Lecture 9 - Studying proteins
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are model organisms ?
They are species that are extensively studied for the understanding of particular biological processes, with the assumption that they can be generalized to other species.
What are some model organism types ?
Prokaryote (bacterium)
Eukaryote (unicellular fungus, like yeast)
Multicellular animal (worm)
Insect
Vertebrate (fish)
Mammal
Plant
Amphibian (vertebrate)
What are the three types of cell cultures ?
Primary cell culture : Cells taken directly from tissues and cultured for the first time. Closely resemble the original tissue.
Secondary/Subcultured cells : cells that have been transferred from a primary culture to a new growth media.
Cell lines : Cells that have adapted to continuous growth in vitro.
derived from primary cultures that have undergone transformation.
What are the two types of cell lines ?
Finite Cell line : Limited number of divisions before cell aging.
Continuous cell line : Can divide indefinitely due to transformation.
What are polyclonal antibodies ?
They are a mixture of antibodies that recognize different antigenic sites on the protein of interest
What are monoclonal antibodies ?
They are identical antibodies that recognize one antigenic site on the protein of interest.
What are some methods to open cells for protein purification ?
Osmotic shock
Ultrasonic vibrations
Ground up in a blender
What does ultracentrifugation do ?
Separates elements of a homogenate according to size and density.
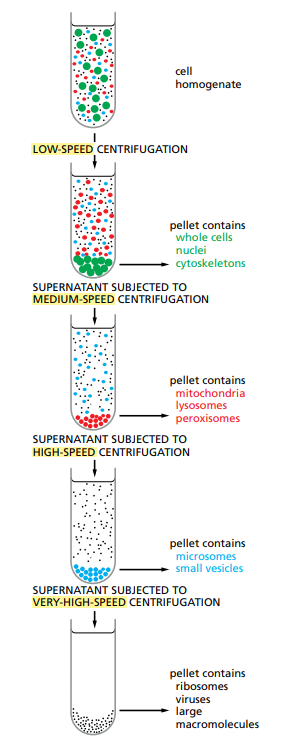
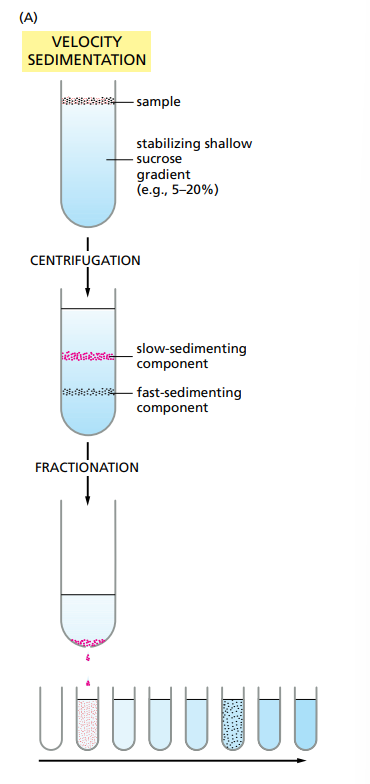
How can you improve separation ?
Using Gradients. A gradient is a solution which gradually gets denser as you go deeper. So slow-sedimenting components stay higher and faster one go lower.
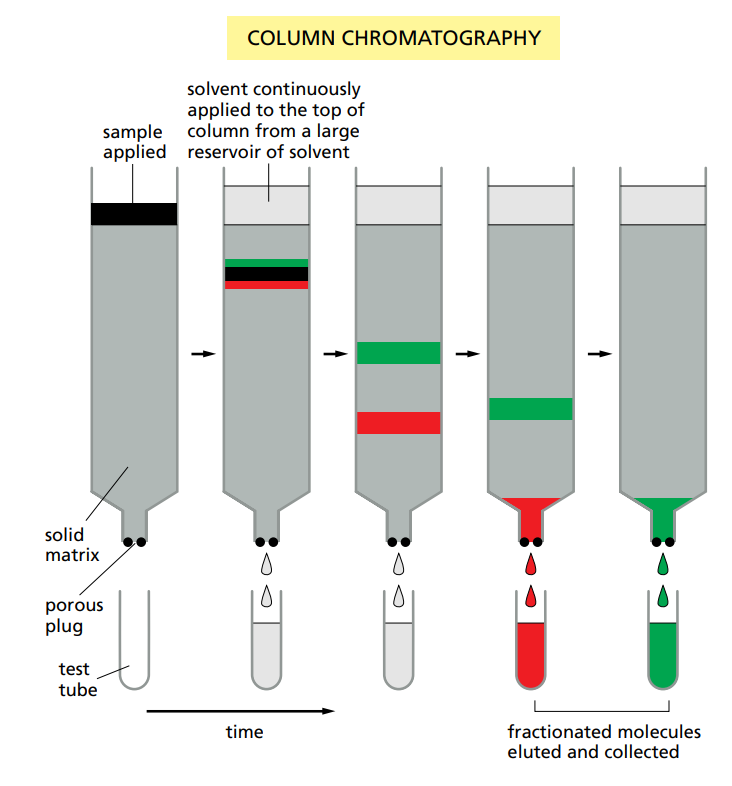
How do you separate the proteins ?
With column chromatography.
How does column chromatography work ?
A mixture of proteins is passed through a porous gel matrix.
Depending on the interaction with the matrix, the proteins are slowed or pass though faster.
The different proteins are collected separately once they come out.
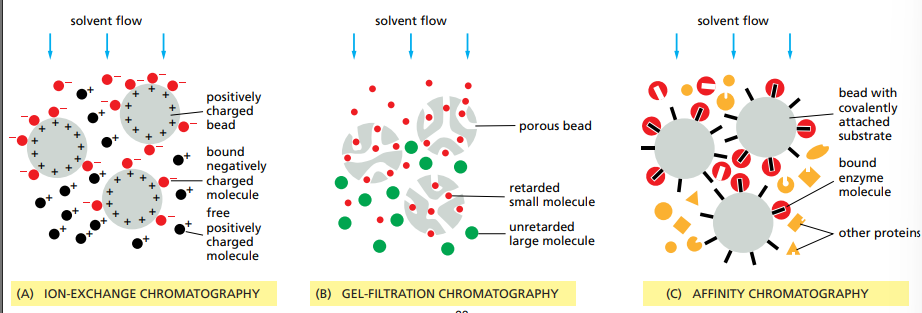
What types of matrices for the columns are there ?
Ion-exchange chromatography (uses charge).
Hydrophobic chromatography (uses hydrophobicity)
Size-exclusion chromatography (Uses molecular weight)
Affinity chromatography (Uses ability to bind to small molecules)
What are protein tags used for ? What are some examples ?
Allows use for affinity matrix or identification.
An example is His-tag which binds strongly to nickel.
What is high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)
It’s a chromatography method which uses special resins composed of tiny spheres and gives out high resolution.
How does SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) work ?
An electric field is applied to the sample so that they will migrate depending on size, charge and shape through pores made up of a cross-linked gel of polyacrylamide. Large proteins are more retarded than smaller ones.
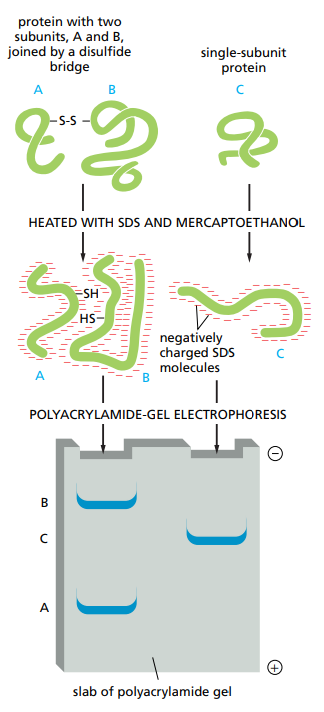
Why is SDS useful ?
The SDS is useful as it binds to the hydrophobic regions of the protein causing their unfolding and release from other proteins or membranes.
What does B-mercaptoethanol do ?
It removes disulfide bonds.
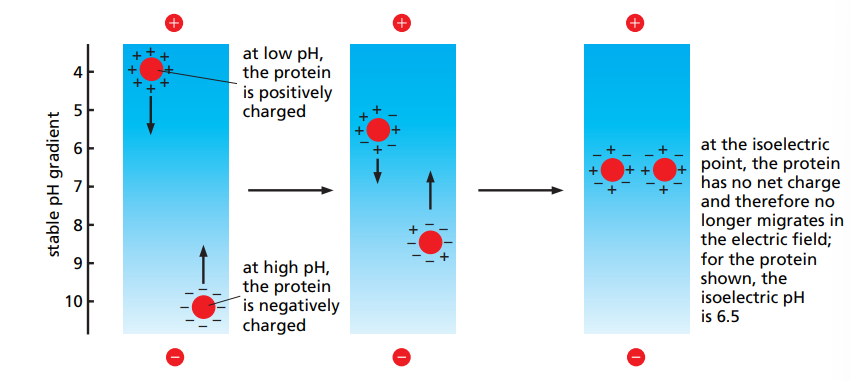
What is 2D-gel electrophoresis and why is it useful ?
Combines two separation methods : D1, separation by intrinsic charge. D2, separation by classical SDS-PAGE.
This is useful for when two proteins have the same size but not the same intrinsic charge.
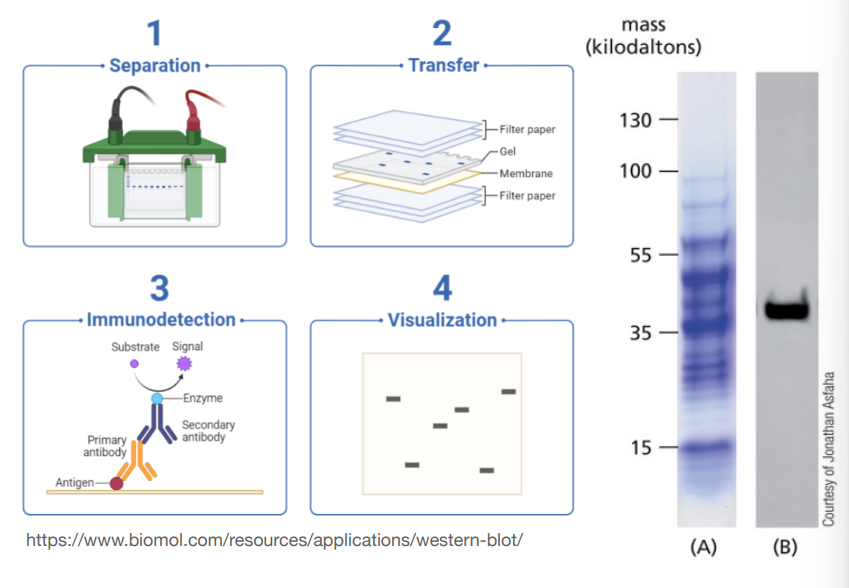
What is Western blot and how does it work ?
It’s an SDS-PAGE but afterwards the protein is detected using a labelled antibody. The protein is transferred from the gel onto a nitrocellulose/nylon membrane and the membrane is soaked in antibody solution.
What are the different blots and their differences ?
Western blot : For protein and the probe is a primary antibody.
Northern blot : For RNA and the probe is RNA, DNA or oligodeoxynucleotide.
Southern blot : For DNA and the probe is a nucleic acid with a sequence homologous to the target DNA.
What methods are used to predict protein structures ?
X-ray crystallography : Uses diffraction spots of X-rays scattered from hitting protein atoms to determine their location through a computational method.
Nuclear magnetic resonance : When exposed to a magnetic field, the nuclei behave as magnets and spin depending on their environment. This allows reconstruction of the protein.
Cryo-Electron Microscopy (CryoEM) : Images samples that are frozen in a thin layer of ice. Uses the different orientations to capture the multiple possible conformations.