BIO 4Q Group Quiz
1/77
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
angiosperms
flowering plants that produce seeds in fruit
Gymnosperms
A plant that produces seeds that are exposed rather than seeds enclosed in fruits
vascular plants
have tissues (xylem and phloem) tissues made of cells that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
non-vascular plants
no vascular tissues consisting of xylem and phloem
Dicot
An angiosperm that has two seed leaves (2 cotyledons)
monocot
An angiosperm that has only one seed leaf (one cotyledon)
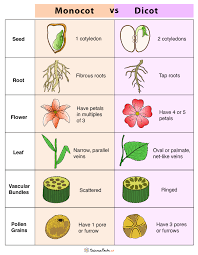
Monocot vs Dicot
Monocotyledons (Monocots):
Seed with one cotyledon
Parallel leaf venation
Floral parts in multiples of three
Fibrous root system
Scattered vascular bundles in stem
Dicotyledons (Dicots):
Seed with two cotyledons
Netted leaf venation
Floral parts in multiples of four or five
Taproot system
Ringed vascular bundles in stem
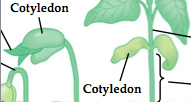
cotyledon
first leaf or first pair of leaves produced by the embryo of a seed plant
used to store food in a seed
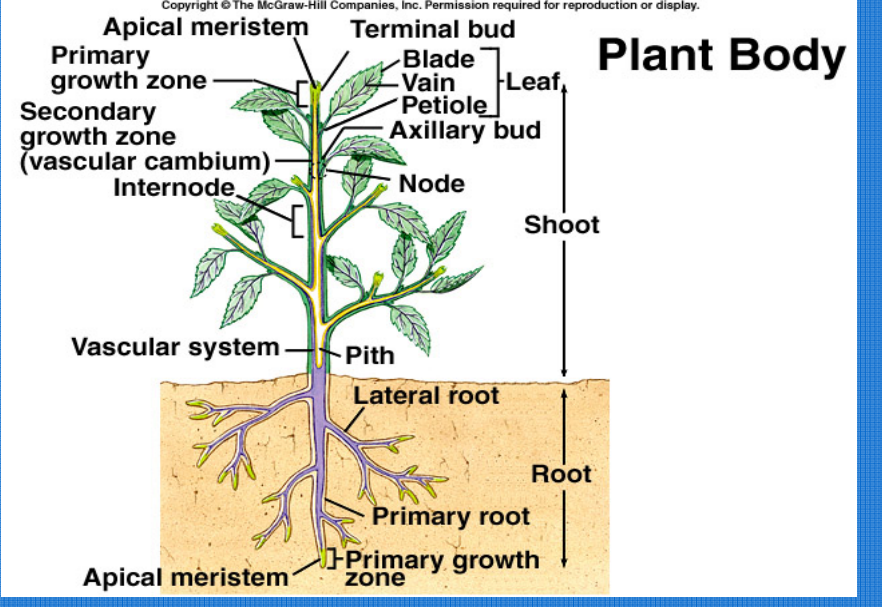
parts of a plant
Shoot System and Root System
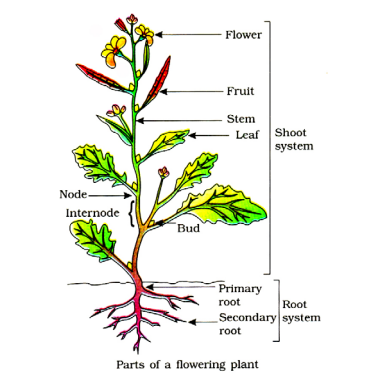
Parts of the shoot system
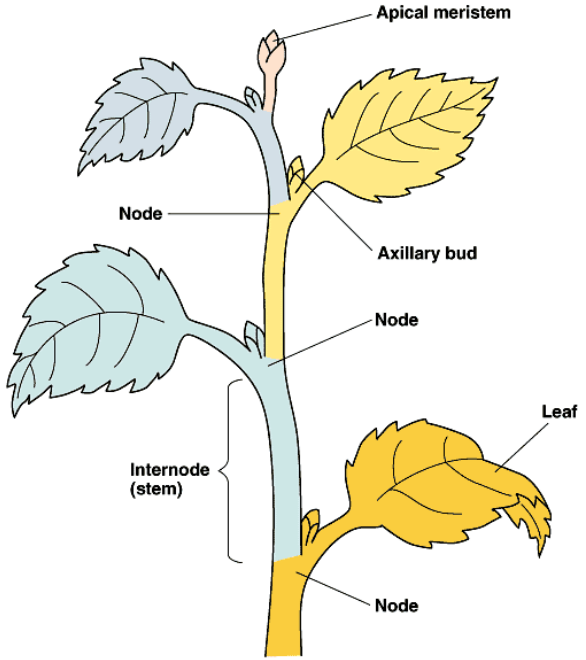
vegetative organs
Leaves: Main photosynthetic organs
Stems: Support, transport, and storage
Roots: Anchor plant, absorb water and nutrients
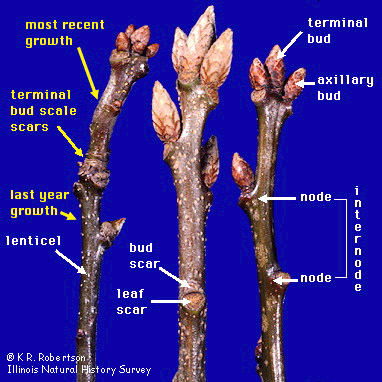
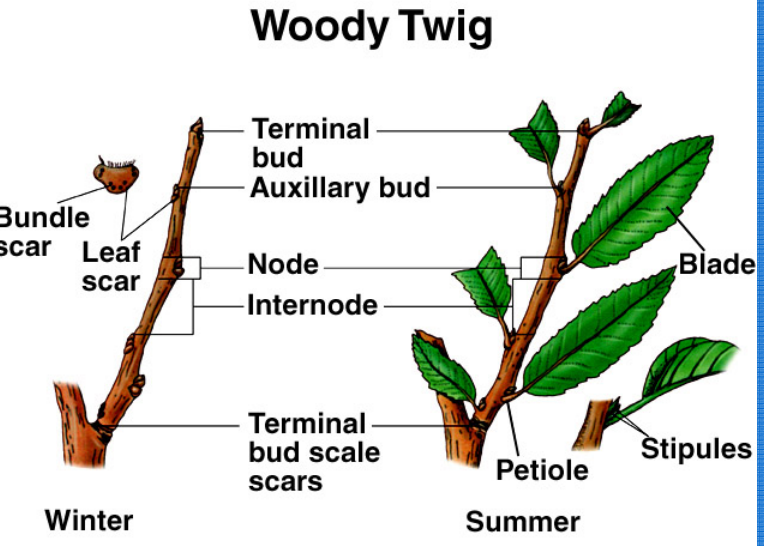
Nodes: Points where leaves, branches, or flowers grow
Internodes: Stem segments between nodes
reproductive organs
Female reproductive organs: ovary, style, stigma
Male reproductive organs: anther, filament
Pollination: transfer of pollen from anther to stigma
Fertilization: fusion of male and female gametes
Seed development: ovule becomes seed after fertilization
Shoot system
positive phototaxis - positive response to light
for:
photosynthesis
reproduction
storage
transport
hormones
Root system
positively geotactic - has a positive response to gravity
For:
anchorage
absorption
storage
transport
hormones
The root can undergo photosynthesis when
modified stem
A potato is
not a root crop
adventitious plant
Adventitious plants are those that grow from parts of the plant other than the seeds, such as roots, stems, or leaves.
ex. Balete - has a hole in the middle because thats where the host plant used to be
FUNCTIONS OF THE ROOT
anchorage
absorbs and transports water and minerals
for food storage (products of photosynthesis)
Types of Roots
Tap root
Fibrous Root / Adventitious Root
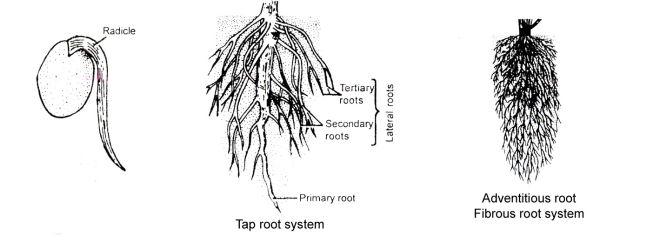
Primary root
arising from germination
secondary root
arising from primary root or secondary root
Tap root
has a distinct primary root
It develops from radicle and made up of one main branch and other sub branches. The primary roots and its branches constitute tap root system. e.g. Dicot roots.
carrots
dicots
the edible part is the tap root
Fibrous Root / Adventitious Root
In some plants, after sometime of the growth of tap root which arises from radicle, stops and then roots, develop from other part of plant, which are branched or unbranched, fibrous or storage, are known as adventitious roots and constitute fibrous root system. e.g. Monocot roots.
Types of growth/germination
simpodial
monopodial
sympodial
a branching pattern where the main stem terminates in a flower or a bud, and growth continues from lateral branches. In this pattern, the main stem does not continue to elongate indefinitely.
monopodial
a growth pattern where the main stem continues to elongate, and lateral branches develop from axillary buds along the main stem. The main stem typically dominates the growth, and the plant tends to have a more upright or single-stemmed habit.
Organization of the root
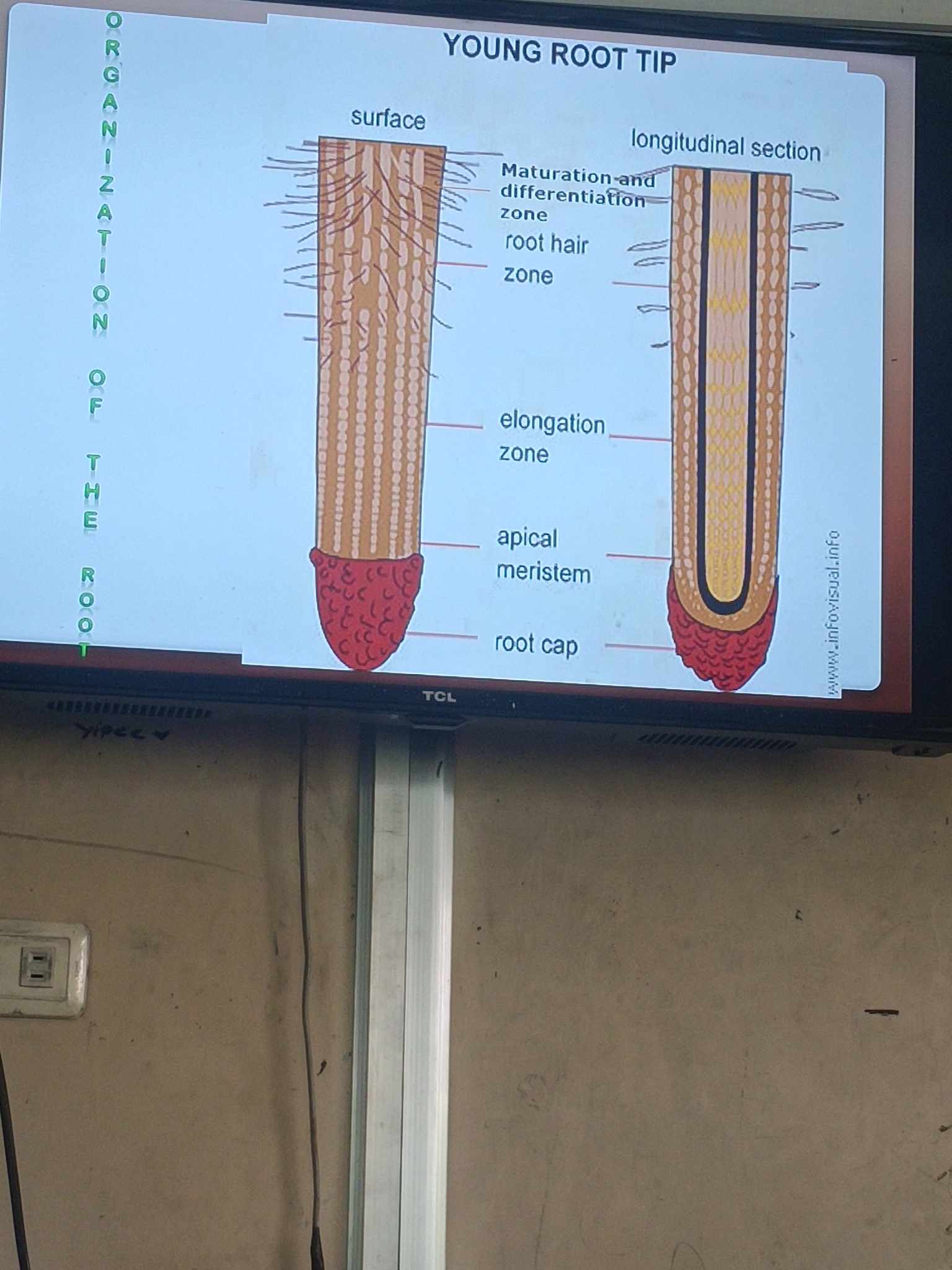
root hair zone
its purpose is to increase surface area for water absorption
Maturation and differentiation zone
no more elongation in this zone
All plants can do primary growth but only some can undergo secondary growth
TRUE
primary growth
increase in length
secondary growth
increase in girth
how will you know if its the maturation zone / region?
the presence of root hairs
Meristem
are cells that keep actively dividing
meristematic zone
indeterminate growth (they can keep growing even when matured)
3 Primary Types of Meristems
protoderm
procambium
ground meristem
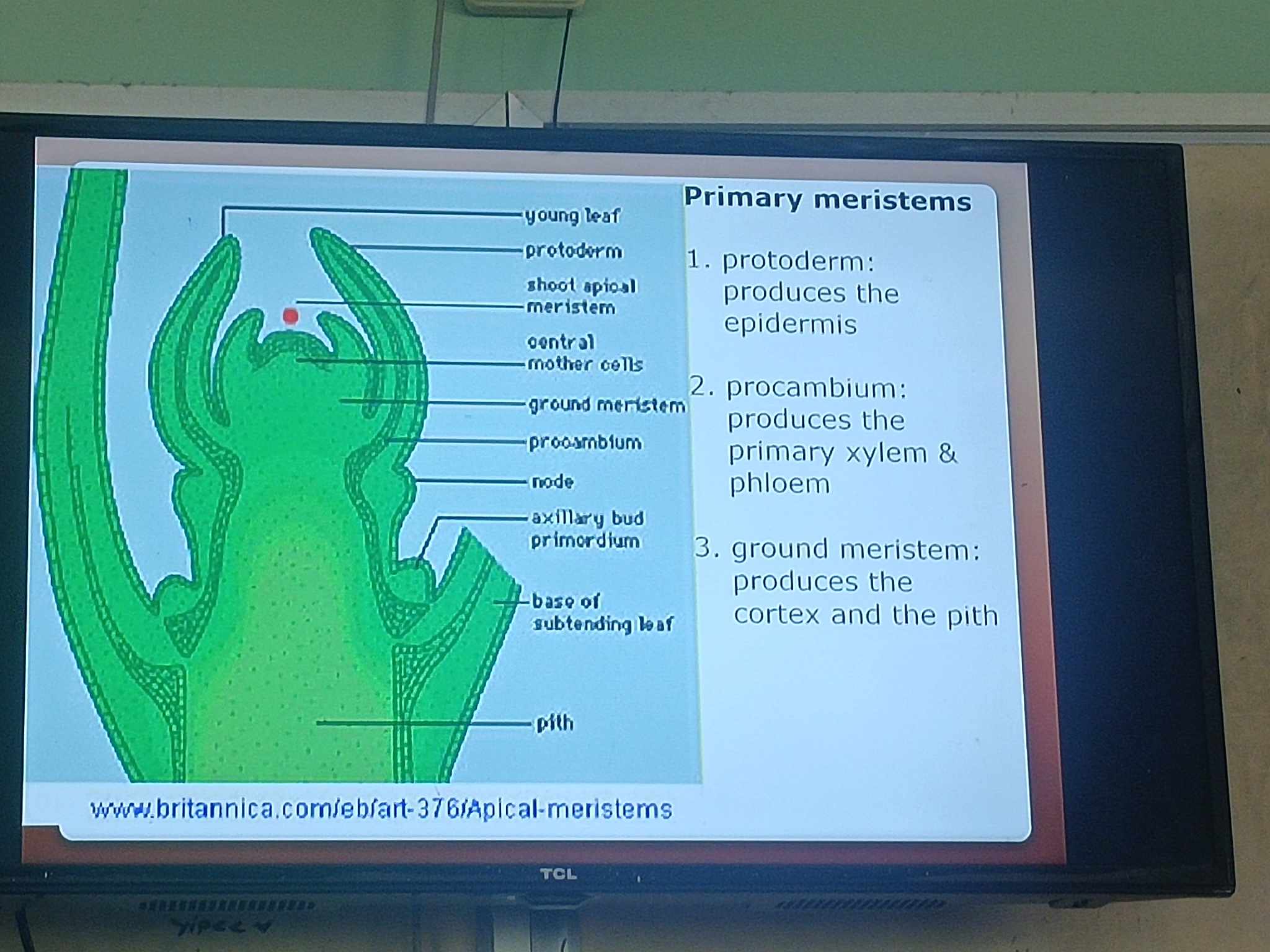
protoderm
give rise to an outer row of cells
produces the epidermis
procambium
appears as a solid cylinder in the center of the root; produces primary vascular tissues
produces primary xylem and phloem
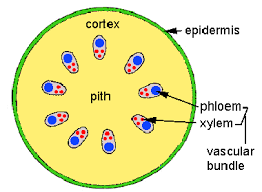
ground meristem
located inside of the protoderm; produces parenchyma cells of the ground tissue
gives rise to cortex and pith (the innermost part of the plant body)
types of plant tissues
Dermal
Ground
Vascular
Primary Tissues
epidermis and root hair
pericycle, primary xylem, primary phloem
endodermis, cortex, pith

types of ground tissues
in order of increasing cell wall strength:
parenchyma - living, thin walled
collenchyma - uneven in rigidity & strength
schlerenchyma - dead cells (not functional), all are thick-walled for rigidity, & strength of organs
collenchyma and sclerenchyma are often found together
DICOT VS MONOCOT ROOT
dicot
2 - 4 xylem arms
no pith '
w/ vascular cambium
monocot
as many as 20 xylem arms
pith
no vascular cambium
plants can produce secondary xylem and phloem if
they have a vascular cambium
Vascular bundles
connected by a cambium:
intrafascicular cambium (inside vascular bundles)
interfascicular cambium (between bundles)
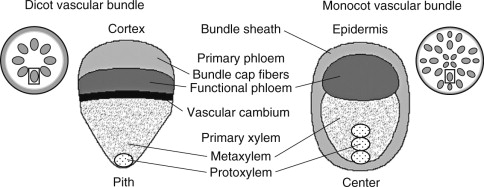
when plant undergoes secondary growth
the primary xylem and phloem move outwards for the secondary xylem and phloem
bark is made up of
phloem
root diversity
adventitious roots / prop root
mycorrhizae - for association with fungi
root nodules - association with bacteria
ginger
is a modified stem
a rhizome
its stripes are the nodules
STEM
located above ground, has more complex organization than roots
supports leaves, flowers, and fruit
conducts the products of photosynthesis
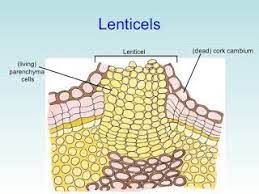
lenticel
for transpiration
allow gases to diffuse in and out of plant tissues
Parts of a woody stem
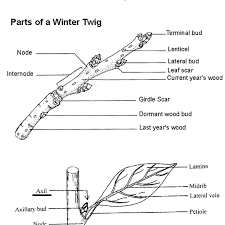
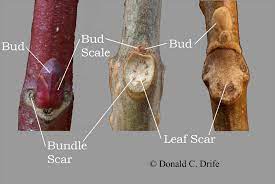
types of scars
girdle scar
lateral bud scale scar
lateral bud scar
leaf scars
Gas exchange structures
stomatal - stomata
lenticular - lenticel (stem)
cuticular - cuticle (root)
epidermis features
cuticle - waxy covering (to prevent water loss
stomata - opening
trichomes/hairs - prevent water loss (glandular trichomes - itchy, allergic reaction)
facilitate opening and closing of stoma
guard cells
wood is
matured xylem
composed of heartwood and sapwood
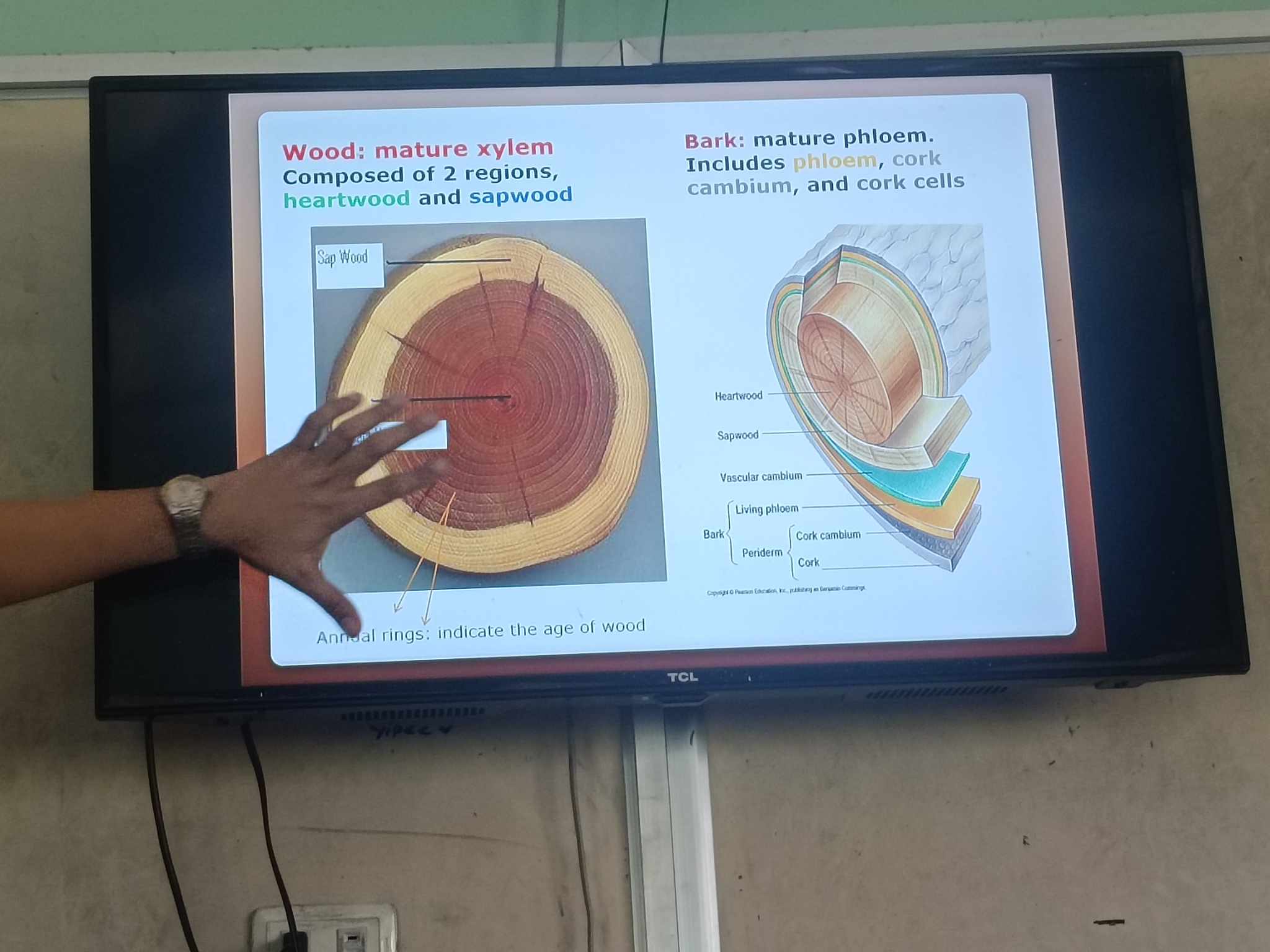
bark is
mature phloem
includes phloem, cork cambium, and cork cells
stem diversity
tendril - a modified stem
rhizomes (scale-like leaf at each node)
bulbs (knob-like stem, fleshy leaves)
tubers (tuber - sollen tip of leaf, each depression on a potato is a node)
runners
cladophyll (leaves - modified as spines)
The response of a tendril being touched is called
thigmonasty
thigmorphogenesis
represents an adaptive response by plants to mechanical stimuli in their environment
banana tree
no stem
leaves
solar energy collectors
dicot leaf vs monocot leaf

variations in leaf structures
presence of more than one layer of epidermis
presence of stomatal crypts (sunken stomate) w/ hair
development of bullate (bulliform - they cover exposed stoma) cells

glass cells
to defend against herbivores
TYpes of leaves
palmately compound leaf (1 common point of attachment)
pinnately compound leaf (most are even numbered)
simple leaf (blade in one node)
rachis
extension of a petiole
small petiole
petiolule
phyllotaxy
arrangement of leaves around the stem
whorled
spiral (a modified alternate)
two-sided decussate - opposite
alternate
opposite
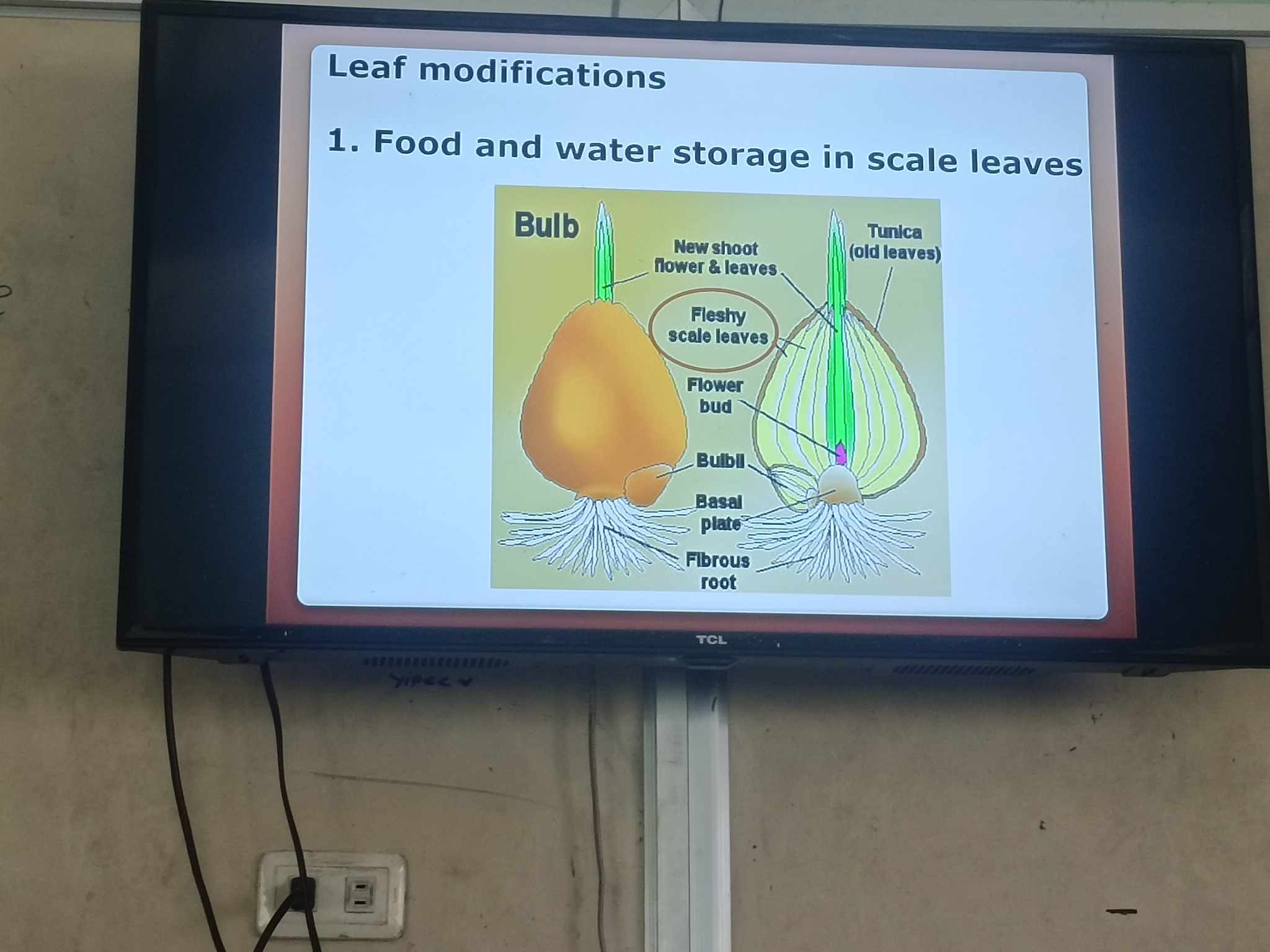
leaf modifications
food and water storage in scale leaves (onion)
thickened and fleshy leaves for water storage (jade plants)
insectivorous plants (ex. pitcher plant and sundew)
Parts of an onion
pitcher plant sci name
Sarracenia sp.
sundew
Drosera rotundifolia
CAM Plants
close their stomata during the day and take up CO2 at night
Orchids, Cacti, euphorbias
C4 Plants
maize and sugarcane