Organic chemistry Questions
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
building block of nucleic acids are
A. amino acids
B. organic bases
C. fosphates
D. Nucleotides
D. Nucleotides
cytosine, uracil and thymine are ------ derivatives
A. pyrrole
B. furan
C. pyridine
D. Pyrimidine
D. Pyrimidine
adenine and guanine are -------- based bases
A. purine
B. pyrrole
C. pyridine
D. Pyrimidine
A. purine
palmitic acid and stearic acid are
A. saturated
B. unsaturated
C. both of them
A. saturated
oleic acid and linoleic acid are
A. saturated
B. unsaturated
C. both of them
B. unsaturated
fats molecules most part is
A. nonpolar
B. polar
C. Ionic
A. nonpolar
lipids are produced by dehydration of
A. glycerol and fats
B. ethyleneglycol and fatty acids
C. glycerol and fatty acids
C. glycerol and fatty acids
glycerol is important part of lipid formation it is a
A. monoatomic alcohol
B. diatomic alcohol
C. triatomic alcohol
D. no alcohol is
C. triatomic alcohol
sucrose contains two sugar units -
A. glucose and glucose
B. glucose and mannose
C. glucose and fructose
D. glucose and galactose
C. glucose and fructose
reduction of sugar aldehyde group produces
A. alcohol
B. ketone
C. carboxylic acid
A. alcohol
the shown structure is
A. galactose
B. fructose
C. glucose
D. Mannose
C. glucose
five-membered ring structure is called as a
A. puranose
B. pyranose
C. furanose
D. Fructo
C. furanose
fructose when forms closed ring structure, it is
A. six-membered
B. five-membered
C. four-membered
D. doesn't form
B. five-membered
six-membered colsed sugar unit is called as a
A. furanose
B. pyranose
C. furan
D. Pyrrole
B. pyranose
insulin, proteine is composed of ..... polypetide chains
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
B. 2
starch molecular formula is
A. C6H10O5
B. C6H12O6
C. (C6H10)6)n
D. (C6H10O5)n
D. (C6H10O5)n
secondary structure has 2 type structures: ............. and .............
A. coiled and sheet
B. alpha-helix and sequence
C. alpha-helix and coiled
D. alpha-helix and beta-sheet
D. alpha-helix and beta-sheet
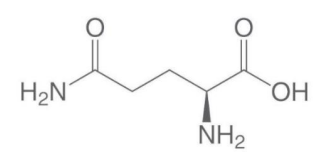
the structure is formula of
A. Glu
B. Asn
C. Asp
D. Gln
D. Gln
what is name of the given amino acid
A. serine
B. cysteine
C. methionine
D. Lysine
B. cysteine
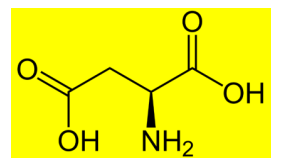
the following amino acid shows .......... properties
A. neutral
B. acidic
C. Basic
B. acidic
proteins are able to adopt ----- type of structures (confrmations)
A. 3
B: 2
C: 4
D: 5
C: 4
the amino acid Arg is a .......... amino acid
A. acidic
B. neutral
C. Basic
C. Basic
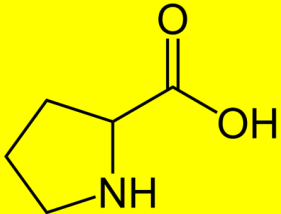
37. what compound is shown in photo?
A. Threonine (Thr)
B. Proline (Pro)
C. Ser
D. Gln
B. Proline (Pro)
the name of the amino acid is
A. Trp (tryptophane)
B. Thr (threonine)
C. Leucine (Leu)
D. Val (valine)
B. Thr (threonine)
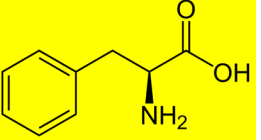
the shown structure belongs to
A. Trp
B. Tyr
C. Phe
D. Pro
C. Phe
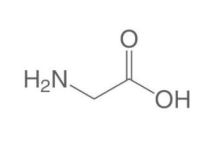
the given amino acid is
A. Gly
B. Ala
C. Leu
D. no amino acid
A. Gly
Histidine is ............... amino acid
A. acidic
B. basic
C. Neutral
B. basic
NH2-CH(R)-COOH HCl = ?
A. NH2-CH(R)-COOCl H2O
B. NH2-CH(R)-COOHCl
C. NH3-CH(R)-COOCl
D. NH3-CH(R)-COOHCl
D. NH3-CH(R)-COOHCl
NH2-CH(R)-COOH NaOH=...............H2O
A. NH2-CH(R)-CONa
B. NH2-CH(R)-COOHNa
C. NH2-CH(R)-COONa
D. no reaction
C. NH2-CH(R)-COONa
general formula of amino acids at neutral pH, is
A. NH3-CH(R)-COOH
B. NH2-CH(R)-COO
C. NH3-CH2-COO
D. NH3-CH(R)-COO
D. NH3-CH(R)-COO
the given compound is organic .........
A. salt
B. acid
C. base
D. none of above
A. salt
CH3-(CH2)4-CH2-NH-C6H5, the name of this amine is
A. heptyl aniline
B. phenylheptyl amine
C. phenylhexyl amine
D. hexylphenyl amine
D. hexylphenyl amine
the given structure containes nitro group (NO2) as substutuent. the correct name will be
A. N-methylnitro phenyl
B. N-methylnitro aniline
C. N-methyl-3-nitro aniline
D. none of above
C. N-methyl-3-nitro aniline
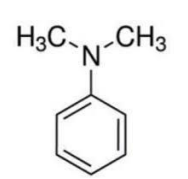
the following stuctural formula is of
A. N-methylphenylamine
B. dimethyl aniline
C. N-dimethyl aniline
D. none of them
C. N-dimethyl aniline
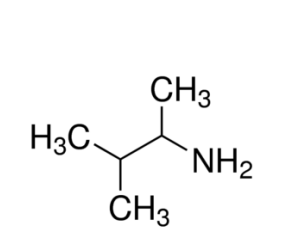
the following compound is
A. methlpropyl amine
B. 2-methylpropyl amine
C. dimethylpropyl amine
D. propyldimethyl amine
C. dimethylpropyl amine
C6H5NH2 HCl =
A. C6H5Cl NH3
B. C6H5NH3Cl
C. C6H5 NH3Cl
D. no reaction
B. C6H5NH3Cl
amine can be synthesize by reaction R-Cl 2NH3 =R-NH2 ....... , another product will be
A. NH2Cl
B. N2
C. NH3Cl
D. NH4Cl
D. NH4Cl
CH3-N-CH2CH3(CH3) is ....................amine
A. primary
B. secondary
C. tertiary
D. none of above
C. tertiary
CH3-CH2-NH-CH3 is a..................... amine
A. primary
B. secondary
C. tertiary
D. is not amine
B. secondary
the structure belongs to
A. acetal
B. phenylacetal
C. acetophenyl
D. acetophenone
D. acetophenone
R-COONa H2SO4 = R-COOH .....
A. Na2S
B. NaOH S
C. Na2SO3
D. Na2SO4
D. Na2SO4
if you oxidize primary alcohols, what will be final oxidation product?
A. secondary alcohol
B. aldehyde
C. carboxylic acid
C. carboxylic acid
during oxidation of aldehydes, form
A. alcohols
B. carboxylic acids
C. Ketones
B. carboxylic acids
R-CN 2H2O = R-COOH ....
N2
NH3
NH4OH
NO
NH3
silver mirror reaction, finish it R-CO 2[Ag(NH3)2]OH = R-COOH ... ... ...
A. Ag, N2, H2O
B. Ag2O, NH3, H2O
C. AgOH, N2, H2O
D. Ag, NH3, H2O
D. Ag, NH3, H2O
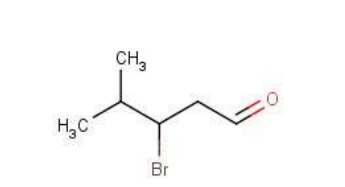
the following structure is of the compound
A. 3-bromo-4-methylpentanol
B. 3-bromo-4-methylpentanal
C. 3-bromo-2-methylpentanal
D. none of above
B. 3-bromo-4-methylpentanal
R-COH Cu(OH)2 →
A. RCOOH CuO
B. RCOOH Cu2O
C. RCOOH CuO H2O
D. RCOOH Cu2O H2O
D. RCOOH Cu2O H2O
R-CHOH-R' [O] → finish reaction
A. R-CH2OH
B. R-COOH
C. R-CO-R'
D. no oxidation
C. R-CO-R'
Oxidation prouct of ethylene is: CH2=CH2 [O]
A. formic acid
B. formaldehyde
C. acetaldehyde
D. none of above
C. acetaldehyde
ethylene glycol is a ................. alcohol
A. monoatomic
B. diatomic
C. Triatomic
B. diatomic
final product of alcohol oxidation, is
A. aldehyde
B. ketone
C. carboxylic acid
D. none of above
C. carboxylic acid
R-CH=CH2 H2O =
A. R-CH2-OH
B. R-CHOH-CH3
C. no reaction is uccuring
B. R-CHOH-CH3
ethers form by ........................... dehydration of alcohols
A. intramolecular
B. intermolecular
C. none of above
D. both of them
B. intermolecular
R-OH HO-R' , what will be organic product
A. ester
B. ether
C. no reaction
D. R-CH2OH
B. ether
tertiary alcohol's oxidation produce
A. aldehydes
B. ketones
C. no oxidation
C. no oxidation
by oxidation of secondary alcohols, form
A. aldehydes
B. ketones
C. no oxidation
B. ketones
finish reaction R-COH H2 =
A. R-CHOH
B. R-CH2OH
C. R-CO
B. R-CH2OH
R-C(OH)-R'R'' is a formula of ................... alcohol
primary
secondary
tertiary
none of above
tertiary
R-CH2Cl NaOH = ............ NaCl
A. R-CH2
B. R-OH
C. R-CH2OH
C. R-CH2OH
the number of heptane isomers is
A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9
D. 9
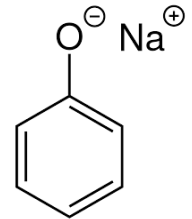
the compound is organic compound, but it acts as
A. acids
B. salts
C. bases
D. none of them
B. salts
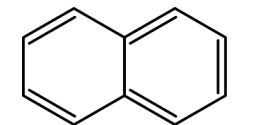
the aromatic condenced structure belongs to
A. biphenyl
B. dibenzene
C. antracene
D. Naphtalene
D. Naphtalene
hexane isomer's number is
A. 3
B. 4
C. 5
D. 6
C. 5
what will be correct name of the compound?
A. 1,4-dimethyl-2,4-dichlorobenzene
B. 1,4-dichloro-dimethylbenzene
C. 1,4-dichloro-2,5-methylbenzene
D. 1,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylbenzene
D. 1,4-dichloro-2,5-dimethylbenzene
during sulphonation of benzen, -------- is obtained
A. C6H5SO3
B. C6H5SO2
C. C6H5SO3H
D. C6H5SO4
C. C6H5SO3H
C6H6 HNO3 = ..... H2O
A. C6H6NO3
B. C6H5NO3
C. C6H6NO2
D. C6H5NO2
D. C6H5NO2
CH3-CH2-CH=CH2 HBr =
A. CH3-CH2-CH2-Br
B. CH3-CH2-CHBr-CH3
C. no reaction
B. CH3-CH2-CHBr-CH3
in alkenes, the hybridization type is
A. sp
B. sp3
C. sp2
D. non of them
C. sp2
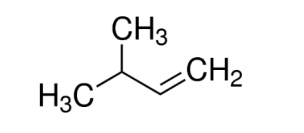
this compound is called as
A. 2-methylbuten-3
B. 3-methylbutene-1
C. 2-methylbutene-1
D. none of them
B. 3-methylbutene-1
select the correct name of the compound
A. 2,3-dimethylhexene-3
B. 2,3-dimethylhepten-3
C. 2,5-dimethylhepten-3
D. 2-methylhepten-3
C. 2,5-dimethylhepten-3
Ethylene on reaction with bromine forms which among the following product
A)BrH2C-CH2Br
B)BrH2C=CH2Br
C)Br2HC=CHBr2
D)Br2HC-CHBr2
A)BrH2C-CH2Br
Which among these is not a structural isomer of the compound C4H8
A. butene-1
B. butene-2
C. butene-3
D. 2-methylpropene
C. butene-3
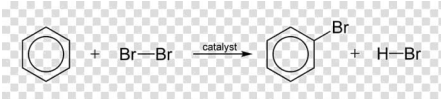
The following reaction is an example of
A. electrophilic substitution
B. nucleophilic substitution
C. radical substitution
D. none of above
A. electrophilic substitution
R-Br OH− → R-OH Br− reaction is an example of
A. electrophilic addition
B. electrophilic substitution
C. nucleophilic substitution
D. nucleophilic addition
C. nucleophilic substitution
109. give the correct name to the following compound
A. 2-bromo-3-chloro-3,4-methyl-4-nitrphexane
B. 2-bromo-3-chloro-3,5-methyl-5-nitrphexane
C. 2-bromo-3-chloro-3,5-methyl-5-nitrpheptane
D. 2-bromo-3-chloro-3,5-dimethyl-5-nitroheptane
D. 2-bromo-3-chloro-3,5-dimethyl-5-nitroheptane
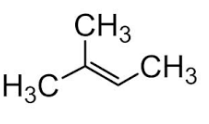
give the following compounds the correct name
A. 1-methylbutene-1
B. 2-methylbutene-1
C. 2-methylbutene-2
D. none of above
C. 2-methylbutene-2
Identify correct step representing SN1 mechanism for the cleavage of ether with HI.
A. 1 and 3
B: 2 and 3
C: 1 and 4
D: 2 and 4
B: 2 and 3
Select the incorrect option
A. The aromatic hydrocarbon has a pleasant aroma (smell)
B. Some of the aromatic compounds are ring-shaped
C. Aromatic hydrocarbon can be either mono or polycyclic
D. Benzene is the simplest hydrocarbon
B. Some of the aromatic compounds are ring-shaped
Identify the correct statement which is related to aromatic hydrocarbon
A. It has only sigma bonds
B. It has only pi bonds
C. It has a sigma and two pi bonds
D. It has a sigma and delocalized pi bond
D. It has a sigma and delocalized pi bond
Which among the following is not an example of Acyclic compound
A. Acetaldehyde
B. ethane
C. cycloporane
D. Isobutane
C. cycloporane
Aliphatic compound is the other name for
A. Acyclic compounds
B. cyclic compounds
C. Closed chain compounds
D. none of above
A. Acyclic compounds
The substituent in the chain is named by replacing the "ane" in the alkanes by
A. ane
B. ene
C. one
D. Yl
D. Yl
Identify the smallest alkane which can form a ring structure (cycloalkane)
A. butane
B. methane
C. propane
D. Ethane
C. propane
Which among the following is NOT both a molecule and a compound?
A. C6 H12 O0
B. H2O
C. CO2
D. NaCl
D. NaCl
Atoms undergo bonding in order to ?
A. Attain stability
B. lose stability
C. move freely
D. increase energy
A. Attain stability
Which among the following is not an example of hydrogen bond?
A. H20
B. liquid HCl
C. NH3
D. CHCl3
E. CHCl3
B. liquid HCl
If a bond is made up of a large number of organic compound, then the bond is termed as?
A. ionic bond
B. covalent bond
C. metallic bond
D. dipolar bond
B. covalent bond
peptide name of GlyAlaProCysMet will be
A. glycinealanineprolinecysteinemethionine
B. glycinalaninprolincysteinmethionin
C. glycylalanineprolinecysteinemethionine
D. glycylalanylprolylcysteylmethionine
D. glycylalanylprolylcysteylmethionine