triple paper 1 chemistry content (to be continued)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are transition metals and their common properties?
Don’t belong to a specific group, as they can have different numbers of electrons on their outer shells
Conduct electricity in solid and liquid states
Shiny when freshly cut
Form coloured compounds
Useful as catalysts
When transitions metals react, they lose electrons to form ions with different charges (unlike group 1 metals)
What differences do transition metals have compared to group 1 metals?
Transition metals usually have:
Higher melting points
Higher densities
Greater strength + hardness
Lower reactivity than group 1 metals
What is a catalyst?
A substance that decreases activation energy
Provides an alternate reaction pathway
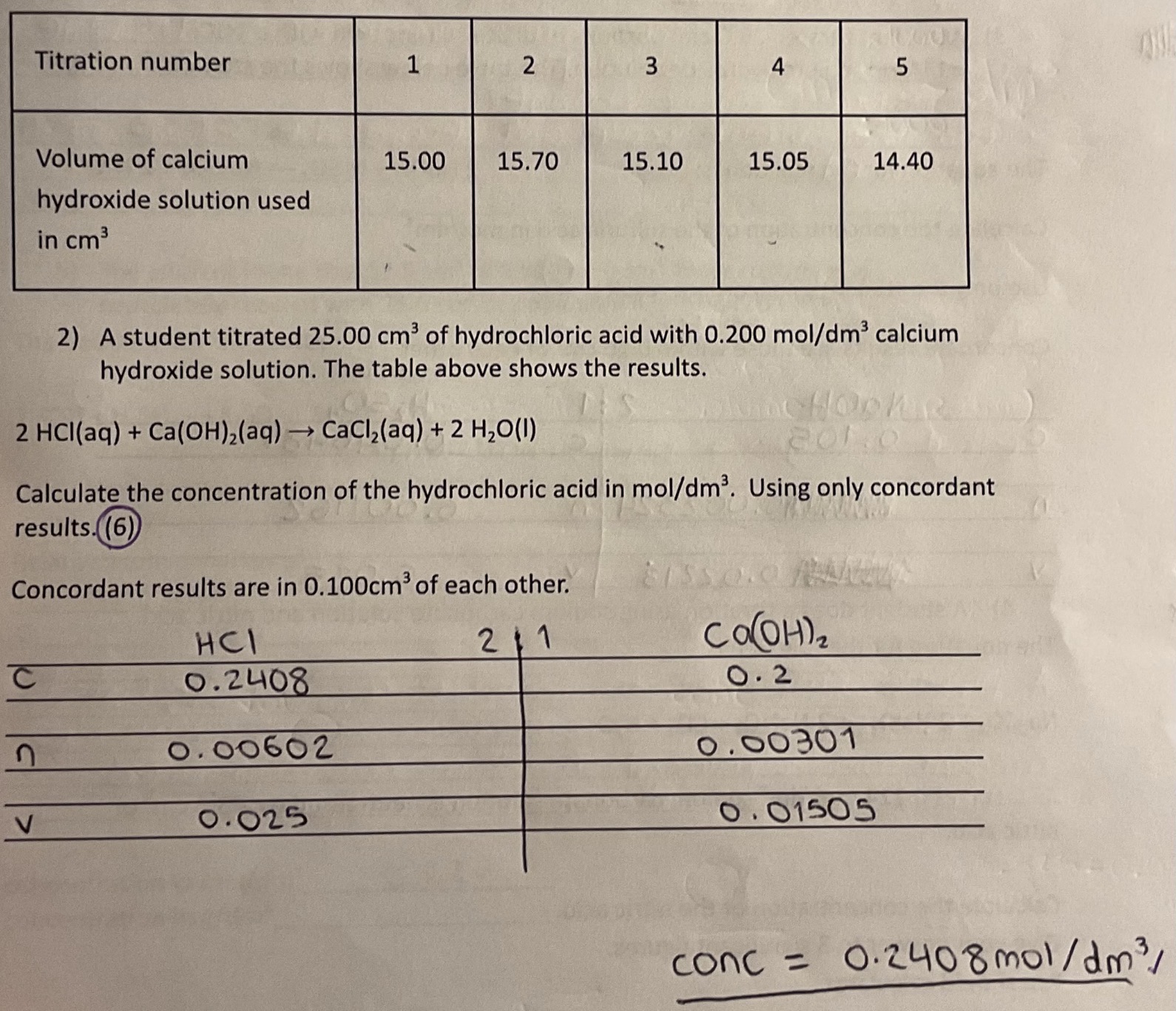
Required Practical: titrations
Use a volumetric pipette to put 25cm³ sodium hydroxide into a conical flask on a white tile.
Add 5 drops of phenolphthalein to the conical flask and swirl to mix.
Use a funnel to fill the burette with sulfuric acid to the 0cm³ line. Place the conical flask under it.
Open the tap, constantly swirl the flash and look for a colour change of pink to colourless. Upon colour change, close the tap to release the acid drop by drop.
Read the burette scale (at the bottom of meniscus) and record the volume of acid added.
What is the formula for concentration?
Concentration (mol / dm³) = moles (mol) / volume (dm³)
Practice titration calculation questions like the one shown!
What is a simple cell made from?
Connecting two metals with different reactivity in contact with an electrolyte.
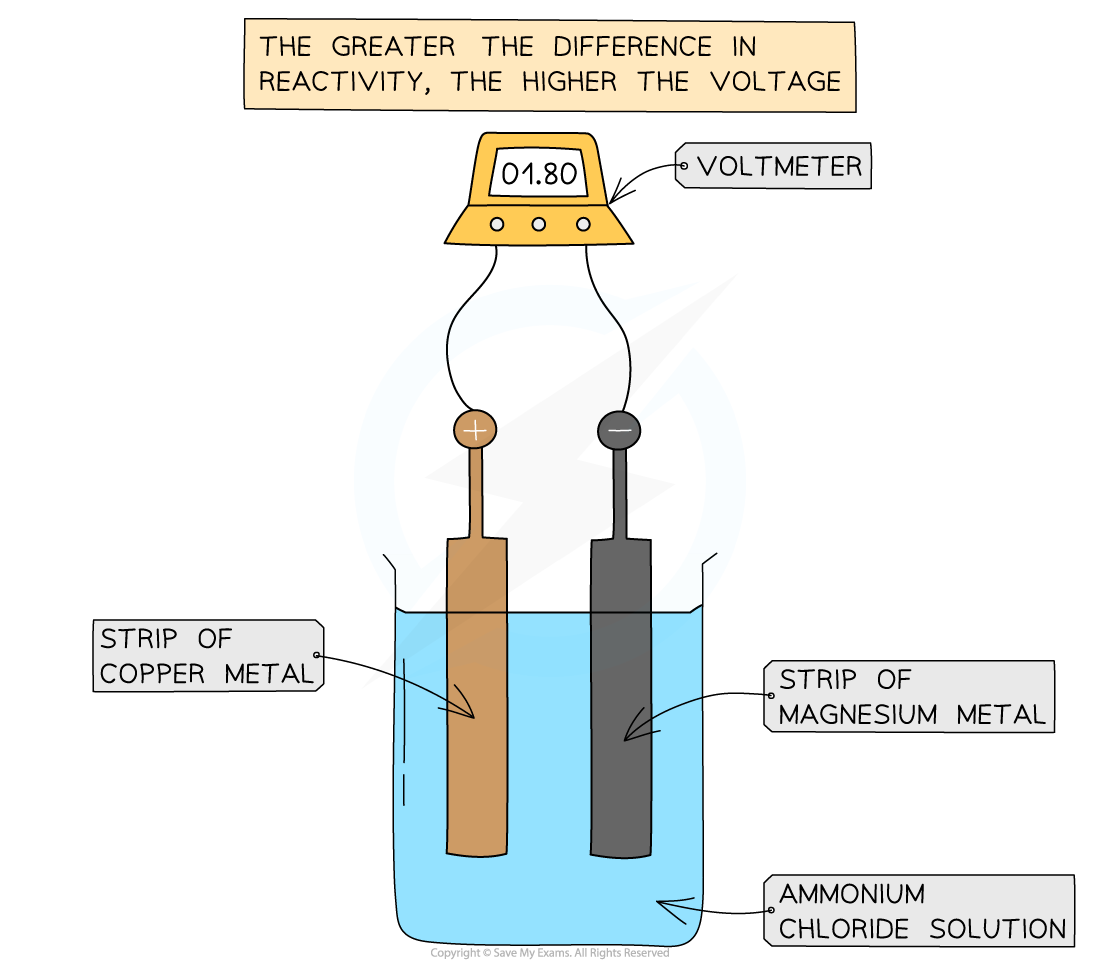
What affects the voltage of a cell?
The higher the difference in reactivity, the higher the voltage. Two of the same metals produces no voltage.
The electrolyte also affects the voltage.
What’s the difference between a non-rechargeable and rechargeable cell?
Non-rechargeable cell: voltage is produced until one of the reactants is used up (e.g. alkaline batteries)
Rechargeable cell: the chemical reactions can be reversed when an external circuit is supplied
What is a battery?
Two or more cells connected in series to produce a greater voltage.
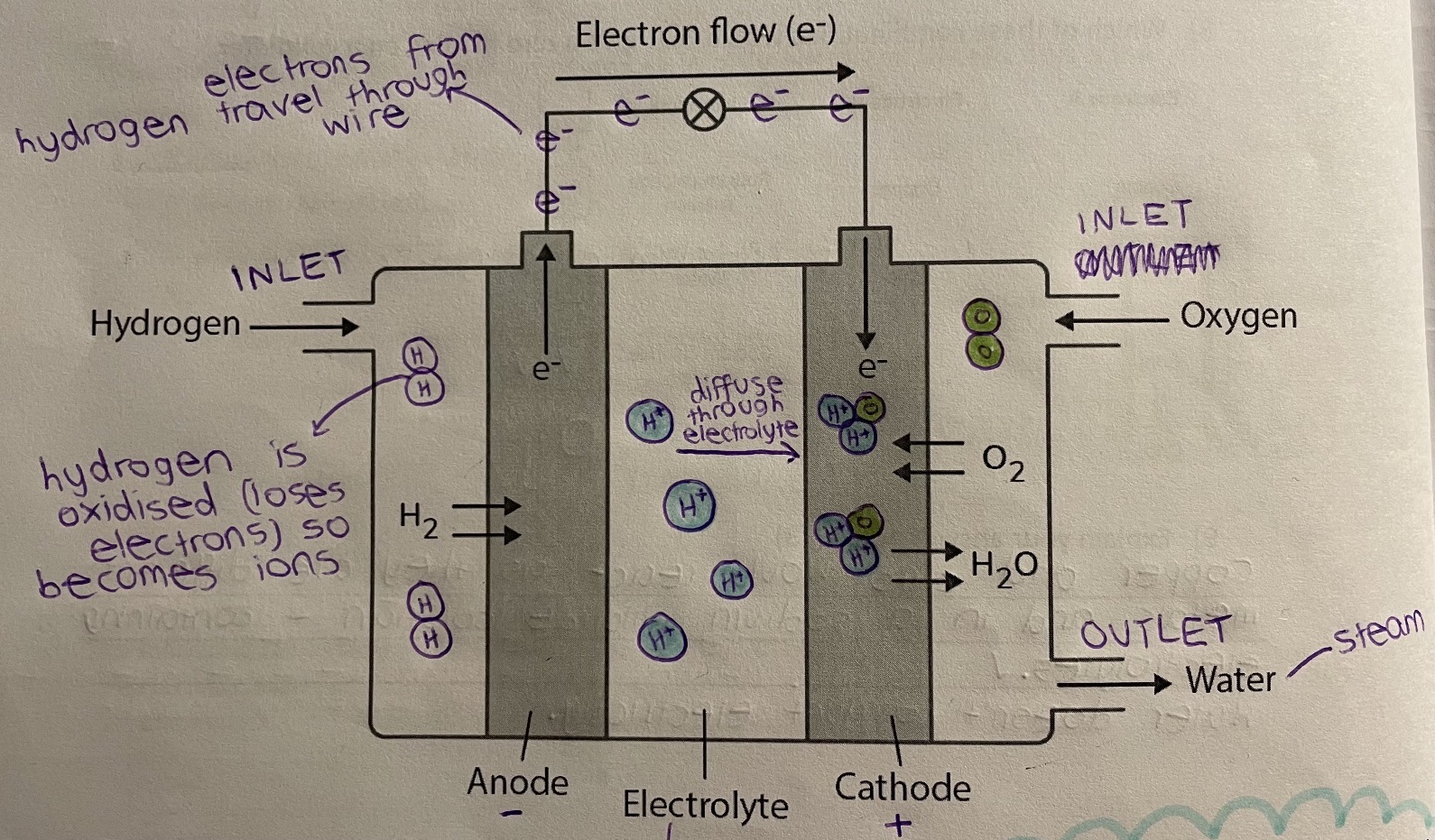
What powers a hydrogen fuel cell?
They produce an electric current continuously when supplied with a constant fuel (hydrogen) and oxygen.
What is the anode (-) half equation?
H2 → 2H+ + 2e–
What is the cathode (+) half equation?
4H+ + O2 + 4e– → 2H2O
What is the hydrogen fuel cell overall equation?
2H2 + O2→ 2H2O
Advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells compared to rechargeable batteries
Hydrogen fuel cells
Can produce electricity as long as hydrogen is supplied
Don’t get less efficient the longer they run
Hydrogen is explosive
Rechargeable batteries
Run out and need to be recharged
Get less efficient over time and eventually need replacing
No dangerous fuels are required with rechargeable batteries
What happens in a hydrogen fuel cell?
Hydrogen enters, then is oxidised (loses electrons) in the anode (-). The flow of electrons from the hydrogen generates electricity. The hydrogen ions (+) then diffuse through an electrolyte to the cathode (+), where they join with oxygen atoms to form water molecules.