Unit 1, AOS1, Chapter 3C: Active Transport
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Define Active Transport
Movement of molecules across a semipermeable membrane against their concentration gradient (low to high) that requires energy, usually in the form of ATP
Identify the 2 types of Active Transport
1. Active Transport (protein-mediated)
2. Bulk Transport
List the 3 steps of Active Transport
1. Binding (molecule binds to a transport protein)
2. Conformational Change (energy release causes the protein pump to change shape)
3. Release
Provide 2 reasons a cell might require active transport of molecules
A cell might require higher concentrations of a molecule within the cell for metabolic activities or to manipulate water movement (osmosis) by changing the areas of low and high solute concentration
Define Bulk Transport
Bulk transport is a type of active transport that moves large molecules or groups of molecules - such as amino acids, proteins, signalling molecules, or pathogens - into or out of the cell using vesicle
Identify the 2 types of bulk transport
1. Endocytosis
2. Exocytosis
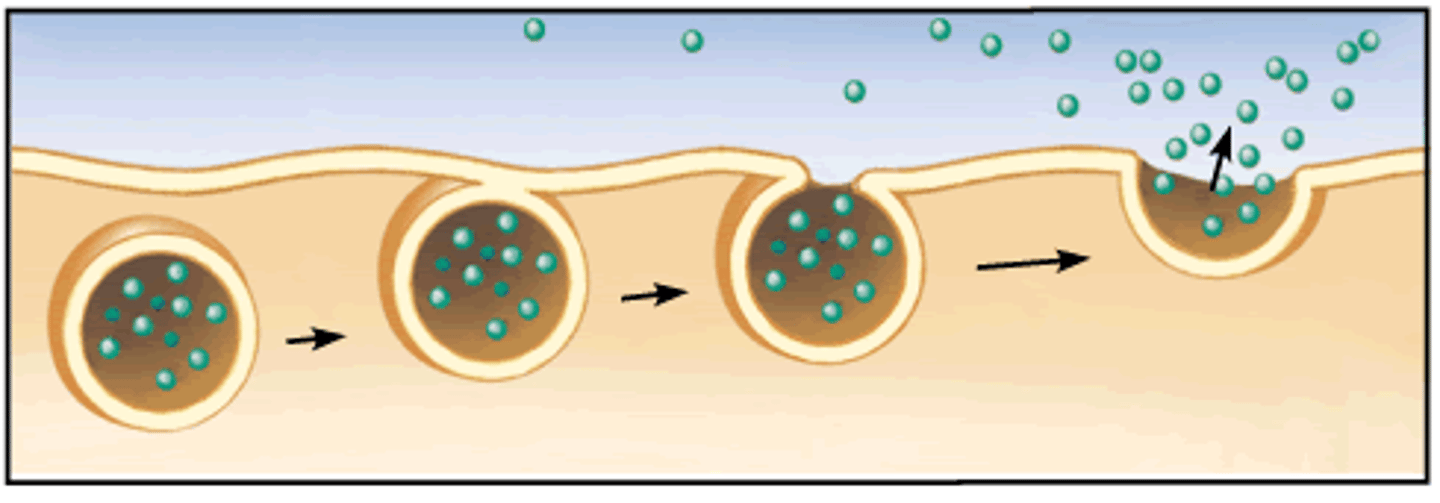
Identify the 3 steps of Exocytosis
1. Vesicular transport
2. Fusion
3. Release
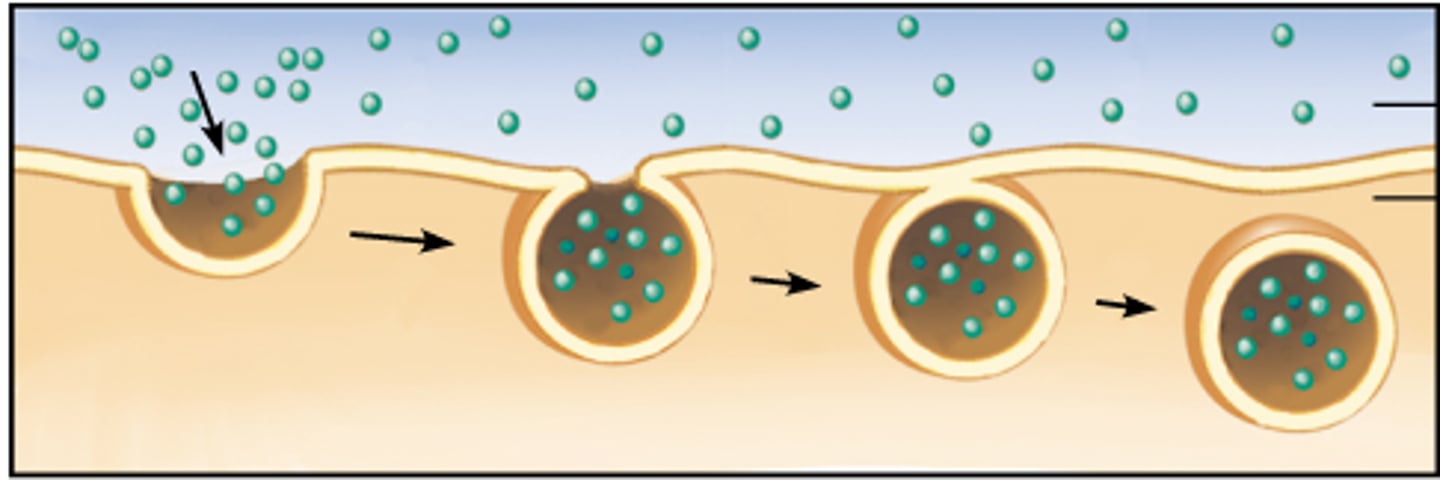
Identify the 3 steps of Endocytosis
1. Fold
2. Trap
3. Bud
Suggest what may occur if a cell engulfs an invader or toxin
A lysosome may fuse with the vesicle to digest its contents
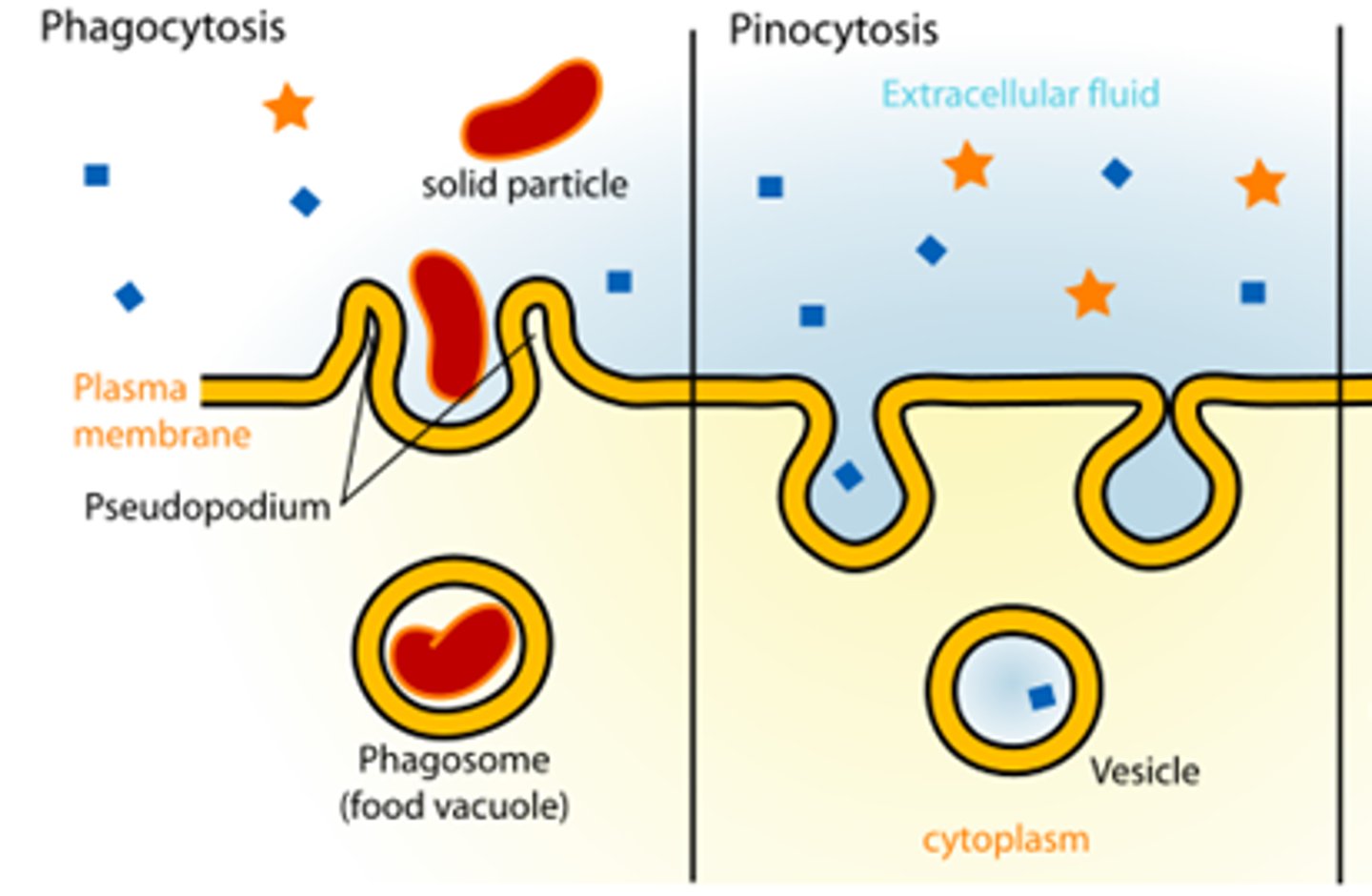
Identify the 2 types of Endocytosis
1. Phagocytosis (cell-eating: solid materials, food particles)
2. Pinocytosis (cell-drinking: dissolved molecules)