Intro To Medical Mycology: Yeasts: Candida and Cryptococcus
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is medical mycology
Study of fungi (yeast, mold, dermatophyte, dimorphic fungi)
Important to know many drugs have been derived from fungi as well
Are fungi unicellular or multicellular
Can be unicellular (yeast) or multicellular (mold)
Cell structure of fungi
True nucleus with membrane bound organelles
Genetic material of fungi
Multiple linear chromosomes located in the nucleus
Replication of fungi
Sexual or asexual by spores (mold)
Asexual budding (yeasts)
Metabolism of fungi
Heterotrophs, absorb nutrients after secreting digestive enzymes
Ribosomes of fungi
Have ribosomes but not a drug target (eukaryotic, too similar to humans)
Cell wall of fungi
Made of chitin, beta glucans, and mannoproteins
Cell membrane of fungi
Made of phospholipids and ergosterol (similar to human cholesterol)
Dimorphism
Switching between yeast and invasive filamentous form (pseudohyphae), seen in some C. albicans
Budding
Asexual reproduction of yeast
Bud forms on the parent cell and the nucleus splits between the two buds, the result is a blastoconidium (budding spore)
Sexual reproduction of yeast
Cryptococcus is the only one that does it, forms basidiospores
Natural reservoir of Candida
Normal flora (GIT, oral tract, GU tract, skin folds)
Natural reservoir of Cryptococcus neoformans
Soil, bird poop
Natural reservoir of Cryptococcus gatti
Trees (wood, bark, leaves) especially eucalyptus trees
How are yeast transmitted
- Opportunistic pathogens (breach of barrier, disruption of normal balance)
- Inhalation
- Direct contact (least common)
Pathogenesis of Candida
Opportunistic pathogen, grows when host immune system is compromised or when there is a disruption in normal flora that causes candida overgrowth (ex. antimicrobials)
It can adhere and invade into cells, adhesion triggers it to switch to pseudohyphae form that penetrate host cells and induce engulfment
Can disseminate into other sites (brain, kidneys, heart, joints)
Virulence factors of Candida
- Morphological plasticity
- Adhesins
- Invasin
- Hydrolytic enzymes
- Candidalysin
Morphological plasticity
Virulence factor of Candida
Changing forms from yeast to pseudohyphae
Adhesins of Candida
Allow for biofilm formation and adherence
Invasin
Virulence factor of Candida
Facilitates host entry by endocytosis or active penetration
Hydrolytic enzymes of Candida
Break down host proteins
Candidalysin
Virulence factor of Candida
Forms pores in host cells
How does Candida evade immune system
- Cell wall masking with mannoproteins that are less immunogenic
- Morphological switching
- Biofilm formation
Microscopy of Candida
Appears as gram positive, large, budding
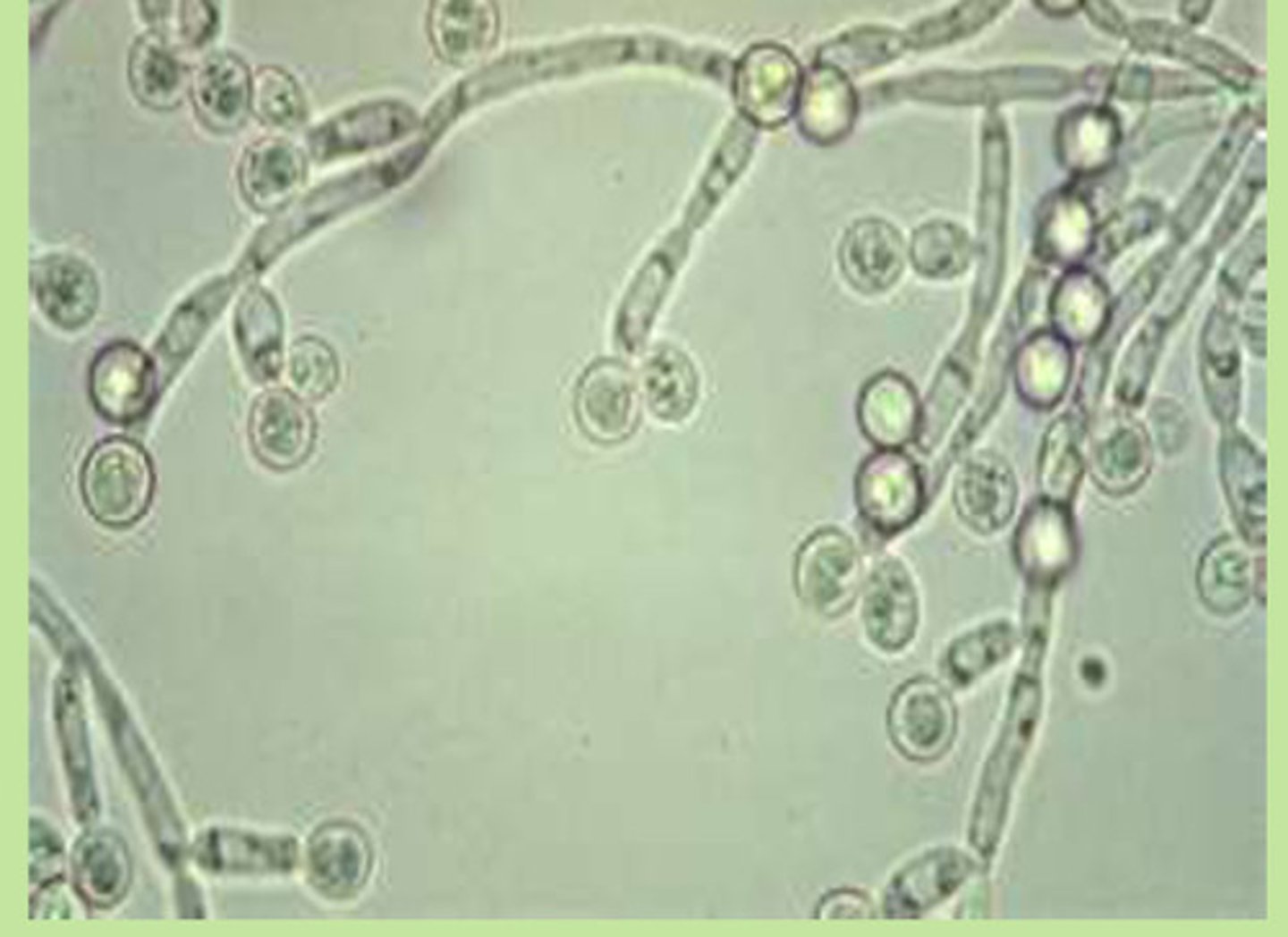
Culture of Candida
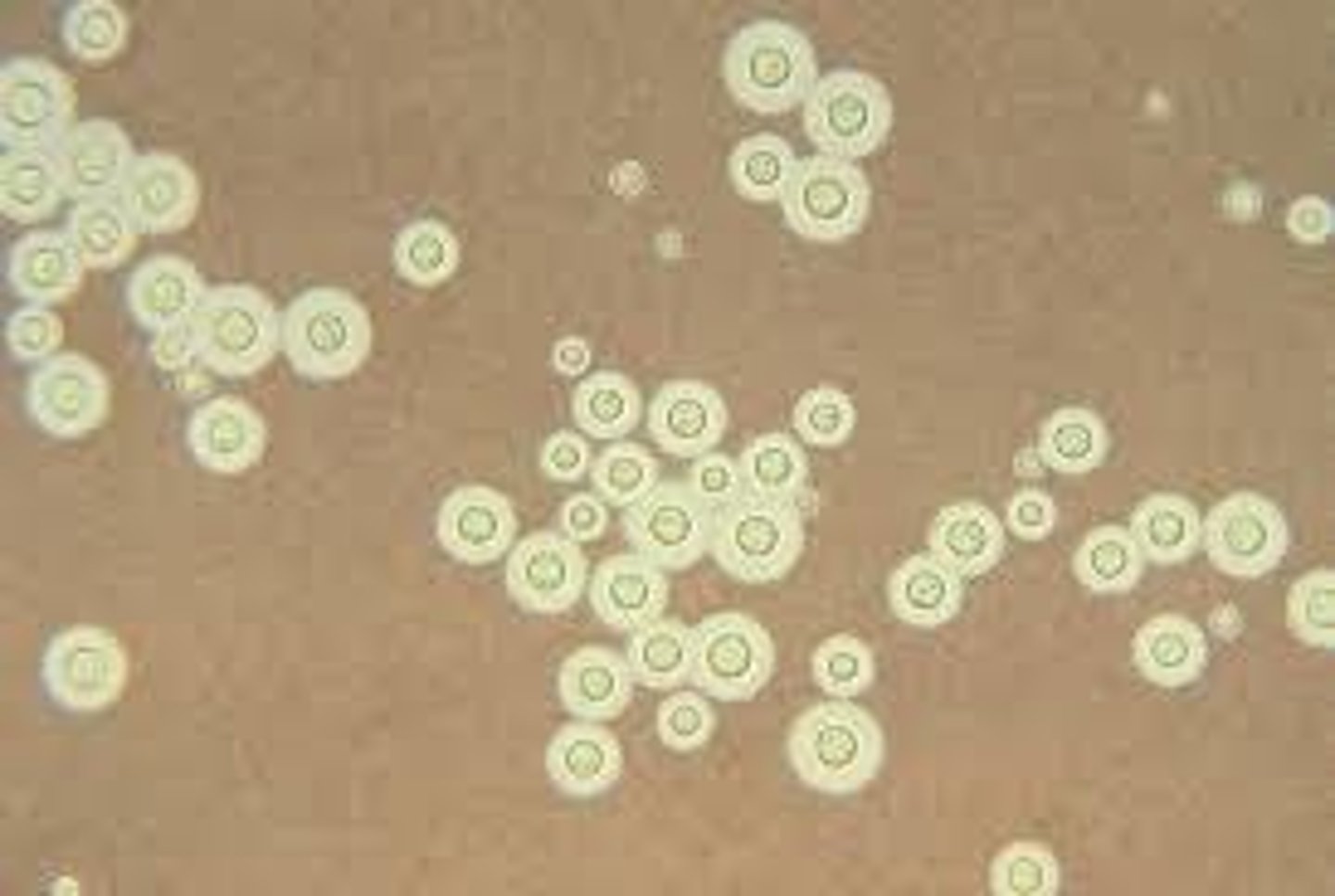
Can be grown on fungal media
Beta-D-glucan serology
Shows presence of fungi, not specific to yeast
Fungi have beta glucan on the cell wall
Germ Tube Test
Test specifically for C. albicans, see hyphae and budding within hours in this specific media
Chromogenic media and Candida
C. albicans appears green on chromogenic media
Molecular/proteomic tests to ID Candida
- MALDI TOF
- Nucleotide sequencing
- PCR
Pathogenesis of Cryptococcus
Inhaled from the environment and taken up into the alveolar macrophages which move around, promoting the spread of cryptococcus outside of the lungs
Can disseminate going to skin, CNS, bones, and prostate
Trophism for CNS (prefers CNS), can cross the BBB by staying within phagocytes or breaching the tight junctions of the epithelial cells
Virulence factors of Cryptococcus
- Polysaccharide capsule
- Melanin
- Urease
Polysaccharide capsule of Cryptococcus
Antiphagocytic
Melanin
Virulence factor of cryptococcus
Protects from oxidative stress
Urease
Virulence factor of cryptococcus
Produces ammonia which damages host cell membranes, promotes dissemination, escape from the phagosome, and entry to the BBB (affecting tight junctions)
Titan Cells
Cryptococcus avoids immune system by being too large for macrophages to engulf
Microscopy of Cryptococcus
Seen with india ink stain, halo around the cell as it cannot take up the stain
Cryptococcal antigen test
Tests specifically for cryptococcus capsule, effective
Performed on CSF or serum
Molecular/Proteomic ID for Cryptococcus
- MALDI TOF
- Nucleic acid sequencing
- PCR
What testing methods are used for Candida
Superficial infection is usually a clinical diagnosis, do not need testing