ANA300 - Motor and Sensory Pathways
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Pathways consist of ______
a series of neurons which communicate at synapses
Number of ____/____ varies
neurons/pathway
Neuronal cell bodies located in ____ or ______
ganglia, nuclei
____, _____ occurs within ganglia or nuclei at synaptic relays
processing, modulation
Axons group to form ____ in the PNS and ____ in the CNS
nerves, tracts
In the CNS, pathways are ______ while in the PNS, pathways are arranged _____
functionally segregated, regionally
Pathways are _______, usually _____
bilaterally paired, usually crossed
Somatic motor pathways control ______ and consist of a _____ and ______
Skeletal muscle, upper motor neuron, lower motor neuron
Upper motor neuron cell body usually at _____, and axon usually _____, projecting onto LMN
higher centres, decussates
LMN cell body resides in the ________ or in the _________. The axon travels through either a ____ or _____
motor nucleus of a cranial nerve, ventral horn of the spinal cord, cranial, spinal nerve
In the ____ for control of skeletal muscles in the body, cell bodies of LMNs are located in the _____
spinal cord, ventral horn
Axons of the LMN reach their target muscle by travelling in the ____, _____, _____ to NMJ
ventral root, spinal nerve, peripheral nerve
In the _____ for control of skeletal muscle in the face, cell bodies of the LMN are located in ___________
brainstem, cranial nerve nuclei
Axons of LMNs reach their target muscle by travelling in a ____ to the NMJ
cranial nerve
The ____ os the only neuron that contacts the muscle and can therefore influence it, ()
LMN, “final common pathway”
LMNS are typically _____ with ______ that receive and integrate all incoming signals
large neurons, extensive dendritic trees
In the brainstem, LMNs form a series of _____ associated with certain _____
Motor nuclei, cranial Ns
In the spinal cord, LMNs form _____
ventral horns
LMNs controlling ______ located at ______, innervating ______ controlling posture and balance
axial musculature, all spinal levels, ipsilateral muscles,
LMNs controlling _____ found in _____ and _____ only, forming the ______ portion of the ventral horn (C5-T1, L2-S2)
distal limb muscles, cervical, lumbosacral levels
LMNS are innervated by ________ consisting of _____
Descending pathways, upper motor neurons
In the lateral pathway, UMNS descend in the _______; include the __________
lateral funiculus, lateral corticospinal tract
In lateral pathways, UMNs innervate LMNs of the ______ to control _____
lateral ventral horn, distal limb muscles
The lateral corticospinal tract allows for ________
skilled, asymmetric limb movement
The corticospinal tract originates in _____ of the _____ which contains cell bodies of UMNs
primary motor cortex, precentral gyrus
Axons of the UMN traverse the ________ of the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem
subcortical white matter
At the junction of the _____ and ____, most fibres of the CST ____ and descend ____ in the lateral funiculus. The remainder descend _______ as the _____
medulla, spinal cord, decussate, contralaterally, ipsilaterally, MCST
Axons of the LCST synapse on LMNs in the _____ which innervate _______ for discrete, skilled movement
lateral ventral horn, distal limb musculature
_______ concern themsleves with our internal environment
interoceptors
______ concern themselves with our external environment such as ____ and ____
exteroceptors, special senses, somatosensation
Conscious sensation is the small fraction of sensory input that reaches _________________ in the _________, determining the ____ and ____ of sensation
modality-specific primary sensory cortex, contralateral cerebral hemisphere, location, nature
Somatosensory pathways consist of a ______—
3 neuron chain
The primary neuron is ________, with its cell body located in a ______ of the PNS
pseudounipolar, ganglion,
For a somatosensory pathway in the body, the axon travels in a ________, _____, and ____ and its cell body is located in a _____
peripheral nerve, spinal nerve, dorsal root, DRG
The cell body of the secondary neuron is either in a ______ of the spinal cord or a _____. It’s axon projects to the ______
dorsal horn, brainstem nucleus, contralateral thalamus
In somatosensory pathways, the axon of the _____ decussates
secondary neuron
The cell body of the tertiary neuron is in the ______ of the thalamus. Its axon projects to the ____
VP nucleus, Primary SS cortex
In the dorsal columns, the _______ and _______ sense touch, vibration, and conscious proprioception ____ and ____ T6 respectively
fasciculus gracilis, fasciculus cuneatus, below, above
Spinothalamic tract in the _______ senses _____, _____, and _____
Ventral lateral fasciculus, pressure, pain, temperature
In the spinothalamic tract, primary neuron cell bodies lie in _____ in the PNS and project to CNS via _____
dorsal root ganglia, dorsal roots
In the spinothalamic tract, secondary cell bodies lie in the ____ of the spinal cord
dorsal horn
Axons of the secondary neurons in the spinothalamic tract ____ and ascend to become the ______ in the brainstem
decussate, spinal lemniscus
Cell bodies lie in the _____ of the thalamus and project to _________
VP nucleus, primary SS in post central gyrus
As you ascend in the spinal cord, more and more ____ are added to the STT
axons
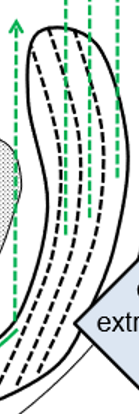
Left-Right
Cervical
Thoracic
Lumbar
Sacral/coccygeal
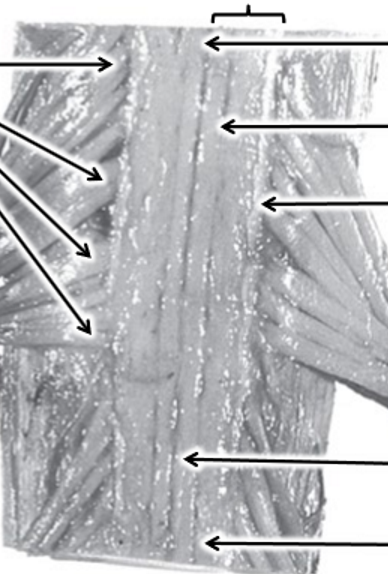
Left and right, top to bottom
C7 Dorsal rootlets
Dorsal column
Dorsal median
Dorsal intermediate
Dorsal lateral
Fasciculus gracilis
Faciculus cuneatus
In dorsal columns/medial lemniscus system, primary neurons lie in ________ and project to the CNS via ___
dorsal root ganglia, dorsal roots
For the lower body, primary neurons of the ____ ascend in the _______
dorsal columns, ipsilateral fasciculus gracilis
The secondar neuron cell bodies are in the ___ of the medulla, and axons ____, ascending _____ as the ______ through the brainstem
nucleus gracilis, ducussate, contralaterally, medial lemniscus
Tertiary neruonal cell bodies in the ____ and project to _____ in the _____
VP thalamus, 1 SS cortex, postcentral gyrus
For the upper body, pimrary neuronal cell bodies lie in _____ and project to the CNS via ___
dorsal root ganglia, dorsal roots
For the upper body, primary neurons ascend in the _________
ipsilateral fasciculus cuneatus
Secondary neurons of of dorsal columns in the upper body: cell bodies in the _____. Axons _____ and ascend ______ in the _____ through the brainstem
Nucleus cuneatus, decussate, contralaterally, medial lemniscus
For tertiary neurons sensing from the upper body, cell bodies in the _____ and project to ________ in the postcentral gyrus
VP thalamus, primary SS cortex

Motor cortex
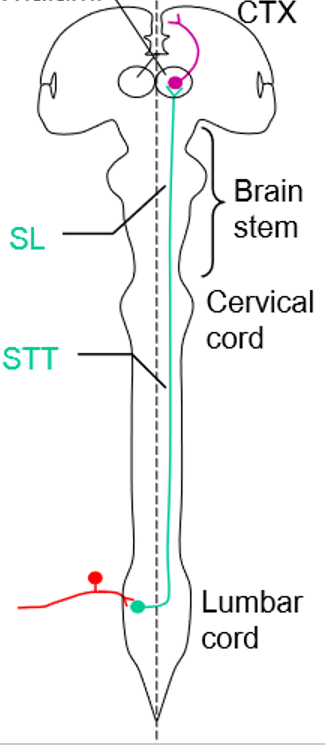
Spinothalamic tract
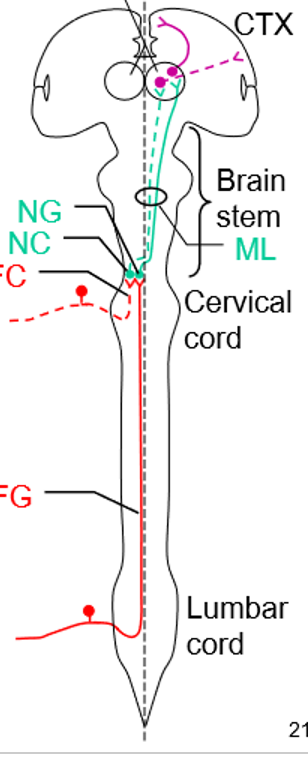
Dorsal column system