Lesson 8.4. Antiparasitic Agents
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
Protozoal infections
amebiasis, giardiasis, trichomoniasis, Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) infection, trypanosomiasis, leishmaniasis, and malaria
Helminth Infections
roundworms, tapeworms, and filariasis
Ectoparasite Infections
parasites on skin surface; scabies and pediculosis
Nitroimidazoles
its nitro group generate ROS (superoxide radicals) that damages key cellular components (e.g. DNA/RNA) leading to protozoal cellular death
Aromatic ester-amide
inhibit pyruvate: ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR) → no formation of dactyl thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) complex → no lactic acid formation (lactic acid is essential metabolite for protozoa survival)
amebiasis, giardiasis and trichomoniasis
use of Nitroimidazoles and Aromatic Ester Amides
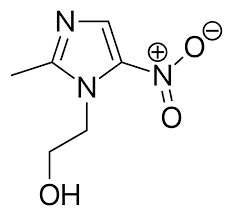
Metronidazole Structure
NITROIMIDAZOLES
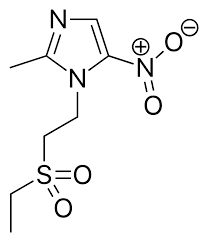
Tinidazole Structure
NITROIMIDAZOLE
Nitazoxanide
AROMATIC ESTER AMIDES
prodrug for Tizoxanide
ester is hydrolyzed into OH
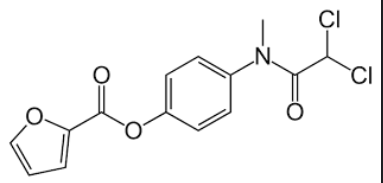
Nitazoxanide Structure
AROMATIC ESTER AMIDES
Diloxanide Structure
AROMATIC ESTER AMIDES
Emetine
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
alkaloidal antiprotozoal that induce vomiting
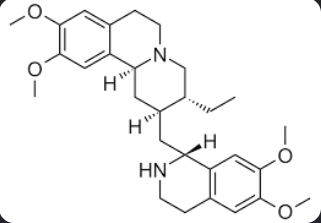
Emetine Structure
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
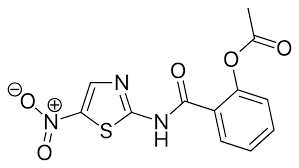
Iodoquinol
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
used as luminal amebicide chelates ferrous ions
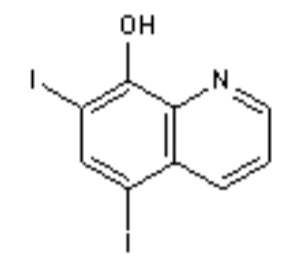
Iodoquinol Structure
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
Paromomycin
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
antiprotozoal
aminoglycoside
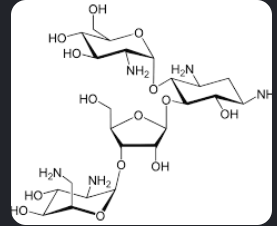
Paromomycin Structure
OTHER ANTIPROTOZOAL AGENTS:
Pneumocytsis carinii pneumonia (PCP)
common life-threatening condition among immunocompromised patients (e.g HIV, organ transplant, cancer patients)
TMP-SMX (Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole)
Drug of Choice for PCP
TMP-SMX Structure
AGENTS FOR PCP:
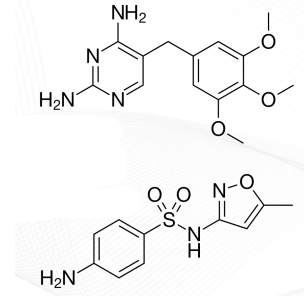
Pentamidine
2ND LINE DRUGS FOR PCP:
amino groups binds DNA causing interference in DNA synthesis
inhibits topoisomerase II
Pentamidine Structure
2ND LINE DRUGS FOR PCP:
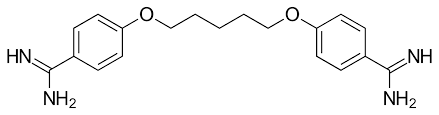
Atovaquone
2ND LINE DRUGS FOR PCP:
has structural similarity with Co-Q10 hence activity on ETC complex
inhibits nucleic acid/ATP synthase
Atovaquone Structure
2ND LINE DRUGS FOR PCP:
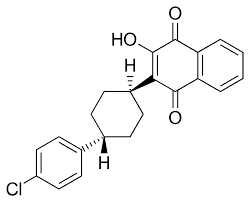
Tritryps Agents
agents used to combat infections caused by: Leishmania spp, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Trypanosoma brucei gambiense/rhodisiense
neglected parasitic tropical diseases (NTDs)
Infections caused by Leishmania spp, Trypanosoma cruzi, and Trypanosoma brucei gambiense/rhodisiense are classified as _____________________________
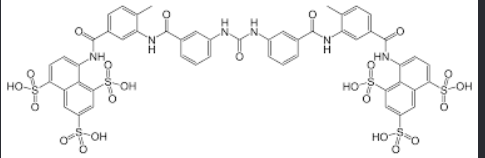
Suramin
AGENTS FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
has 6 sulfone groups
inhibits dihydrofolate reductase, thymidine kinase, glycolytic enzymes
Suramin Structure
AGENTS FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
Eflornithine
AGENTS FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
irreversible inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) → blocks putrescine synthesis → no polyamine for membrane potential/ATPase
Eflornithine Structure
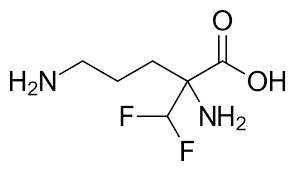
Melarsoprol
AGENTS FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
inhibits trypanothione reductase with trivalent As (high affinity for -SH in proteins)
Melarsoprol Structure
AGENTS FOR AFRICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
Benznidazole
AGENTS FOR AMERICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
contains nitro-imidazole ring
prodrug that is metabolized into a nitroso intermediate → interferes with trypanothione
Benznidazole Structure
AGENTS FOR AMERICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS

Nifurtimox
AGENTS FOR AMERICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS
contains nitro-furan ring
prodrug that generates ROS → damages trypanosomes DNA and trypanothione reductase
Nifurtimox Structure
AGENTS FOR AMERICAN TRYPANOSOMIASIS

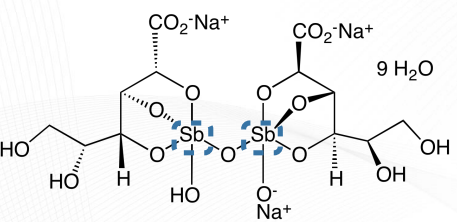
Stibogluconate
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS
contains trivalent/pentavalent Sb
induces apoptosis on Leishmania by acting in biopolymers
Stibogluconate Structure
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS
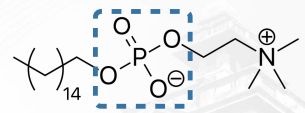
Miltefosine
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS
orally active agent with unclear MOA vs Leishmania
Miltefosine Structure
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS
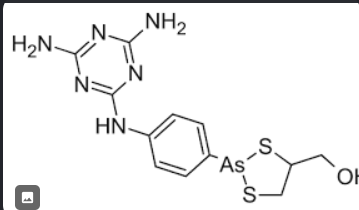
Antimony Potassium Tartrate
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS
tartar emetic
inorganic agent previously used for Leishmaniasis
Antimony Potassium Tartrate Structure
AGENTS FOR LEISHMANIASIS

Quinolines
ANTI-MALARIAL AGENTS
Includes natural and synthetic derivatives (e.g., quinine, chloroquine, mefloquine)\
prevent the conversion of toxic hematin to non-toxic hemozoin, leading to accumulation of toxic heme and death of the malaria parasite
Antifolates
ANTI-MALARIAL AGENTS
Inhibit folate metabolism in Plasmodium (e.g., sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine)
targets dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) similar to trimethoprim
Artemisinin and derivatives
ANTI-MALARIAL AGENTS
natural product of chinese medicine (qinghaosu) or from sweetworm wood (Artemissia annua)
MOA is unknown but the endoperoxide bridge in its structure is believed to generate reactive oxygen species (radicals) that interact with hemozoin, damaging the malaria parasite
Quinine
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
natural agent first extracted from Cinchona
Quinine Structure
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
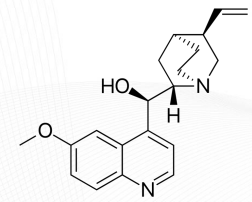
Primaquine
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
artificial agent that is considered as a “radical cure”
Primaquine Structure
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
Chloroquine
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
artificial agent
C7-Cl gives higher activity
Chloroquine Structure
QUINOLINE ANTIMALARIALS
Proguanil
ANTIFOLATE ANTIMALARIALS
lead compound, prodrug for cycloguanil
Proguanil Structure
ANTIFOLATE ANTIMALARIALS

Pyrimethamine
ANTIFOLATE ANTIMALARIALS
developed from proguanil given usually with sulfadoxine to mimic TMP-SMX
Pyrimethamine Structure
ANTIFOLATE ANTIMALARIALS
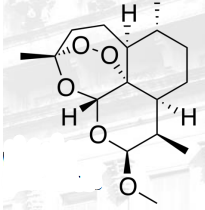
Arteminol/Dihydroartemisinin
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
source molecule for other derivative
Arteminol/Dihydroartemisinin Structure
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
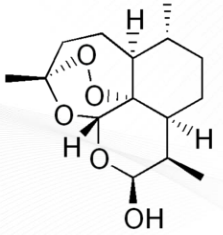
Artemotil
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
lipid-soluble derivative
Artemotil Structure
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
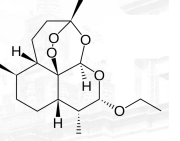
Artesunate
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
water-soluble derivative
Artesunate Structure
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
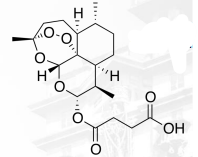
Artemether
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
lipid-soluble derivative
Artemether Structure
ARTEMISININ ANTIMALARIALS
Anti-helminthic Agents
agents are used for parasitic helminthic infection (e.g. round worms, tape worms, filariasis)
fumarate reductase
MOA OF ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:
a. inhibits ______________________ (benzimidazoles)
b. induces _________________ in the helminth parasite (other agents)
a = ?
muscular paralysis
MOA OF ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:
a. inhibits ______________________ (benzimidazoles)
b. induces _________________ in the helminth parasite (other agents)
b = ?
Benzimidazoles
ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:
a. ____________ - Mebendazole, Thiabendazole, and Albendazole
b. __________ - Ivermectin (for river blindness), Praziquantel (fluke infection), Pyrantel pamoate, Diethylcarbamazine, Piperazine
a = ?
Other agents
ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:
a. ____________ - Mebendazole, Thiabendazole, and Albendazole
b. __________ - Ivermectin (for river blindness), Praziquantel (fluke infection), Pyrantel pamoate, Diethylcarbamazine, Piperazine
b = ?
Mebendazole Structure
ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:

Thiabendazole Structure
BENZIMIDAZOLES:
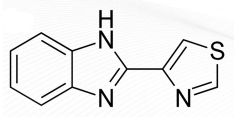
Albendazole Structure
BENZIMIDAZOLES:

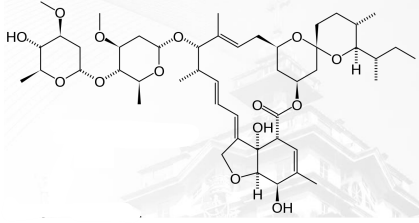
Ivermectin Structure
OTHER ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:
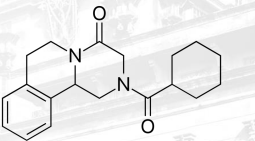
Diethylcarbamazepine Structure
OTHER ANTI-HELMINTHIC AGENTS:

Praziquantel Structure
OTHER ANTI-HELMINTIC AGENTS:
Sarcoptes scabiei
ECTOPARASITES:
a. scabies
b. pediculosis
c. other ectoparasites
a = ?
Pediculus humanus
ECTOPARASITES:
a. scabies
b. pediculosis
c. other ectoparasites
b = ?
Cimex reticularis
ECTOPARASITES:
a. scabies
b. pediculosis
c. other ectoparasites
c = ?
Spinosad
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
mixture of macrocyclic lactones that paralyzes parasite by hyper exciting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
Benzyl alcohol
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
not an insecticide
instead, it eradicates lice by asphyxiation, blocking their respiratory spiracles and preventing gas exchange
Lindane
ECTOPARASITES AGENTS:
blocks GABA receptor leads to parasite paralysis
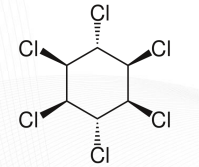
Lindane Structure
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
Pyrethrin
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
P-I R = -CH3, P-II R = -CO2CH3
binds to Na channel resulting to paralysis
Pyrethrin Structure

Permethrin
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
used for scabies, lice and also against mosquitos
Permethrin Structure
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS
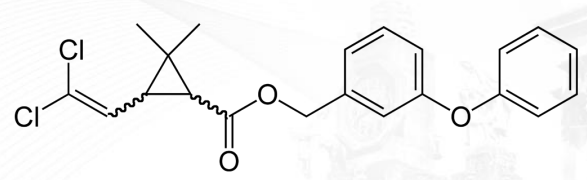
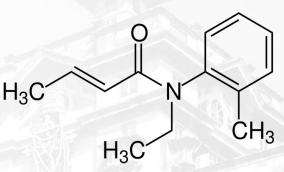
Crotamiton
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS:
scabicical agent approved by FDA
Crotamiton Structure
ECTOPARASITE AGENTS