MGCR 293 Chapter 11: Oligopoly Models and Equilibrium
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to oligopoly models, their characteristics, and market equilibria.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Oligopoly
A market structure characterized by a few firms dominating the market, leading to interdependence in pricing and output decisions.
Cournot model
A non-collusive model of quantity-setting competition where firms choose output simultaneously. Products in the market are homogeneous. Assume that:
the market demand for a product is linear function.
there are two firms competing in the market for a one period game. This is called a situation of duopoly.
Reaction functions and the cournot model
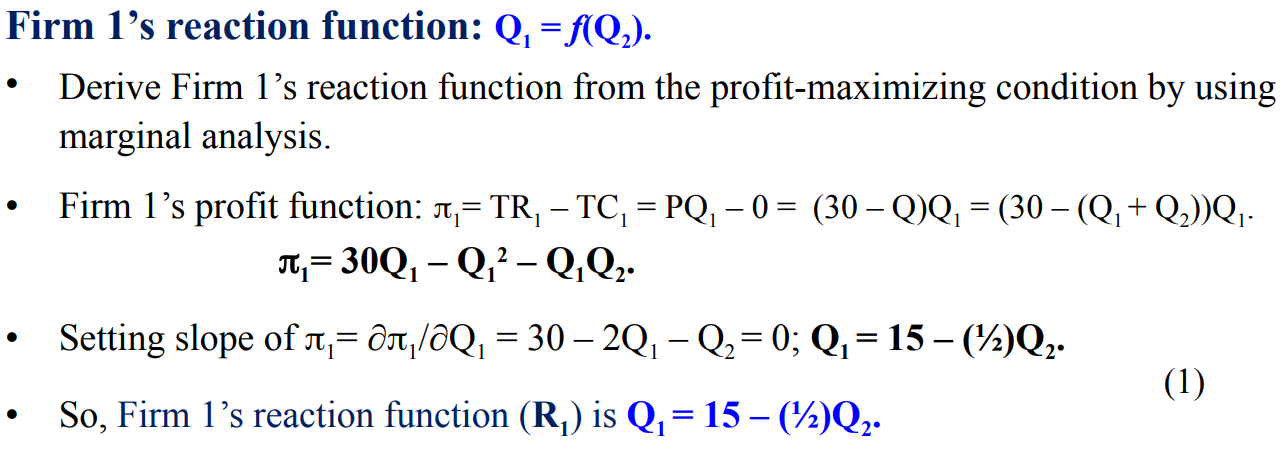
The relationship between a firm’s profit-maximizing output, given the amount of output produced by the other firm.
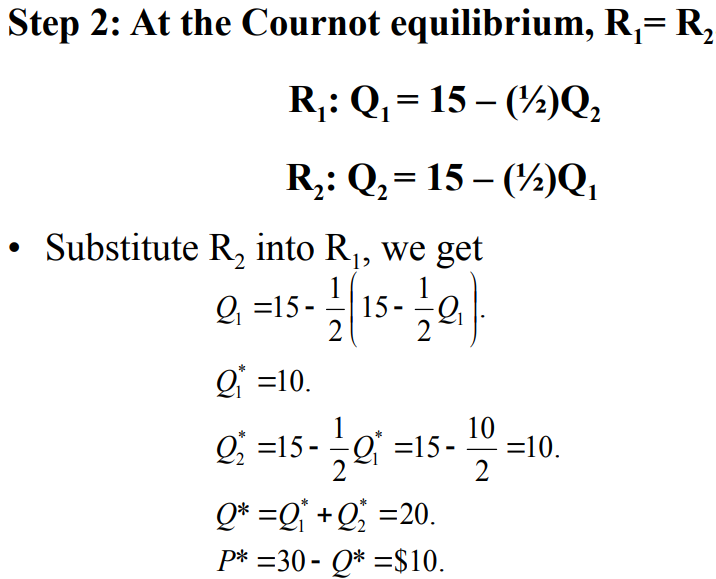
Firm 1’s reaction function is Q1=f(Q2)
Firm 2’s reaction function is Q2=f(Q1)
Cournot equilibrium
The Cournot equilibrium happens at the intersection of the reaction curves of Firm 1 and Firm 2. No firm wants to change its output level because they do not find any other output level that gives them higher profit.
Collusive model
An oligopoly model where firms cooperate to maximize joint profits by setting a total output.
Stackelberg model
A sequential quantity-setting game where one firm (the leader) sets output first, and another firm (the follower) reacts.
Price leadership model
A model where a dominant firm sets the price for the market, and smaller firms follow that price.
Equilibrium in Oligopoly
A situation where each firm, given what the other firms are doing, has no reason to change its output or pricing strategy. The equilibrium determines the oligopolistic firm’s output (Q*) and price (P*) that maximize its profit affecting all other firms in the market.

Interdependence
A characteristic of oligopolistic markets wherein the actions of one firm significantly affect the decisions of others.
Homogeneous products
Products that are identical in nature, leading to competition based on price rather than product differentiation.
Differentiated products
Products that are distinguished from one another by features, branding, or quality, which affects competition strategies.
Barriers to entry
Obstacles that make it difficult for new entrants to enter a market, such as high capital costs or regulatory requirements.
Reactions Functions
The relationship between a firm's optimal output and the output of a competing firm in an oligopoly.
Nash equilibrium
A situation in a game where no player can benefit by changing their strategy while the other players keep theirs unchanged.
Cartel
An agreement among competing firms to regulate prices and outputs, effectively behaving as a monopoly.
Profit-maximizing condition
The condition where a firm maximizes profit by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost (MR = MC).
Market demand curve
A curve that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded by consumers.
Simultaneous game
A type of game where players choose their strategies at the same time, without knowing the other players' choices.
Characteristics of an oligopoly
A few firms dominate the market.
Interdependence and competitive interaction among firms.
This is the most outstanding feature of oligopoly
Since there are only a few dominant firms in the markets, any decision by one firm affects all other firms in the oligopolistic market.
Products: A firm may produce either homogenous (e.g., steel) or differentiated products (e.g., apple music).
High barriers to entry (e.g., high entry cost of capital investments and specialized inputs, government’s subsidies).