CHAPTER 6
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
the first law of thermodynamics states that the total disorder of a system always increases
FALSE- the second law of thermodynamics
The potential energy in a chemical bond is defined as chemical energy
TRUE
At Equilibrium , the concentrations of the reactants equals that of the products
FALSE- Rate of Formation
Reactions that reach an equilibrium point are reversible
TRUE
ATP synthesis is exergonic
FALSE Endergonic
Enzymes alter the equilibrium point of a reaction
FALSE- activation energy
Enzymes dont change the DG of a reaction
TRUE
The rate of catalyst is proportional to the concentration of the enzyme
TRUE
If an enzyme is bound by an allosteric activator, the enzyme will convert from a low-affinity state to a high affinity state
TRUE
Ribozymes are enzymes
FALSE - biological catalysts
The term that best describes all of the chemical reactions of a cell, incluing acquisition and use of molecules and energy, is ______
Metabolism
The removal of a phosphate group during an enzyme catalyzed reaction takes
About 10 milliseconds
A child swinging on a swing utilizes which type of energy
Kinetic, potential, and chemical energy
The ultimate fate of the energy used by organisms is
Conversion into heat
In molecules, the constant motion of the atoms is an example of ______ energy, while the arrangement of atoms and bonds is an example of ____ energy
Kinetic; potential
Which system is considered a closed system
Earth
Which system is considered an open system
Human
According to the first law of thermodynamics
Energy only changes form
Which statement is a part of the first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be neither created or destroyed
What is the ultimate source of energy for almost all organisms
The Sun
During every energy transformation, it can be said that
the entropy of the universe increases
Which example would have a negative charge in entropy
water freezing
Which equation is used to calculate the free energy associated with a reaction
G= H-TS
Although energy cannot be created or destroyed, energy transformation are not 100% . WHY?
Energy is lost as an increase in entropy
If a reaction is endergonic, what can we infer about the reaction
G must be positive
Which two factors determine whether a reaction is spontaneous
Enthalpy and entropy
If a reaction is spontaneous then G is ___ and the reaction is ____
Negative; exergonic
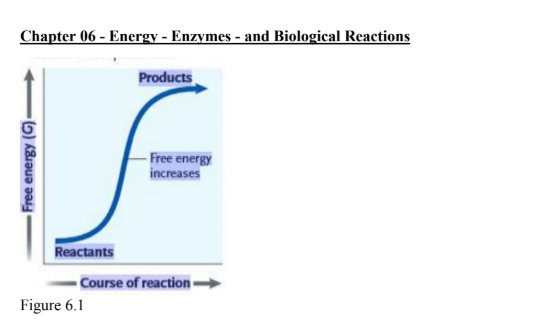
what can be inffered from the graph
this reaction is endergonic with a positive G
In an exothermic reaction
the products have less potential energy than the reactants
Reversible reactions in a cell rarely reach equilbrium because
the products are generally reactants in other reactions and are thus immediately used
When an enzyme catalyzed reaction reaches equilibrium
the rate of the forward and reverse reaction are equal
Identify the exergonic reaction in the list below
Burning wood for a campfire
Which statement is true for exergonic reactions
The products have less free energy than the reactants
Which reaction is most likely to have more products than reactants when it reaches equilibrium
-100 kcal the most negative one
An exergonic reaction will have a
negative change in enthalphy
Eating and digesting a candy bar for energy during a sports event is a good example of
catabolism
the breakdown of glucose into carbon dioxide ,water, and ATP is an example of a
catabolic pathway
Energy from ATP is trasnferred to the reactant of an endergonic reaction by addition of a _______ to that molecule
Phosphate
How does energy coupling allow chemical reactions that are not spontaneous to proceed
the energy from the exergonic reaction is transferred to the substrate to destabilize it
How do cells overcome the erngy requiremnt of endergonic reactions
coupling endergonic and exergonic reactions
Where does energy for ATP synthesis come from
catabolism of complex molecules into simpler molecules
Approximately how many ATP molecules are hydrolyzed and resynthesized each second in a typical cell
10 million
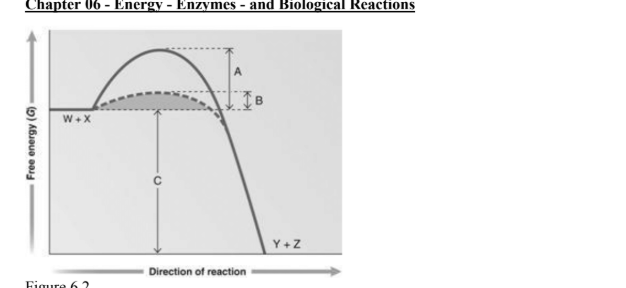
answer the question using the graph. Which portion of the graph shows the activation energy in the absence of an enzyme
A
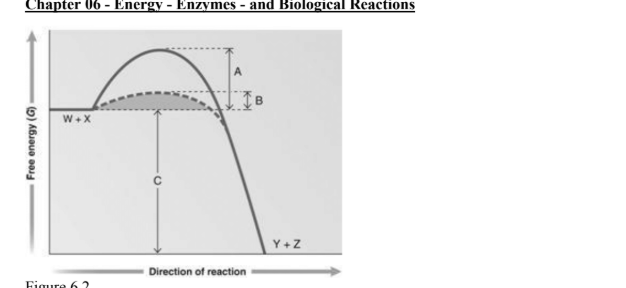
Which portion of the graph shows the activation energy in the presence of enzyme
B
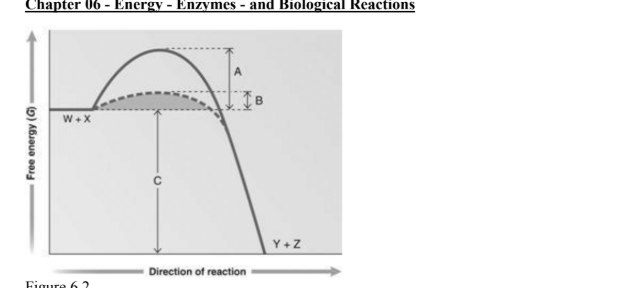
Which portion of the graph shows the free energy of the reaction
C
The conversion of a diamond into graphite is a spontaneous reaction. Why are most women walking aorund with diamond rings and not graphite rings
the energy of activation is very high
Enzymes aid in metabolism by
stabilizing the transition state
Enzymes
change the rate of a reaction
What is the primary determinant of the function and specificity of an enzyme
The enzymes conformation
enzymes function primarily by
increasing the probability that the reactants will come into close proximity to each other in the proper orientation for forming the transition state molecule
Enzymes are ____ catalysts
Protein
You modify the primary sequnce of an enzyme in a region that will be the active site when the protein is properly folded. What is the predicted outcome of this change>>??
the enzyme will not bind to the substrate properly
What is the difference between cofactors and coenzymes
Cofactors can be inorganic or organic, coenzymes are organic cofactors
What is the name of the specific region of an enzyme responsible for catalysts
Active site
Coenzymes that bind tightly to enzymes are called
prosthetic groups
What happens to an enzyme after it has catalyzed a reactions
it returns to its original state
What is the purpose of ionic groups in the active sites of enzymes
to alter the substrate in a way that favors catalysts
If an enzyme is saturated
the reaction is being catalyzed at the maximum rate
you do an experiments adding increasing amounts of substrate to a solution containig an enzyme and a ph buffer. If you graph the results with substrate concentrations on the x axis and reaction rate on the y what wil you find over time
the rate of the reaction will increase rapidly then level off as it reaches saturation.
In competive inhibition
inhibitor binds to and directly blocks the active site of the enzyme
How does the cell overcome inhibition from irreversible inhibitors
by degrading the enzyme inhibitor complex and generating new enzymes
In order to prevent hair loss in men an inhibitor of the enzyme that converts test to a different androgen DHT is used. The inhibitors are steroids similar to test . what would you classify this inhibition
Competitive
Allosteric inhibition are often
products of the reactions that they regulate
What happens when an enzyme is bound by an allosteric activator
the enzyme transitions form a low affinity state to a high affinity state

Why does the cruve sharply drop after 45 C instead of mirroring the slop of the linge goin from 0-40 C
The enzyme begins to denature above a certain temperature eliminating all cataltic activity of the protein
If an enzymes optimal temp is 37 C then the enzyme
activity will drop at temperature above 37 C and likely be eliminated by 60 C
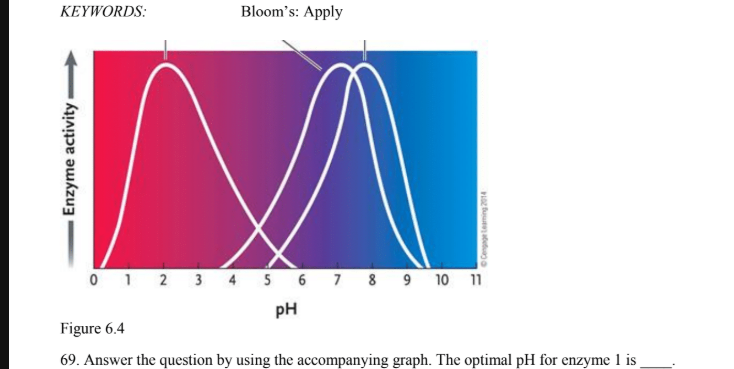
the optimal ph for enzyme 1 is ?
3
The optimal pH for enzyme 2 is
7
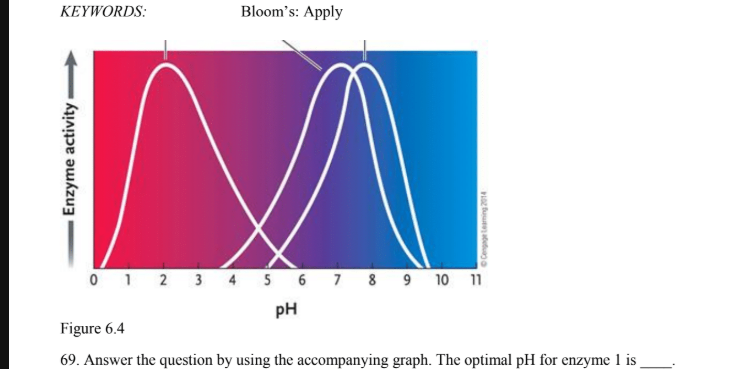
if all three enzymes catalyze the same reaction and your experimental conditions require a ph of 8 which enzyme would you choose
Enzyme 3
What is the optimal ph of most enzymes
7
Is a ribozyme a true enzyme
no because it is not a protein
Zhang and CECE’s experiments confrimed which feature of ribozyme activity
Ribozymes catalyze formation of bonds between amino acids in protein synthesis
Ribozymes are
RNA catalysts
How did Zhang and Cech puring the RNA molecules that were able to catalyze the linkage between two amino acids
passing the reaction mixture through a column that binds biotin
The discovery of ____ suggested that nucleic acdis likely existed prior to proteins
ribozymes
Because of some of the problems with explaining how the first RNA organisms originated, an alternative possibility has been proposed in which
a different form of life existed before the RNA world
Coupled reaction
The linking of an exergonic reaction with an endergonic reaction that allows a cell to drive a nonspontatneous reaction to completion
equilibrium point
a state in which the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction
Metabolic pathway
A series of chemical reactions where the products of one reaction are the reactants for a subsequent reaction
Catalyst
A substance that facilitates a chemical reaction without itself being consumed by the reaction
Activation Energy
A series of chemical reaction where the products of one reaction are the reactants for a subsequent reaction
Active site
the portion of the enzume that binds to a reactant or reactants
Substrate
the reactant molecules that binds to an enzyme
Transition state
An intemrediate arrangement of unstable bonds between atoms that can proceed towards either the reactants or products of a reaction
Allosteric regulation
the product of the reaction interacts with an enzyme in a noncompetitive way to inhibit or enhance enzyme activity
Protein synthesis
Endergonic
Digestion of a candy bar
exergonic
A dead cell
Equilibrium
reactions where DG is negative
Exergonic
A reaction where DG is positive
endergonic
the rate of synthesis equals the rate of degradation
Equilibrium