ANAPHY: Skeletal System
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
134 Terms
Bones, Cartilages, Tendons, Ligaments
Components of the Skeletal System
ligaments
bone → bone
tendons
bone → muscles
Support, Protection, Movement, Storage, Blood Cell Production
Functions of Skeletal system
collagen, ground substance, water and minerals
The skeletal system matrix always contains:
Collagen
tough, rope-like protein that gives strength and toughness
Ground Substance
calcium and phosphorus
Water
serves as moisturizer and avoid friction
Tendons and Ligaments
These components have an ECM of large amounts of collagen fibers
Collagen and Proteoglycans
ECM of Cartilage
Collagen
ECM of Cartilage that makes it tough
Proteoglycan
ECM of Cartilage that makes it smooth and resilient
Cartilage
Relatively rigid, but springs back to its original
Collagen and Minerals
ECM of bone
Collagen
ECM of bone that lend flexible strength
Minerals
ECM of bone that lend compression strength
Long, Short, Flat, Irregular
Shape Classification of Bones
Long
Long than wide
Long
Shape of tibia, fibula, femur, radius, ulna
Short
long as they are wide
Short
shape of carpal and metacarpal
Flat
Relatively thin and flat
Flat
Shape of skull, scapula, sternum
Irregular
not short, not long, not flat
Irregular
shape of vertebrae and facial bones
Diaphysis
shaft; bone tissue outside
Epiphysis
round ends that is spongy
Metaphysis
space between diaphysis and epiphysis
Articular Cartilage
Covers the epiphysis; reduces friction
Epiphyseal Line
juvenile; young individuals
Epiphyseal Plate
found in adults
Compact Bone
heavy bone found at the margins
Medullary Cavity
Space in diaphysis; location of red and yellow marrow
Red Bone Marrow
Juvenile; where RBC is produced
Yellow Bone Marrow
Adults; fats and adipose are produces
Periosteum
Thin layer that surrounds the bone (outer and inner)
Endosteum
Thin layer that surrounds the inner alignment of the bone
Compact bone
outer part of the diaphysis
Osteon
structural unit of compact bone
Lamella
ring/layers in the bone
Lacunae
spaces between the lamella; where bone cells are located
Canaliculus
tiny canal-like; cracks in the lamella; transports nutrients and removes wastes through diffusion
Central canal
center of osteon; contains blood vessels
Spongy bone
located at the epiphysis of long bones and center of other bones
Spongy bone
It has no osteons
Trabeculae
interconnecting rods; spaces containing marrow; filled with blood vessels
Osteoblasts
formation, repair and remodeling of bone; creates new bone matrix
Osteocytes
maintain the bone matrix and form osteoblast
Osteoclast
Repair and remodeling by removing existing bone
Bone reabsorption
Process of repair and remodeling by removing existing bone in Osteoclast
Intramembranous ossification
Bone formation that occurs within the connective tissue
Endochondral Ossification
Bone formation that occurs within the hyaline cartilage
ossification
formation of bone by osteoblasts
Intramembranous ossification
Osteoblast lines up on the surface of connective tissue fibers and begin depositing bone matrix to form trabeculae
Ossification centers
Where Intramembranous ossification process begins
trabeculae
radiates out from the centers; constantly remodeled; enlarge or replace
Anencephaly
inborn baby without skull
Endochondral Ossification
bone formation is within a cartilage model
Cartilage model
is replaced by bone during endochondral ossification
Primary ossification center
It is intially formed; bone formation in the diaphysis of a longbone
Secondary ossification center
Bone center formation in the epiphysis
Bone growth
occurs by the deposition of new bone lamellae onto existing bone or connect
Appositional growth
As osteoblasts deposit a new bone matrix on the surface of bones between the periosteum and the existing bone matrix, the bone increases in width, or diameter.
Bone growth in length
Which is the major source of increased height in an individual, occurs in the epiphyseal plate.
Endochondral ossification
Bone growth in length occurs through
Chondrocytes
It increase in number on the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate
Epiphyseal plate
The osteoblasts start forming bone by depositing bone lamellae on the surface of the calcified cartilage.
Bone repair
Broken bone causes bleeding and a blood clot forms.
Callus
It forms a fibrous network between 2 fragments
Cancellous bone
This is slowly remodeled to form compact and cancellous bone.
Bone
is a major storage site for calcium.
Calcium
moves into bone as osteoblasts build new bones.
Calcium
moves out of bone as osteoclasts break down other bones.
Calcium homeostasis
Is maintained by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and calcitonin.
Parathyroid hormone and calcitonin
Calcium homeostasis by
Foramen
Hole
Process
Projection
Condyle
Smooth and rounded end
Meatus
canal-like passageway
Tubercle
lump of bone
80 bones
How many bones in the Axial skeleton
skull, vertebrae column, thoracic cage
Axial skeletons consists of
20 bones
how many bones in skull
8 bones
how many bones in cranial
14 bones
how many bones in facial
Mandible
this facial bone moves freely
6 bones - 3 each
how many bones in Auditory ossicle
26 bones
how many bones in vertebral column
25 bones
how many bones in thoracic cage
Hyoid
It is considered to be a floating bone
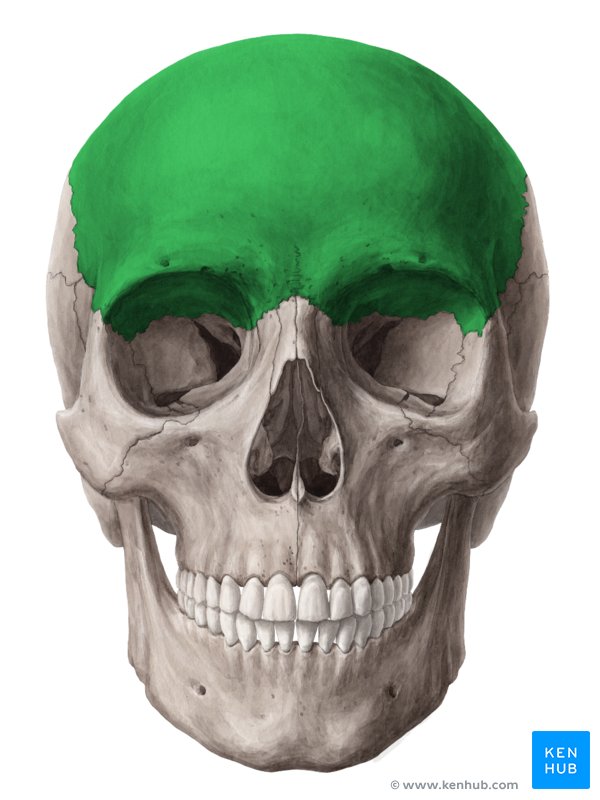
Frontal
Anterior part of cranium
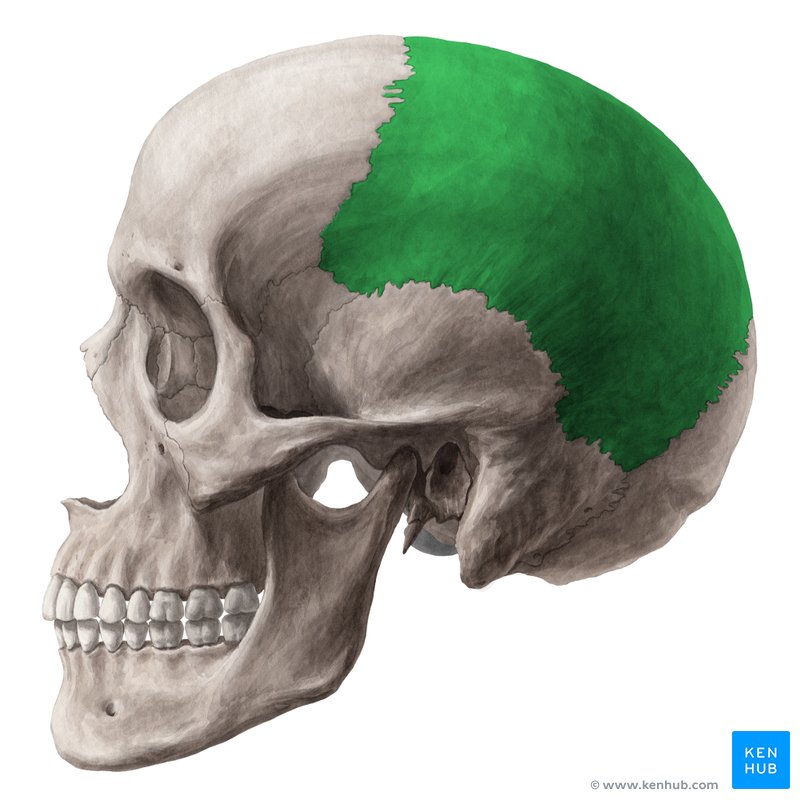
Parietal
sides of cranium
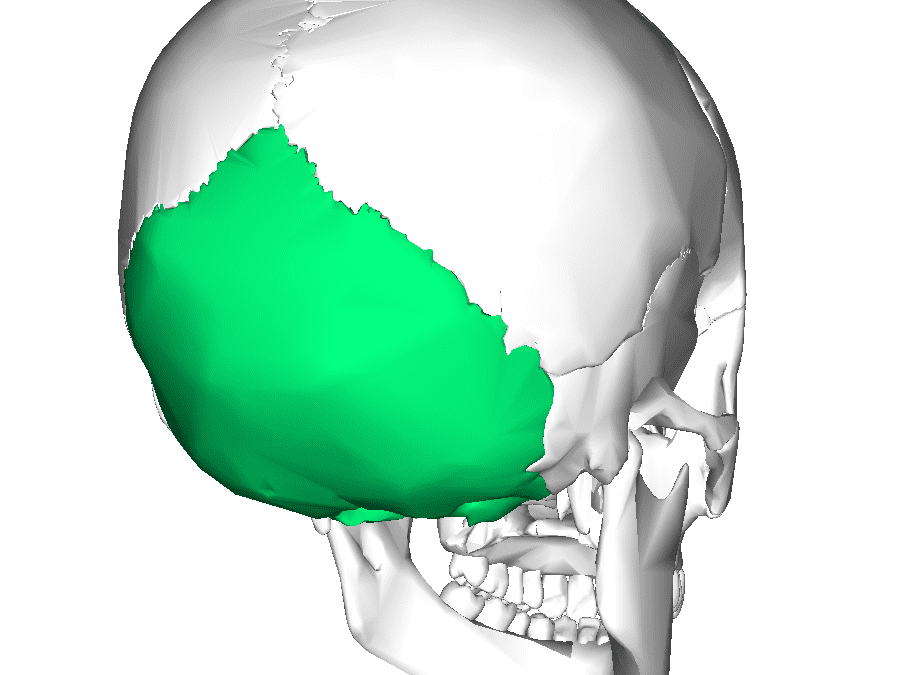
Occipital
posterior/floor of cranium
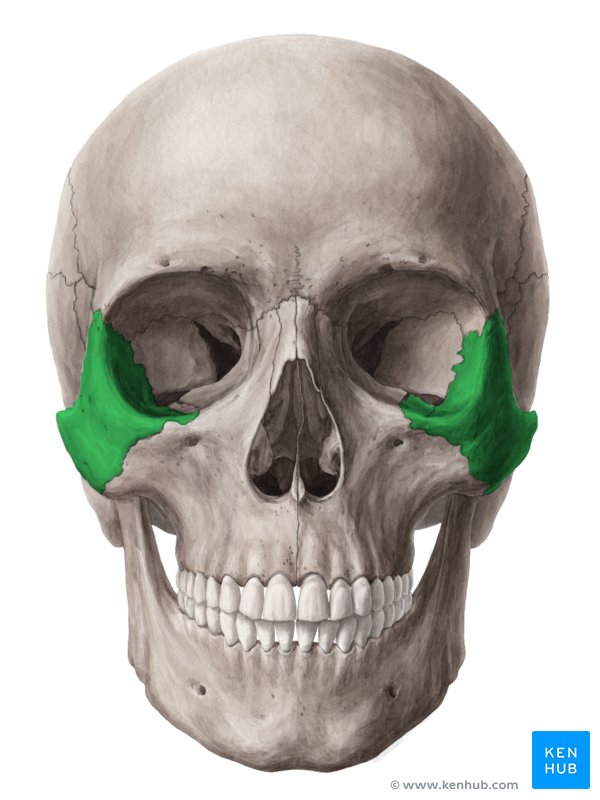
Temporal
Inferior to parietal bones
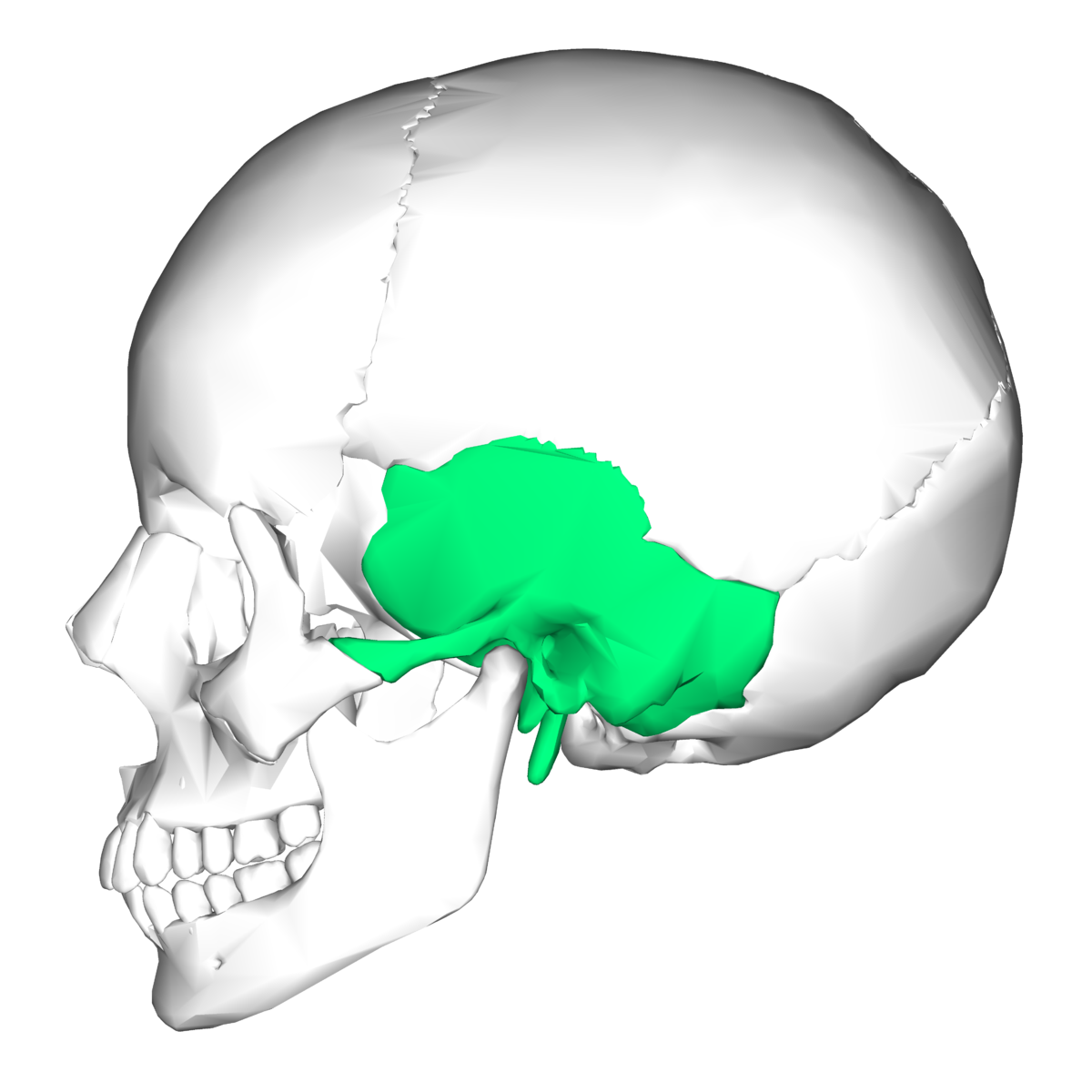
Sphenoid
Forms part of cranium floor; lateral position of eye orbits
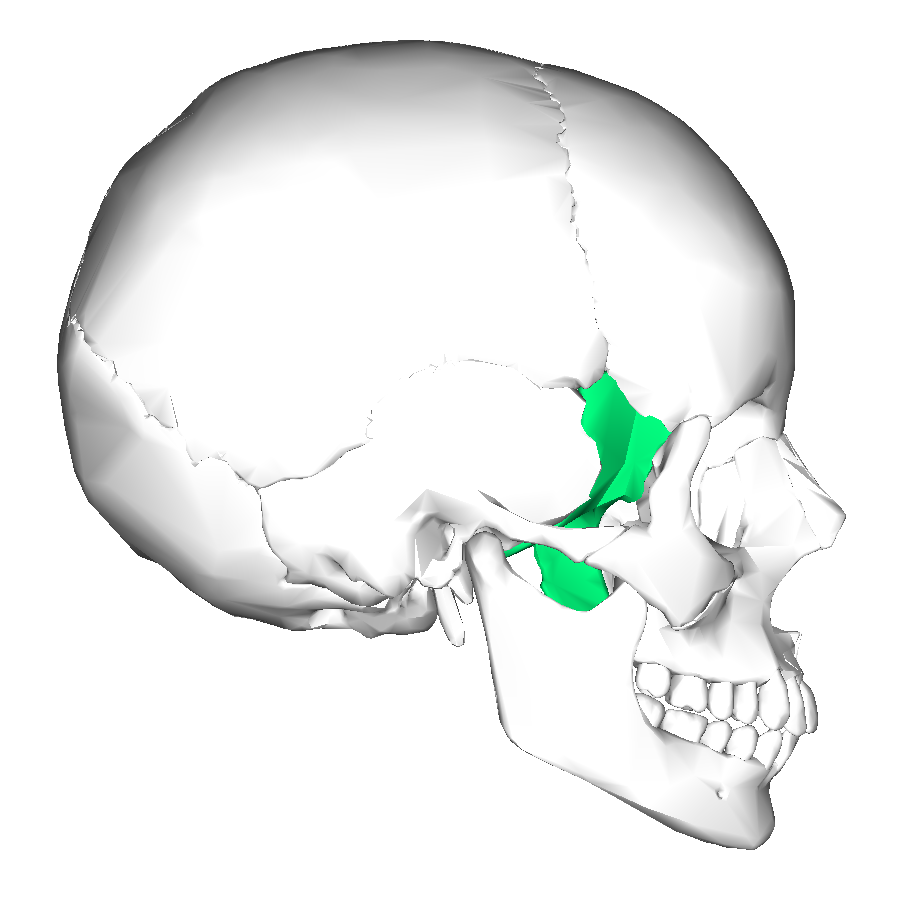
Ethmoid
Anterior position of cranium; roof of nasal cavity
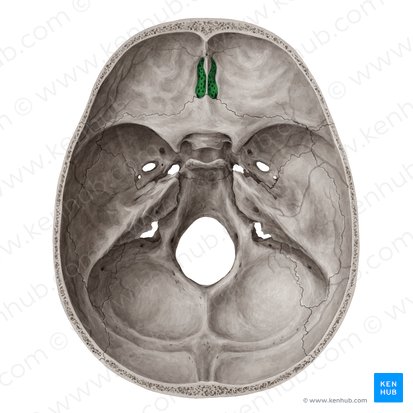
Maxillae
forms upper jaw; anterior of hard palate; also known as maxillary sinus
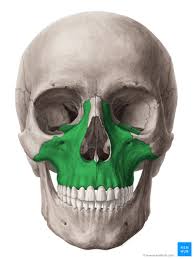
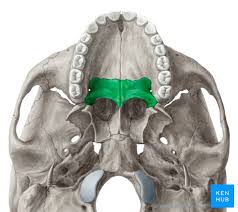
Palatine
posterior position of the hard palate
Zygomatic
cheek bones; lateral wall of each eye orbit