cgs 2301 - chemical senses
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
chemical senses
taste and smell
mechanical senses
vision, audition, and touch
gustation (taste) function
not eating things that will kill you
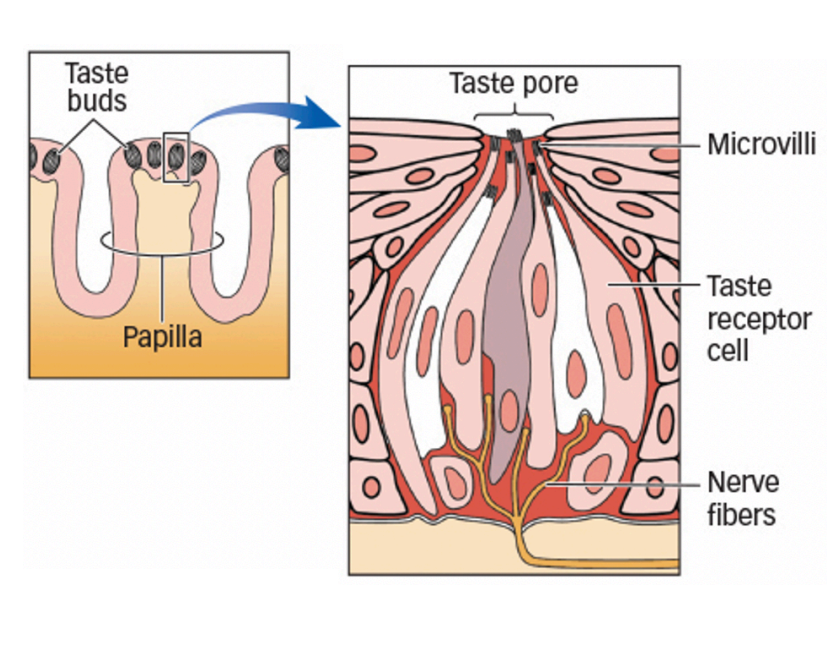
order of structures
bumps (papillae) contain taste buds
taste buds house taste receptor cells
microvilli react to tastant molecules
top to bottom: taste pore, microvilli, taste receptor cell, nerve fibers
five categories of tastants
sweet, sour, salt, bitter, and umami
note: contrary to popular belief diff region of the tongue don’t correspond with diff tastants → all taste receptors can detect all five basic types of taste
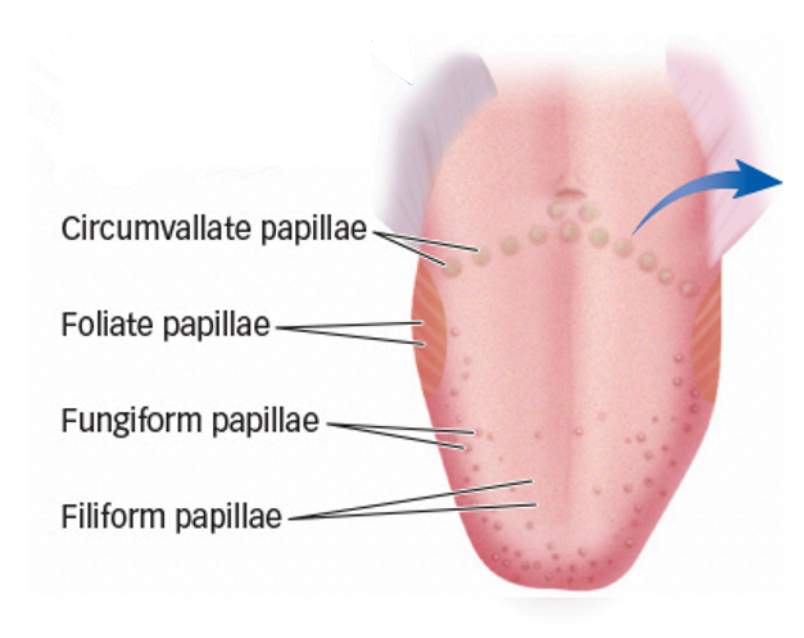
anatomy of papillae
front to back of mouth:
circumvallate papillae: more sensitive to bitter
foliate papillae: more sensitive to sour
fungiform papillae
fillform papillae: lot of them, don’t have any taste buds, detect texture not taste
olfaction function
smell
social behaviors and survival (if something is safe, like smell smoke or poison)
olfactory pathway
odorants dissolved by olfactory epithelium (a structure)
olfactory receptor neurons turn chemical info into info our brain can understand, then send info to glomeruli in olfactory bulb
olfactory bulb transmits info to olfactory cortex
info goes directly from nose to brain
mnemonic: Every Red Nose Braves Cold
axons project to which areas?
long term memory
limbic system (memory, emotions)
this is why emotional memories can associate w smells
how does smell relate to social behavior?
PET scan study w hetero men, homo men, and hetero women presented with testosterone based odorant
significant activation in hypothalamus for hetero women and homo men