#1 Population ecology
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Genet
genetically distinct individuals
Every new genet is a new ramet, but not vice-versa
Ramet
physiologically independent but not genetically distinct individuals
Population
A group of individuals of the same species that interact in space and time
Community
A group of plant species that coexist in the same environment and interact with each other and their physical surroundings
Density-dependent factors
Factors where population density affects growth or other dynamics (e.g., competition).
Give an example of a density-dependent factor
Intraspecific competition — competition among individuals of the same species
How does increasing density affect density-dependent factors?
They become more powerful as density increases
Density-independent factors
Factors that impact population dynamics regardless of population density
e.g., extreme weather events
Can fire be both density-independent and dependent? Explain
Yes — normally fire is independent, but if animals alter vegetation to influence fire frequency or intensity, it becomes density-dependent
What does λ (lambda) represent in population ecology?
The finite population growth rate
showing how population size changes from one time step to the next
What does it mean if λ > 1.0? (greater than)
The population is growing
more births/immigrants than deaths/emigrants
What does it mean if λ = 1.0?
The population remains stable in size
What does it mean if λ < 1.0?
The population is declining
more deaths/emigrants than births/immigrants
What is the Population Growth Equation?
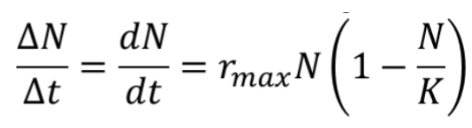
In the Population Growth Equation, what does N represent?
Population size at a given time
In the Population Growth Equation, what does ΔN/Δt or dN/dt represent?
Change in population size over time (growth rate)
In the Population Growth Equation, what does rmax represent?
The maximum per capita rate of increase
intrinsic growth rate under ideal conditions
In the Population Growth Equation, what does K represent?
Carrying capacity — the maximum population size the environment can sustain
In the Population Growth Equation, what does (1 - N/K) represent?
The density-dependent term that slows growth as N approaches K
In the Population Growth Equation, what happens when N is small?
Growth is fast and nearly exponential
In the Population Growth Equation, what happens when N approaches K?
Growth slows and levels off
What does the Population Growth Equation look like when you are comparing two species?
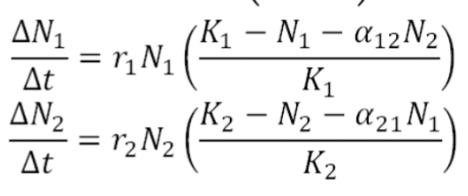
In the Population Growth Equation→ comparing two species, what do r₁ and r₂ represent
The intrinsic (maximum) growth rates of species 1 and 2
In the Population Growth Equation→ comparing two species, what does α₁₂ represent?
The effect of species 2 on species 1 (in units of species 1)
In the Population Growth Equation→ comparing two species, what does α₂₁ represent?
The effect of species 1 on species 2 (in units of species 2)
In the Population Growth Equation→ comparing two species, what does
(K₁ − N₁ − α₁₂N₂)/K₁ show?
How intra- and interspecific competition reduce growth for species 1
same for species 2 in the other equation
What was the purpose of the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study?
To determine whether deer browsing was causing American ginseng population decline in West Virginia
How many populations were monitored, and for how long in the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study?
Seven populations, from 2000–2004
What did researchers track for each plant in the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study?
growth stage
survival
reproduction
deer browsing evidence
What was the observed mean λ with deer browsing in the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study?
0.973 — indicating population decline.
What was the simulated mean λ with no browsing in the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study? (when they took out the browsed plants)
1.021 — indicating population growth
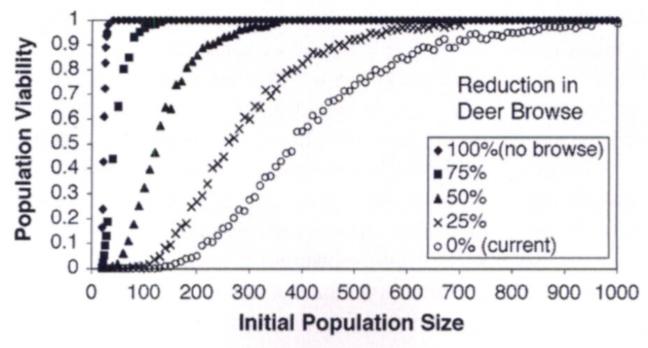
What does this graph represent from the McGraw & Furedi (2005) – American Ginseng Study?
population viability analysis (PVA)
What does a population viability analysis (PVA) estimate?
A population’s risk of extinction over time.
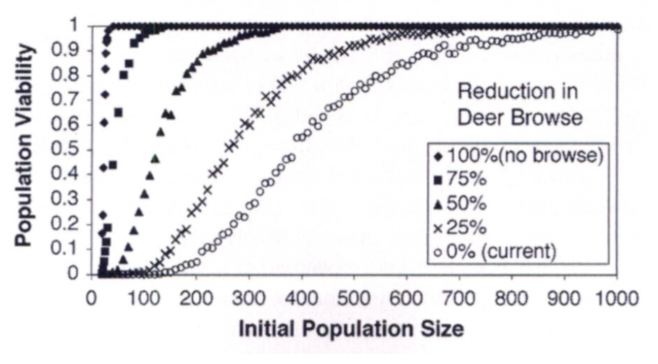
In the population viability analysis of the American Ginseng Study, what was the “viable” population threshold?
A 0.95 probability of survival over 100 years
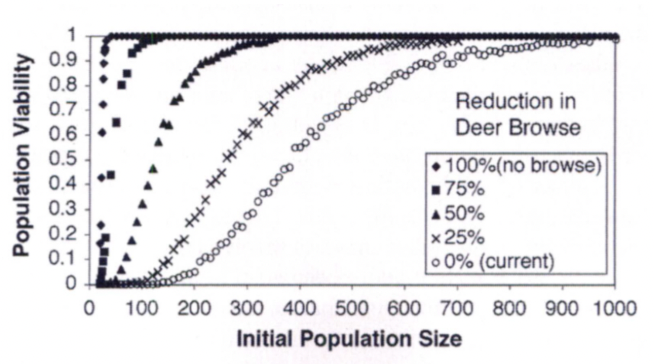
In the American Ginseng Study, how did browsing affect viability?
Heavy browsing reduced viability and required larger populations to persist
~800 plants (to get to the viable population size)
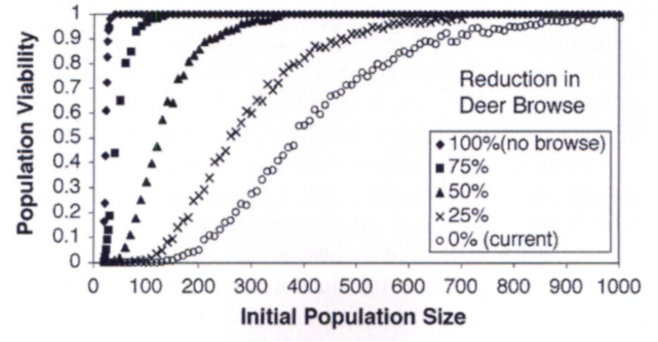
In the American Ginseng Study, what happened when browsing was reduced by ≥ 75 %?
Populations remained viable at much smaller sizes
What does Population ecology focus on?
how individuals of the same species interact and how populations change
done by modeling populations
Why do ecologists model populations?
To understand and predict population growth, decline, and structure
What are age-structured models used for?
Animals
where chronological age determines survival and reproduction
How are populations divided in age-structured models?
Into age classes such as juveniles, adults, and seniors
What are stage-structured models used for?
Plants
where size or developmental stage determines function and reproduction
Why are stage models more appropriate for plants?
size or developmental stage is a much better predictor of a plant's vital rates (survival, growth, and fecundity) than its chronological age
Plants can grow, shrink, or stay the same size, enter dormancy, or revert to earlier stages
What do stage models use to describe transitions?
Probabilities of growth
survival
reproduction between stages
Why do stage models matter?
They capture complex life cycles and predict population viability under factors like herbivory