Wk Ten - Pulmonary Embolism | Pleural Effusion
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is a Pulmonary Embolism?
refers to an obstruction of the pulmonary artery or one of its branches by material that originated elsewhere in the body
What can an embolus be?
fat, gas, amniotic fluid, tumors, septic, foreign bodies, parasites
What happens if an embolus travels?
pulmonary thrombus
What is it called if an embolus stays in place?
Deep Vein Thrombosis
How often does a PE happen?
0.38 per 1000 people
Virchow’s Triad (Thrombosis)
Stasis, Vessel Wall Injury, Hypercoagulability
Major Risk Factors for PE
surgery
lower limb problems
obstetrics
malignancy
immobility
previous VTE
Minor Risk Factors for PE
Cardiovadcular disease
Oestrogens
COPD
Obesity
Bowel disease
inflammatory bowel disease
Thrombophilia
factor V leiden mutation
prothrombin gene mutation
hyperhomocystinaemia
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome
Deficiency of antithrombin II protien C or S
Increased lipoprotien
High concentrations of factor VIII or XI
How does PE happen?
Clot forms
Dislodges
Lodges in lung - leading to inflammation, infarction, abnormal VQ ratio & cardiovascular compromise
3 things that can cause a clot
Hypercoagulable state, Circulatory state, Vascular wall injury
Hypercoaguability Clot Formation
malignancy
prenancy and peripartum period
oestrogen therapy
trauma or surgery
inflammatory bowel disease
nephrotic syndrome
sepsis
thrombophilia
Circulatory Clot Formation
atrial fibrilation
left ventricular dysfunction
immobility or paralysis
venous insufficiency or varicose veins
venous obstructions from tumor obesity or pregnancy
Vascular Wall Clot Formation
trauma or surgery
venepuncture
chemical irritation
heart valve disease or replacement
atherosclerosis
indwelling catheters
PE travels to lung or head?
Lung - PE
Head - Stroke
PE symptoms
dyspnoea
cough
wheezing
hoarseness
chest pain
apprehension
syncope
tachyponea
central chest pain
cynaosis
lower GCS
hypoxia
hypocapnia
fever
PE on an ECG
tachycardia
nonspecific ST segment & T wave
right ventricular strain
atrial arrhythmias
bradycardia
inferior Q waves
POCUS
Point of Care Ultrasound - advanced diagnostic ultrasonography that is performed and interpreted by the attending physician as a bedside test
How to rule out PE?
NO RISK FACTORS
PE management prehospital
supplemental O2
fluids to fix hypotension (250mL IV)
adrenaline
thrombolysis
How is PE managed in hospital?
anticoagulation
IVC filter
Thromolysis
Embolectomy
ECMO
PE MAIN MANIFESTATION
Chest.resp symptoms, Tachycardia/arrest, Other risk factors
Pleural Effusion
A pleural effusion is a disease of excess fluid accumulating in the pleural cavity (between the visceral and the parietal pleura).
Two kinds of Pleural Effusion
Transduative & Exudative
Pathophysiology of Pleural Effusion
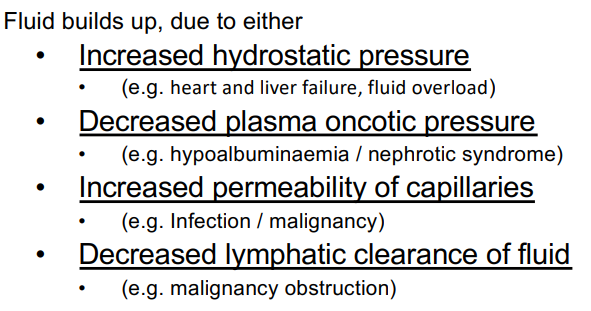
Plasma Osmotic Pressure
9mmHg
Interstitial osmotic pressure
11mmHg
Types of P Effusion
Haemothorax, Empyema, Chylothorax, Cholesterol, Iatrogenic
Haemothorax
Collection of blood (trauma)
Empyema
Collection of pus (infection)
Chylothorax
Milky fluid high in triglycerides (damaged thoracic duct or SVC)
Cholestrol
fluid high in cholestrol build up
Iatrogenic
nasogastric feed or IV solution build up (malinsertion of tubes)
Pleural E Manifestations
gradual dyspneoa
dry cough
chest pain
fever
weight loss
dull percussion
decrease breath sounds
tachycardia
trauma
POCUS
Pleural E Management Pre Hospital
supplemental O2
careful with fluids
keep pts head off bed 30 degrees
lateral decubitis positioning
Pleural E Management In Hospital
treat the cause
diuretics
drain the effusion (thoracentesis)`