Digestive Exam Review
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
the feeding method used to take food into the digestive cavity
ingestion
the splitting of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids in foods into chemical subunits small enough to be absorbed into an animal’s body fluids and cells
digestion
the movement of organic molecules, electrolytes (inorganic ions), vitamins, and water across the digestive epithelium and into the interstitial fluid of the digestive tract
absorption
what are the 3 feeding strategies?
herbivore, carnivore, omnivore
one calorie is defined as
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of pure water by 1o C
1 Calorie (or Kcal) is defined as
1000 calories
what are the forms of malnutrition?
undernutrition, overnutrition, and micronutrient-related deficiencies
carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and vitamins are all
complex organic nutrients
minerals are ___ nutrients
simple inorganic
calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, potassium are all
minerals
what are the essential amino acids?
valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, lysine, and histidine (in infants)
what are the essential fatty acids?
linoleic acid and linolenic acid
describe each type of feeding method:
fluid feeding - ingest liquids that contain organic molecules in solutions (ex. blood or nectar)
suspension feeding - ingest small organisms that are suspended in water
deposit feeding - ingest particles of organic matter from solid material they live in/on (ex earthworms, crabs)
bulk feeding - ingest food items whole or in large chunks (most adult mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians)
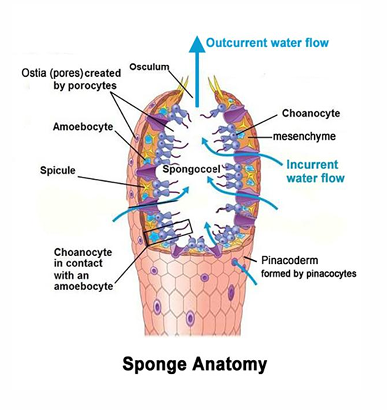
describe intracellular digestion (in sponges)
cells (choanocytes) take in food particles through pores in the body walls by endocytosis
a endocytic vesicle containing food particles fuses with a lysosome to form endolysosome
hydrolytic enzymes digest the food particles into their molecular subunits
undigested food is released by exocytosis
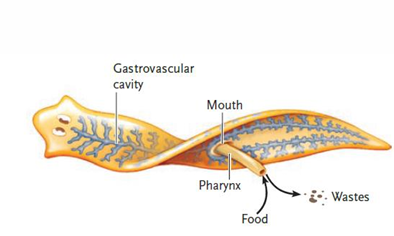
explain the sac-like digestive system in flatworms and cnidarians
single opening - both entrance and exit for food/undigested materials
digestion begins in gastrovascular cavity and is completed intracellularly
extracellular digestion occurs in what type of organism?
all vertebrates, some invertebrates.
in extracellular digestion, ___ secrete enzymes
accessory glands
what are the advantages of extracellular digestion?
greatly expands the range of available food sources, allows animals to eat large batches of food
in ___ digestion, food moves in a single direction through the body
extracellular
what are the 5 successive steps of extracellular digestion?
mechanical processing
secretion of enzymes and other digestive aids
Enzymatic hydrolysis
absorption
elimination
in which step of digestion do organic molecules in the food become broken down into small absorbable units?
enzymatic hydrolysis (third step)
salivary ___ begins the digestion of starch in the ___ step of digestion
amylase, first step (mechanical processing)
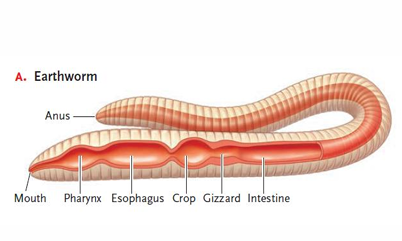
how does digestion work in annelids (earthworms)?
earthworms are deposit feeders.
Muscular movement propels food through the esophagus
food enters crop where it is mixed with mucus
mixture enters gizzard where mechanical processing occurs
then enters intestine where enzymatic hydrolysis occurs
undigested residue expelled through anus
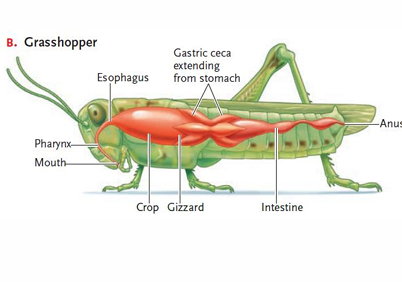
digestion in arthropods
insects use mouthparts to tear plant parts into small particles
salivary secretions initiate digestion in the pharynx
food moves through the esophagus, crop, and gizzard into stomach
enzymatic hydrolysis in gastric ceca
undigested contents move into intestine for further digestion/absorption
water reabsorbed in the distal intestine and wastes expelled through anus
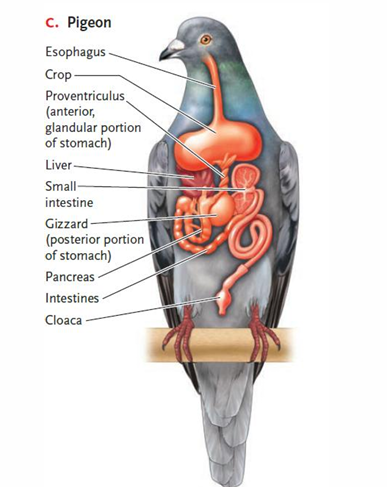
digestion in avians
seeds are moistened by mucus in the saliva
seeds pass through pharynx
esophagus
crop (food stored here)
proventriculus (digestive secretions mix with food here)
gizzard (seeds are ground up here)
intestine (food mixed with bile from the liver and digestive enzymes from the pancreas)
absorption of molecular subunits
undigested residues expelled through anus
the human digestive system consists of a series of specialized digestive regions that are under ___ control
neuoendocrine
list the parts of the GI tract/alimentary canal
mouth → pharynx → esophagus → stomach → small and large intestines → rectum → anus
what are the accessory digestive structures in human digestion?
salivary glands, teeth, tongue, pancreas, liver, gall bladder
organic compounds that are needed in small quantities. most are obtained from food intake, but some people need to supplement.
vitamins
vitamin ___ can be synthesized in the body when the skin is exposed to UV light
D
vitamin ___ is required for blood clotting and is supplied from the ___
K, large intestine
humans require ___ known fat- and water-soluble vitamins in their diet
13
what are the fat soluble vitamins?
vitamins A, D, E, K
what are the water-soluble vitamins?
vitamins of the B complex and C
minerals are ingested as
compounds or ions in solution
list the macrominerals
calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium, potassium, chloride, and sulfer
list the microminerals (or trace minerals)
iron, copper, manganese, selenium, fluoride, cobalt, and iodine
hypernatremia
too much sodium, elevates BP
excessive iron results in
hemochromatosis. liver, heart, pancreas, and blood vessel damage
name the mineral: involved in bone and tooth formation, blood clotting, neural and muscle action?
calcium
name the mineral: involved in HCl formation in stomach, contributes to body’s acid-base balance, necessary for neural function and water balance
Chlorine
name the mineral: Required for many enzymes, in bones and teeth, ATP processing
magnesium
name the mineral: in bones and teeth, component of nucleic acids, ATP and phospholipids; energy processing
phosphorus
name the mineral: muscle and neural function, water balance; muscle and neural function; main positive ion in cell
potassium
name the mineral: Acid-base balance; water balance; muscle and neural function; main positive ion in extracellular fluid
sodium
name the mineral: component of body proteins
sulfur
name the mineral: thyroid hormone function
iodine
name the mineral: component of hemoglobin, myoglobin, and electron carriers
iron
name the mineral: component of many enzymes and some transcription factors; protein synthesis; DNA synthesis; cell division; immunity; wound healing
zinc
list the four major layers of the gut
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa
innermost layer of the GI wall. contains epithelial and glandular cells, lines the inside of the digestive tract. also contains some connective tissue and smooth muscle
mucosa
thick layer of elastic connective tissue that contains neuron networks (the enteric nervous system), blood and lymph vessels, and small glands. second innermost layer of the GI tract
submucosa
formed by two smooth muscle layers (circular and longitudinal) that play an essential role in mechanical processing and in moving materials along the digestive tract
muscularis
what is peristalsis? where does it come from?
peristalsis is a wave of contractions that passes along the gut, constricting the git and pushing the digestive contents onward. It is produced by the muscularis layer of the GI tract
contraction of the ___ muscles and relaxation of the ___ muscles lengthens the gut, and vice versa.
contraction of circular muscles and relaxation of longitudinal muscles = lengthened gut
the outermost layer of the GI wall, made of serous membrane. This layer is actually the visceral layer of the peritoneum.
serosa
movement of food through the digestive tract is regulated by ___ present at the junction between various regions
sphincter muscles
what are sphincter muscles?
smooth muscles that contract and relax to push the contents from one region to another
sphincter between the pharynx and the esophagus
pharyngoesophageal sphincter (or upper esophageal sphincter)
sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach
gastroesophageal sphincter
sphincter between the stomach and the duodenum
pyloric sphincter
sphincter between the ileum and the cecum
ileocecal sphincter
what is the final sphincter in the digestive tract?
the anal sphincter
what disease causes unpleasant symptoms due to the backflow of stomach acids into the esophagus?
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
what happens if GERD is left untreated?
can cause precancerous lesions such as seen in Barrett esophagus (chronic inflammation)
trace the journey of food through the GI tract.
mouth → pharynx → esophagus → stomach → small intestine → large intestine → anus
starch digestion begins in the
mouth
the ___ prevents the movement of food into the respiratory tract
epiglottis
what is the main function of the stomach?
store food and aid in mechanical breakdown of food by disrupting the chemical bonds in food through the action of acid and the enzyme pepsin
the stomach also produces an intrinsic factor for…
the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine
in addition to the outer longitudinal and middle circle layer, the stomach has another muscle layer called the ___. what is its role?
oblique muscle layer. its roles are to strengthen the stomach wall and mix and churn for the formation of chyme
what are rugae?
the prominent folds in the stomach when it is relaxed. these go away as the stomach stretches
protein digestion begins in the ___ by the enzyme ___
stomach, pepsin
when is chyme formed? where does it go from there
partially digested food at the end of the stomach digestion is called chyme. it moves through the pyloric sphincter into the duodenum (small intestine)
what are gastric pits?
shallow depressions of the mucosal layer containing gastric glands
gastric juice contains (name each secretion and what cell they’re secreted from)
pepsinogen - secreted by chief cells
hydrochloric acid - H+ and Cl- ions secreted by parietal cells (combine to form HCl in the lumen of the stomach)
mucus - produced by goblet cells
what is the importance of hydrochloric acid in the stomach?
keeps the stomach contents at a low pH, kills microorganisms, helps break plant cell walls and connective tissues in meat, activates pepsinogen to active pepsin
most absorption (90%) occurs in the
small intestine
the absorptive ability of the small intestine is increased by
increased surface area by the folds in the small intestine, which are covered by intestinal villi, which are covered by microvilli
as compared to the rugae of the stomach, permanent folds in the intestine…
do not disappear when the small intestine fills
pancreatic enzymes aid in
proteolytic digestion (protein digestion by breaking polypeptide chains)
___ secretes bile that is stored in the ___ for discharge into the ___
liver, gallbladder, small intestine
what do bile salts do?
break down into small lipid droplets to facilitate the digestion and absorption of lipids
list the three parts of the small intestine and their main function
duodenum - receives chyme from the stomach, mixes it with pancreatic enzymes and bile
jejunum - bulk of chemical digestion and absorption
ileum - longest and final segment of the small intestine
the liver stores excess glucose in the form of ___
glycogen
the liver synthesizes lipoproteins that
transport fats and cholesterol
this organ detoxifies ethyl alcohol and other toxic chemicals and drugs, as well as inactivates steroid hormones
the liver
what is the hepatic portal vein?
the vein that leads to the liver
the ___ is known as the “large bowel”
large intestine
the large intestine begins at the ___ and ends at the ___
end of the ileum, anus
list the parts of the large intestine
cecum, colon, rectum, terminates at the anal sphincter.
the colon can be subdivided into
ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoidal
<10% of nutrient absorption is underway in the ___
large intestine
the ___ sphincter regulates the movement of substances from the ileum and the cecum
ileocecal
the cecum…
collects and stores materials from the ileum and begins the process of compaction
the rectum…
serves as a temporary storage space for feces
the large intestine secretes ___ and ___
mucus and bicarbonate ions
reabsorption of water occurs in ___. what else is reabsorbed?
the large intestine. ions, bile salts, and vitamins
the intestinal probiotic organisms residing in the large bowel produce:
useful metabolites, fatty acids, and vitamins such as vitamin K, folic acid, biotin, pantothenic acid
bacteria convert bilirubin into ___, and oxidation produces ___. these result in what?
urobilinogens and stercobilinogens; urobilins and stercobilins. these give feces its characteristic color