5. biochemical relationships
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
BIOCHEMICAL RELATIONSHIPS
scientists now analyse structure of many diff chemicals (e.g. proteins) in organisms, alongside DNA, to find relationships between of organisms
known as molecular phylogeny- not all scientists interpret results in same way
evidence from molecular phylogeny might support or conflict with relationships based on morphology
GEL ELECTROTROPHES 1
comparisons between the AA sequences of similar proteins in diff species are also used to classify them or trace their evolutionary pathways
this is a variation of chromatography which is used to separate DNA or RNA fragments, proteins or AAs according to their size and charge
chemicals to be compared are placed in wells in a gel medium in a buffering solution
known DNA or RNA fragments, proteins or AAs are also placed in as a comparison
GEL ELECTROTROPHES 2
for identifying DNA, the big DNA molecule is cut using restriction endonuclease enzymes- cut the DNA at specific sites
DNA fragments are then added to the gel containing a dye (e.g. EtBr, ethidium bromide)- binds to fragments
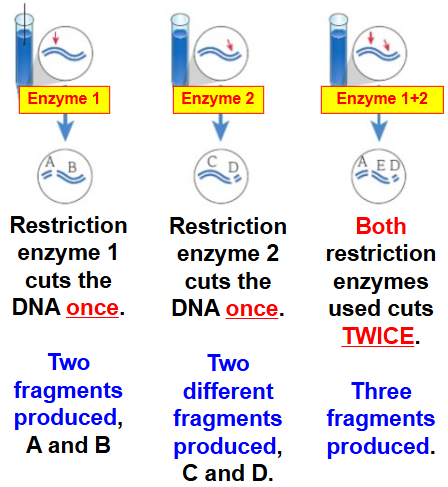
GEL ELECTROTROPHES 3
electric current is passed through the gel and DNA fragments move towards the pos electrode (anode) because DNA is neg charged due to its phosphate group
fragments move at different rates depending upon their mass and charge
once the electrophoresis is complete the plate is placed under UV and DNA fluoresces so the patterns of bands can be identified- can be compared to known samples
MORE BIOCHEMICAL RELATIONSHIPS
evidence from biochemistry is playing an important role in extending our understanding of classification and evolution
vertebrates and echinoderms (star fish, sea urchins etc.) appear from morphological evidence to come from one line of ancestors and the annelid worms, molluscs and arthropods (including insects) from another
biochemical evidence appears to confirm this unlikely relationship- shows that phosphagens, molecules that provide the phosphate group for the synthesis of ATP in muscles, are of 2 different sorts
phosphocreatine occurs almost exclusively in the muscles of vertebrates and echinoderms whist phosphoarginine occurs in the other groups
MORE BIOCHEMICAL RELATIONSHIPS- BLOOD
analysis has shown that any one group contains only one type of blood pigment
all vertebrate and many of the invertebrates have haemoglobin, all polychaete worms have chlorocruorin and all molluscs and crustaceans have heamocyanin
MORE BIOCHEMICAL RELATIONSHIPS- DNA
analysis of the sequence of AAs in particular proteins can help show the relationship within higher groups such as a phylum
single AA changes are used to plot relationships
combination of DNA analysis and protein analysis can bring some unlikely relationships to light