OIA1011 CRITICAL TEMPERATURE
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
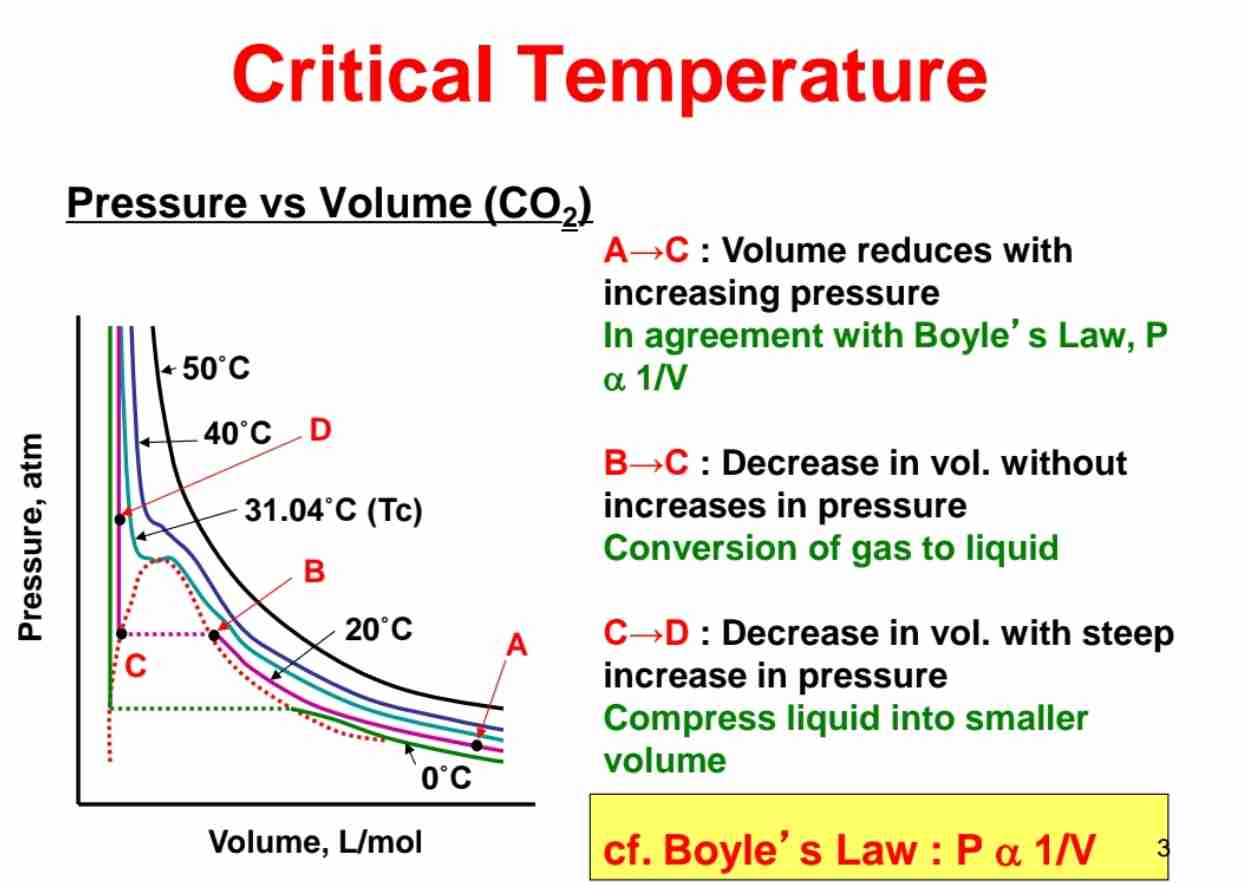
Definition of Critical Temperature (Tc)
The temperature which above, a substance cannot exist as liquid, no matter how much pressure is applied.
The temperature which density of gas = density of liquid, which no surface is formed.
Define Critical Pressure (Pc)
The pressure required to liquify a substance vapour at its critical temperature.
Define Critical Point.
End point of pressure-temperature curve that designate conditions where liquid & it’s vapour can coexist.
At higher temperatures, gas cannot liquefied by pressure alone.
At Critical Point, phase boundaries vanish as it is defined by Critical Temperature & Critical Pressure.
Define Triple Point.
The temperature & Pressure at which three phases (gas, liquid & solid) of substance coexist in thermodynamics equilibrium.
Liquefaction of Gases
Achieved by cooling below boiling point or via Joule-Thomson effect.
Joule-Thomson Effect
Cooling of gas due to expansion without external heat exchange.
Mechanism Liquefaction of Gases using Joule-Thomson Effect.
As gas expands, molecules become far apart, where attraction force between molecules weaker.
Average speed decreases as molecules further apart due to low kinetic energy, which causes temperature to decrease.
Hence, gas cooler after expansion until neighbouring molecules captured together to form liquid phase.
Relationship Between Boiling Point and Critical Temperature
Tb/Tc≈0.6 for most substances.
Linde Refrigerator
Device for cooling gases repeated expansion cycles.
Practical Example of Liquefaction
Liquefying oxygen (−183∘C) using expansion methods.
How intermolecular forces affect liquefaction of gases?
Stronger forces increase Tc, enabling liquefaction at higher temperatures.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals
Aerosol systems use principles of liquefied gas for drug delivery.
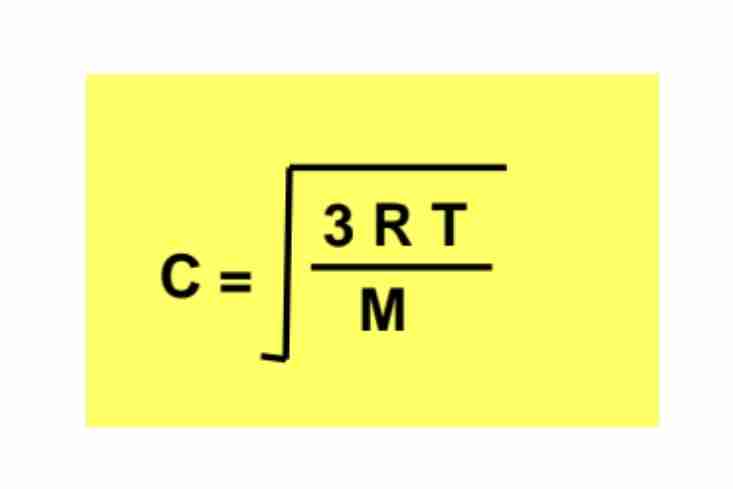
Formula for Molecular Speed
C=3RTM , where C is root-mean-square speed.