Muscle Physiology I: Foundational Concepts of Muscle Contraction
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is total muscle tension?
the magnitude of the force a muscle can apply on a bony lever
Active Tension is a vector with…?
magnitude
2 points of application (proximal & distal)
an action line
direction of pull
What is strength?
the maximum amount of force a muscle or group of muscles can generate in a specific movement pattern
What are factors that influence strength?
muscle cross sectional area
age
gender
previous training and conditioning
hormones, anthropometrics, type of muscle fibers, etc
What is the relationship with the cross section of our muscles as we age?
decreased muscle mass
decreased cross sectional area
decreased number and size of muscle fibers
decreased number of motor units
What is sarcopenia?
the natural loss of muscle mass and strength as we age
What type of exercise is slow twitch muscles used in?
aerobic exercise
What are some characteristics of a slow twitch- type 1
long duration
requires constant energy
slower rate of fatigue
What type of exercises are Fast Twitch II A and B muscles (anaerobic) used in?
rapid, short-duration movements that require power and speed: sprinting, jumping, and powerlifting
What are characteristics of anaerobic (glycolytic) muscles?
high rate of contractions
produces quick powerful bursts of speed
fatigues quickly
What is passive tension?
tension developed in the noncontractile parallel elastic structures of the muscle (blood and nerve vessels, elastic proteins)
What is active tension?
tension developed by the contractile elements of the muscle
How is active tension initiated by?
crossbridge formation, movement of thick and thin (actin and myosin) filaments
At what sarcomere length does a muscle fiber develop maximal isometric tension?
There is an optimal sarcomere length at which a muscle fiber develops maximal isometric tension
What does the muscle length tension relationship describe?
how the force a muscle can produce changes depending on its length
What is the muscle length-tension relationship when the muscle is at its optimal length?
muscles generate the most force when they are at a medium length
What is the muscle length-tension relation when the muscle is too short?
the fibers are crammed together and there’s not enough room for the fibers to pull efficiently, reduces force production
What is the muscle length-tension relationship when a muscle is too long (too stretched)?
the fibers can’t overlap enough to create many cross-bridges, so the muscle can’t produce much force
What is active insufficiency?
the reduced ability of a muscle to generate force when it is excessively shortened
Why does active insufficiency occur?
the muscle fibers (action and myosin) have too much overlap, reducing the number of effective cross-brides that can form
Where does active insufficiency occur in?
primarily two-joint (or multi-joint) muscles when they are shortened across all the joints they cross
What is an example of active insufficiency?
hamstrings during hip extension and knee flexion
What is passive insufficiency?
the limitation in range of motion or flexibility because a muscle is stretched to its maximum length
what causes passive insufficiency?
the muscle cannot lengthen further without injury, as it’s being stretched across all the joints it spans
Where does passive insufficiency occur in?
primarily two-joint (or multi-joint) muscles when stretched across all joints they cross
What is an example of passive insufficiency?
hamstrings during hip flexion and knee extension
What occurs to the antagonist and agonist in passive insufficiency?
the antagonist is in a position of passive insufficiency (maximally stretched) to allow complete ROM of the agonist
When it comes to the force/time relationships, time is related to…?
speed and type of contraction
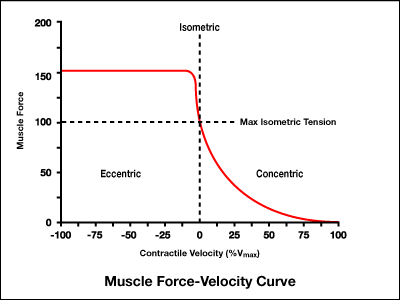
What is force-velocity relationship with an isometric contraction?
at zero velocity, force is greater than with concentric
What is the order of force production from greatest to least?
eccentric > isometric > concentric
Why does an eccentric contraction produce the most force?
Cross-Bridge Mechanics: Actin and myosin filaments are pulled apart while still generating tension, allowing for a greater contribution of passive elastic elements (e.g., titin).
Resistance to Stretch: The muscle resists elongation, which increases tension.
Fewer Energy Costs: Eccentric contractions require less ATP compared to concentric contractions, so muscles can sustain higher forces for longer.
Why does an isometric contraction produce a moderate force?
the muscle maximizes cross-bridge formation without changing its length
Why does a concentric contraction produce the least force?
Cross-Bridge Cycling: The actin and myosin filaments slide past each other rapidly, reducing the time available for optimal cross-bridge formation.
Energetic Cost: Concentric contractions are more energy-intensive than eccentric, limiting their efficiency
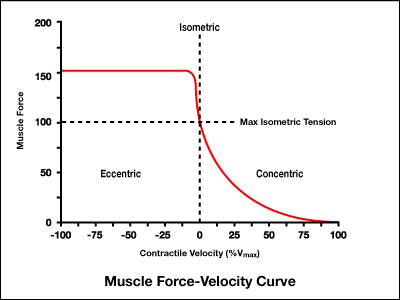
What does the force-velocity chart state about a concentric contraction?
slower the shortening, greater the force
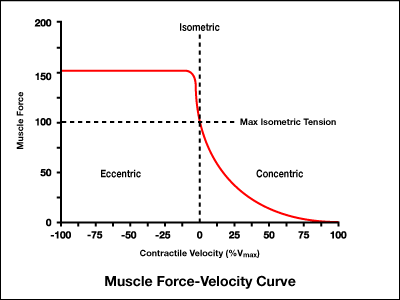
What does the force-velocity curve chart state about an eccentric contraction?
can generate more force than isometric or concentric
The ability for a muscle to produce torque depends on…?
Active tension
# motor units & size of motor units
frequency of nerve impulses
fiber type
type of contraction
velocity of contraction
length of muscle--># of cross bridges
As well as…
moment arm (T=F x MA)
Passive Tension