BIO 107: Unit 3 - Ch 11 Muscle Tissue
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be sure to enable 'answer with term' in the Practice Test and Learn feature.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
What are the skeletal muscle levels of organization from largest to smallest?
What are these levels of:
Skeletal Muscle
Muscle Fascicle
Muscle Fiber
Myofibril
Sarcomere
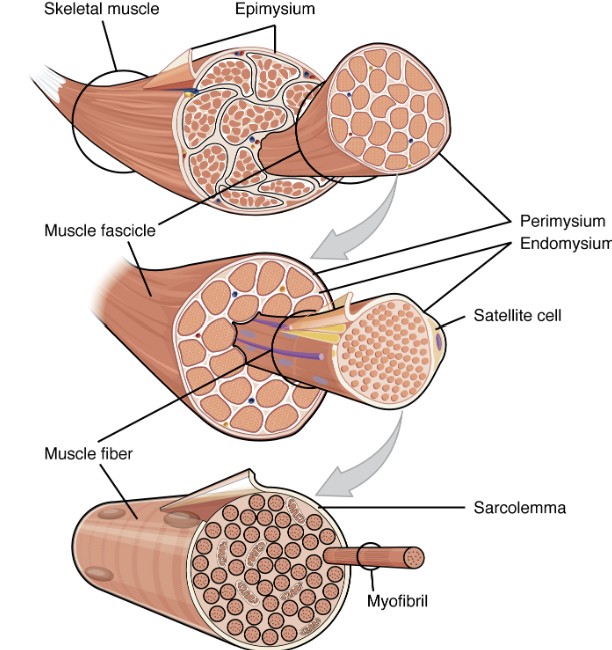
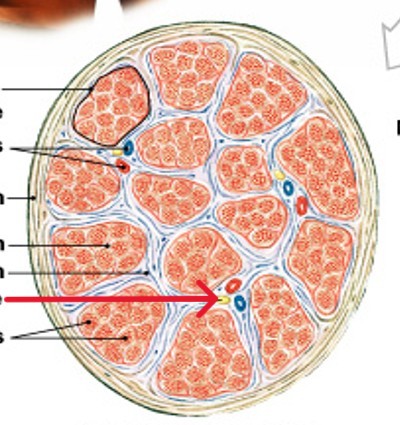
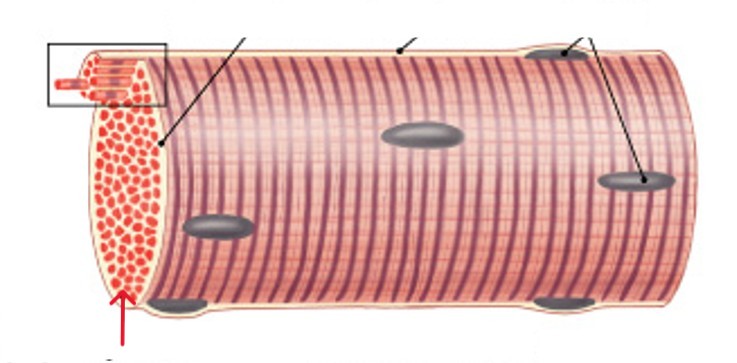
What is the epimysium layer of muscle tissue?
Which connective tissue layer of the muscle is:
Surrounds entire muscle, connects to deep fascia
Separates muscle from surrounding tissues
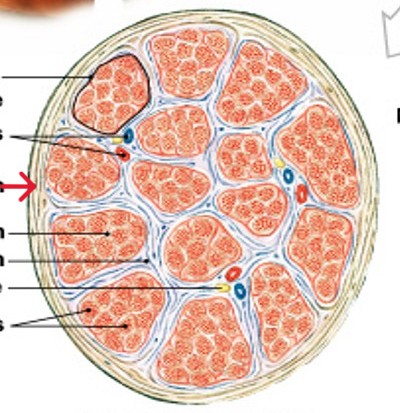
What is the perimysium layer of muscle tissue?
Which connective tissue layer of the muscle is:
Surrounds muscle fiber bundles (fascicles)
Contains blood vessel and nerve supply to fascicles

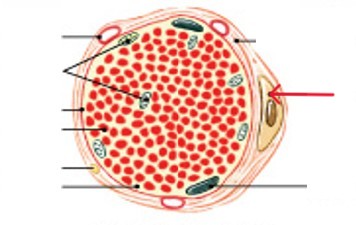
What is the endomysium layer of muscle tissue?
Which connective tissue layer of the muscle is:
Surrounds individual muscle cells (muscle fibers)
Contains capillaries and nerve fibers contacting muscle cells
Contains satellite cells (stem cells) that repair damage
What are satellite cells?
What are the stem cells that repairs damaged muscle tissue?
What are nerves?
What controls the muscle cell and allow voluntary movement?
What are the functions of muscle?
What are these functions of:
Produce skeletal movement
Maintain body position
Support soft tissues
Guard body openings
Maintain body temperature
Store nutrient reserves
What are the functions of blood vessels in muscle?
What are these functions of:
Supply large amounts of oxygen
Supply nutrients
Carry away wastes
What is a direct connection?
Which type of muscle connection is:
Muscle to bone (rare)
What is a tendon connection?
Which type of muscle connection is:
Bundle at ends
What is an aponeurosis connection?
Which type of muscle connection is:
Broad sheet (abs)
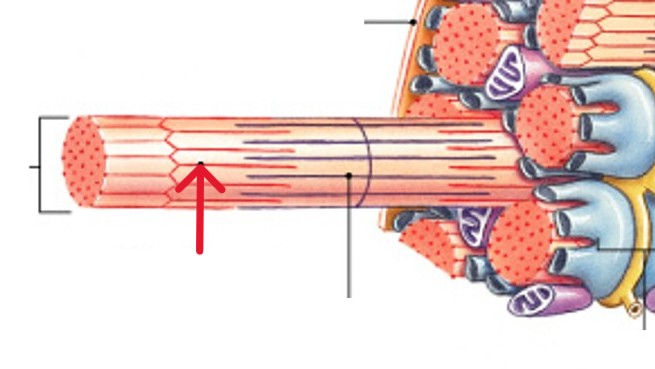
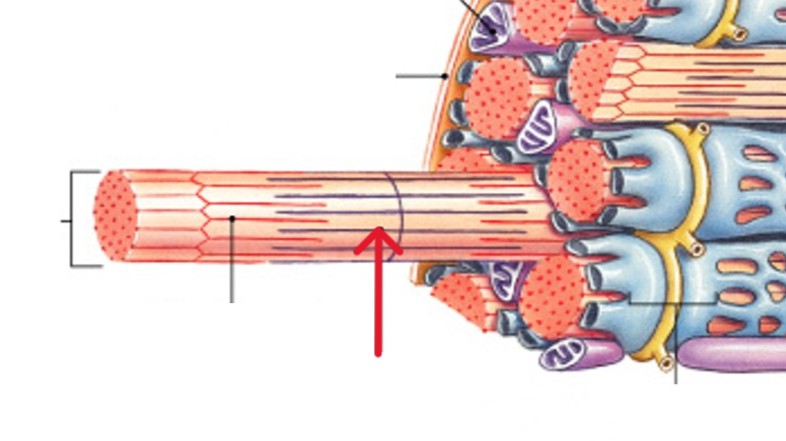
What are skeletal muscle fibers?
What type of cells are:
Very long
Develop from cells called myoblasts
Become very large
Contain hundreds of nuclei
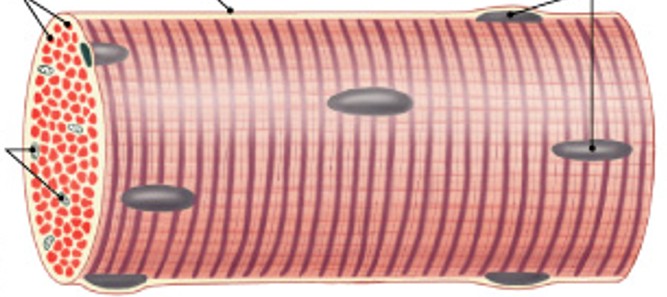
What is the sarcolemma of the muscle fibers?
Which part of the muscle fibers is:
The cell membrane of a muscle cell
Maintains a transmembrane potential
Surrounds the sarcoplasm (cytoplasm of muscle cell)
What is the sarcoplasm of the muscle fibers?
Which part of the muscle fibers is:
The cytoplasm of muscle cell
What are the transverse tubules (T tubules) of the muscle fibers?
Which part of the muscle fibers is:
Transmit action potential through cell
Allow entire muscle fiber to contract simultaneously
Filled with extracellular fluid
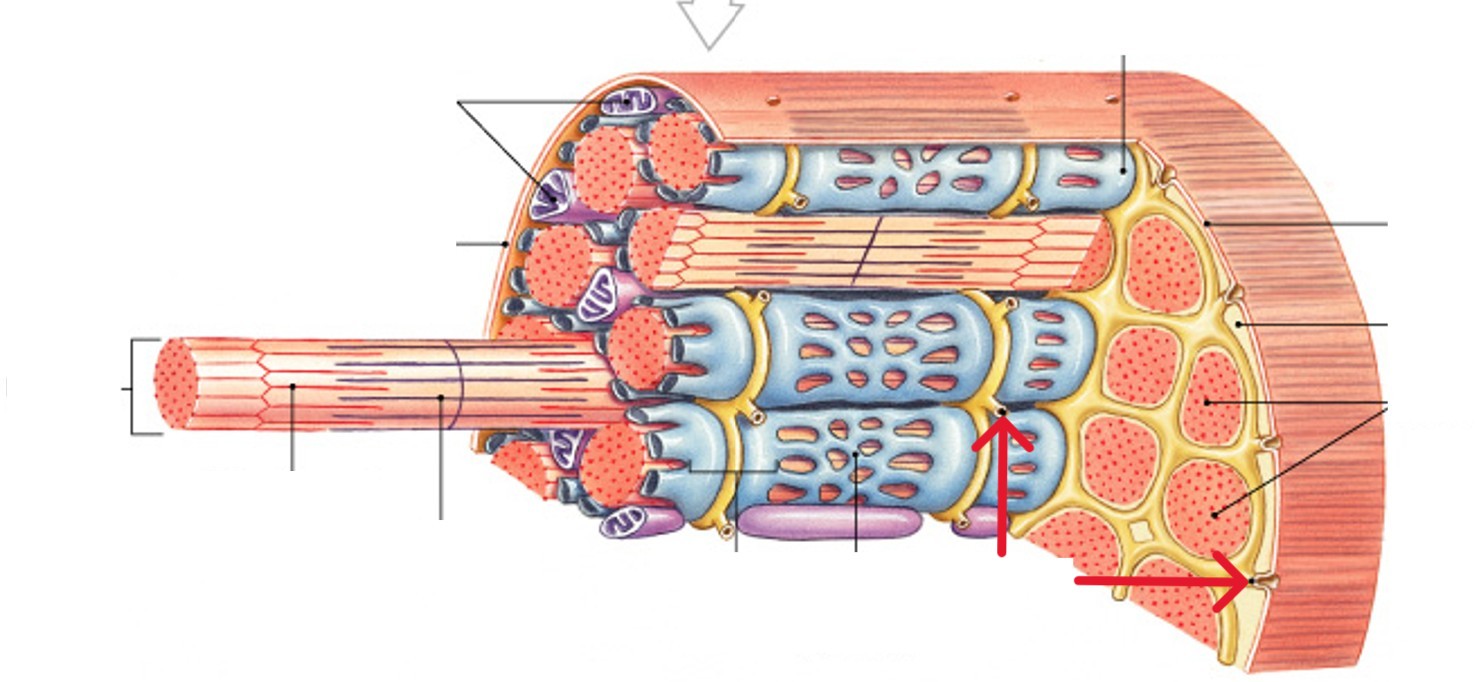
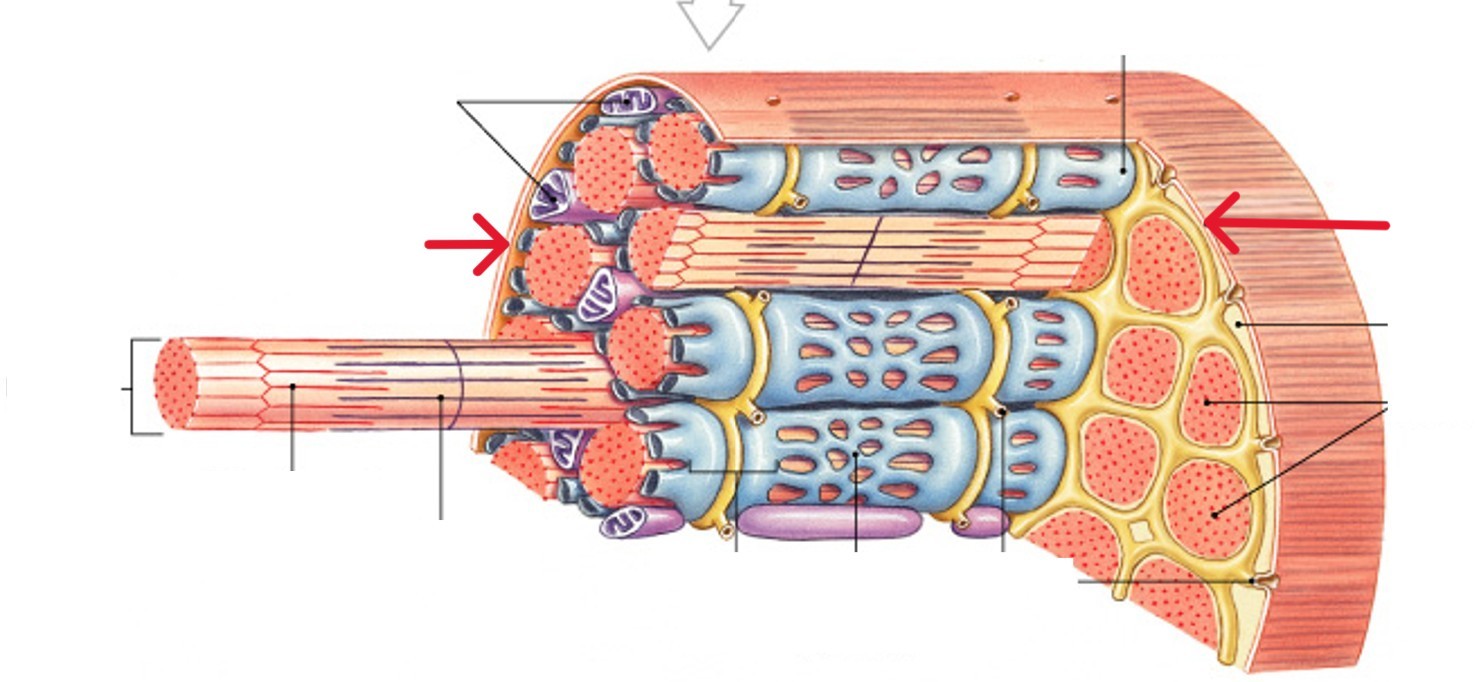
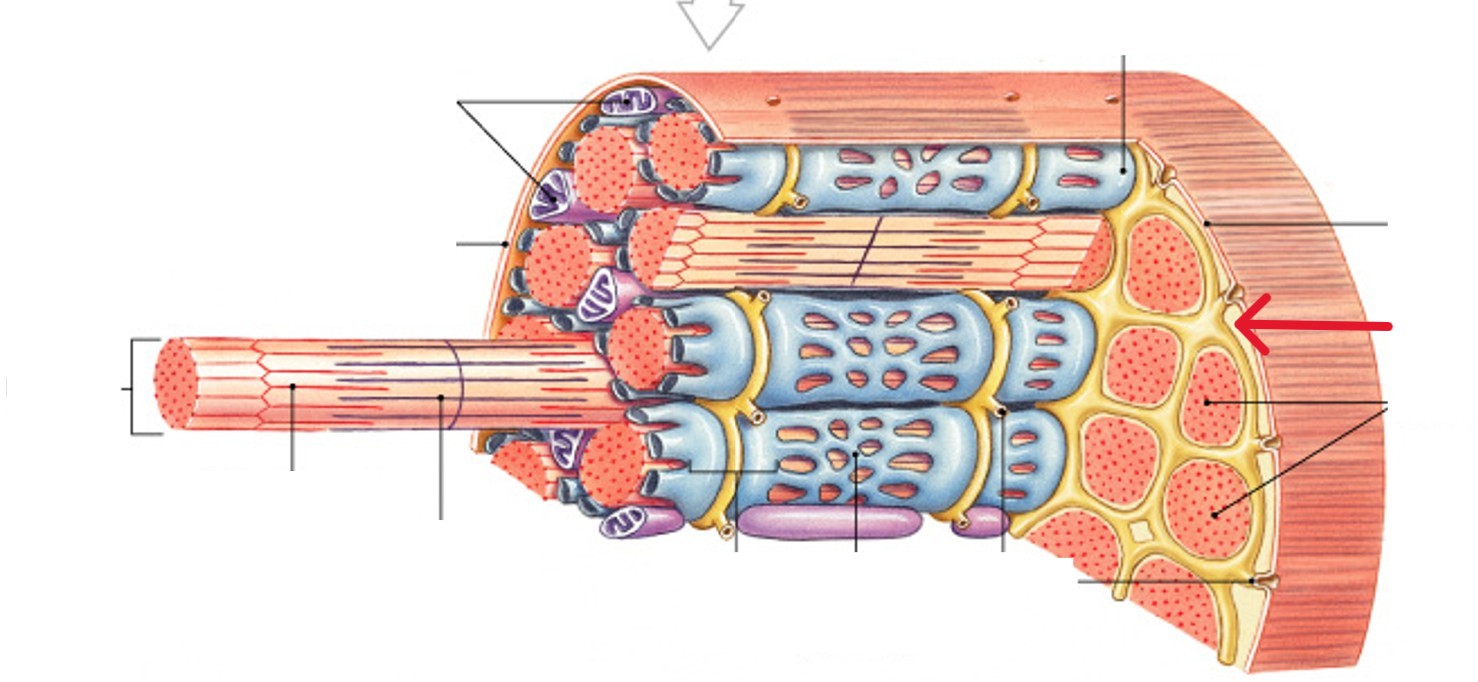
What are the myofibrils of the muscle fibers?
Which part of the muscle fibers is:
Subdivisions within muscle fiber
Each muscle fiber contains thousands
Made up of bundles of protein filaments (myofilaments)
What are thin filaments?
Which type of myofilaments are made of the protein actin?
What are thick filaments?
Which type of myofilaments are made of the protein myosin?
What are sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) of the muscle fibers?
Which part of the muscle fibers is:
A membranous structure surrounding each myofibril
Contains a high concentration of calcium ions
Forms chamber attached to T tubules
Helps transmit action potential to myofibril
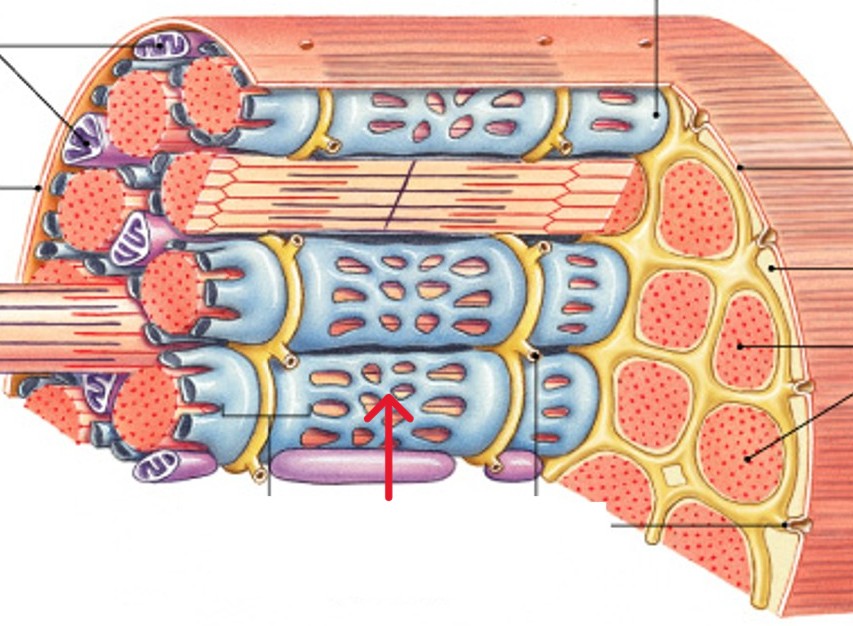
What are sarcomeres?
What is the smallest functional units of muscle (contractile units)?
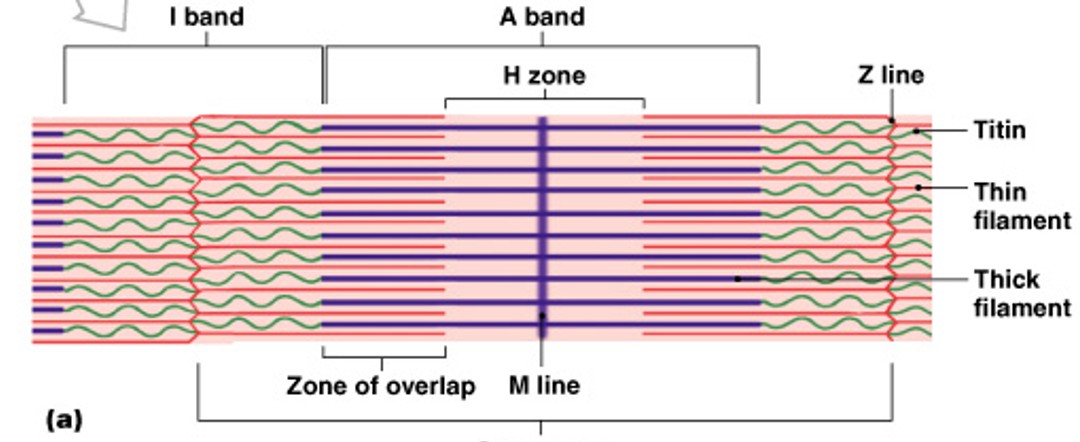
What is the A-band in sarcomere?
Which part of the sarcomere is:
The center of sarcomere, equals length of thick filament
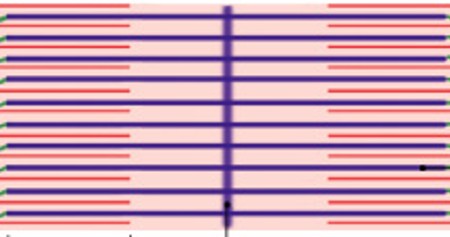
What is the M-line of the A-band?
Which part of the A-band is:
The center of the A-band, thick filament
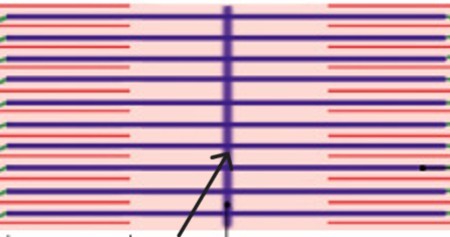
What is the H-zone of the A-band?
Which part of the A-band is:
Area of thick filament with no thin filaments
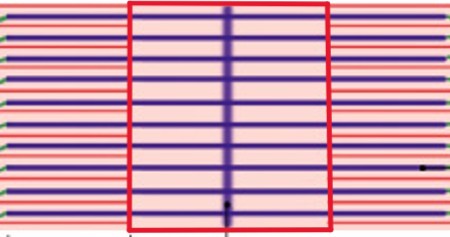
What is the Zone of Overlap of the A-band?
Which part of the A-band is:
Area where thick and thin filaments overlap (darkest of dark)

What is the I-band in sarcomere?
Which part of the sarcomere is:
Contains thin filament only
What is the Z-lines of the I-band?
Which part of the I-band is:
Mark the boundary between adjacent sarcomeres
What is the titin of the I-band?
Which part of the I-band is:
Elastic protein, keeps thick and thin filaments aligned
What are the functions of sarcomere?
What are these functions of:
Transverse tubules encircle the sarcomere near zones of overlap
Ca2+ released by SR causes thin and thick filaments to interact
What is the F/G actin of thin filament proteins?
Which of the four thin filament proteins is:
2 twisted rows of globular G actin
The active sites on G actin strands bind to myosin
What is the Nebulin of thin filament proteins?
Which of the four thin filament proteins is:
Holds F actin strands together
What is the tropomyosin (door) of thin filament proteins?
Which of the four thin filament proteins is:
Is a double strand that covers G actin
Prevents actin-myosin interaction
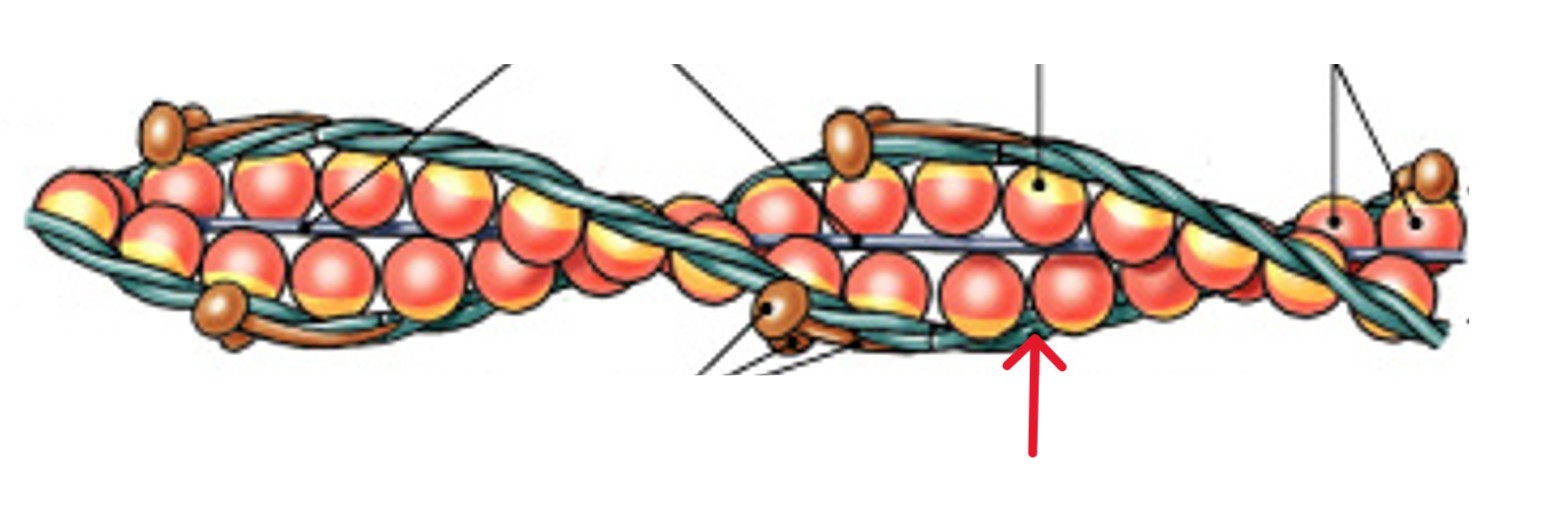
What is the troponin (lock) of thin filament proteins?
Which of the four thin filament protein is:
A globular protein
Binds tropomyosin to G actin
Binds with Ca2+ to unlock active sites
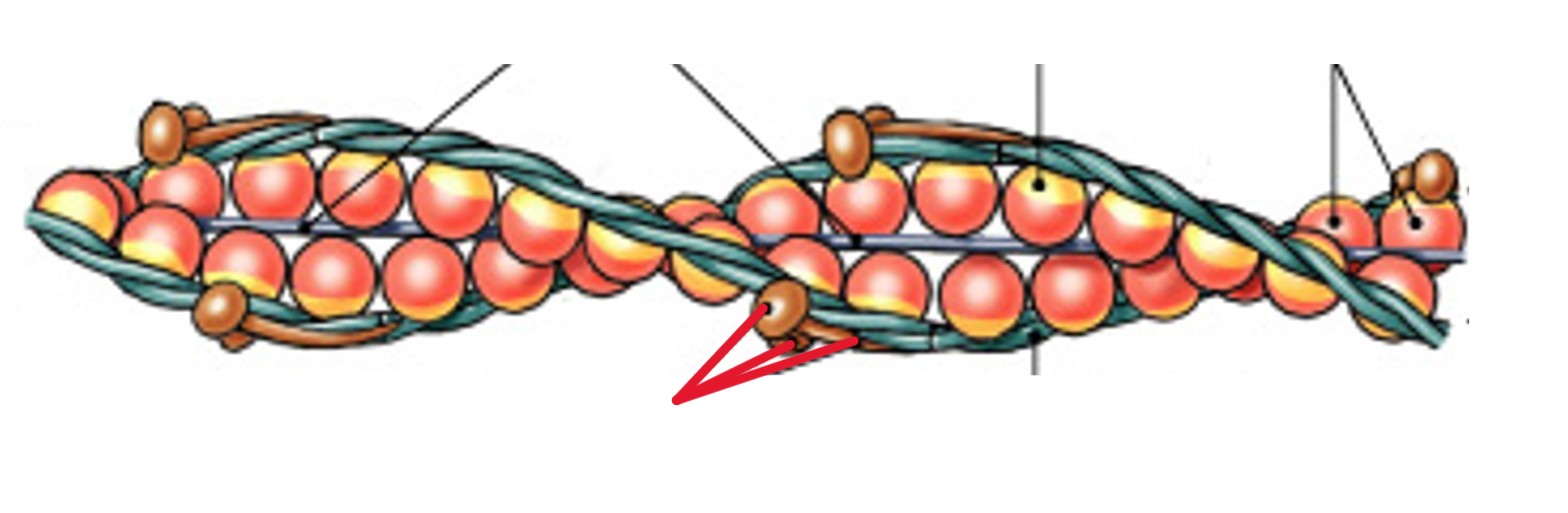
What are thick filaments (myosin) of muscle fibers?
What part of the muscle fibers is:
Contain twisted myosin subunits
Contain titin strands that recoil after stretching

What is the head of the thick filaments (myosin)?
Which part of the thick filaments (myosin) is:
Made of 2 globular protein subunits
Projects toward nearest thin filament (actin)

What is the tail of the thick filaments (myosin)?
Which part of the thick filaments (myosin) is:
Binds to other myosin molecules
Points toward M-line
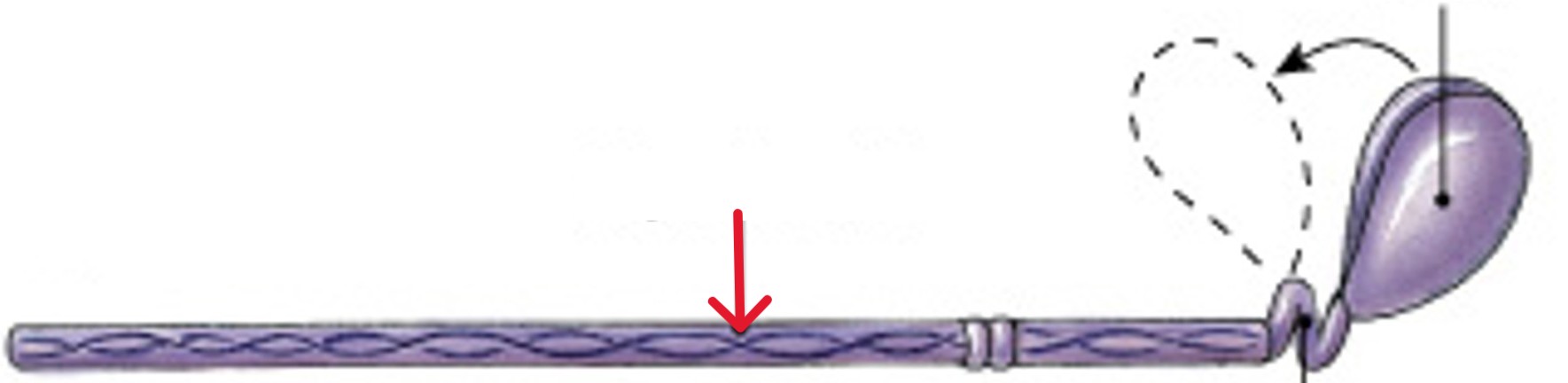
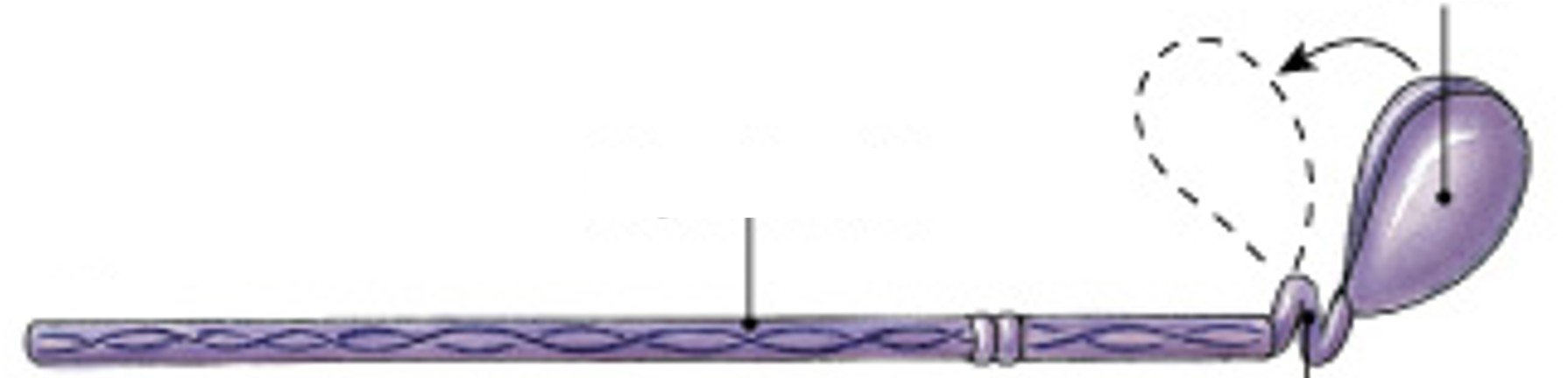
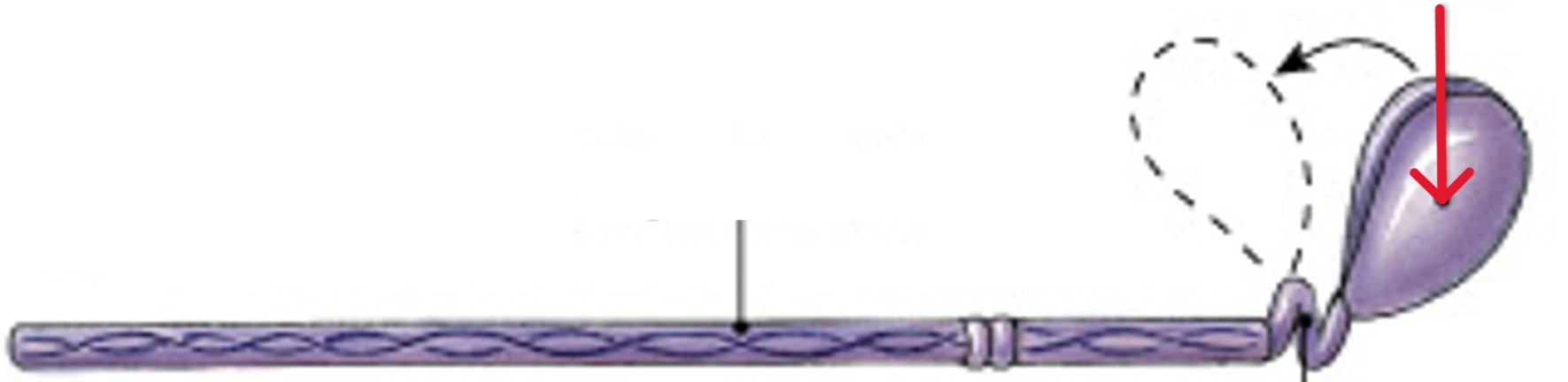
What is hinge of the myosin molecule?
Which type of myosin action is:
Lets head pivot at its base, power stroke

What is cross-bridges of the myosin molecule?
Which type of myosin action is:
Connection made when myosin head connects with G actin active sites
What is calcium (key)?
What binds to receptor on troponin?
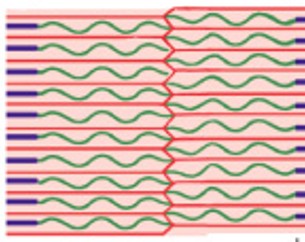
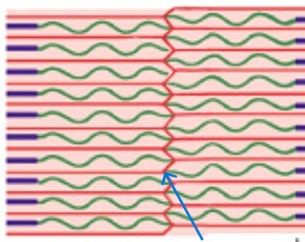
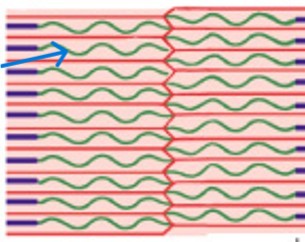
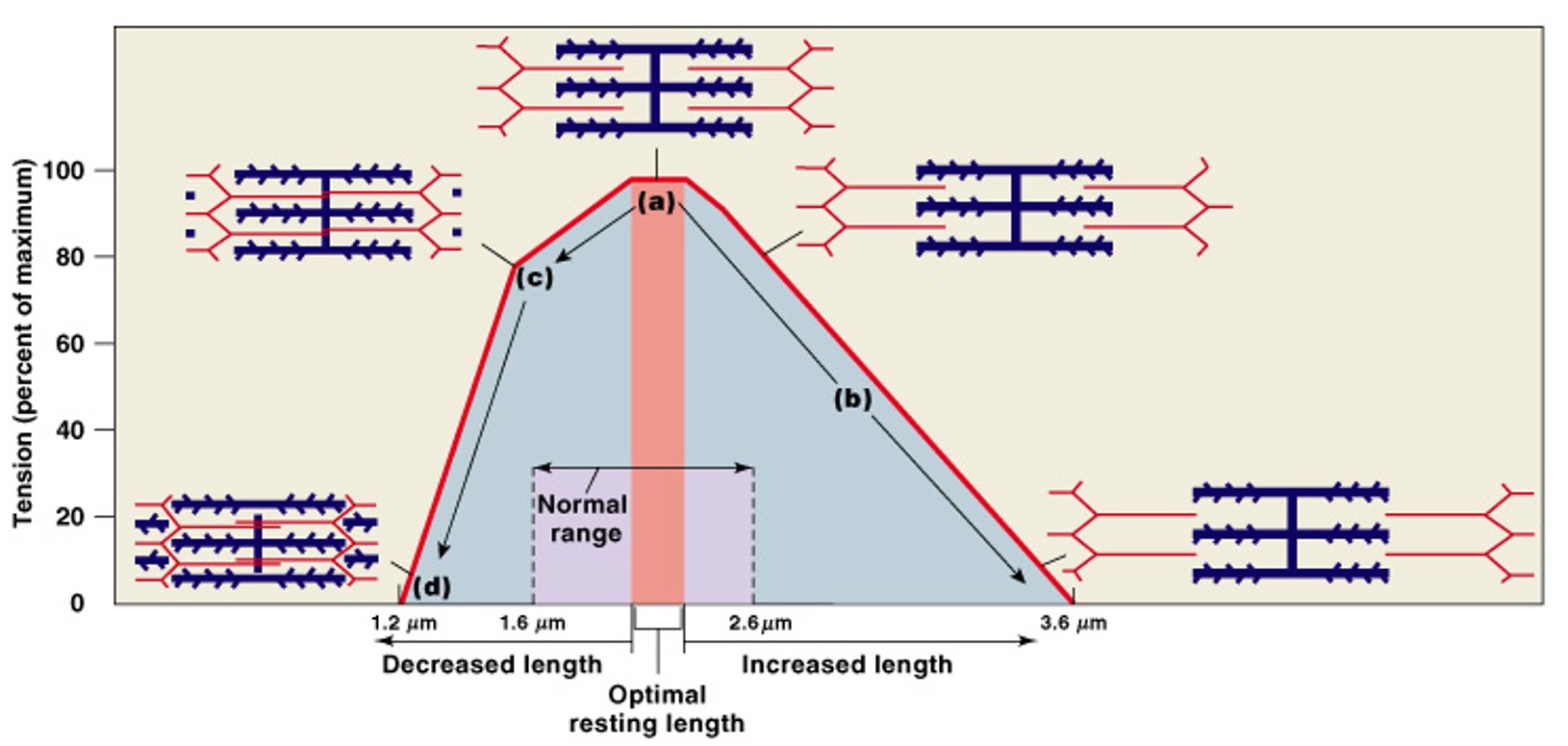
What is the sliding filament theory?
Which theory of muscle contraction has:
H-zones & I-bands get smaller
Zones of overlap get larger
Z-lines move closer together
Width of A-band remains constant

What is the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle innervation?
Where do neuron meets muscle fiber in skeletal muscle innervation?
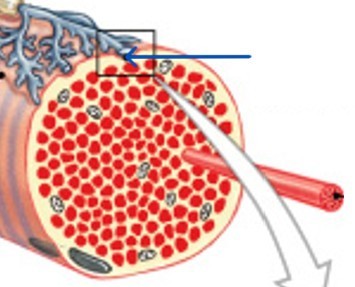
What is the synaptic terminal in skeletal muscle innervation?
What part of the skeletal muscle innervation is:
Releases neurotransmitter (acetylcholine or ACh)
Into the synaptic cleft (gap between synaptic terminal and motor end plate)
Branch ends of the axon at neuromuscular junction
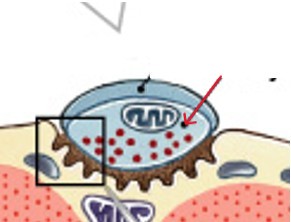
What is the motor end plate in skeletal muscle innervation?
What are membranes that send and receive ACh in skeletal muscle innervation?
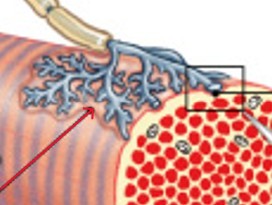
What is action potential in skeletal muscle innervation?
What is the sudden change in the transmembrane potential in skeletal muscle innervation?
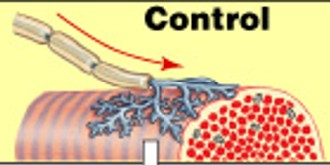
What is acetylcholine or ACh in skeletal muscle innervation?
What is a neurotransmitter that changes permeability & properties of another cell’s membrane in skeletal muscle innervation?
What is the process and steps of muscle stimulation?
What is this the process of:
Action potential arrives
Release of ACh
ACh binds at Motor End Plate
Action Potential in Sarcolemma
Repolarize
What is the first step of muscle stimulation?
Which step of muscle stimulation is:
Action potential arrives

What is the second step of muscle stimulation, after action potential arrives?
Which step of muscle stimulation is:
Release of ACh
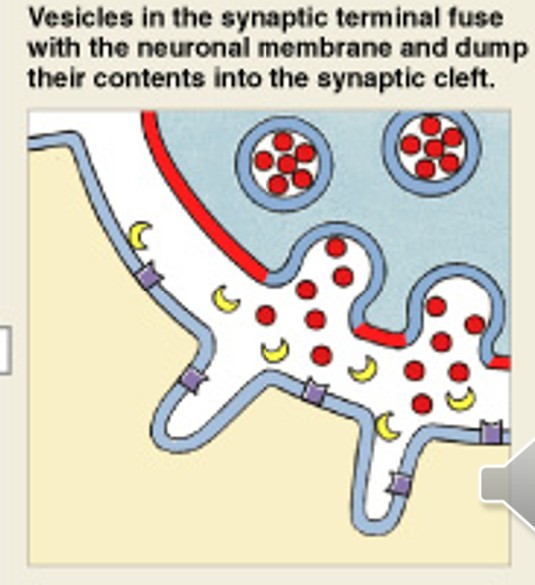
What is the third step of muscle stimulation, after release of ACh?
Which step of muscle stimulation is:
ACh binds at Motor End Plate

What is the fourth step of muscle stimulation, after ACh binds at Motor End Plate?
Which step of muscle stimulation is:
Action Potential in Sarcolemma
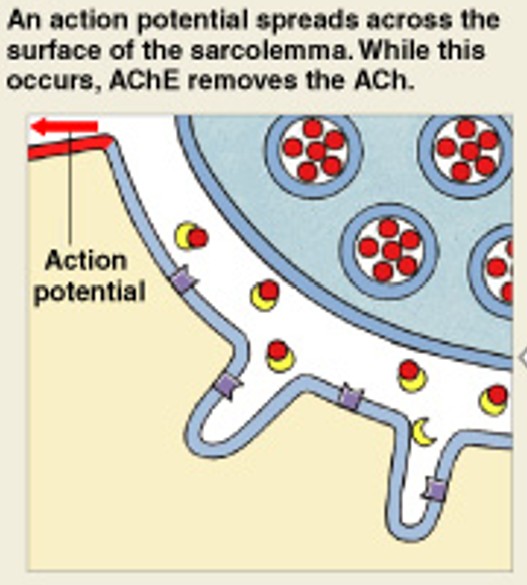
What is the fifth step of muscle stimulation, after action potential in Sarcolemma?
Which step of muscle stimulation is:
Repolarize
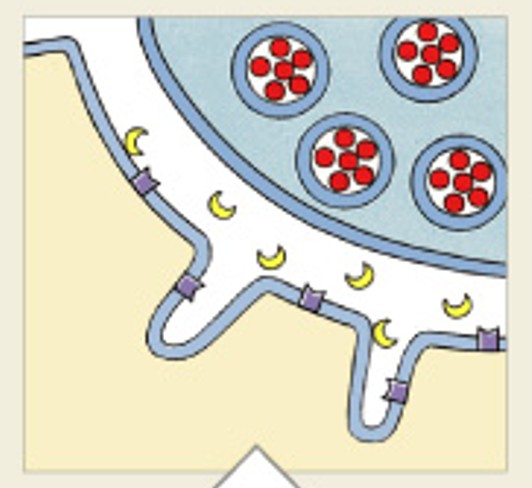
What is the process and steps of contraction cycle?
What is this the process of:
Exposure of active sites
Formation of cross-bridges
Pivoting of myosin heads
Detachment of cross-bridges
Reactivation of myosin
What is the 1st step of the contraction cycle?
Which step of the contraction cycle is:
Exposure of active sites

What is the 2nd step of the contraction cycle, after exposure of active sites?
Which step of the contraction cycle is:
Formation of cross-bridges

What is the 3rd step of the contraction cycle, after formation of cross-bridges?
Which step of the contraction cycle is:
Pivoting of myosin heads
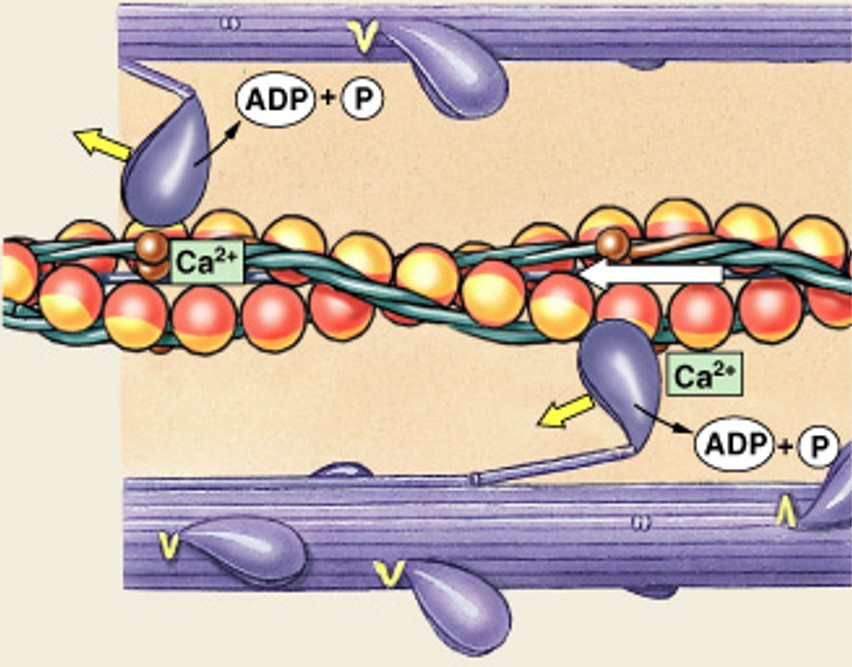
What is the 4th step of the contraction cycle, after pivoting of myosin heads?
Which step of the contraction cycle is:
Detachment of cross-bridges
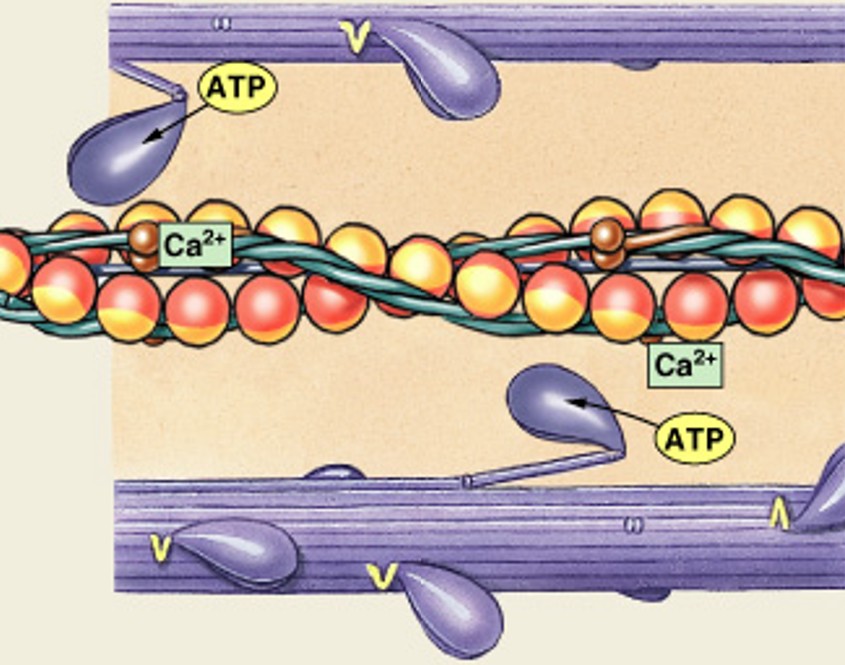
What is the 5th step of the contraction cycle, after detachment of cross-bridges?
Which step of the contraction cycle is:
Reactivation of myosin
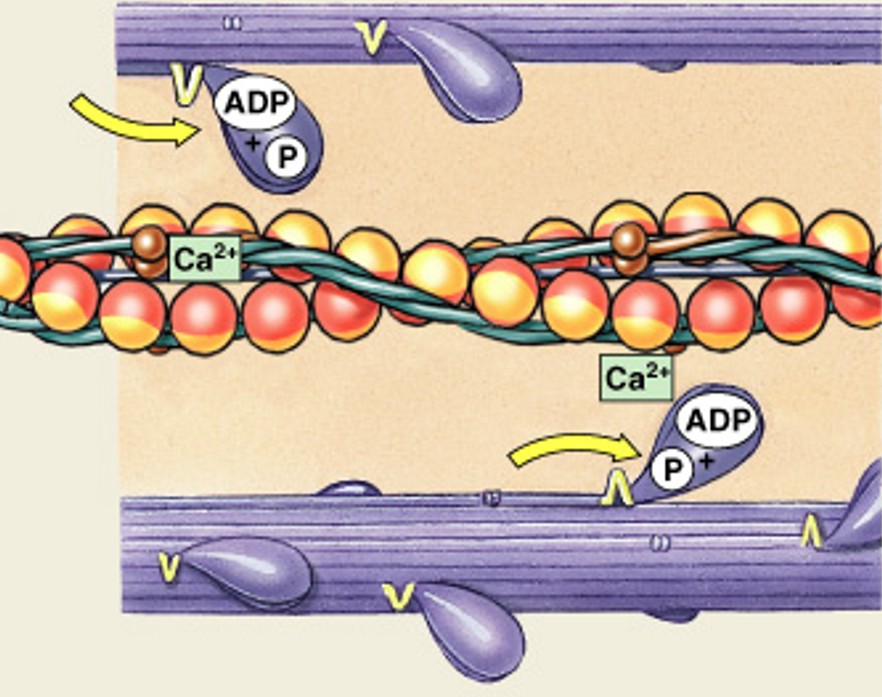
What is rigor mortis?
What occurs after death causing fixed muscular contraction?
What are the 3 phases of twitch?
What are these phases of:
Latent period
Contraction phase
Relaxation phase
What is the latent period of twitch?
Which phase of twitch is:
The action potential moves through sarcolemma causing Ca2+ release
What is the contraction phase of twitch?
Which phase of twitch is:
Calcium ions bind
Tension builds to peak
What is the relaxation phase of twitch?
Which phase of twitch is:
Ca2+ levels fall
Active sites are covered
Tension falls to resting levels
What is the relaxation phase at the end of stimulation?
What is the end of stimulation at neuromuscular junction, and runs out of energy (ATP) to power contraction → contraction stops?
What are treppe stimulations?
Which type of stimulations are:
Repeated stimulations immediately after relaxation phase (stimulus frequency < 50/second)
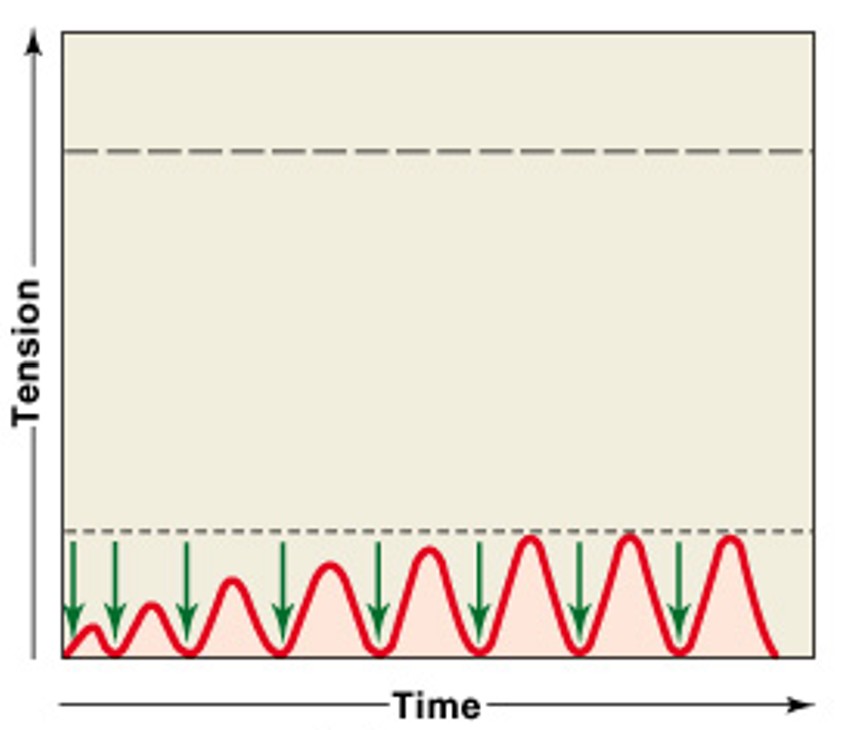
What is wave summation?
Which type of stimulations are:
Repeated stimulations before the end of relaxation phase (stimulus frequency > 50/second)
Causes increasing tension or summation of twitches

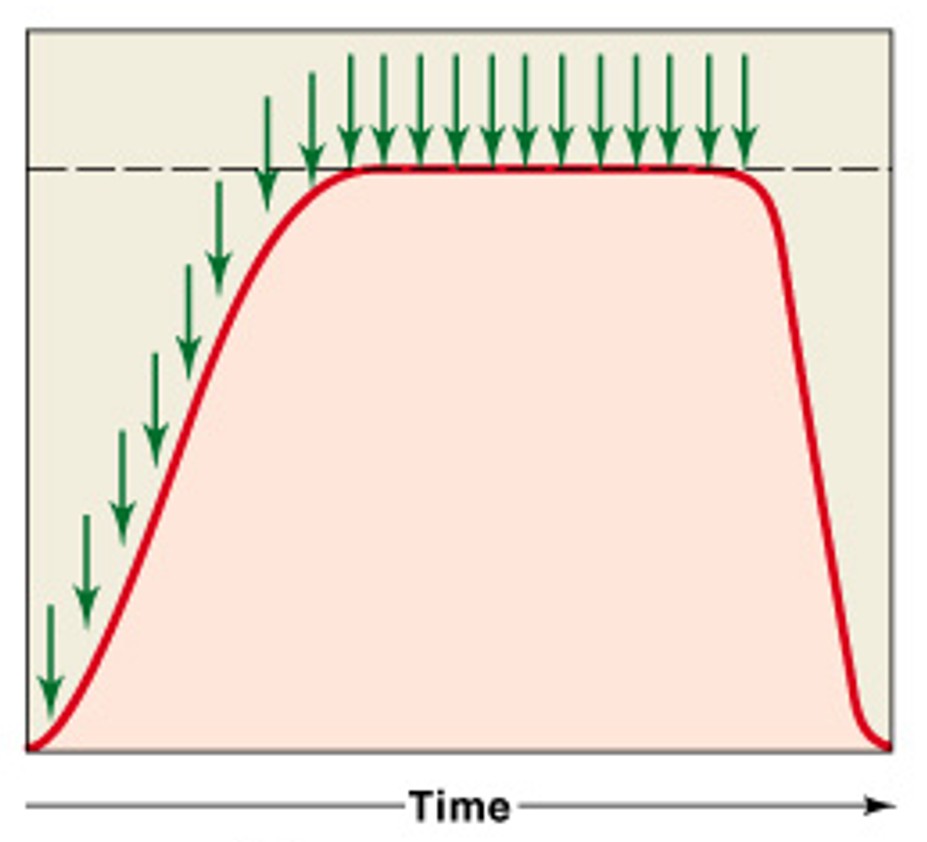
What is incomplete tetanus?
Which type of tetanus is:
If rapid stimulation continues and muscle is not allowed to relax, twitches reach maximum level of tension

What is complete tetanus?
Which type of tetanus is:
If stimulation frequency is high enough, muscle never begins to relax, and is in continuous contraction
What is motor units in a skeletal muscle?
What part in the skeletal muscle is:
Contain hundreds of muscle fibers
Contract at the same time
Controlled by a single motor neuron
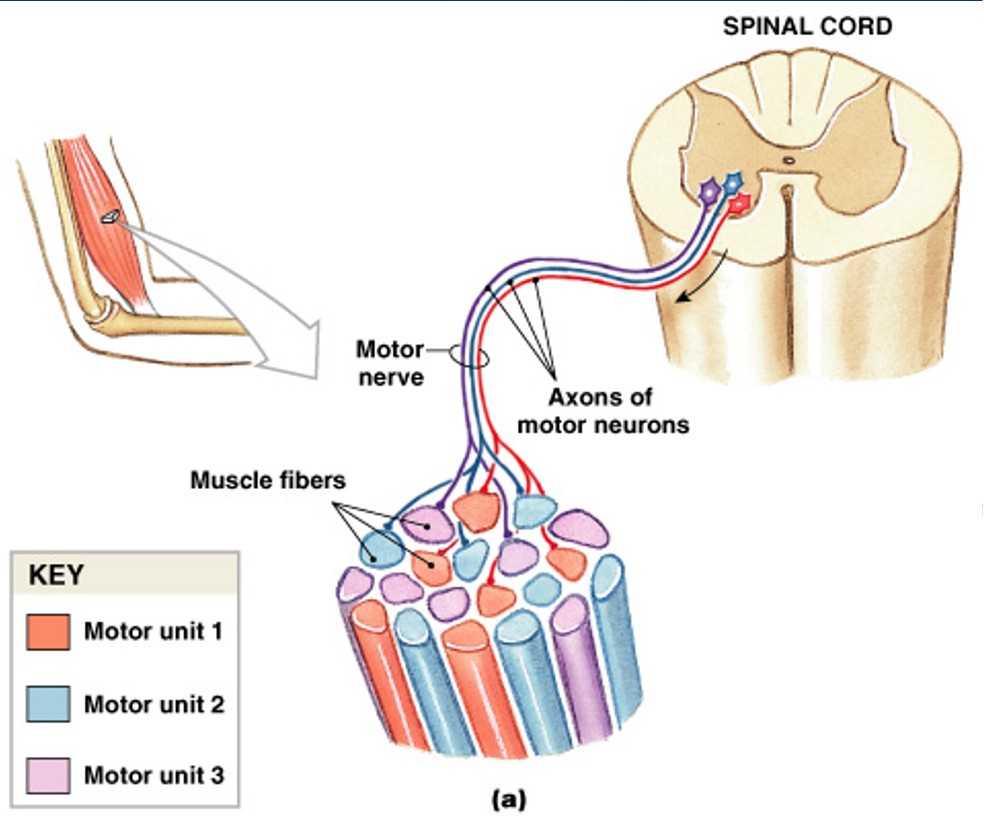
What is recruitment (multiple motor unit summation)?
Which type of muscle tension/contraction is:
In a whole muscle or group of muscles, smooth motion and increasing size or number of motor units stimulated
What is maximum tension?
Which type of muscle tension/contraction is:
Achieved when all motor units reach tetanus, and can be sustained only a very short time
What is sustained tension?
Which type of muscle tension/contraction is:
Less than maximum tension
Allows motor units to rest in rotation
Increasing muscle tone increases what?
What increases metabolic energy used, even at rest?
What are isotonic contractions?
How do the skeletal muscle changes length - resulting in motion?

What is concentric contraction of isotonic?
Which type of isotonic contraction is:
Muscle tension > resistance
Muscle shortens
What is eccentric contraction of isotonic?
Which type of isotonic contraction is:
Muscle tension < resistance
Muscle lengthens
What are Isometric contractions?
How do skeletal muscle develops tension, but is prevented from changing length?

What are the functions of muscle metabolism?
What are these functions of:
Sustained muscle contraction uses a lot of ATP energy
Muscles store enough energy to start contraction
Muscle fibers must manufacture more ATP as needed
What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
What is the active energy molecule?
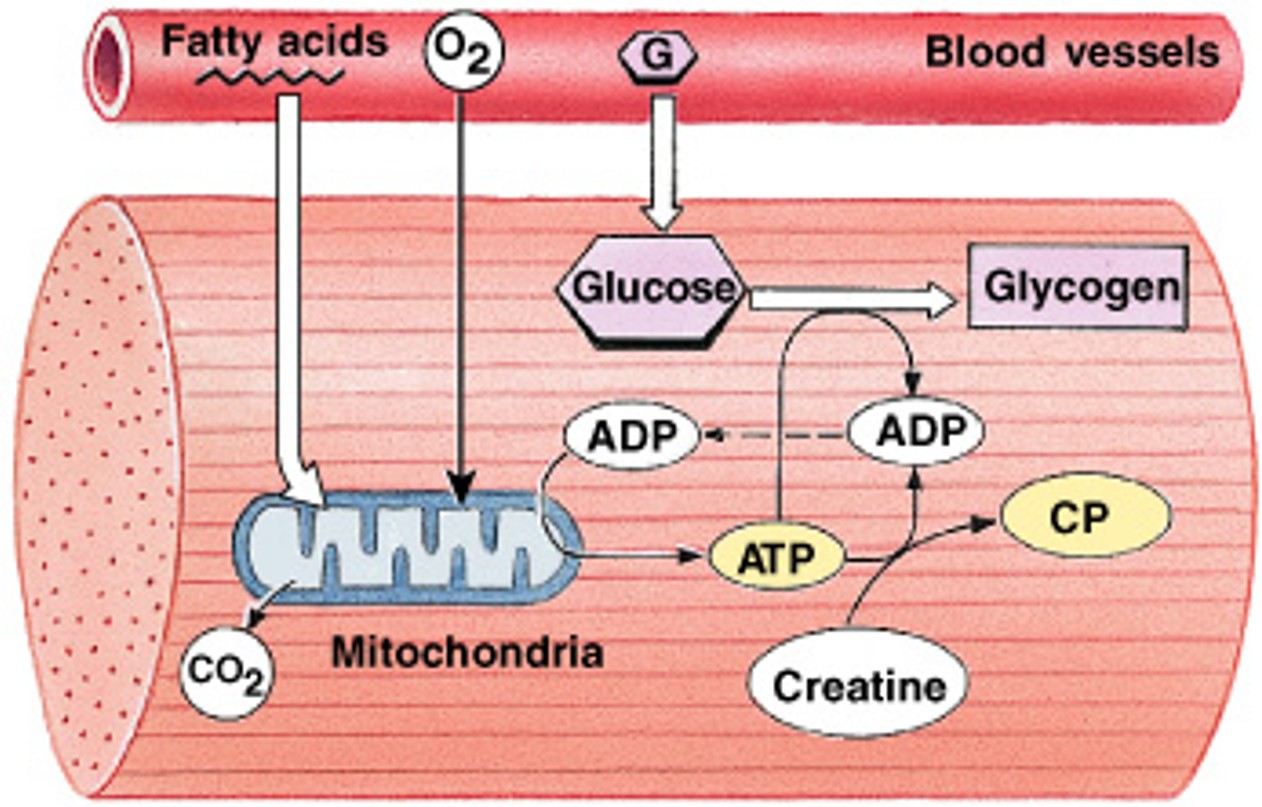
What is creatine phosphate (CP)?
What is the storage molecule for excess ATP energy in resting muscle, and when used up other mechanisms must generate ATP?
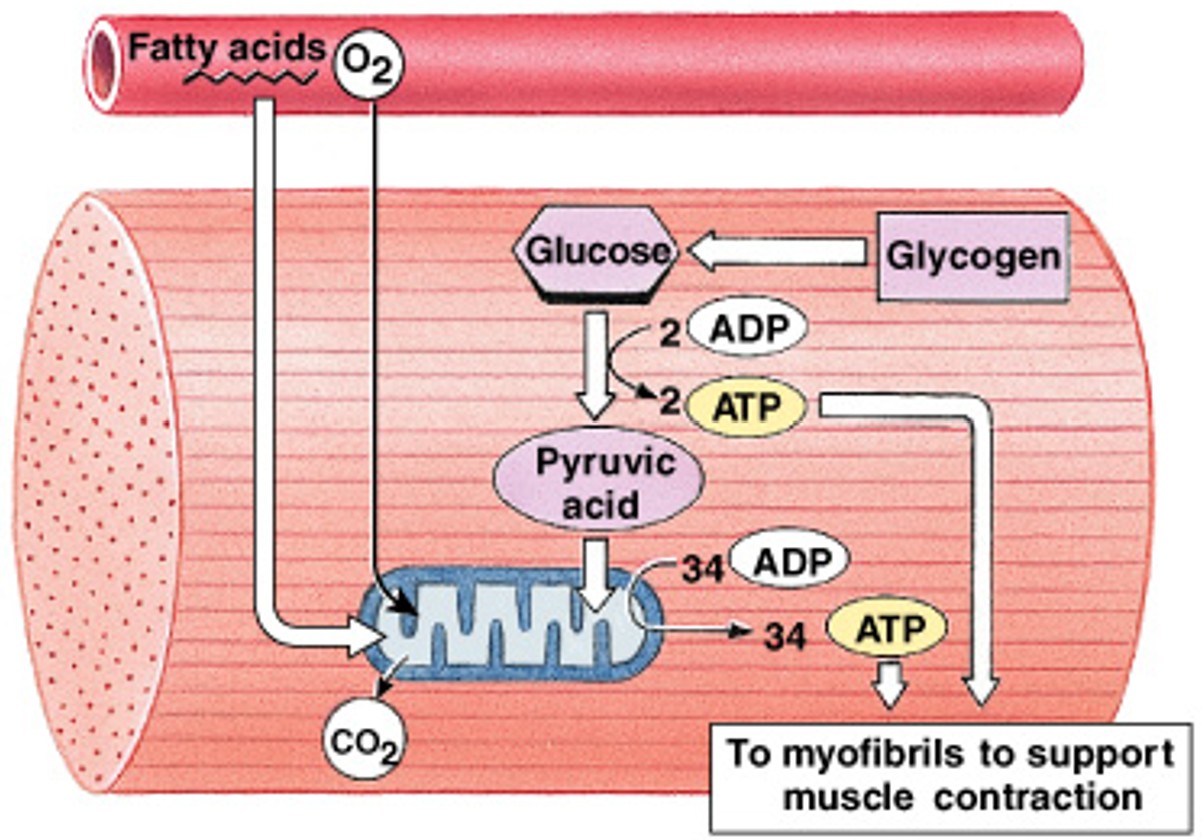
What is aerobic metabolism?
Which type of ATP generation is:
In the mitochondria with oxygen
What is anaerobic glycolysis?
Which type of ATP generation is:
In the cytoplasm without oxygen
What is muscle fatigue?
What occurs when the muscle can no longer perform a required activity?
What are the results of the muscle fatigue?
What are these results of:
Depletion of metabolic reserves
Damage to sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum
lactic acid build-up - low pH
Muscle exhaustion and pain
What is the recovery period of muscle?
What is the time required after exertion for muscles to return to normal?
What is the Cori cycle?
What is the removal and recycling of lactic acid by the liver - back to glucose?
What is the growth hormone & testosterone?
Which hormone does the following:
Stimulate synthesis and enlargement of skeletal muscles
What are the thyroid hormones?
Which hormone does the following:
Raise the level of metabolism (energy consumption)
What is the epinephrine hormone?
Which hormone does the following:
Increase duration of stimulation and force of contraction
What is power in muscle performance?
What is the maximum amount of tension produced?
What is endurance in muscle performance?
What is the amount of time an activity can be sustained?
What are fast fibers of skeletal muscle?
Which type of skeletal muscle fibers is:
Contract very quickly, strong contractions, fatigue quickly
Have large diameter, large glycogen reserves, few mitochondria
Pale (chicken breast)

What are slow fibers of skeletal muscle?
Which type of skeletal muscle fibers is:
Are slow to contract, slow to fatigue
Have small diameter, more mitochondria
Have high oxygen (blood) supply
Contain myoglobin (binds oxygen)
Dark (chicken legs)
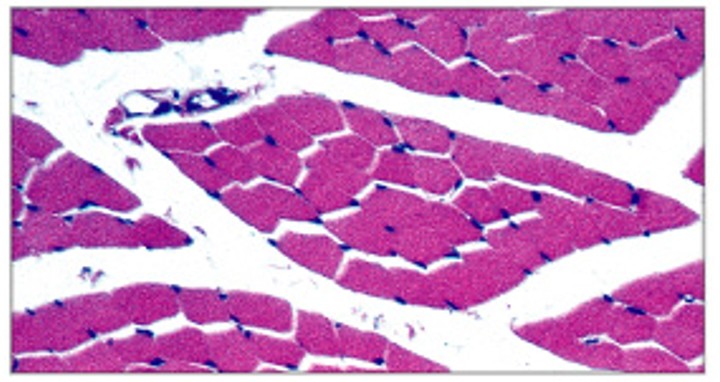
What are intermediate fibers (pink) of skeletal muscle?
Which type of skeletal muscle fibers is:
Are mid-sized, have low myoglobin
Have more capillaries than fast fiber, slower to fatigue
Most human muscles - mixed fibers - pink
What is muscle hypertrophy?
What is muscle growth from heavy training?
What is muscle atrophy?
What is the lack of muscle activity reduces muscle size, tone, and power?
What is anaerobic endurance?
Which type of endurance is:
Activities: 50-meter dash, weightlifting
use fast fibers
fatigue quickly with strenuous activity
Improved by
frequent, brief, intensive workouts
hypertrophy
What is aerobic endurance?
Which type of endurance is:
Activities - prolonged activity
supported by mitochondria
require oxygen and nutrients
Improved by
repetitive training (neural responses)
cardiovascular training
