What does abnormality mean?
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
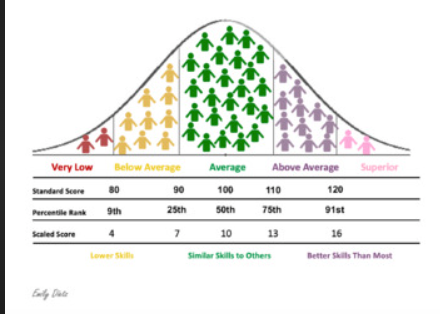
Statistical deviation
states that human behaviour is abnormal if it falls outside the range that is the average (normal) from most people
their behaviour is statistically rare
typically behaviour is more than 2 standard deviations away from the mean
WEAKNESS of standard deviation
Doesn’t differentiate between desirable and undesirable characteristics - e.g. IQ charts those who have IQ of 130 - not seen as undesirable or abnormal
lacks validity if used on its own to define abnormality
Graph can be seen as subjective - the cut off point can be set too high or too low
how from the norm do you have to be classified as abnormal
e.g. depression - 80% of symptoms are normal but the 20% - suicidal though are abnormal
may fail to diagnose who needs help and support
STRENGTHS of standard deviation
real life application
can diagnose intellectual disabilities
for example anorexia - BMI scale to see if anorexia is mild/severe - different treatments for both
helps clinicians decide which level of intervention/help is required
Definition of social norms
implicit rules about how we ought to behave in society. Anything that violates these norms is considered abnormal
can be changed over time and from culture to culture e.g. homosexuality - later accepted and part of social norm
Definition of Deviation from social norms
a person behaves different from accepted standards of behaviour in a community or society
Name some ways behaviour can deviate from society
unpredictable
causes observer discomfort
violates moral standards
even irrational thoughts
Evaluation of Deviation from social norms
Weakness
we must always have to take context into account
quite subjective as a definition when diagnosing
e.g. naked cycling - normally get arrested but for charity it is normal
Weakness
has cultural relativism
can be seen as not normal behaviour in a different culture
social norms vary from culture to culture
e.g. hearing voices - seen normal in some cultures other cultures would find abnormal
Weakness
allows professionals to classify anyone who went against social attitudes - abuses their human rights
subjective
e.g. nymphomania - controls females promiscuity (seen to have borderline personality disorder) - men would get away with their promiscuity
some e.g. Magdalene laundries - unmarried mothers detained and babies adopted
Strength
distinguishes between desirable and undesirable characteristics
helps clinicians to diagnose psychiatric disorders
e.g. antisocial personality disorder - can cause then to act reckless and violate the right of others
What is FFA
Failure to function adequately
Failure to function Adequately
have expectations on how people should act and live their lives - cannot meet these obligations (abnormal)
if individuals behaviour or thinking affect there well-being, becomes a danger to own safety and danger to others - considered abnormal
What are the 3 signs that determine when someone is not coping (Rosenham & Seligman)
no longer conforms to standard interpersonal rules e.g. respecting others personal space or eye contact
experiences sever personal distress
persons behaviour becomes irrational/dangerous to themselves or others
e.g. anorexia or anxiety
Evaluation of FFA (Failure to Function Adequately)
Weakness
based on subjective judgements
individual may believe they are functioning adequately whilst others will think they are not
e.g. odd or eccentric behaviour such as suffragettes hunger strike
context of the situation is important to know
may be hard to hold down job, support family or prejudice and money issues
do not fully know so cannot easily diagnose them
e.g. suffragettes and hunger strike - unpredictable but understanding
Weakness
culturally relative - cultures have different beliefs and practices - what’s normal to them may not be normal to other cultures
could explain why lower class and non - white patients - often diagnosed with mental disorders due to non traditional lifestyle and judgement from others
Strength
provides a threshold for when people need help
if symptoms become worse - more likely to seek help as it effects daily living
can focus on those who need it more
Weakness:
many do not recognise they are ill
illnesses that have psychotic breakdown - assumes rest of the world is mad
they go undiagnosed e.g. schizophrenia and bipolar
What is DIMH
Deviation from Ideal Mental Health
Deviation from Ideal Mental Health
6 characteristics that are used to identify ideal mental health - not all possessed seen as abnormal
What are the 6 characteristics of DIMH that Jahoda proposed
Self attitudes - have high self esteem
Self actualization - willing to achieve their full potential
Coping with stress - can cope in stressful situations
Autonomy - can make own decisions and are independent
Accurate Perception of reality - have a realistic view of the world
Adaptation to environment - can work well in new environments and enjoy leisure
Evaluation of DIMH (Deviation from Ideal Mental Health)
Weakness
according to this - nobody is normal - very few would achieved full criteria
set up to high standards
e.g. teenagers never have full autonomy over their lives
Weakness
cultural dependant and biased especially the west
personal autonomy - western notion
some cultures e.g. Japan - collectivist culture and community more important than individual development
also some stress levels - good to achieve (motivation in sports)
Strengths
positive attitude towards human behaviour - focuses on what makes us health
e.g. - self actualization - good to self improve and set goals
based on humanistic approach -holistic approach taken
useful to identify when someone needs help - can get therapists - a thorough approach
What are the 4 types of abnormality
Statistical Deviation
Deviation from social norms
Failure to Function Adequately
Deviation from Ideal Mental Health