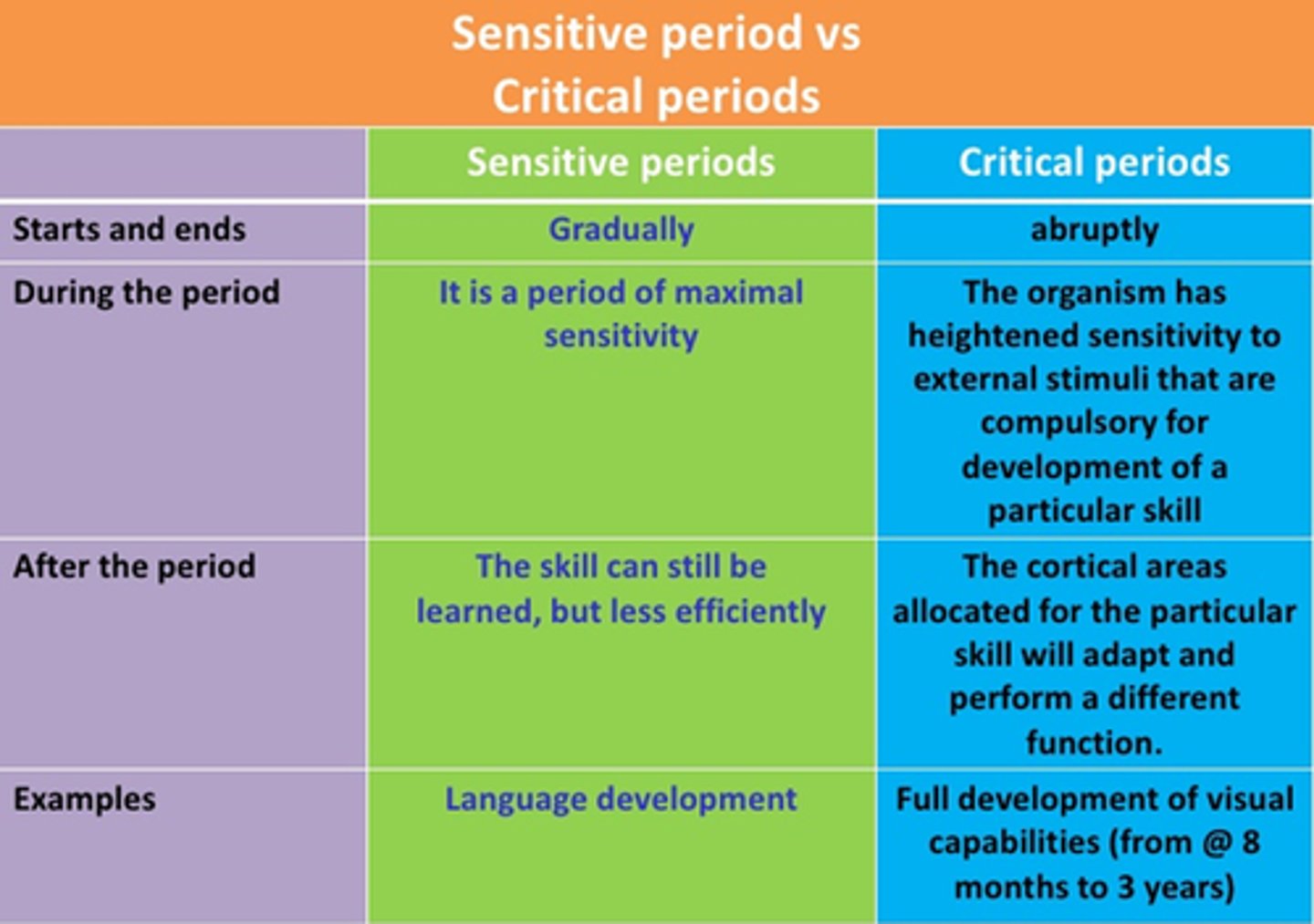
Sensitive periods
times in development when a person is particularly open to learning a certain skill

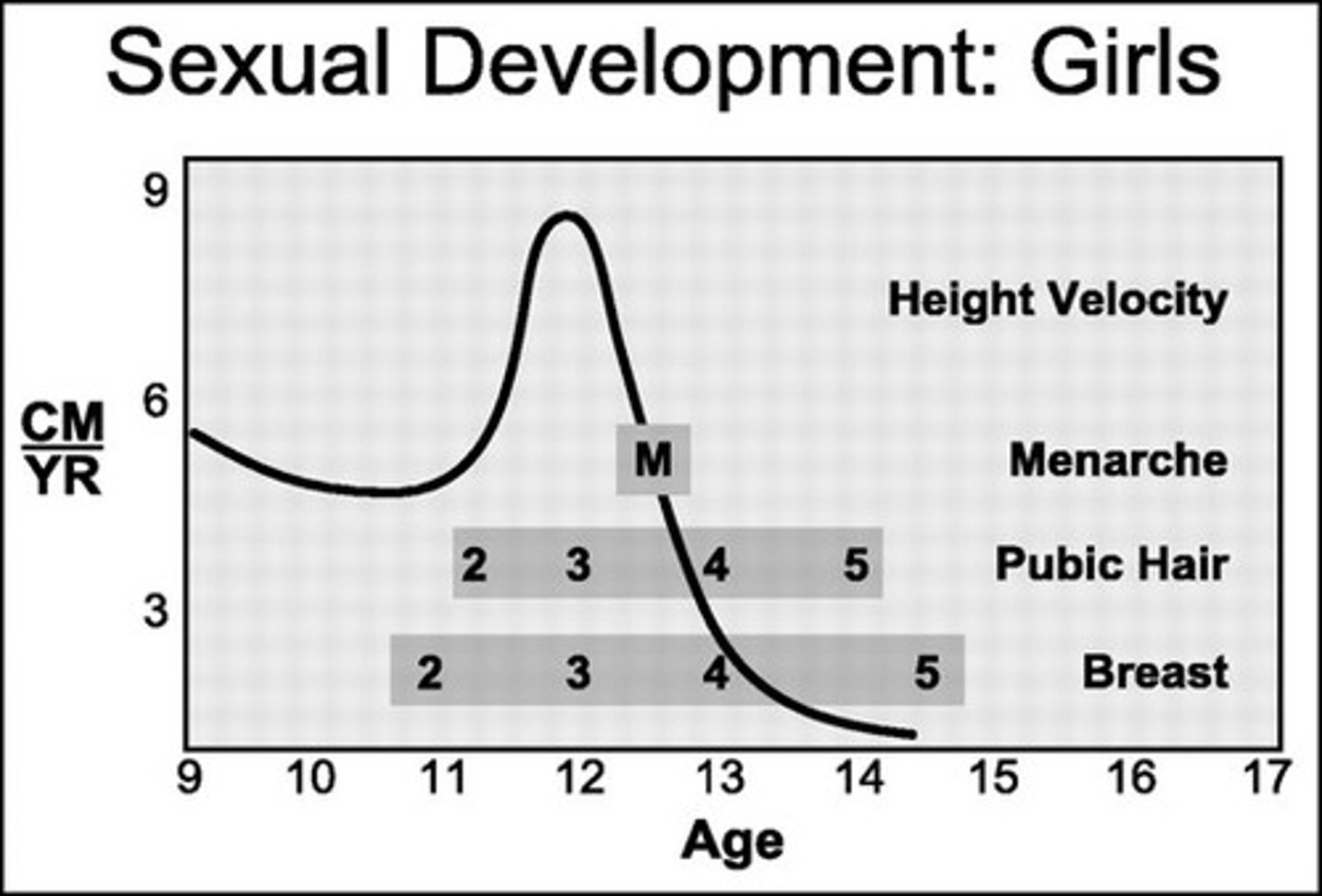
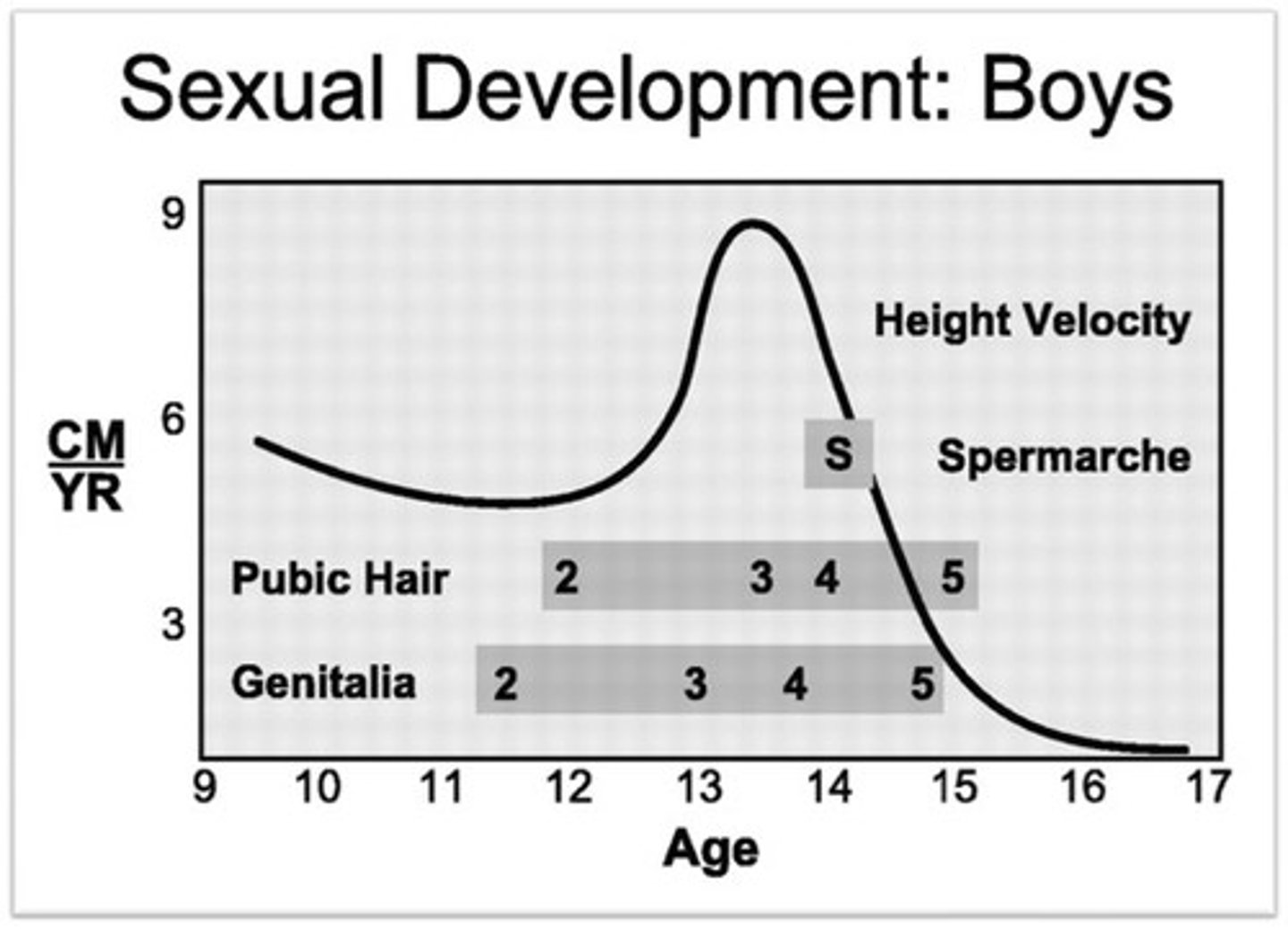
Growth spurt
a relatively sudden and rapid period of physical growth during puberty
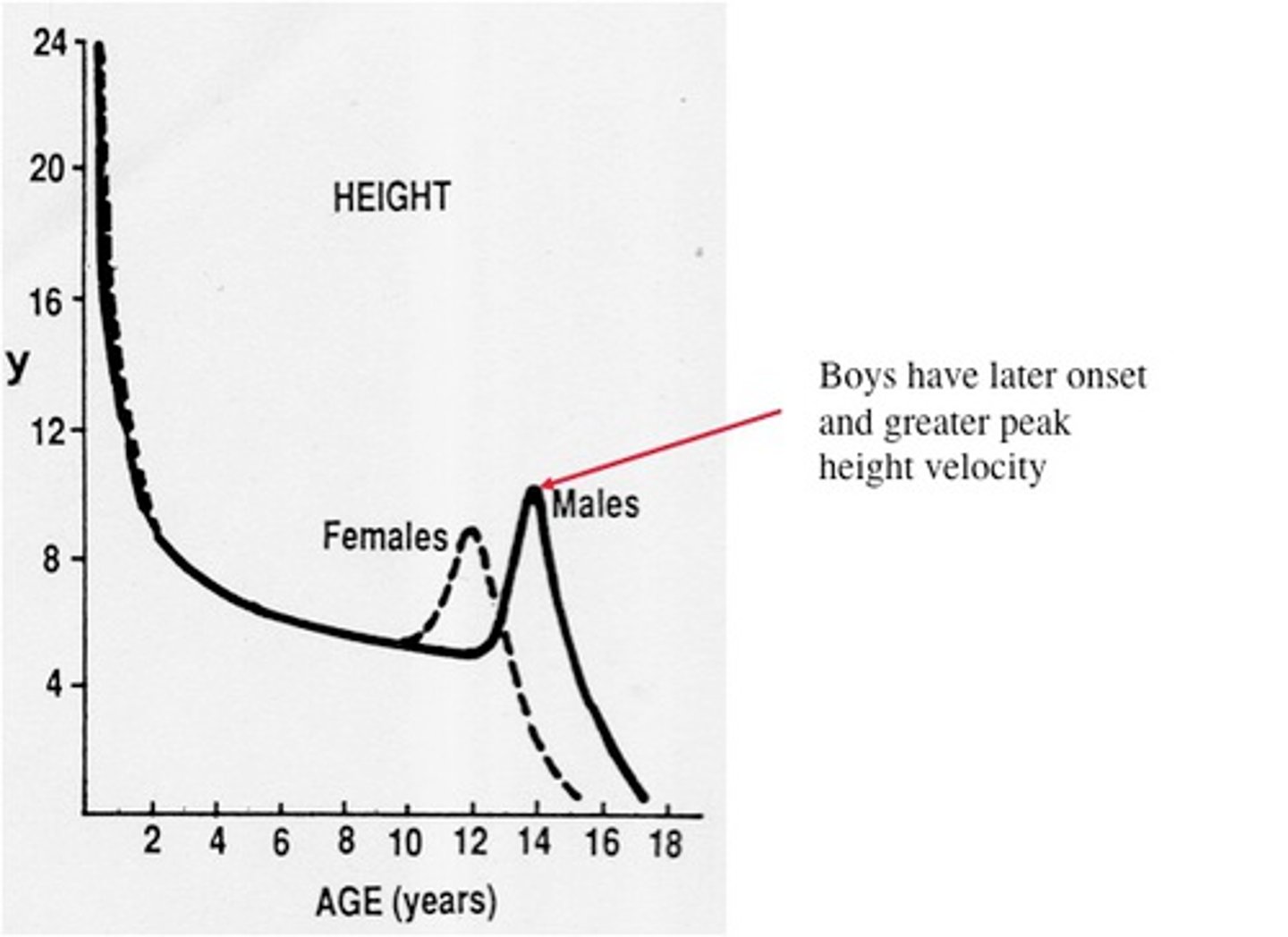
Puberty
the period of maturation during which a person becomes capable of reproducing
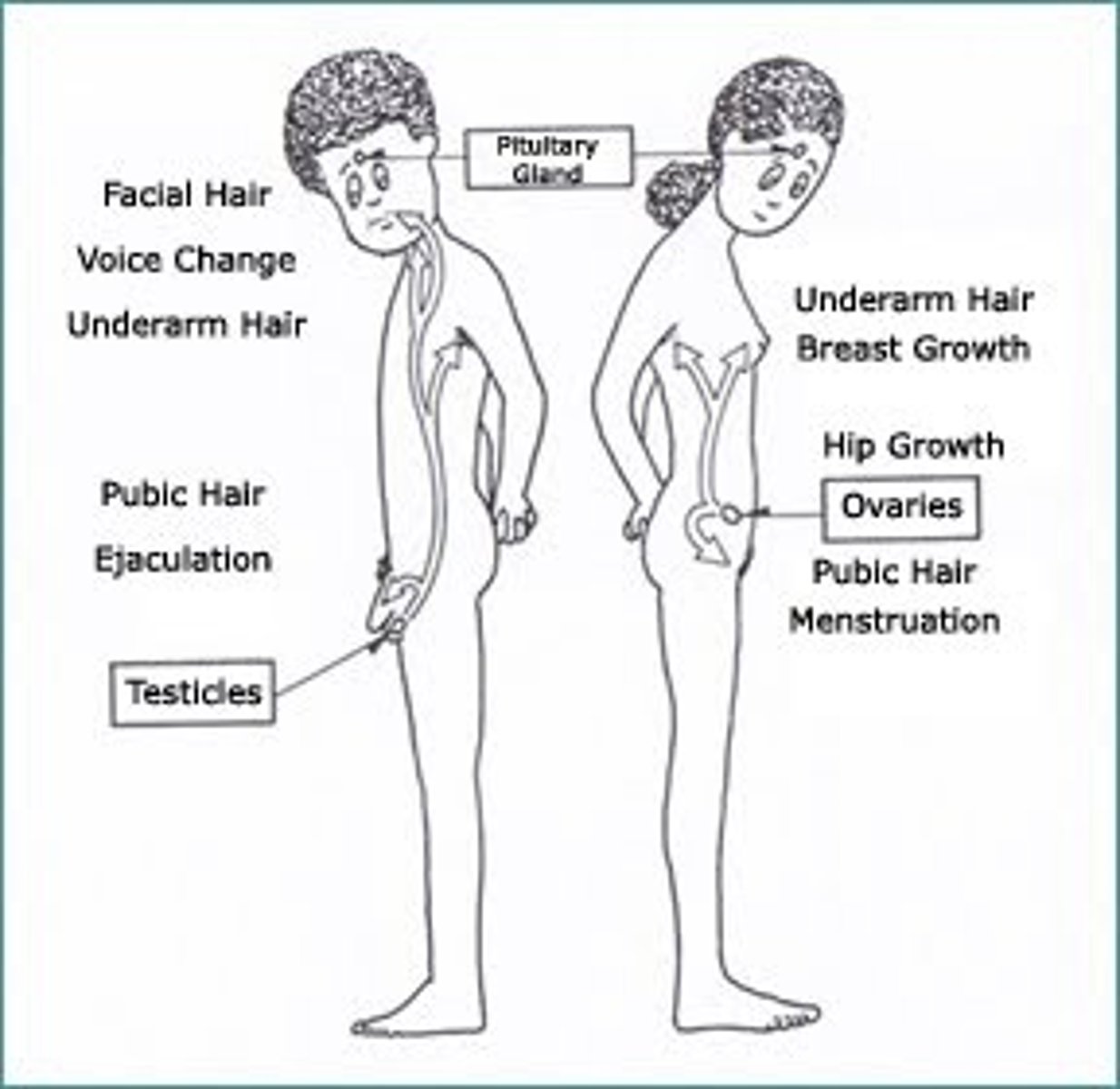
Primary sex characteristics
the body structures (ovaries, testes, and external genitalia) that make sexual reproduction possible

Secondary sex characteristics
aspects of sexual maturity not directly related to reproduction, such as voice quality, facial hair, and breast size

Menarche
the first occurrence of menstruation
Spermarche
first occurrence of ejaculation
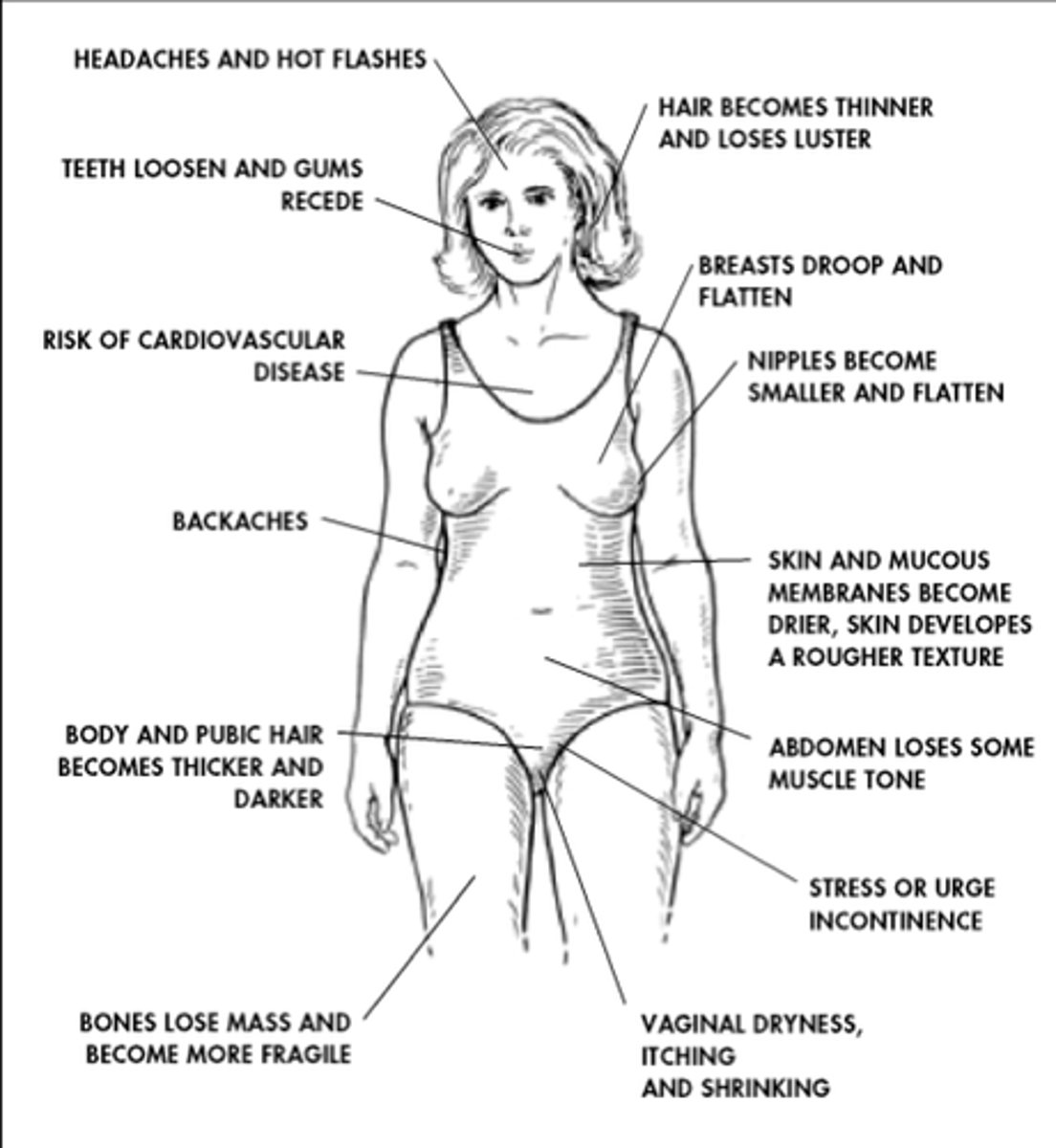
Menopause
the natural cessation of menstruation (and related biological changes) as a woman's ability to reproduce declines
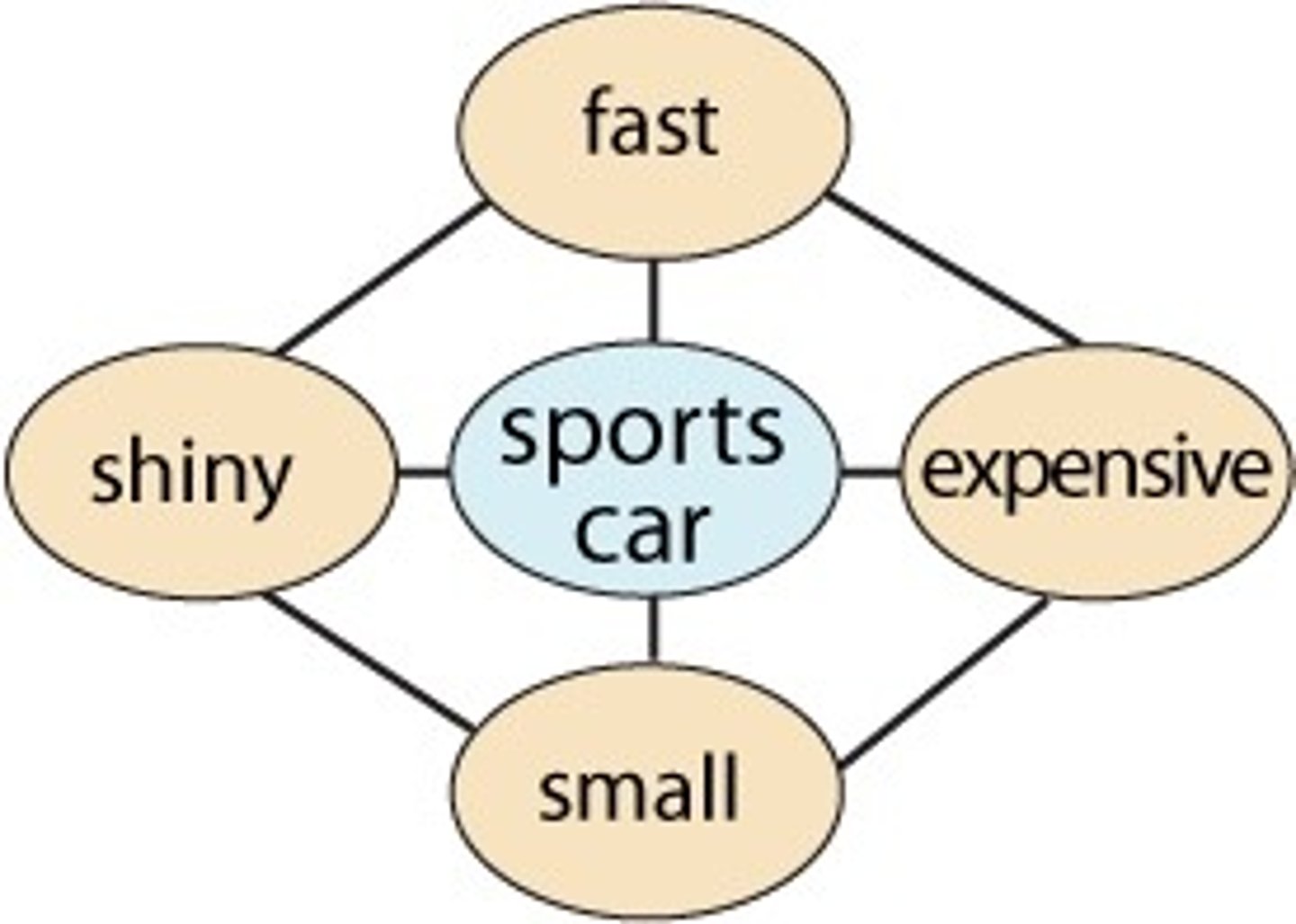
Schema
a concept or framework that helps organiz and interpret information
Assimilation
interpreting new experiences according to existing schemas and adapting them into one's collection of schemas

Accommodation
when new information causes a person to modify their current understandings (schemas)

Sensorimotor stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from birth to about 2 years of age) during which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities

Preoperational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) during which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic

Concrete operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 6 or 7 to 11 years of age) during which children gain the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete events

Formal operational stage
in Piaget's theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) during which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts

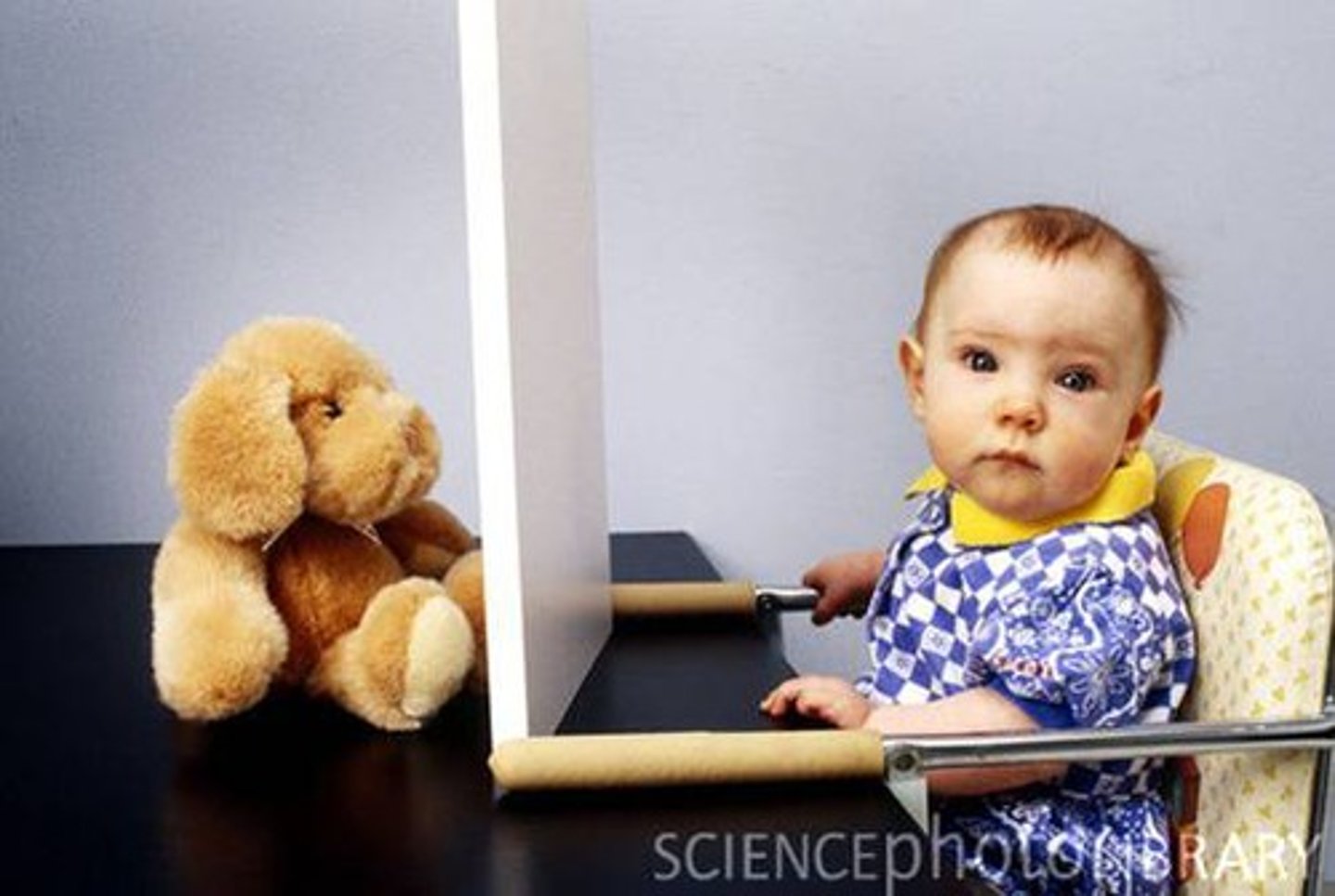
Object permanence
the understanding that objects continue to exist even when out of view

Mental symbols
mental concepts that represent real objects

Pretend play
make-believe activities in which children create new symbolic relations, acting as if they were in a situation different from their actual one

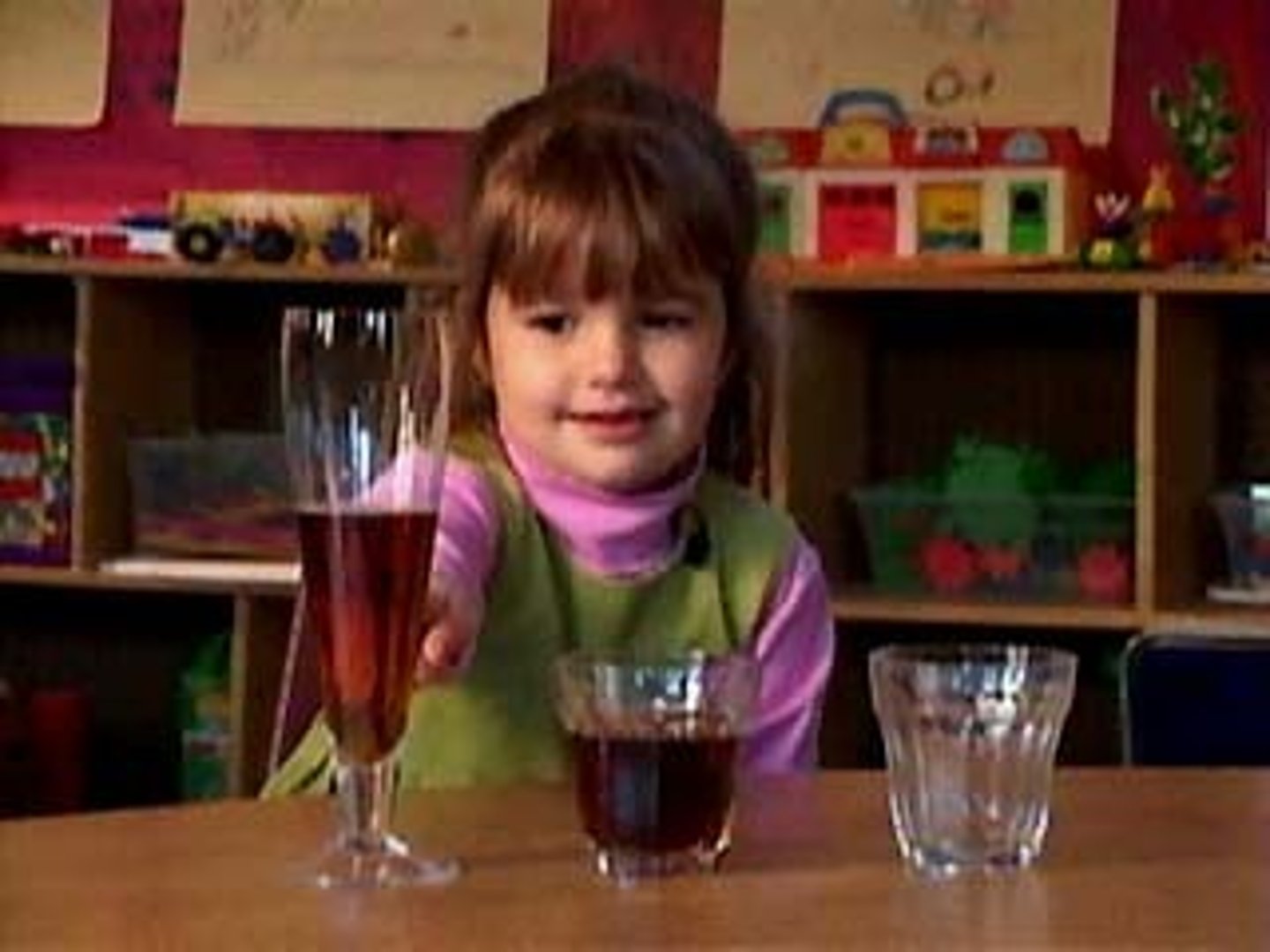
Conservation
a principle of concrete operational reasoning that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in form

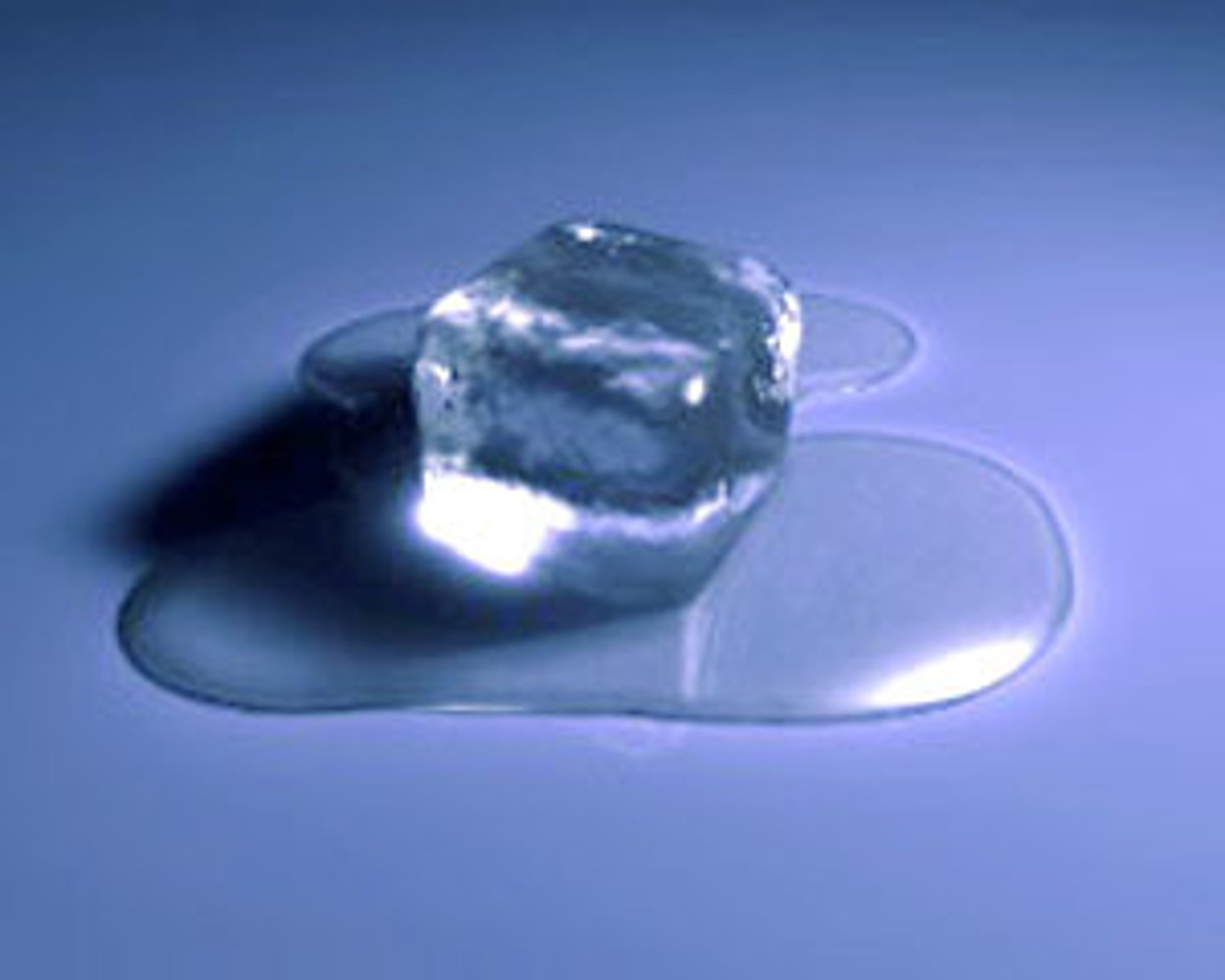
Reversibility
the understanding that some things that have been changed can be returned to their original state (e.g., water → to ice → to water)

Animism
the belief that objects have lifelike qualities and are therefore capable of having feelings, intentions and emotions

Egocentrism
a characteristic of the preoperational stage in which a child has difficulty taking another person's point of view
Theory of mind
an awareness that others have mental states such as knowledge, intentions, and beliefs and that these might differ from one's own

Systematic thinking
approaching problems in a rational, step-by-step, and analytical fashion
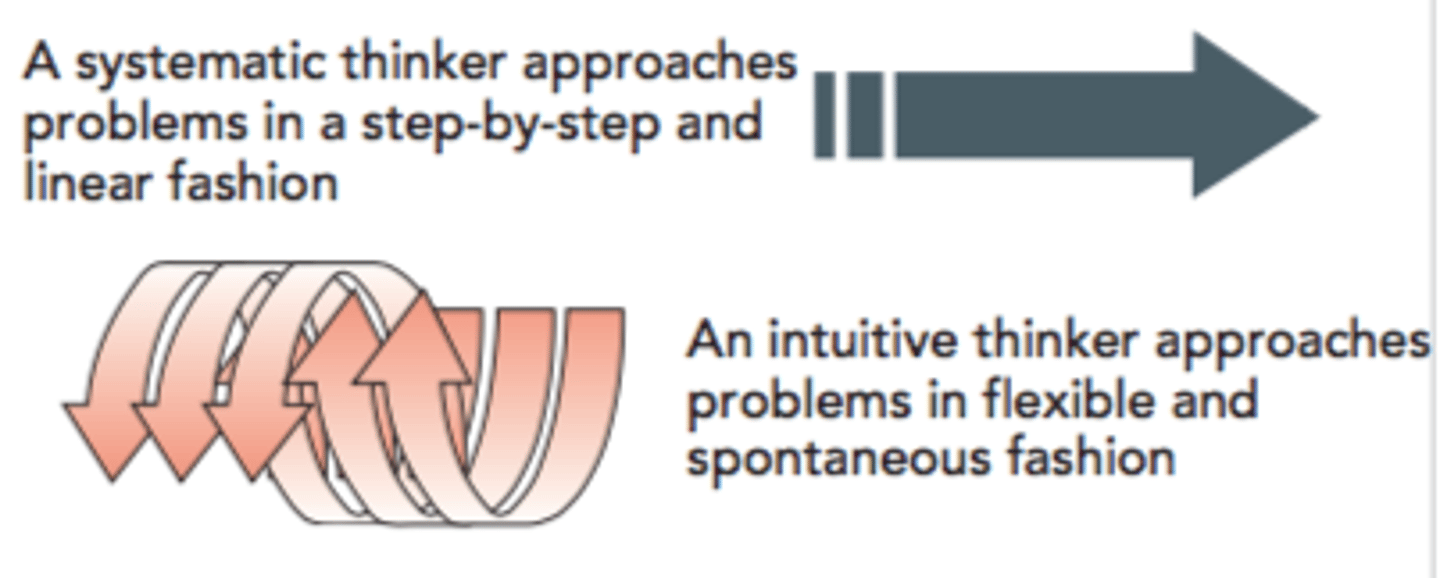
Abstract thinking
thinking in terms of symbols, ideas, and concepts
Hypothetical thinking
thinking that is based on what is possible and not just what is real even when this conflicts with what is accepted as true

Scaffolding
support structures used by teachers that help a learner get to the next level (breaking down new information or skills into pieces that are digestible for a learner)

Zone of proximal development
the difference between what a learner can do without help and what they can do with guidance and encouragement from a skilled coach or partner

Crystallized intelligence
a person's general knowledge, vocabulary, and reasoning based on acquired information

Fluid intelligence
reasoning ability and the use of new information for learning and problem solving

Dementia
a slowly progressive decline in cognitive function, including memory, thinking, and judgment, that is often accompanied by personality changes

Phonemes
the smallest units of sound that are recognizable as human speech
Morphemes
the smallest units of meaning within a language

Semantics
the study of meaning in a language and how people learn to understand what utterances in a language communicate
Grammar
the set of rules in a language that explain how parts of speech are used in both writing and speaking

Syntax
the rules in a language for arranging words into grammatically sensible sentences, clauses and phrases

Cooing
pleasant vowel-like noises made by infants, beginning around 2 months of age

Babbling
a stage of language development at about 4 months when an infant experiments with articulate sounds, but does not yet produce any recognizable words
One-word stage
the stage in speech development from about 9-18 months during which a child speaks mostly in single words

Telegraphic speech
when children use simple sentences, often composed of just a noun and verb, that adhere to the basic rules of grammar

Overgeneralization of language rules
when children use grammar in an irregular way as they are learning the rules (e.g., "I runned", "he hitted", "you buyed")

Behavioral perspective
a theory suggesting that behavior is learned and is shaped by observable, environmental factors

Classical conditioning
a learning process that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a behavior (e.g., salivation)
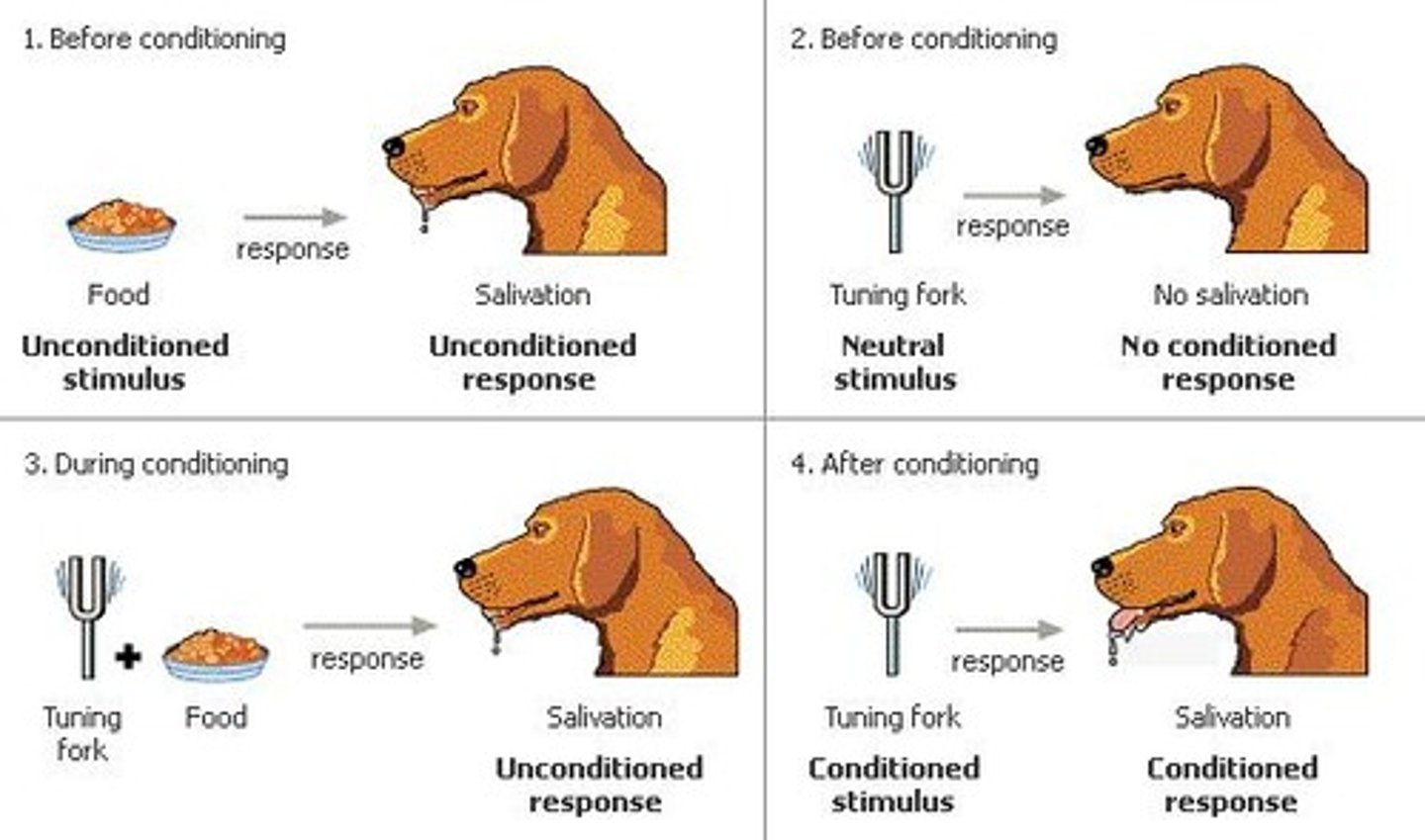
Association
when a subject is conditioned to connect a stimuli with another stimuli, and this results in a specific behavior
