2.2 all cells arise from other cells
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are the 3 stages in the cell cycle
Interphase
Mitosis
Cytokinesis
What occurs in interphase
S-phase - DNA replicates semi conservatively, leading to 2 chromatids joined at a centromere
G1/G2 - number of organelles and volume of cytoplasm increases, protein synthesis
What occurs in mitosis
nucleus divides
To produce 2 nuclei with identical copies of DNA produced by parent cell
What are the 4 stages of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
What occurs in prophase
chromosomes condense, becoming shorter/ thicker (so visible)
Nuclear envelope breaks down
Centrioles move to opposite poles forming spindle network
What occurs in the metaphase
spindle fibres attach to chromosomes by their centromeres
Chromosomes align along equator
What occurs in anaphase
spindle fibres shorten/ contract
Centromere divides
Pulling chromatids (from each pair) to opposite poles of the cell
What occurs in telophase
chromosomes uncoil, becoming longer/ thinner
Nuclear envelope reforms into 2 nuclei
Spindle fibres/ centrioles break down
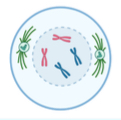
What stage of photosynthesis is the picture
Prophase
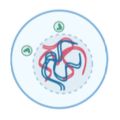
What stage of the cell cycle is the picture
Interphase
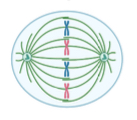
What stage of photosynthesis is the picture
Metaphase
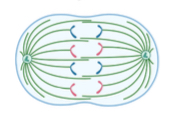
What stage of photosynthesis is the picture
Anaphase
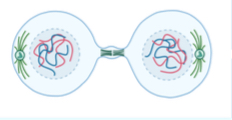
What stage of photosynthesis is the picture
Telophase
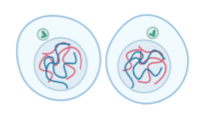
What stage of the cell cycle is the picture
Cytokinesis
Why do some eukaryotic cells not undergo the cell cycle
within multicellular organisms, not all cells retain the ability to divide (e.g neurons)
Only cells that retain this ability go through a cell cycle
Explain the importance of mitosis in the life of an organism
parent cell divides to produce 2 genetically identical daughter cells for…
growth of multicellular organisms by increasing cell number
Replacing cells to repair damaged tissues
Asexual reproduction
How are tumours and cancers formed
mutations in DNA/ genes controlling mitosis can lead to uncontrolled cell division
Tumour formed if this results in mass of abnormal cells
What are malignant and benign tumours
Malignant = cancerous, can spread (metastasis)
Benign = non-cancerous
How cancer treatments control rate of cell division — some disruptions spindle fibre activity/ formation
chromosomes can’t attach to spindle by their centromere
So chromatids can’t be separated to opposite poles (no anaphase)
So prevents/ slows mitosis
How cancer treatments control rate of cell division — some prevent DNA replication during interphase
so can’t make 2 copies of each chromosome (chromatids)
So prevents/ slows mitosis
How do prokaryotic cells replicate
By binary fission
Replication of circular DNA
Replication of plasmids
Division of cytoplasm to produce 2 daughter cells (single copy of circular DNA, variable number of copies of plasmids)
Why do viruses not undergo cell division
Because they are non living
Describe how viruses replicate
Attachment proteins attach to complementary receptors on host cell
Inject viral nucleic acid (DNA/RNA) into host cell
Infected host cell replicates virus particles:
nucleic acid replicated
Cell produce viral protein/capsid/enyzyme
Virus assembled then released