Peds EOR Review (not all inclusive!)
1/674
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
675 Terms
"MUDPILES" mnemonic
Agents that can inc. anion gap:
Methanol
Uremia
DKA
Phenols
Iron/INH
Lactate
Ethanol/ethylene glycol
Salicylates
Antidote for:
Acetaminophen
N-acetylcysteine
Antidote for:
Narcotics
Naloxone (Narcan)
MC used analgesic in children
Acetaminophen
Minimal toxic acetaminophen dose for a child
150 mg/kg
The AAP states that "cold" medicines should not be used in children < _____ y/o
6
Respiratory & CNS depression + pinpoint pupils, think ______
Opiate poisoning
Electrolyte abnormalities associated with Salicylate toxicity
Metabolic acidosis + Respiratory alkalosis (HAGMA)
Salicylate poisoning Tx recommended in children
Activated charcoal
"DUMBELS" mnemonic
Cholinergic Crisis:
Diarrhea
Urination
Miosis
Bronchorrhea/Bronchospasm
Emesis
Lacrimation
Salivation
what is an autoimmune bleeding disorder cause by IgG attacking platelet membrane antigens?
Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)
does ITP present with splenomegaly?
NO → superficial bleeding of the skin, nose, and GU tract → sudden onset petechiae, bruising, and/or bleeding
how is ITP diagnosed?
decreased platelets
smear shows megathrombocytes
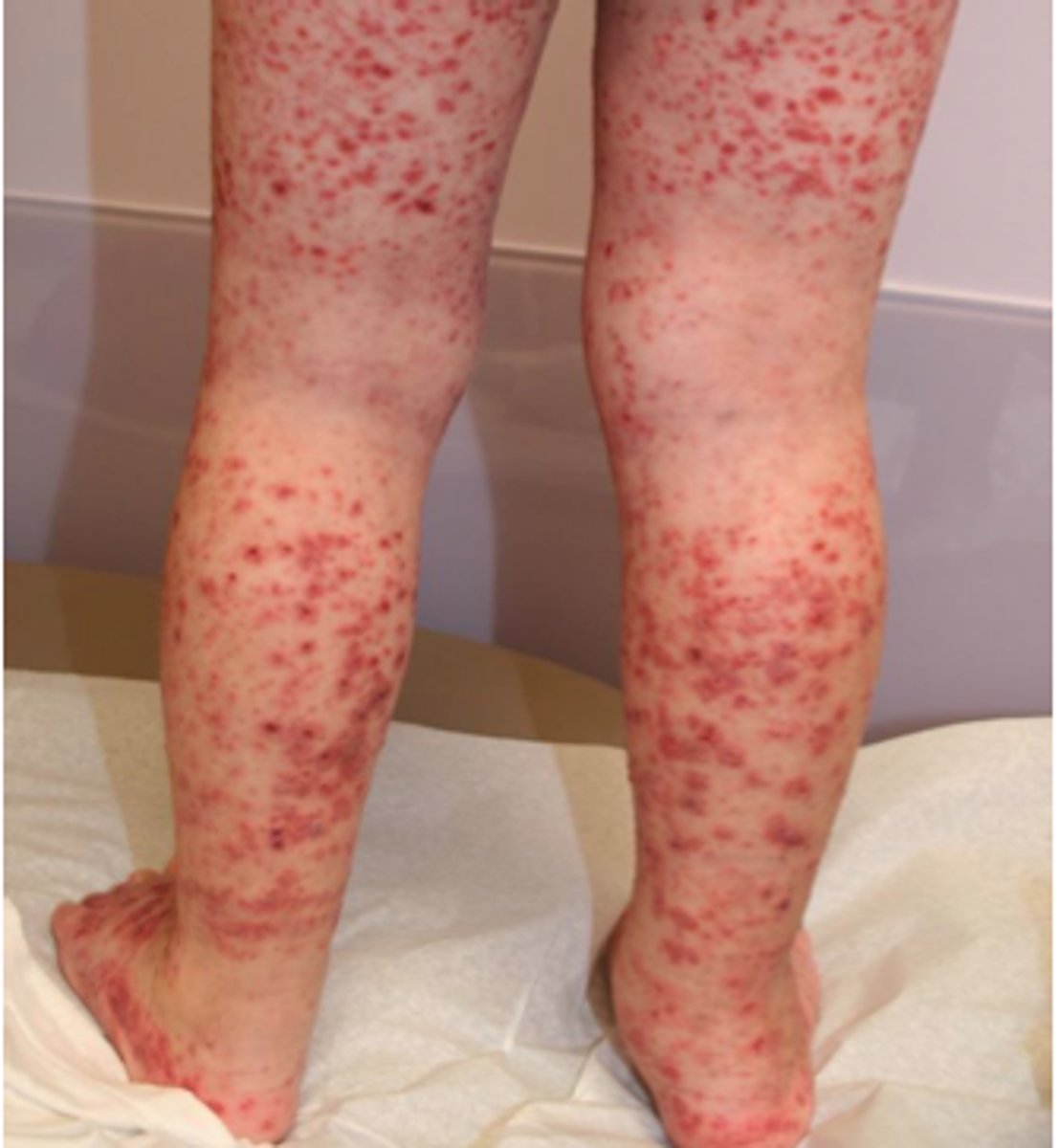
what is the tx for severe/life-threatening ITP?
transfusion
methylprednisolone or dexamethasone
IVIG
which dx is characterized by severe thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, neuro abnormalities?
Thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura (TTP)
also see kidney dz and fever
what is seen on labs in TTP?
increased retic
increased LDH
thrombocytopenia
which dx shows schistocytes on peripheral smear?
TTP → tx with large volume plasmapheresis
what is the MC inherited bleeding disorder?
von Willebrand disease
which dx has prolonged bleeding time, prolonged PTT and is treated with DDAVP?
von willebrand's
what are the s/sx of von willebrand's?
easy bruising
mucosal bleeding
menorrhagia → microcytic anemia
hemarthrosis is rare!
in which dx is there extensive hemorrhage and thrombosis of vital organs?
disseminated intravascular coagulation
also see purpuric ecchymosis and thrombotic events
which dx has prolonged PT, PTT, and thrombin time?
DIC
also elevated fibrin or D-dimer, decreased fibrinogen, decreased factor V and VIII
which dx has delayed clotting and prolonged aPTT, decreased factor VIII?
hemophilia A
normal PT and platelet count
which dx is a deficiency of factor IX?
hemophilia B aka christmas dz → delayed clotting after trauma
which dx has prolonged apTT, normal PT, and decreased factor IX?
hemophilia B
which dx presents as easy bruising, hemarthrosis and forehead hematomas in children?
hemophilia A
and i guess B too?? slide says same s/sx as A
what is the MC childhood leukemia?
ALL "the great imitator"
what confirms dx of ALL?
bone marrow bx → >20% lymphoblasts confirms dx
CXR to detect mediastinal mass
what finding indicates poor prognosis in ALL?
Philadelphia Chromosome translocation
pt presents with fatigue, sweats, and easy bruising. on PE, they have LAD. labs show elevated WBC, prolonged PT and aPTT, and elevated uric acid. what is the likely dx?
ALL → tx w chemo
which dx has characteristic finding of gingival hyperplasia?
AML
also see fatigue, malaise, bone pain, sweats, bleeding, bruising (gingival hyperplasia is the only unique symptom)
which dx shows Auer Rods on blood smear?
AML → pathognomonic finding
which dx has painless LAD, mediastinal mass on CXR, and weight loss?
hodgkin lymphoma
which dx shows Reed Sternberg cells?*
Hodgkin Lymphoma
what are the s/sx of Non-hodgkin lymphoma?
LAD
abd pain
chest pain
cough
fever, weight loss, night sweats
what is the MCV in iron def anemia (IDA)?
microcytic <80
what is the MCV in vitamin B12 and folate deficiency?
macrocytic >100
what is the MCC of vitamin B12 deficiency in children?
malabsorption
which dx presents as demyelination of dorsal columns, peripheral neuropathy, myelopathy, memory loss?
vit B12 deficiency
the Schilling test is used to dx what dz?
rule out pernicious anemia in vit B12 deficiency
differentiates dietary vs. non-dietary
which dx has hyper-segmented neutrophils and increased MCV?
folate deficiency
confirmed by serum and red cell folate levels and vit B12 levels
what is the MC type of primary brain cancer in kids?
medulloblastoma → poorly differentiated neuroepithelial cells that arise in the cerebellum
who is medulloblastoma common in?
males <5 more common
what are the s/sx of medulloblastoma?
nocturnal/morning HA
N/V
AMS
gait ataxia
which brain tumor presents with AMS, HA, visual disturbances, motor impairments, and/or seizures?
astrocytoma → caused by hx of radiation exposure and genetics
where are Ependymomas MC located?
4th ventricle → block CSF flow
which dx is characterized by increased ICP, seizures, and focal deficits?
ependymomas
what is an inherited disorder resulting in production of defective hemoglobin?
sickle cell dz→ MC in AA
homozygous inheritance = disease
heterozygous = trait
what are common s/sx of sickle cell disease?
anemia → pallor, fatigue
hemolysis → jaundice
dactylitis
leg ulcer
priapism
retinal artery obstruction
pain crisis
acute chest syndrome
splenic sequestration
how is sickle cell diagnosed?
elevated retic
smear shows sickle cell
elevated bilirubin
hemoglobin electrophoresis = diagnostic
what is the tx for sickle cell?
hydroxyurea
what is the first value to drop in iron deficiency?
serum ferritin → total body stores → acute phase reactant
what are lab results in IDA?
low serum iron
high TIBC
low ferritin
high RDW
which vitamin aids in absorption of iron?
vit C
what is the MC location of Ewing sarcoma?
diaphysis of long bones
what is the MC location of osteosarcoma?
metaphysis of long bones
correlates with periods of linear growth
when should you obtain a head CT in a child abuse case?
include it always → even if neuro status is normal
which imaging modality detects cerebral edema, interhemispheric subdural hematoma?
CT
victim of shaking
which imaging modality is more sensitive for detecting small subdural hematomas and subtle contusions?
MRI → can also detect brainstem and cervical cord injuries
good at detecting signs of prior/old injuries
what is the MC site of fracture in abuse?
skull
what are the tanner stages?
breast
1. preadolescent
2. breast bud
3. areolar diameter enlarges
4. secondary mound, separation of contours
5. mature female
pubic hair
1. none
2. sparse, long, straight
3. darker, curling, increased #
4. coarse, curly, adult
5. adult, extends to thighs
what is no menarche by 14 with absent secondary sexual characteristics?
primary amenorrhea
no menarche by 16 regardless of secondary sex characteristics
what is secondary amenorrhea?
Absence of menses for 3 months in a woman who has previously menstruated. If a woman has an irregular period, then it must be 6 months
when should the HPV vaccine be given if you receive the first vax prior to age 15?
2 dose series
second dose is 6-12 months later
when should the HPV vaccine be given is the first vax is given after age 15?
3 dose series
0, 2, 6 months
at what age should children visit the dentist by?
by 12 months or after first tooth erupts
when should potty training be initiated?
when child is dry for periods of 2 hrs, knows wet and dry, can pull pants up/down and can indicate bowel movements
what HR indicates bradycardia in children?
infant < 100
toddler < 80
school-aged < 70
adolescents <60
what are causes of tachycardia in peds?
fever
anxiety
hypoxia
hypovolemia
what is the MC etiology of neonatal bacteremia/serious bacterial infection?
group B strep → tx with ampicillin and rocephin or cefotaxime
what is a rapidly progressive encephalopathy with hepatic dysfunction?
Reye's syndrome → caused by viral illness and aspirin use
when should babies be switched to milk from formula?
12 months
when should new foods be introduced to babies?
6 months
what is the ideal nutrition for newborns?
exclusively breastfeeding for the first 4-6 months
what is the bacteremia/SBI tx for infants 39-60 days old and 61-90 days old?
cefotaxine or rocephin
add vanco for MRSA coverage
how do you manage fever in a >3 year old?
antipyretics → tylenol and ibupforen
cooling techniques
fluids
sponging with tepid water
avoid rubbing skin
what are the s/sx of Reye's?
- persistent vomiting, confusion, personality changes, lethargy, hyperactive reflexes
- rapidly progresses to seizures/coma
- increased ICP
- hepatomegaly
insidious progression of a febrile illness over several days suggests which dx?
meningitis
what are the s/sx of meningitis?
infants → fever, irritability, lethargy, bulging fontanelle, poor feeding
older children → decreased responsiveness, vomiting, fever, photophobia, HA
what is the common etiology of meningitis in neonates?
GBS
E. coli
gram-neg bacilli
what are the common etiologies of meningitis in older infants?
S. pneumo
N. meningitidis
what is the MC etio of meningitis in adolescents?
N. meningitidis
which viruses commonly cause meningitis?
enterovirus
arbovirus
HSV
what is the MC finding in shaken baby syndrome?
retinal hemorrhages
assoc. with subdural hematomas
how does subdural hematoma present on non-contrast CT?
concave mass
crosses suture lines
foul smelling breath and unilateral bloody/purulent nasal discharge is a sign of what dx?
nasal FB
which type of burn: epidermis only, painful and erythematous, resolves in 1 week?
1st degree → conservative management
which type of burn: epidermis AND dermis, blister/bleb, red, painful, takes 1-3 weeks to heal?
2nd degree → tx with bacitracin
which type of burn: full thickeness involving epidermis, dermis, subQ tissue; dry, leathery, painless?
3rd degree → requires grafting or healing
IVF if burns >15%
burn center referral criteria
1. Partial thickness burns greater than 10% TBSA
2. Burns that involve the face, hands, feet, genitalia, perineum, or major joints
3. Third degree burns in any age group
4. Electrical burns, including lightning injury
5. Chemical Burns
6. Inhalation injury
7. Burn injury in patients with pre-exsisting conditions
8. Any patient with burns and concomitant trauma
9. Burned children in hospital without qualified personal
10.Burn injury in patients who will require long-term rehabilitative intervention
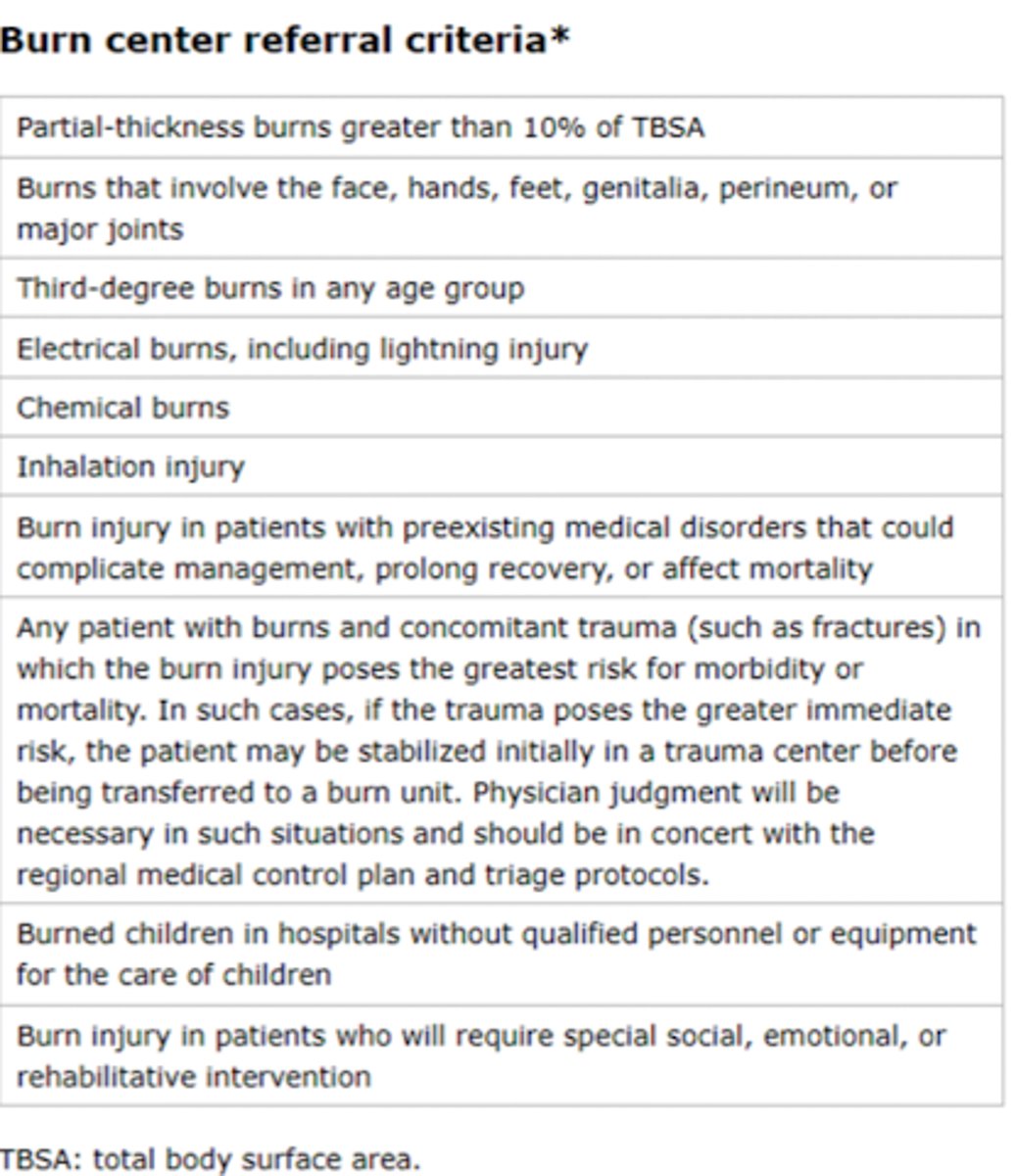
burn criteria for hospital admittance
- children with 5-10% TBSA burn
- full thickness burn 2-5% TBSA
- circumferential burn
- med prob predisposing to infection (DM)
- concern for injury
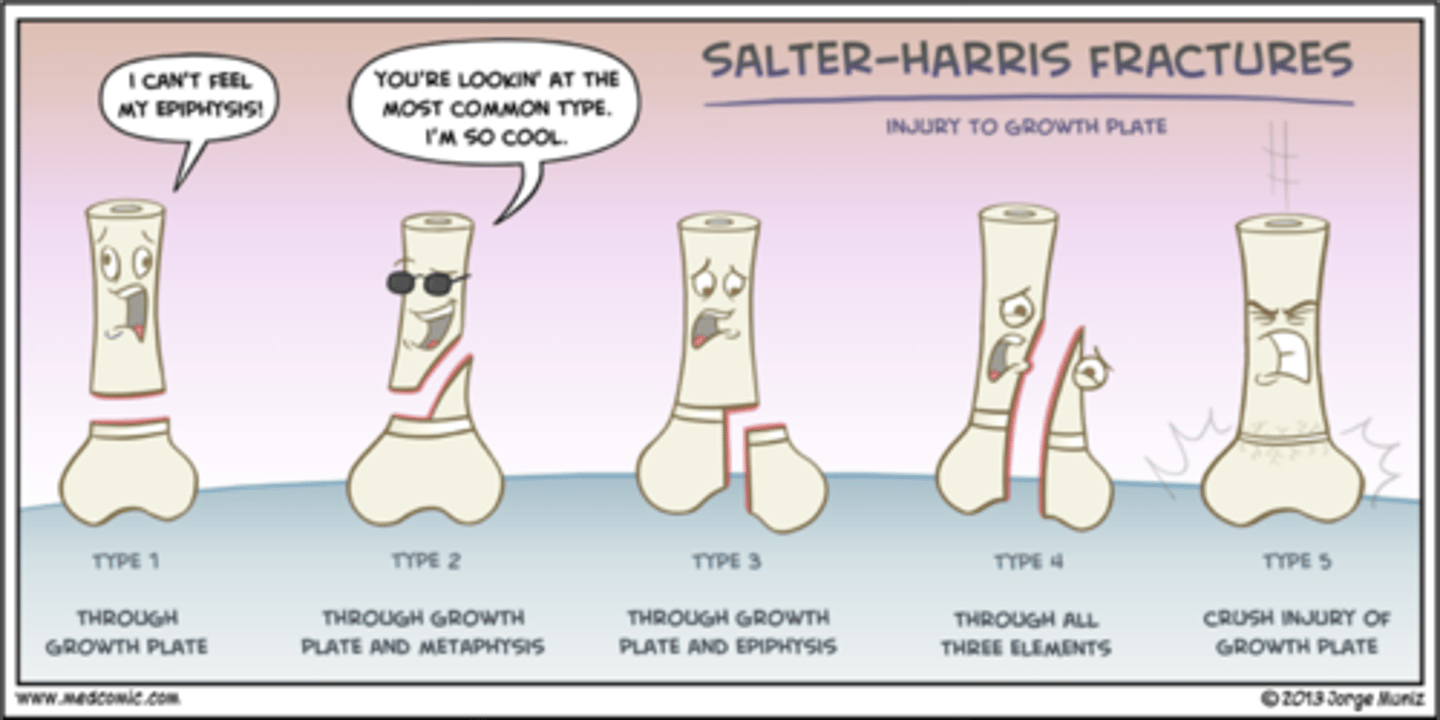
salter harris fractures
............ :|
which drug is commonly used to conscious sedation in peds?
ketamine*
also propofol, precedex, midazolam
which abx are used for animal bites?
augmentin
bactrim
clindamycin
how are asthma exacerbation treated?
hypoxemia → supp O2
bronchospasm→ SABA/cholinergic
inflam → glucocorticoids
raccoon eyes, battle signs, and hemotympanum are all signs of what?
basilar skull fracture → non-contrast CT
what dx shows up as a lens shaped opacity on imaging?
epidural hematoma
what is the MC seizure disorder of childhood?
febrile → temp >100.4
assoc. with infections HHV6 and influenza
what labs should be ordered in febrile seizures?
glucose
calcium
magnesium
electrolytes
when should you give benzos for febrile seizures?
if seizure is >5 mins