Rhinitis/Uticaria/Drug Rxns MLS
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
rhinitis
inflammation of the nasal mucosa
what are the causes of rhinitis?
Infectious-
Bacterial
Viral
Meds
Hormonal
Foods
what are allergen antigens that cause allergic rhinitis?
Seasonal
Spring: flowering shrubs and tree pollens
Summer: flowering plants and grasses
Fall: ragweed and mold
Perennial (Chronic)
Pet dander
Dust mites
Indoor mold
pathophysiology of allergic rhinitis
Type I hypersensitivity reaction
what are the 3 phases of allergic rhinitis?
sensitization phase, early phase allergic response, late-phase reaction
sensitization phase
First contact with a specific allergen: IgE antibody forms and binds to mast cells and basophils
early phase allergic response
Subsequent exposure to antigen: binds to the IgE antibody receptor on the mast cell → stimulates mast cell degranulation
late phase reaction
Chemotaxis of inflammatory cells occurs which triggers a second wave of mediator release
what are symptoms of allergic rhinitis?
Episodic clear rhinorrhea
Sneezing
Lacrimation
Congestion
Pruritus
Cough
what are exam findings of allergic rhinitis?
Nasal mucosa pale and boggy
Conjunctiva congested and edematous
Nasla polyps
Cobblestoning
Allergic “shiners”
Allergic “salute”
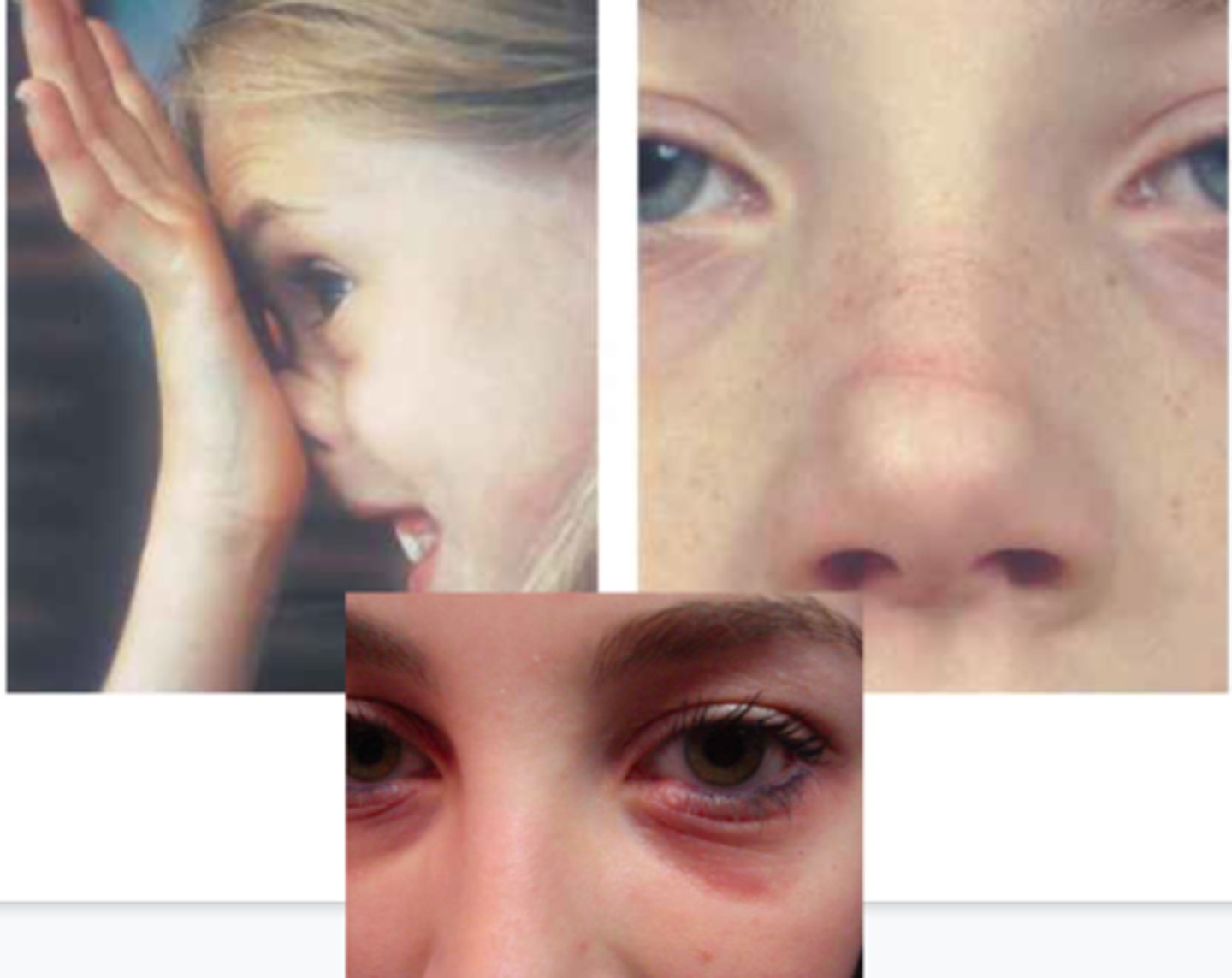
nasal polyps
Benign tumors found on the nasal turbinates, originating in the maxillary and ethmoid sinuses
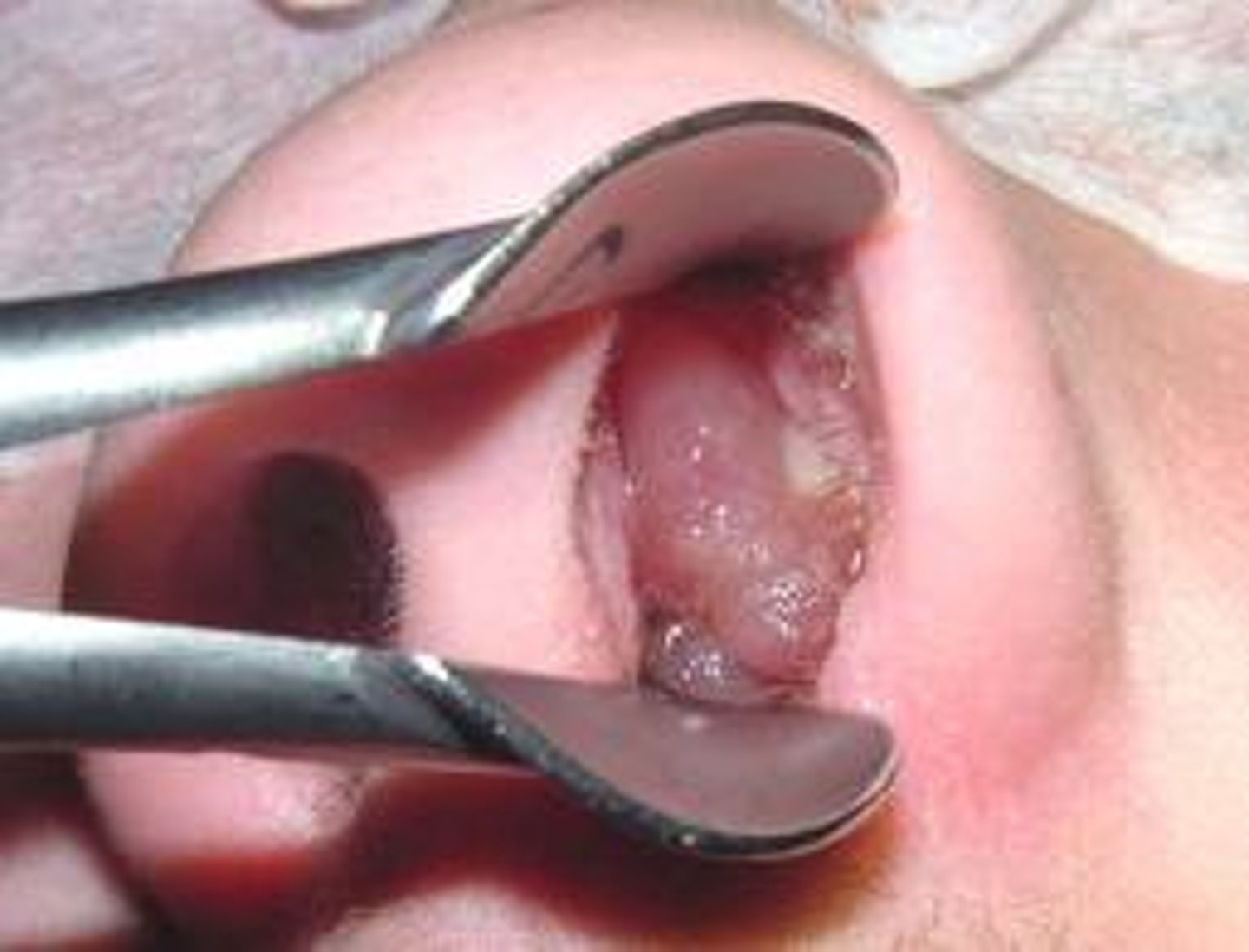
what may patients with nasal polyps have in their history?
Nasal obstruction, hyposomia, secondary sinusitis, Samter Triad, Cystic Fibrosis
Samter Triad
nasal polyps, asthma, aspirin sensitivity
pathophysiology of nasal polyps
Recurrent edema of the submucosa associated with rhinitis
diagnosis of nasal polyps
Physical exam: pale/pearly and translucent nodule(s) of inferior turbinates
Nasal endoscopy
Diagnosis of rhinitis
Clinical based on H & P
Testing
Nasal Secretion: + eosinophils on a microscope slide
Rhinolaryngoscopy
CT or MRI
what testing can be done to help diagnosis the cause of rhinitis?
ntradermal testing
Serum IgE, eosinophils
RAST testing
ELISA
whats the treatment for rhinitis?
Avoidance
Intranasal Steroids
2nd Generation H1 antihistamines
1st Generation H1 antihistamines
Alpha-1 receptor agonists
Cromolyn sodium
Leukotriene Inhibitor
Ipratropium nasal spray
Intranasal antihistamine sprays
Opthalmic antihistamine
Surgical removal of polyps
Referral to allergist
Immunotherapy/Hyposensitization
antihistamines MOA
Competitively blocks H1 receptor on glandular tissue
what are possible complications of allergic rhinitis?
Eustachian tube dysfunction
Chronic sinusitis
Sleep disorders/fatigue
Rhinitis medicamentosa
Rhinitis medicamentosa
Tachyphylaxis to intranasal decongestant which causes rebound congestion and turbinate hypertrophy
Urticaria
“Wheals” or “hives” that abruptly appear and flatten within 24 hours per lesion
pathophysiology of urticaria
Vasodilation and increased permeability causes fluid to leak into dermis
Type I hypersensitivity: IgE mediated response to stimulus
H1
increased capillary permeability
H2
arteriolar and venule vasodilation
what are possible IgE immune mediated causes of urticaria?
Contact allergen
Food allergens
Insect venom
Medications
what are possible non-IgE immunologically mediated causes of urticaria?
Bacterial infections
Viral infections
signs/symptoms of urticaria
Pruritus
Erythematous wheals, varying shapes and locations, well-demarcated borders
what are special forms of urticaria?
Angioedema
Papular urticaria
PUPPP
Dermatographism
how do you diagnosis urticaria?
Clinical
History of known exposure
Histologic skin biopsy
Work-up for potential causes
what are treatment options for urticaria?
Treat underlying cause if possible
H1 and H2 antihistamines
Doxepin
Systemic corticosteroids
Omalizumab (Xolair) injections
what are H1 antihistamines used to treat urticaria?
Diphenhydramine, cetirizine, hydroxyzine, fexofenadine
what are H2 antihistamines used to treat urticaria?
Cimetidine, famotidine
anaphylaxis
Acute multi-organ system reaction to mast cell/basophil mediator release
etiology/pathophysiology of anaphylaxis
Exposure to allergen (IgE-mediated reaction) releases histamine
histamine causes what?
Smooth muscle spasm
Vasodilation
Increased vascular permeability
Increased mucous secretion/edema of target tissues
what are signs/symptoms of anaphylaxis?
Low blood pressure
Hives
Itchiness
Flushing
Shortness of breath
Wheezes or stridor
Hoarseness
Pain with swallowing
Cough
how do you diagnosis anaphylaxis?
Clinical
Elevated serum tryptase and histamine
Serum or skin IgE testing
what are treatment options for anaphylaxis?
IM Epinephrine: Antagonizes effect of chemical mediators
Maintain airway I
V fluids: Isotonic
Oxygen
IV Antihistamines
Bronchodilators
Corticosteroids: Prednisone, 1mg/kg/d
Supine position
what can anaphylaxis cause that can lead to mortality?
Respiratory distress/airway collapse/cardiovascular collapse
Type IV Hypersensitivity
Delayed response mediated by T cells
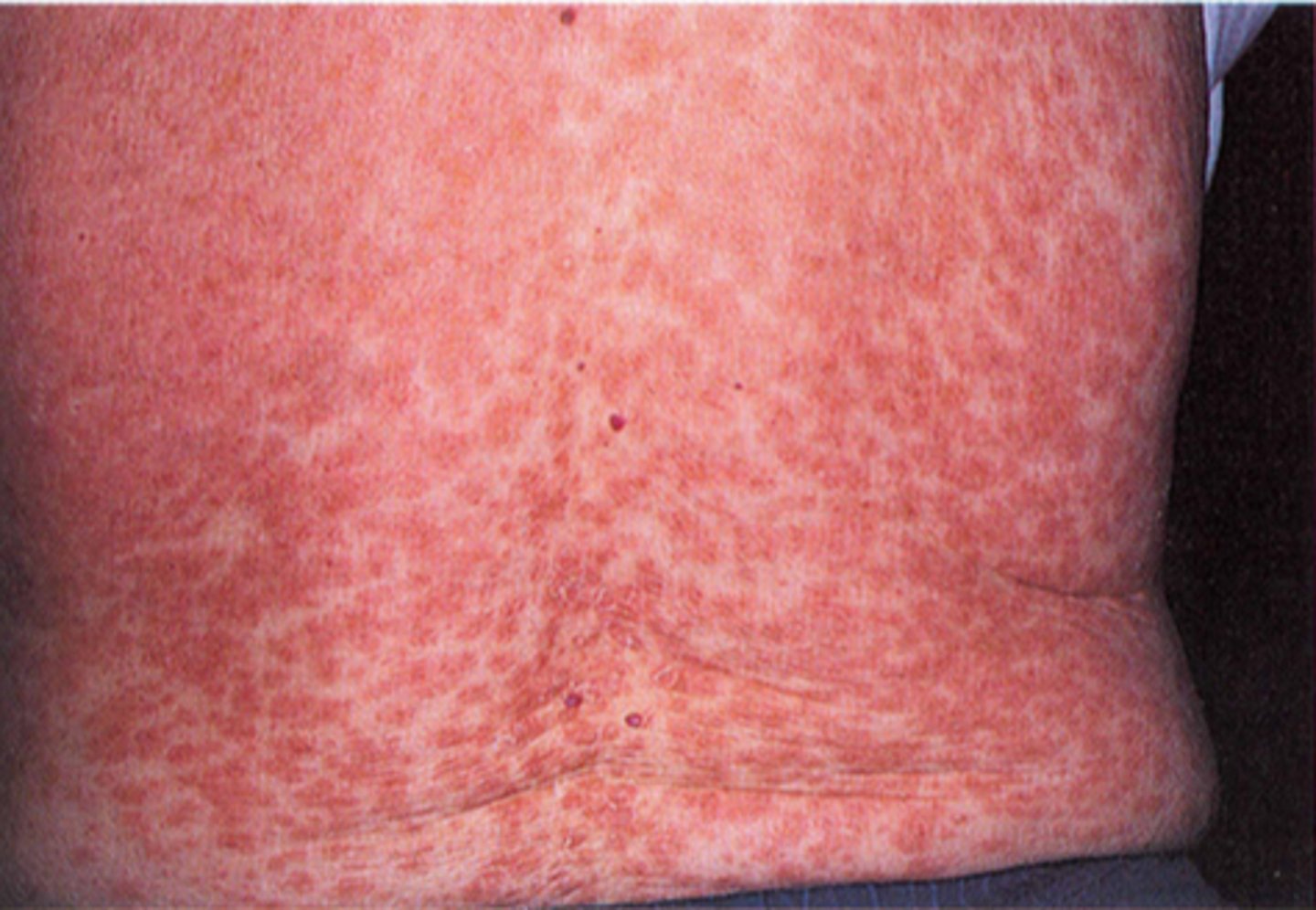
Morbilliform Drug Eruption
95% of all drug eruptions
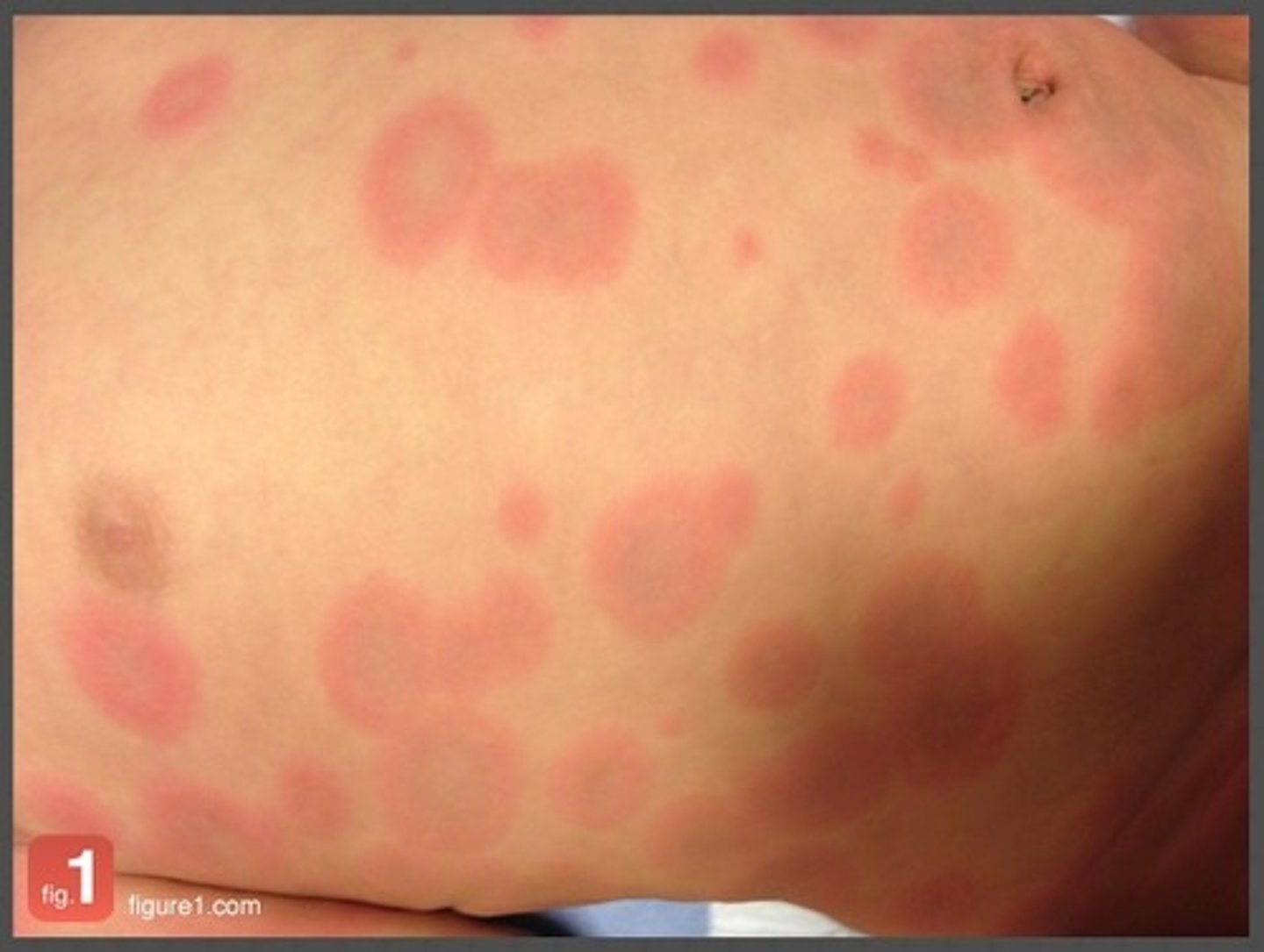
Erythema Mulitforme
- young adults (20-40)
- 1% of population
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)/Toxic Epidermal Necrosis (TEN)
- 2-7 cases per 1 mil people
- more common in immunosuppressed
- females > males
Etiology of Cutaneous Drug Reactions
- medication
- infection
- malignancies
- idiopathic
Medications that can cause cutaneous drug reactions
- anti-seizure medications
- antibiotics
- NSAIDs
- allopurinol
Antibiotics than can cause cutaneous drug reactions
- penicillins
- sulfa
Viral infections that can cause cutaneous drug reactions
- HSV
- AIDS
- Coxsackie
- EBV
Bacterial infections that can cause cutaneous drug reactions
- Group A Strep
- Diptheria
- Mycoplasma
- Mycobacteria
Morbilliform Drug Rash Appearance
- 1-3 weeks after exposure
- generalized multiple patchy/itchy pink/red macules/papules
Important differentiator of morbilliform drug rash
no mucous membrane involvement
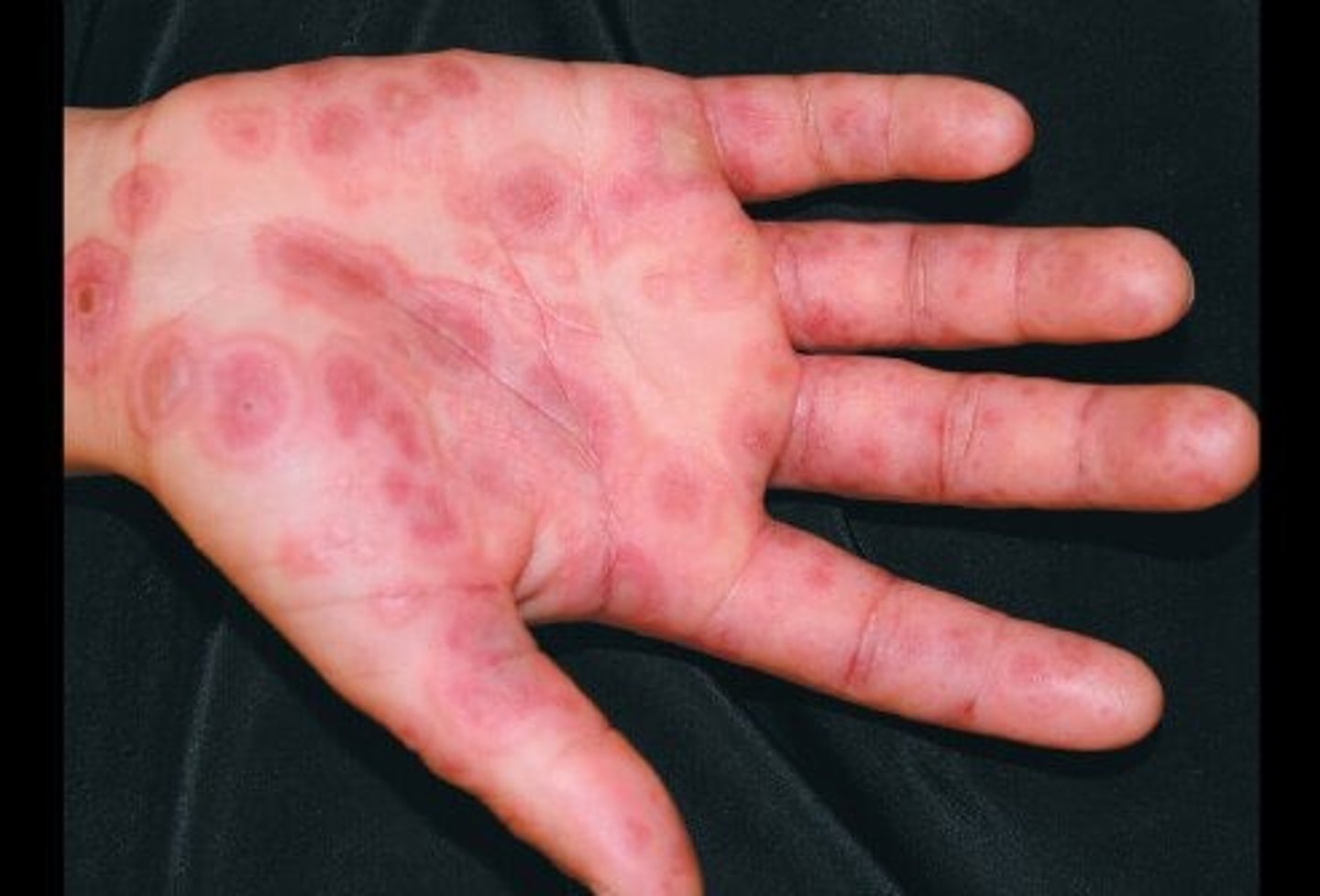
Erythema Mulitforme Minor
classic target lesion
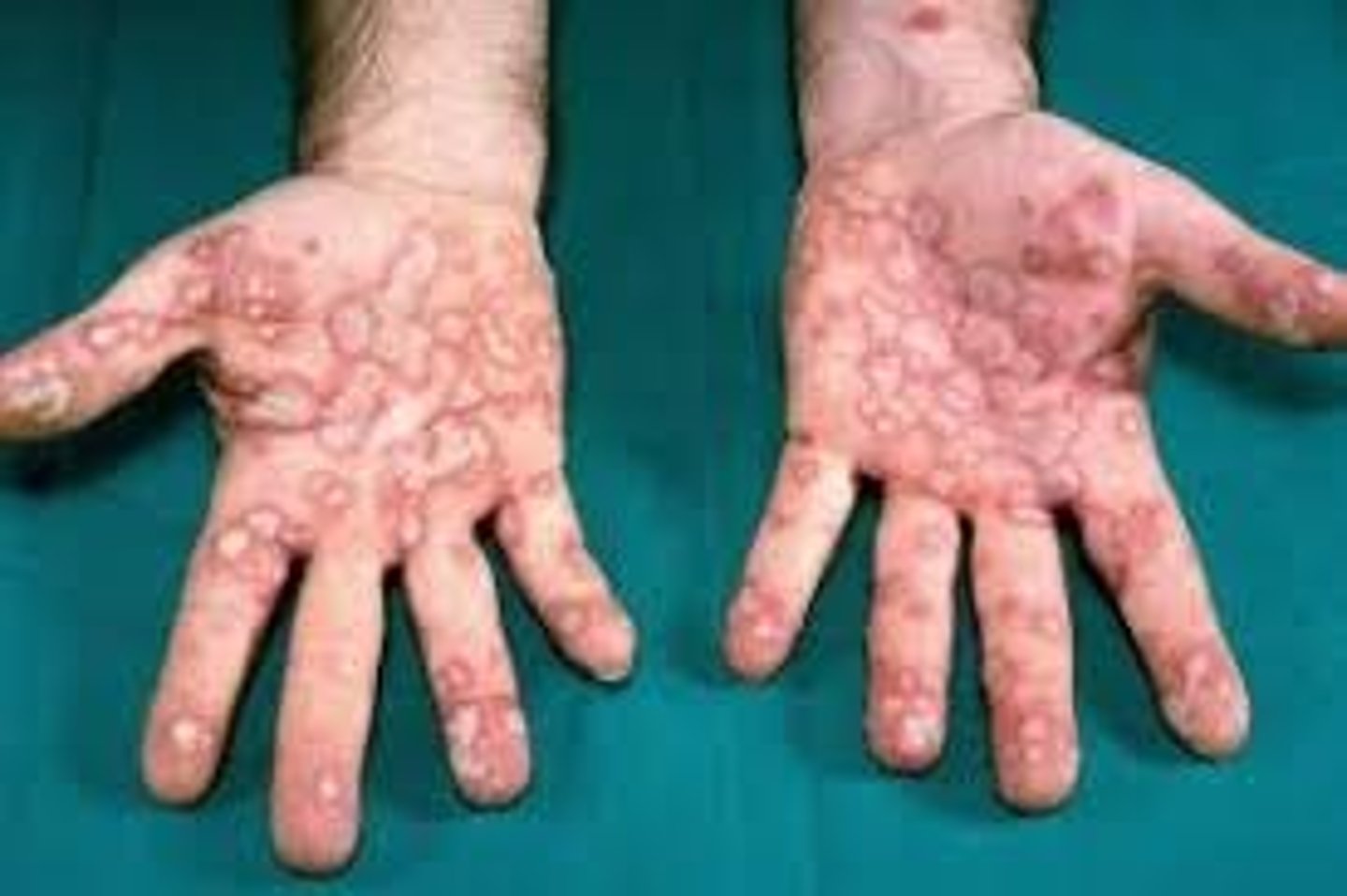
Erythema Mulitforme Major
target lesions with mucocutaneous involvement, up to 10% TBSA
TBSA
total body surface area
SJS TBSA
<10%
TEN TBSA
>30%
SJS/TEN Prodrome
- fever
- flu-like sxs 1-21 days
- follow by mucocutaneous lesions
Cutaneous Lesions of SJS/TEN
- coalescing erythematous macules with purpuric centers turn into vesicles and bullae
- tender/burning
- begin on face and thorax and spread in a systemic distribution
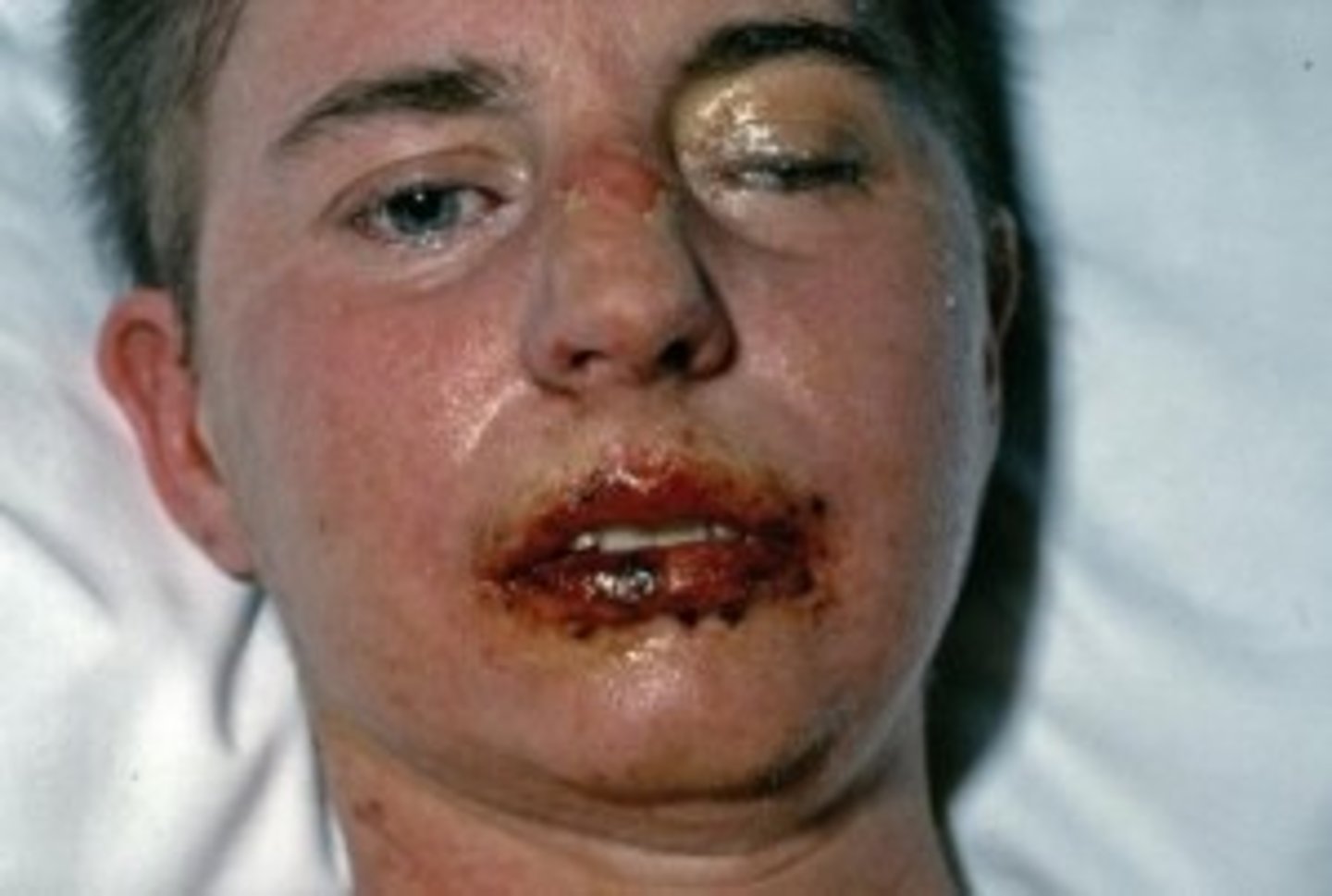
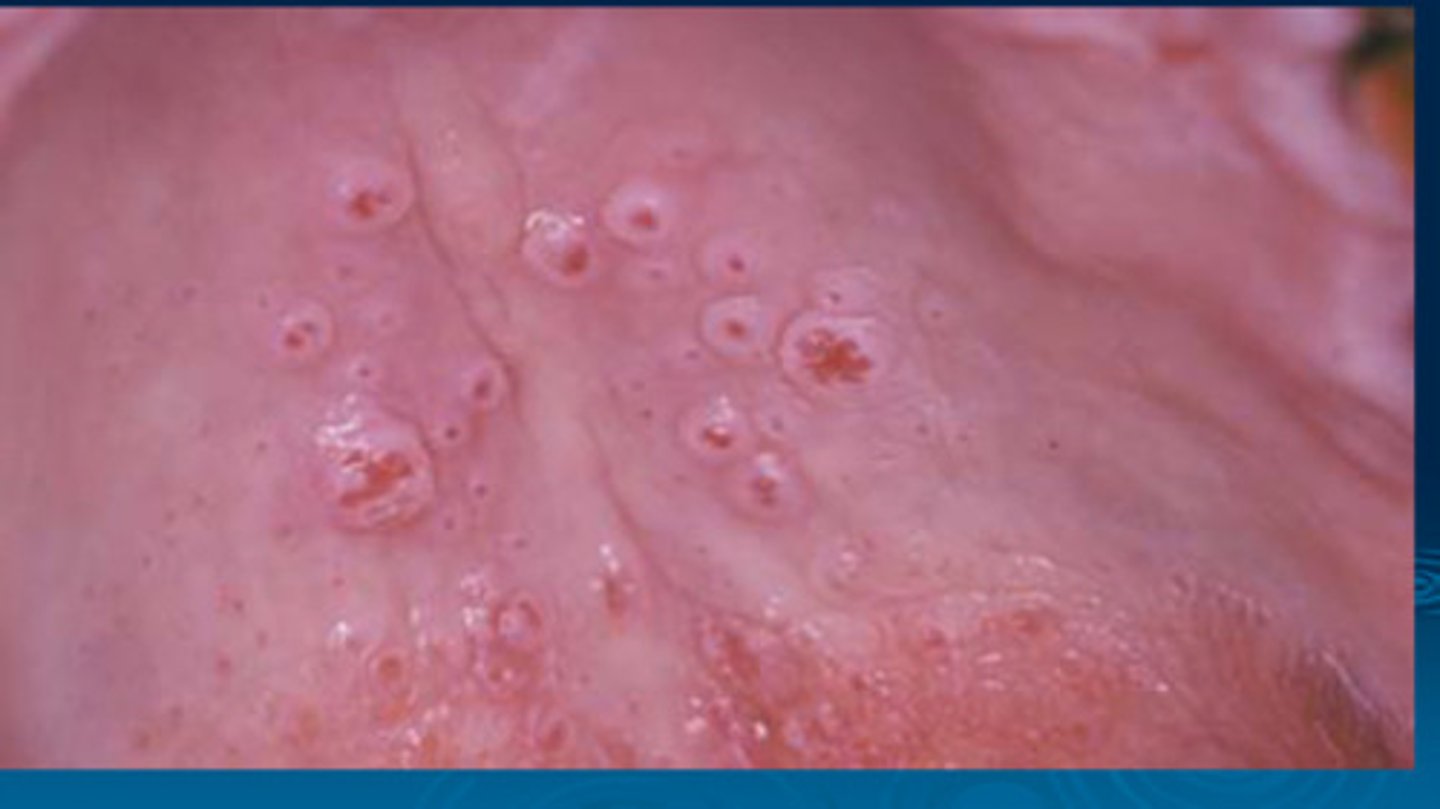
Oral Mucosal Lesions of SJS/TEN
stomatitis
Ocular Mucosal Lesions of SJS/TEN
conjunctival/corneal
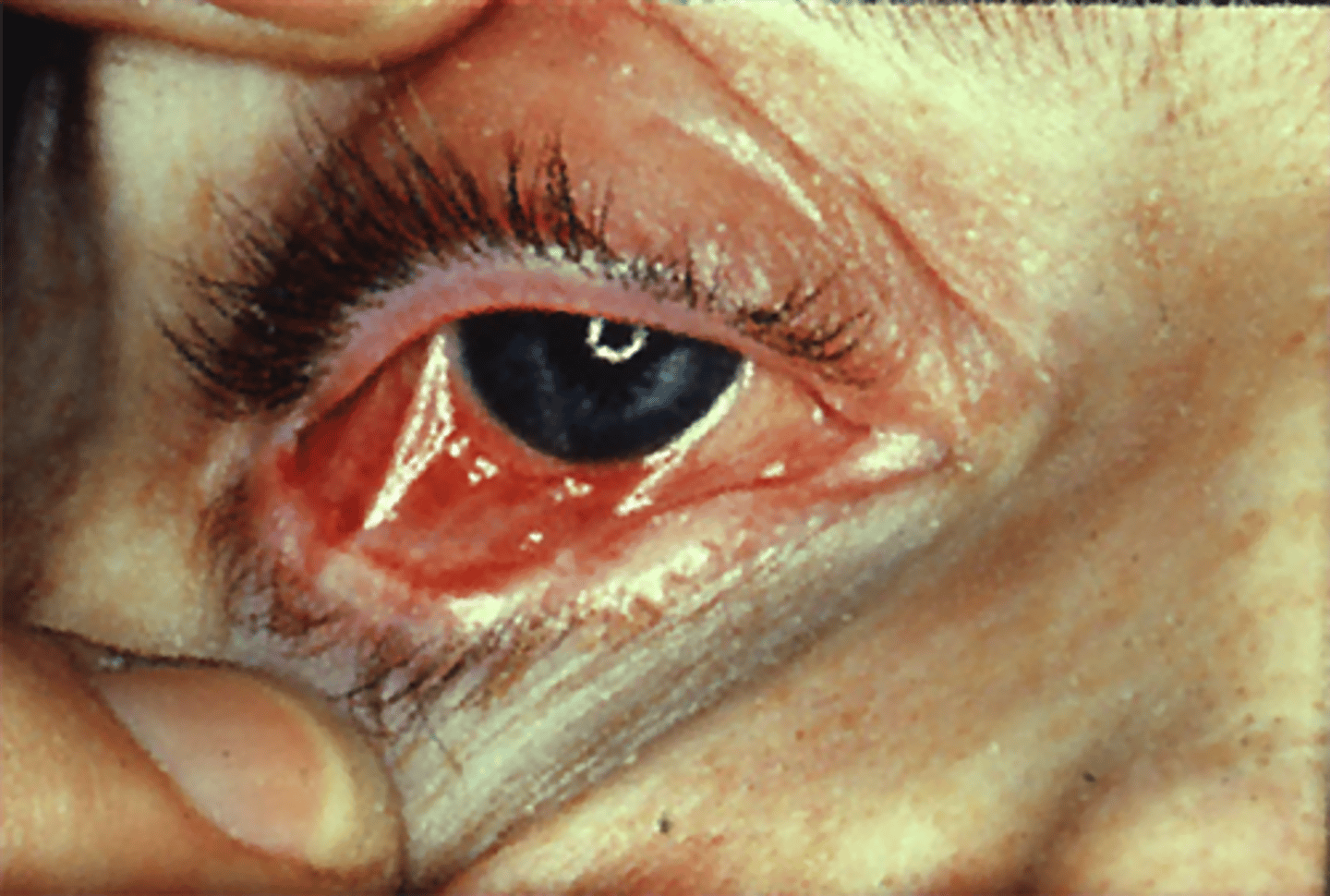
Diagnosis of SJS/TEN
clinical
Biopsy for SJS/TEN
epidermal necrosis, +CD8
Treatment of SJS/TEN
- stop offending agent
- referral to burn unit
- supportive care
- manage airway
Supportive Care Options for SJS/TEN
- wound care
- fluid replacement
- electrolyte replacement
- pain control
When to use antibiotics for SJS/TEN
prophylaxis - open surface area due to skin peeling away leaves pt open to infections
Prognosis of cutaneous drug reactions
good for everything except TEN
Prognosis of TEN
25% mortality