OCR Gateway A GCSE Biology: Challenges of Size
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
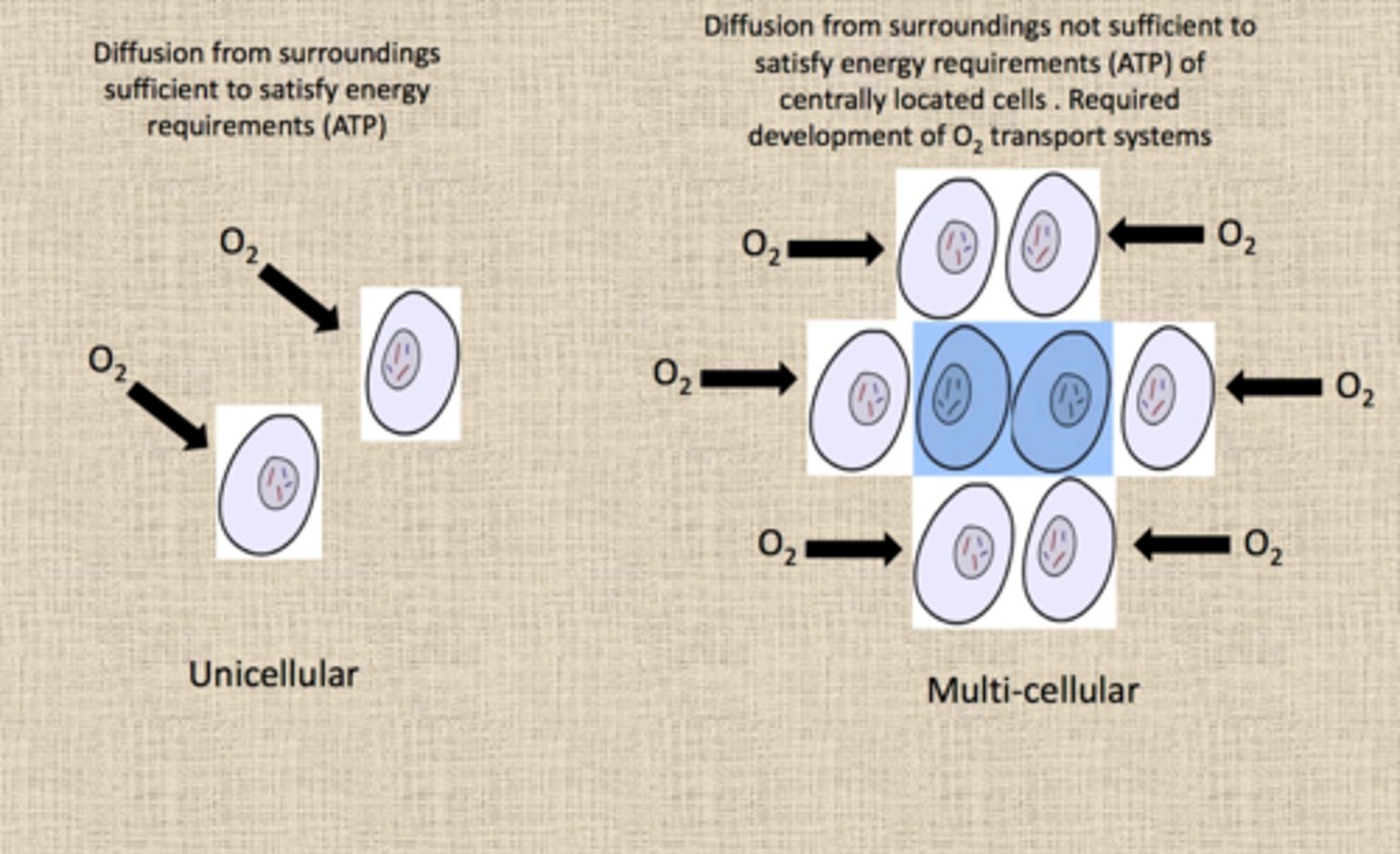
Need for transport systems
Larger organisms have smaller surface area to volume ratios and are unable to directly obtain useful substances from their environment like single-celled organisms can
Transport system
A system that is used for transporting substances around a multicellular living organism
Surface area
The total area of the surface of an object
Surface area to volume ratio
The amount of surface area in relation to how large something is
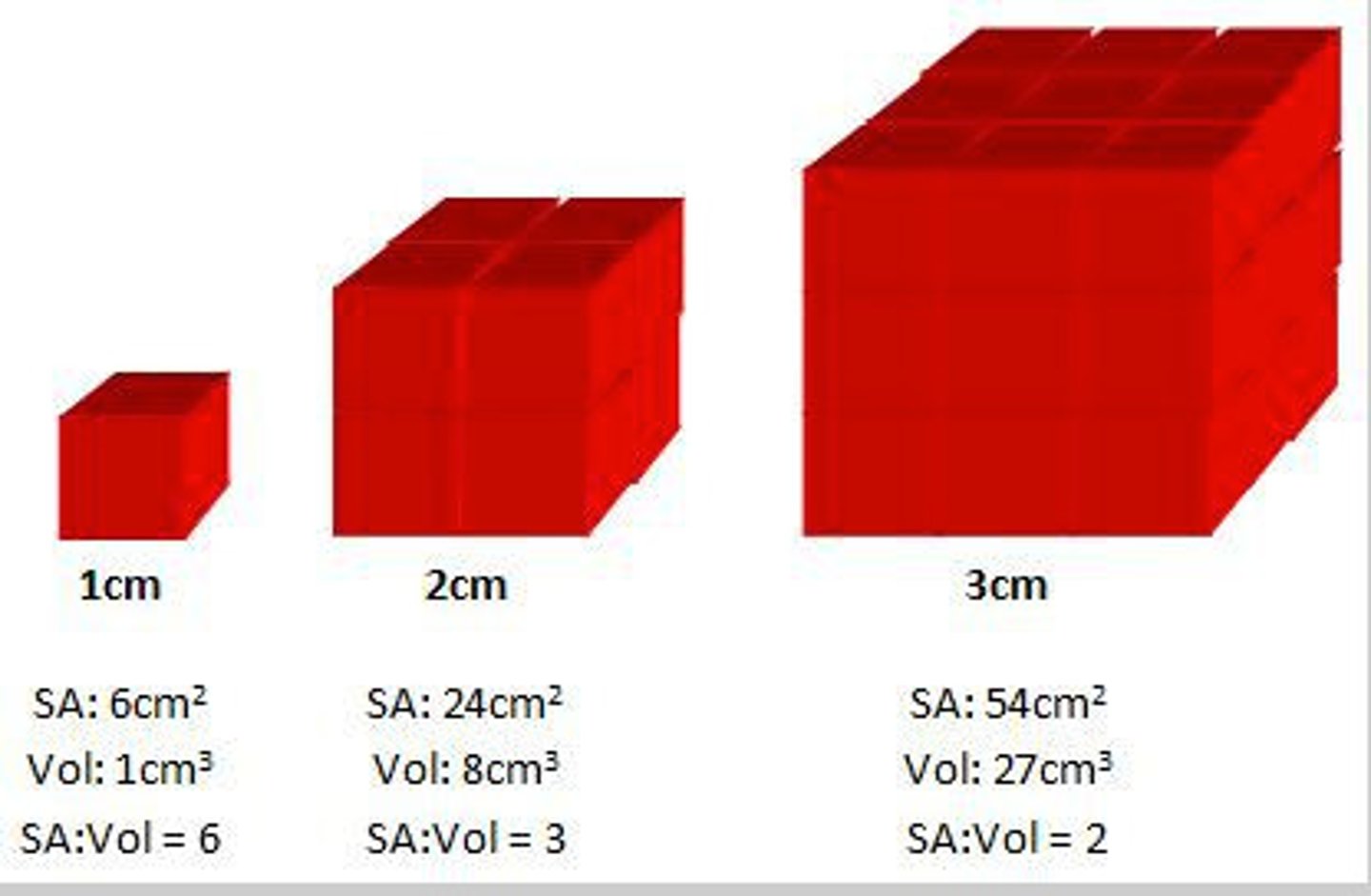
Large surface area to volume ratio
Leads to faster diffusion rates, as there is more room for particles to diffuse through a membrane

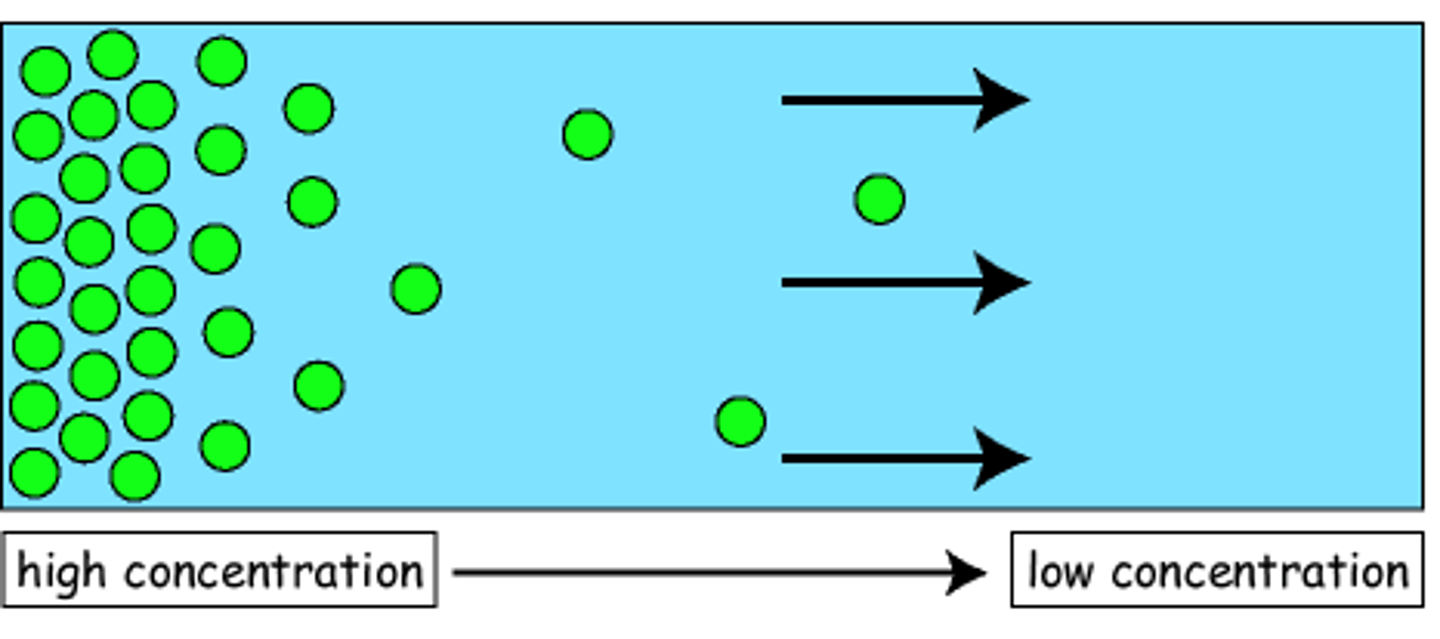
Diffusion
The movement of substances such as gas particles or substances in solution, from a higher concentration to a lower concentration
Gas exchange
When oxygen and carbon dioxide move in and out of cells by diffusion
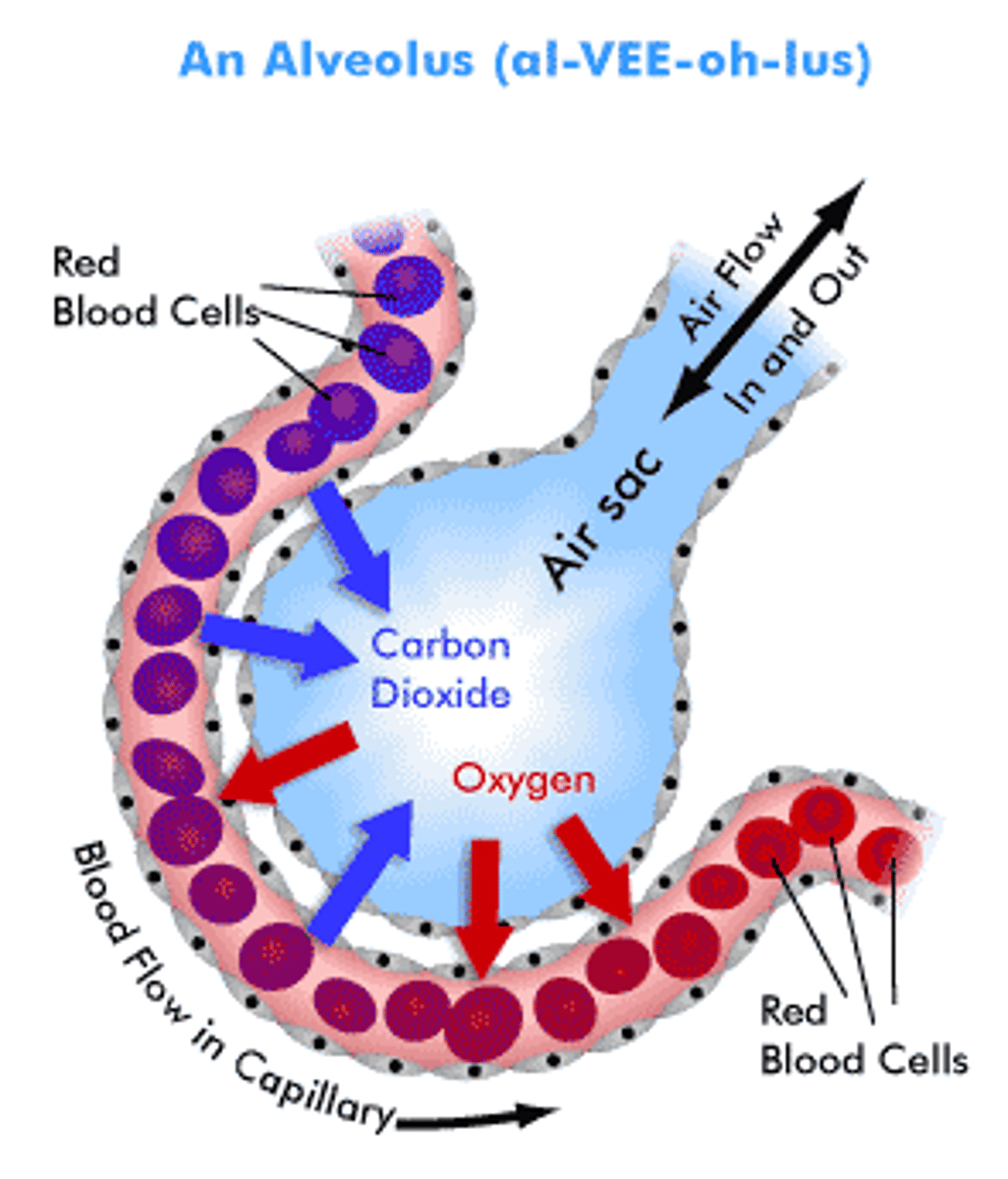
Purpose of gas exchange
Organisms need oxygen for aerobic respiration, they also need to remove carbon dioxide which is a waste product in some organisms

Sites of gas exchange
The alveoli of the lungs, the villi (have microvilli) and respiring cells around the body
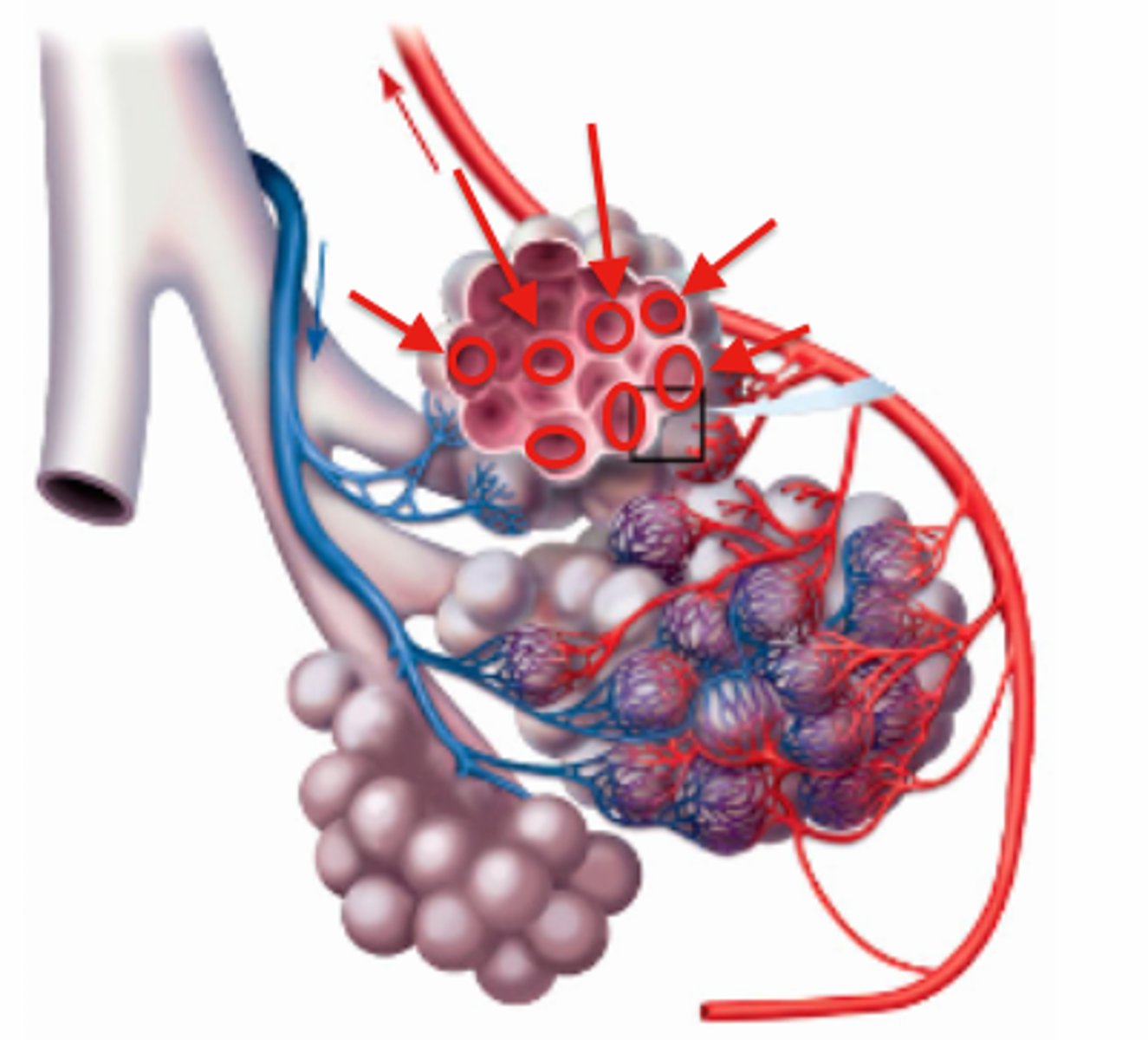
An effective exchange surface …
Has a large surface area, a good blood supply, is well ventilated for gas exchange and has a thin membrane for diffusion
Structures adapted for exchanging materials
Small intestine, kidneys, lungs, gills in fish, roots and leaves in plants all have adaptations such as thin membranes and increased surface area
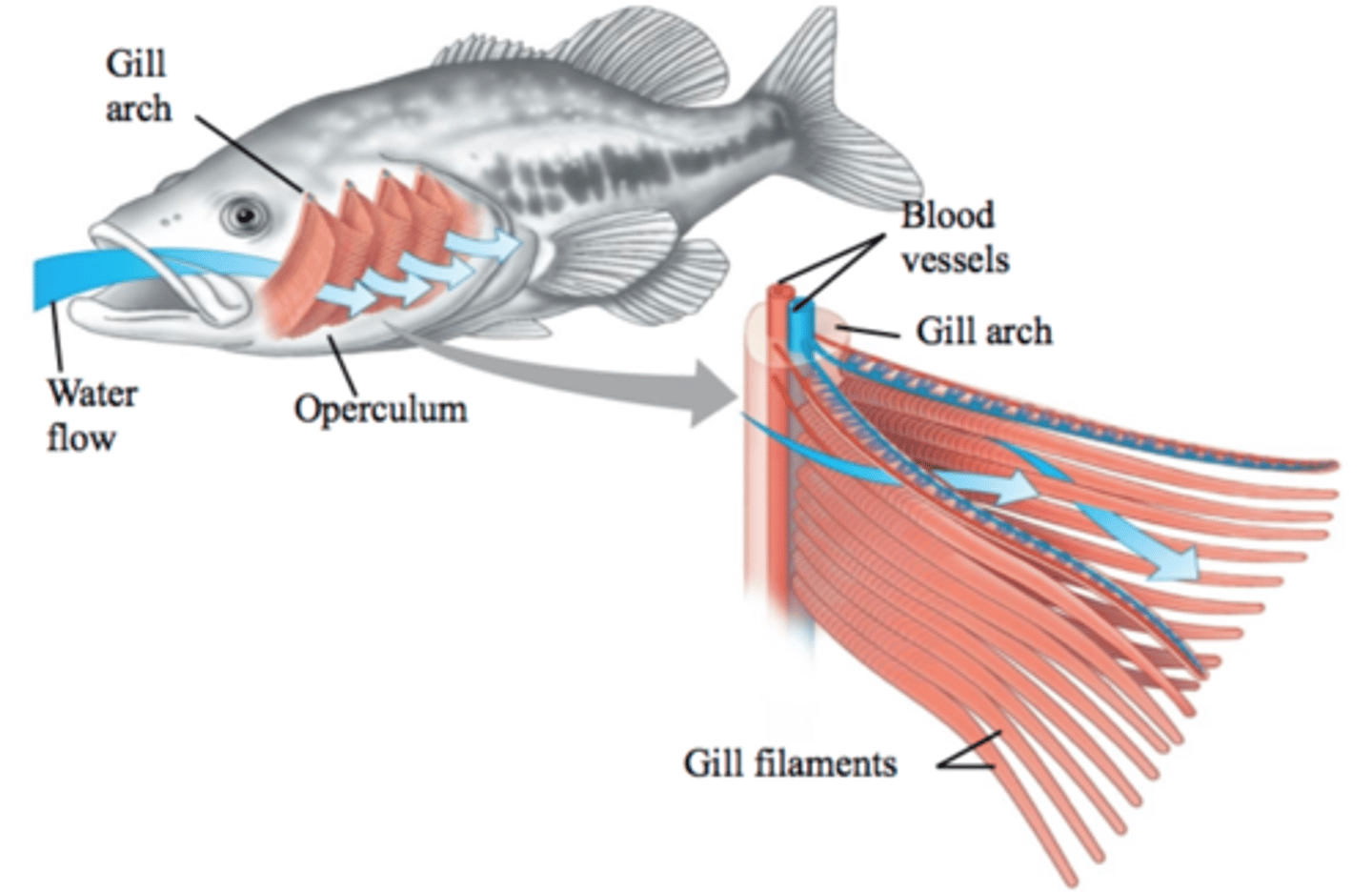
Specific cells, tissue and sacs adapted for exchange
Alveoli in mammal lungs, ciliated epithelial cells in the intestines, gill filaments in fish gills and some amphibian gills, root hair cells in plants, guard cells in plants
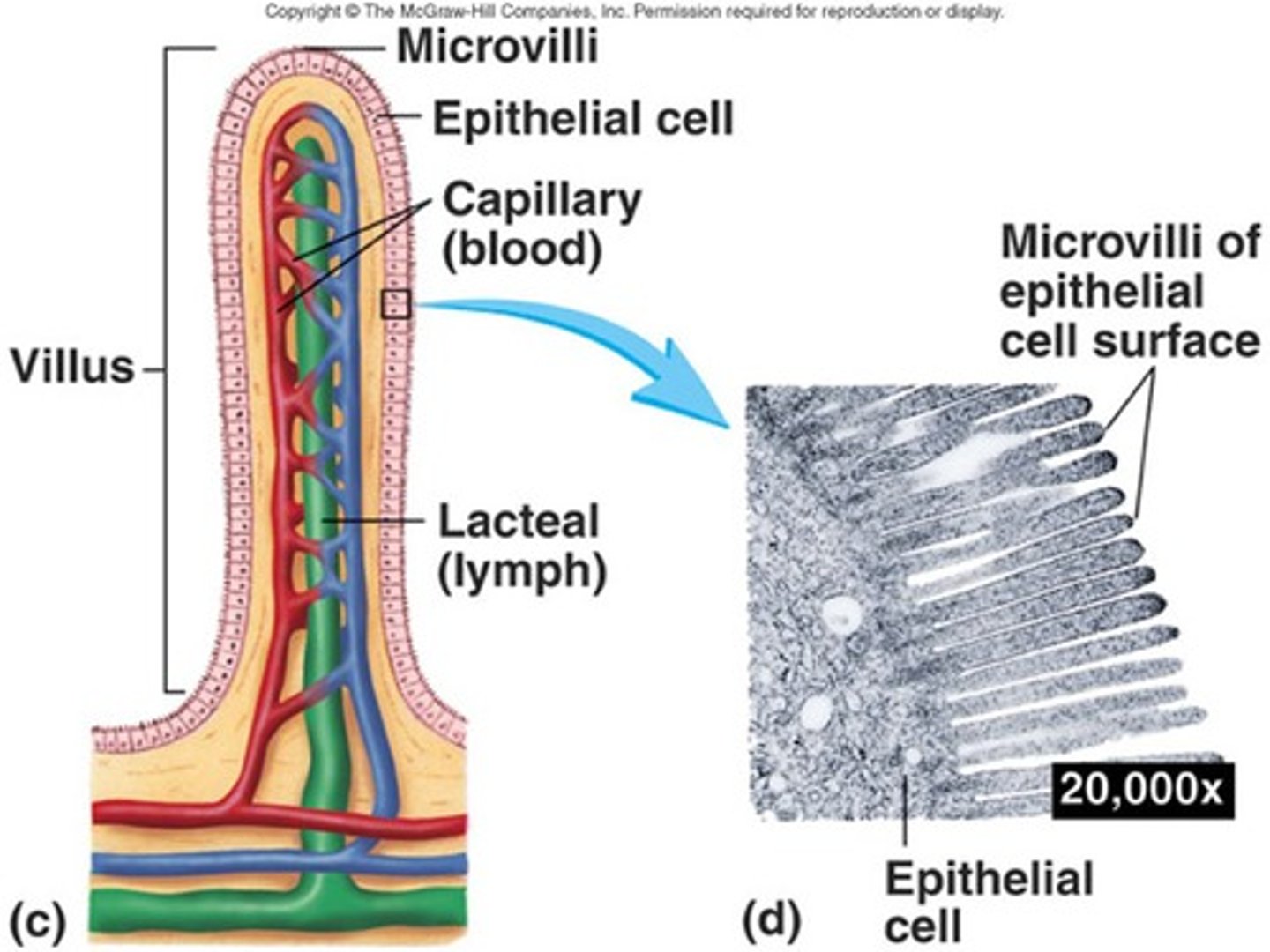
Dissolved food molecules
Products of digestion that are essential for respiration and other important cell functions, these molecules need to be transported by the blood in animals
Urea
A waste product that is filtered and removed from the blood plasma via diffusion in the kidneys
Oxygen
A gas that is needed for aerobic respiration to release energy, oxygen is transported into the body by the respiratory system and around the body by the circulatory system
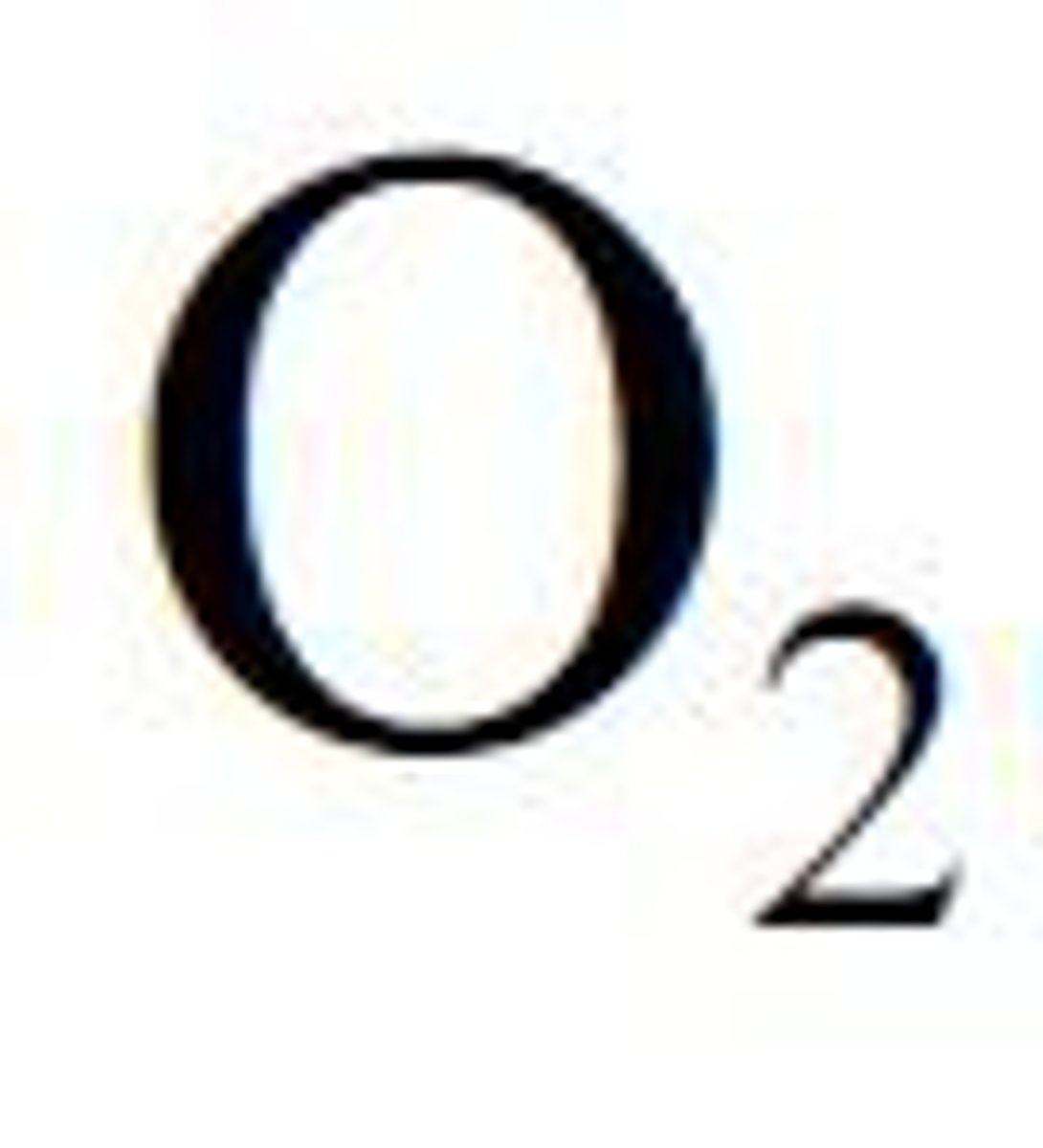
Respiratory system
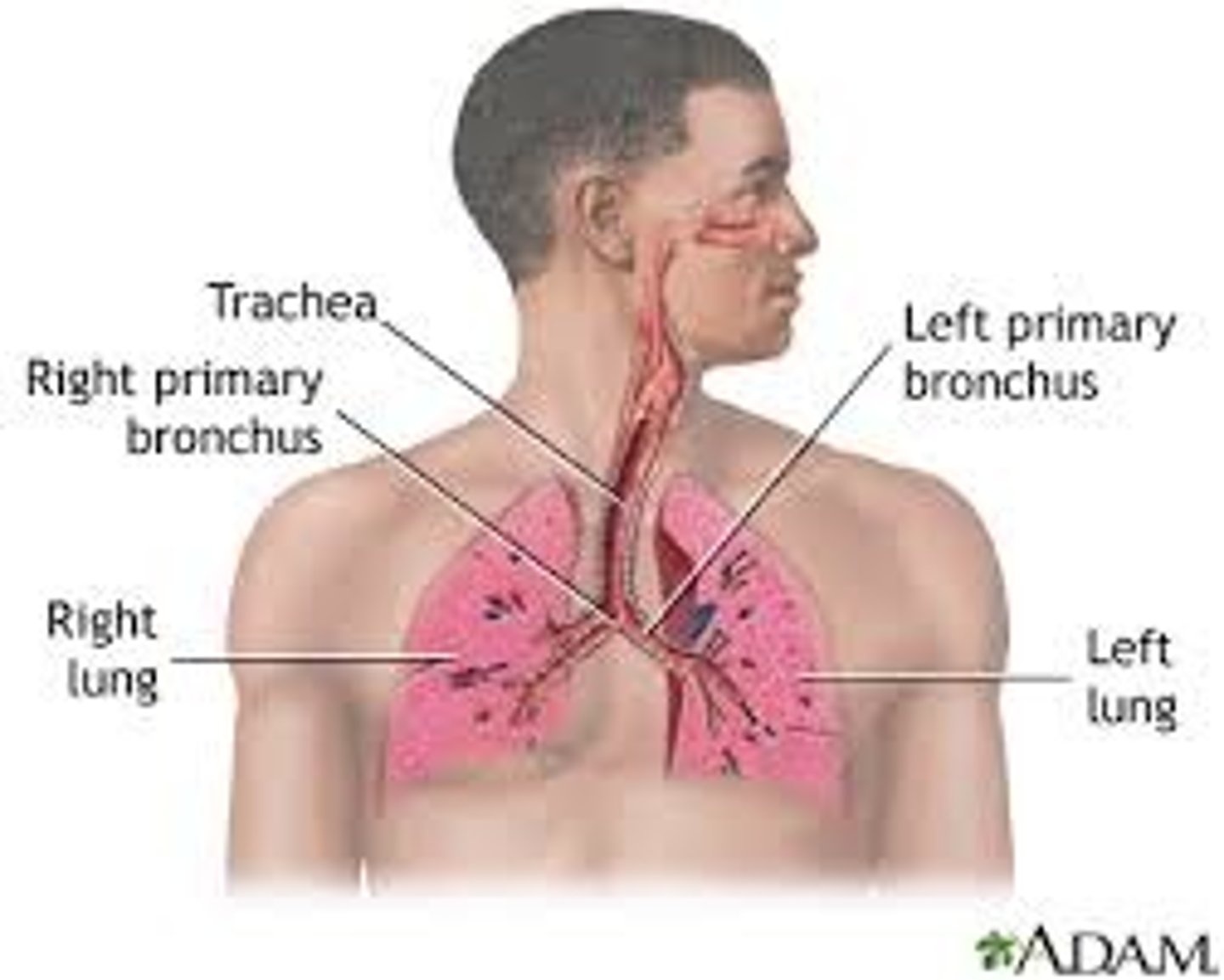
A system of organs, functioning in the process of gas exchange between the body and the environment, consisting of the trachea, bronchi and lungs
Circulatory system
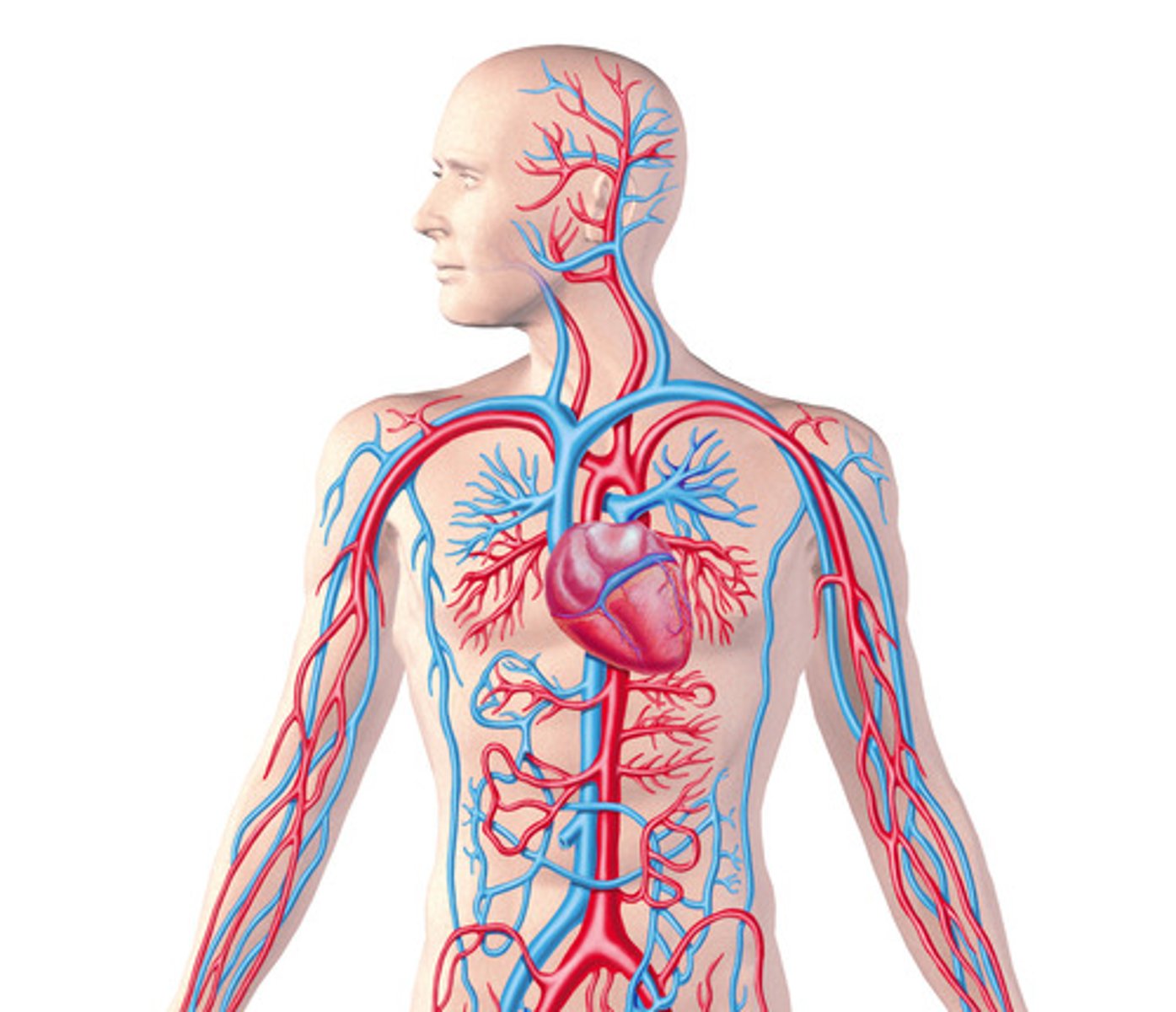
An organ system that transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, waste such as urea, nutrients, hormones and heat around the body
Carbon dioxide
A waste product of respiration that needs to be removed from the body via the circulatory system, also an essential reactant in plants that is transported in to plant leaves via the stomata
Water in animals
Essential for osmosis and cell functions, water is transported around the body by the blood in animals
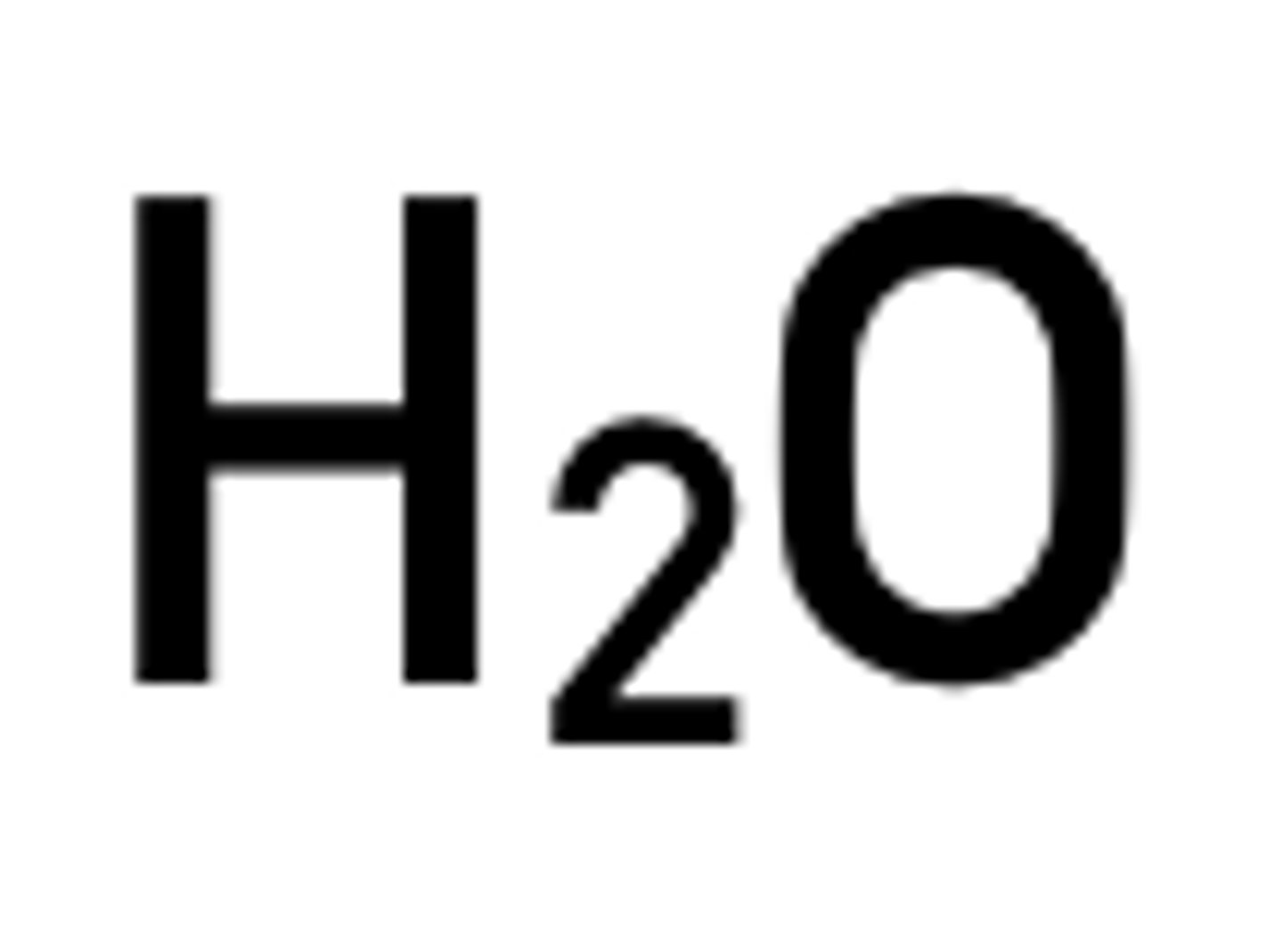
Water and mineral ions in plants
Water and minerals are needed for cell functioning and proper plant development, they are obtained in the roots and are transported to the leaves via the xylem
Gas exchange in plants
Carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant in exchange for oxygen that diffuses out of the plant, this process is regulated by guard cells in the leaves that can open and close the stomata efficiently
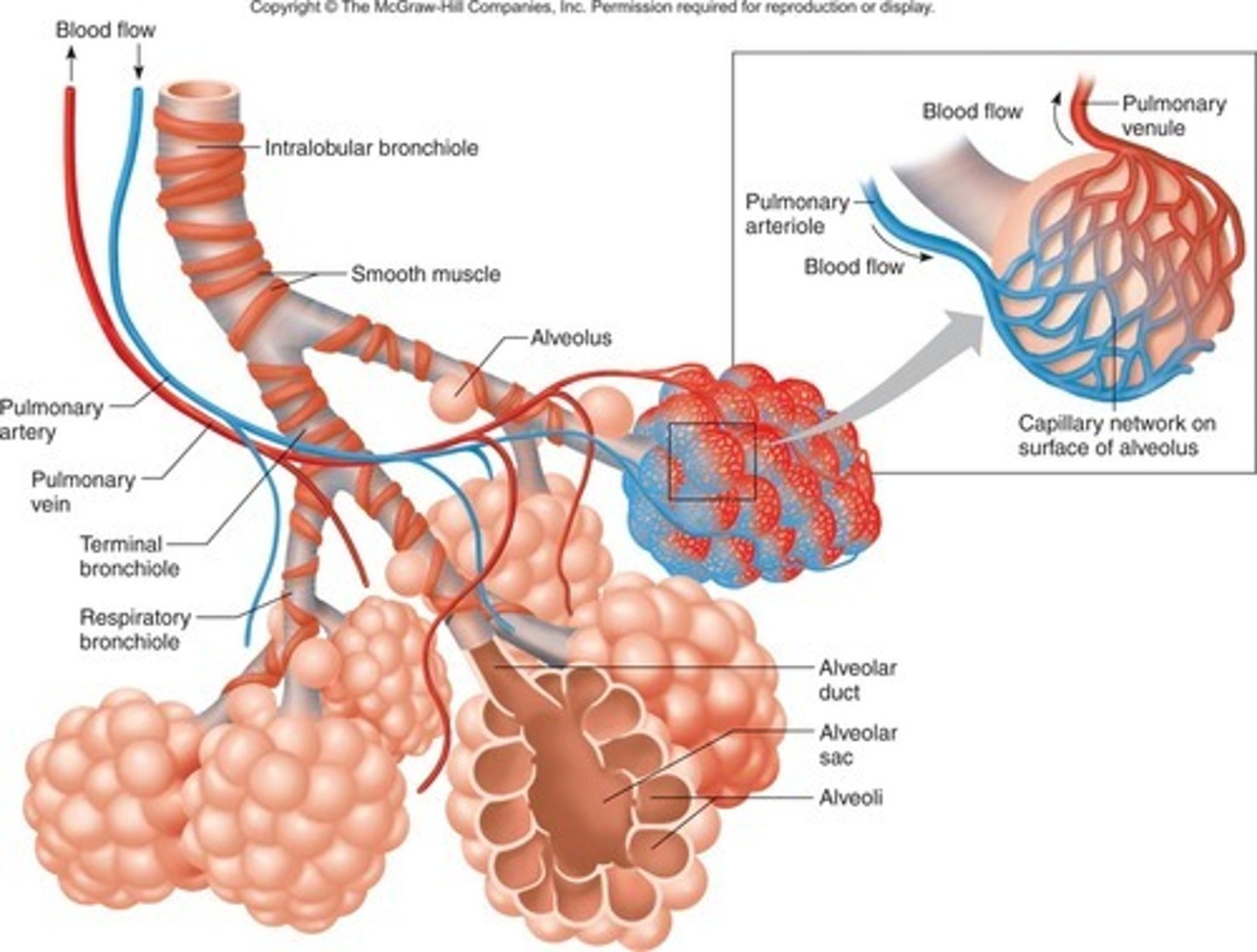
Lungs are…
Are specialised in gas exchange due to the presence of many tiny sacs called alveoli that are adapted for diffusion due to being moist, one cell thick and surrounded by capillaries

Heart
A hollow and muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body, made up of involuntary muscle tissue called cardiac muscle
Lungs
The main organs of the respiratory system, responsible for gas exchange where oxygen is exchange with carbon dioxide in the blood
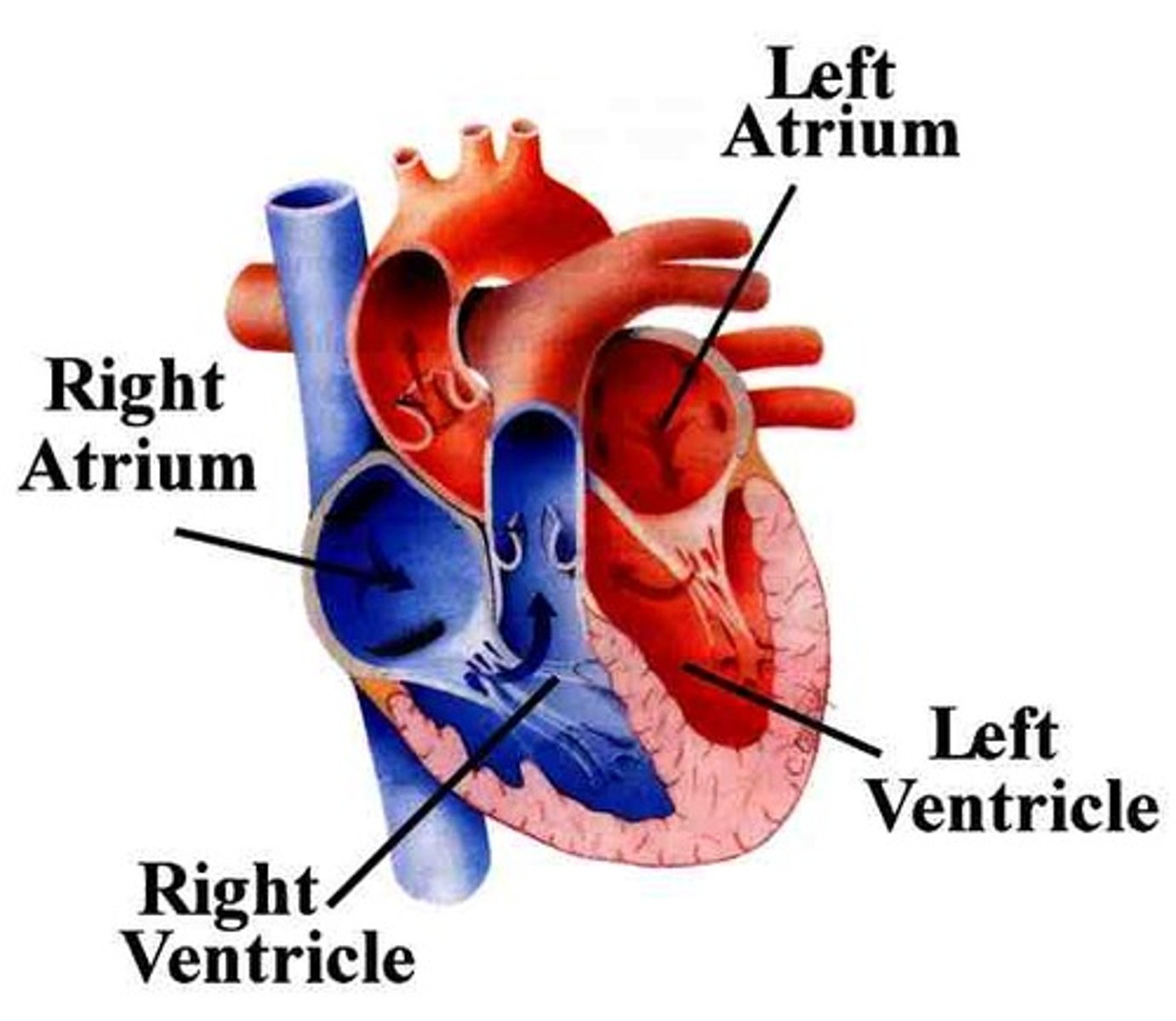
Left ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood to the body through the aorta
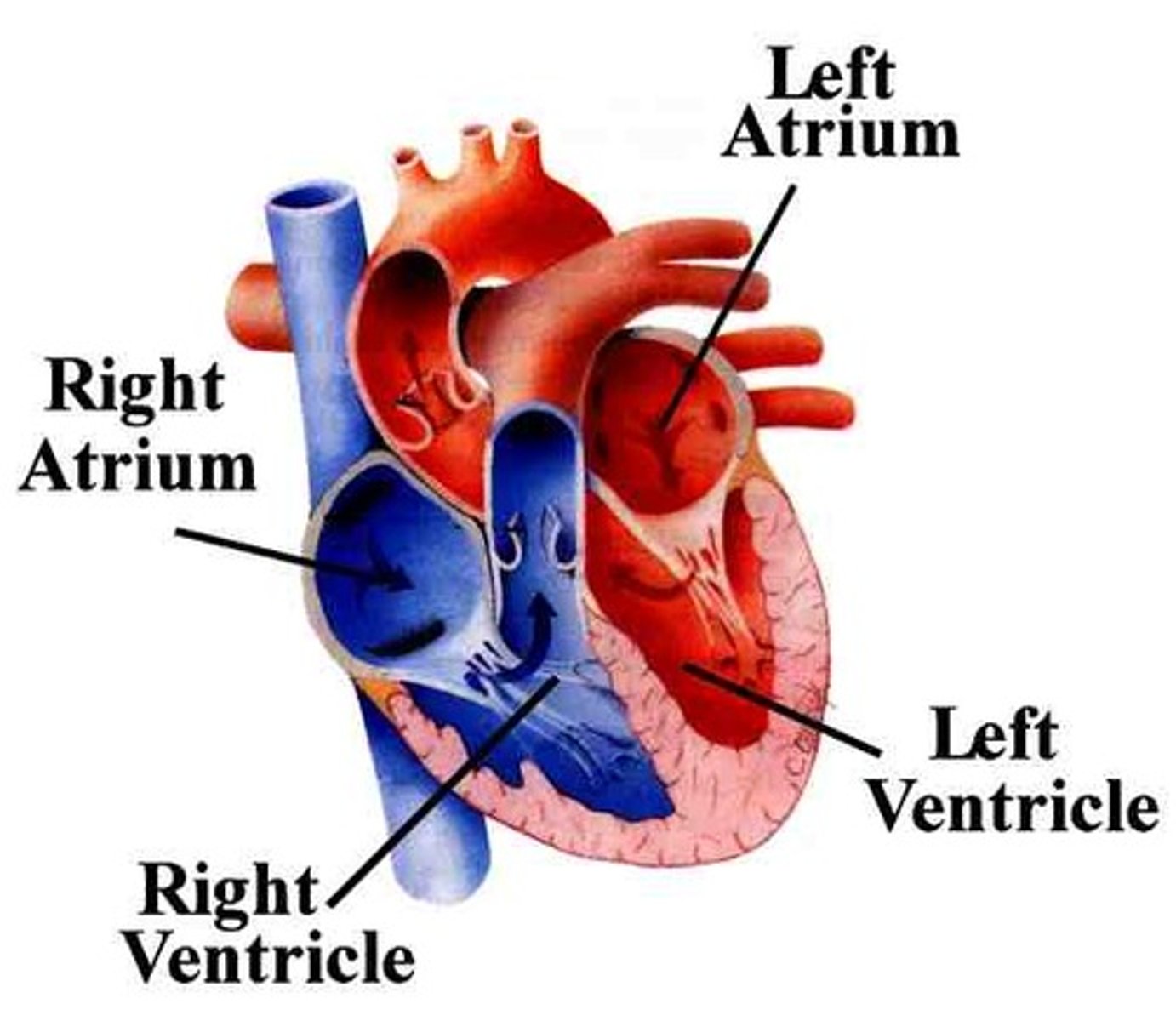
Right ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery
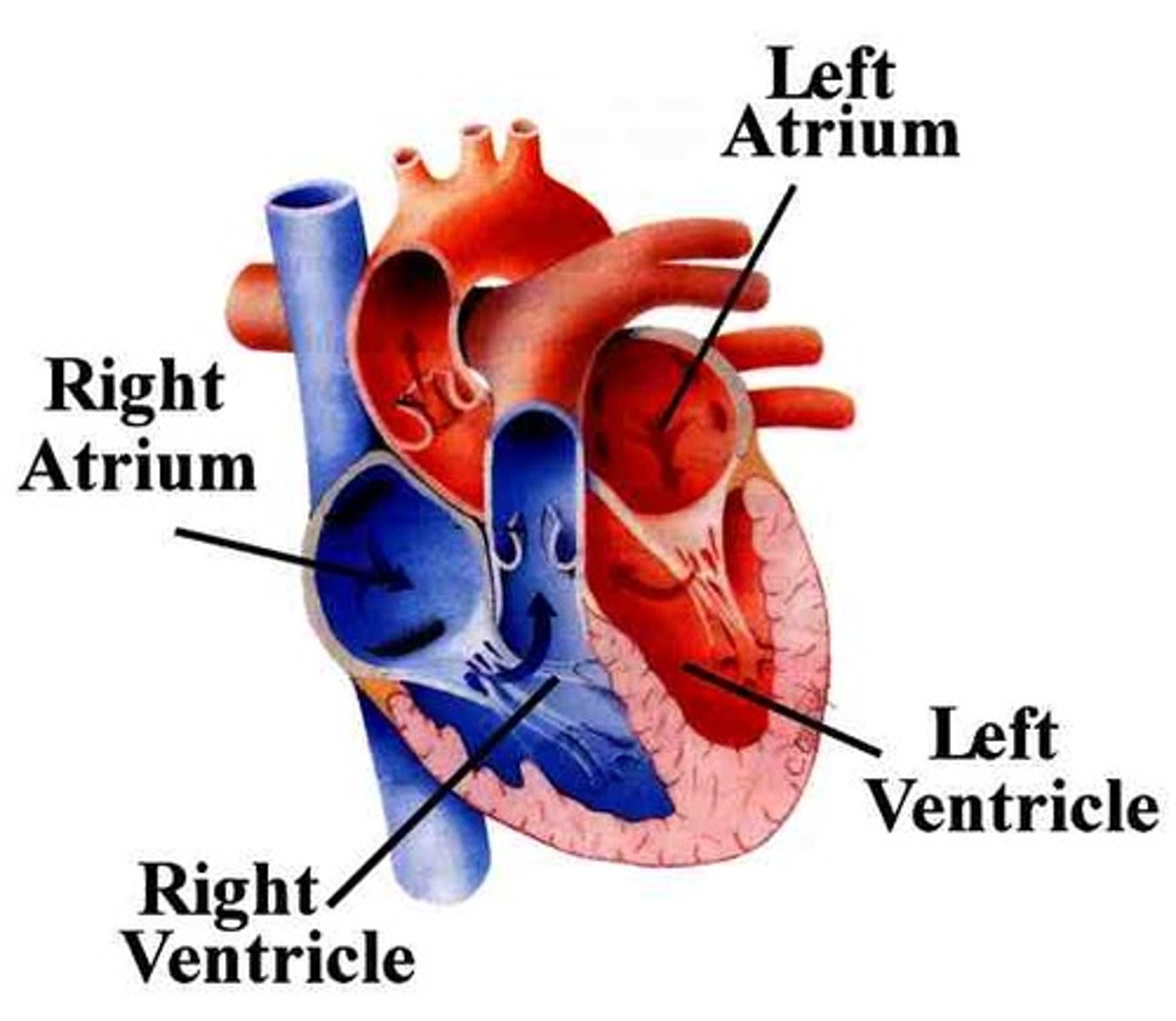
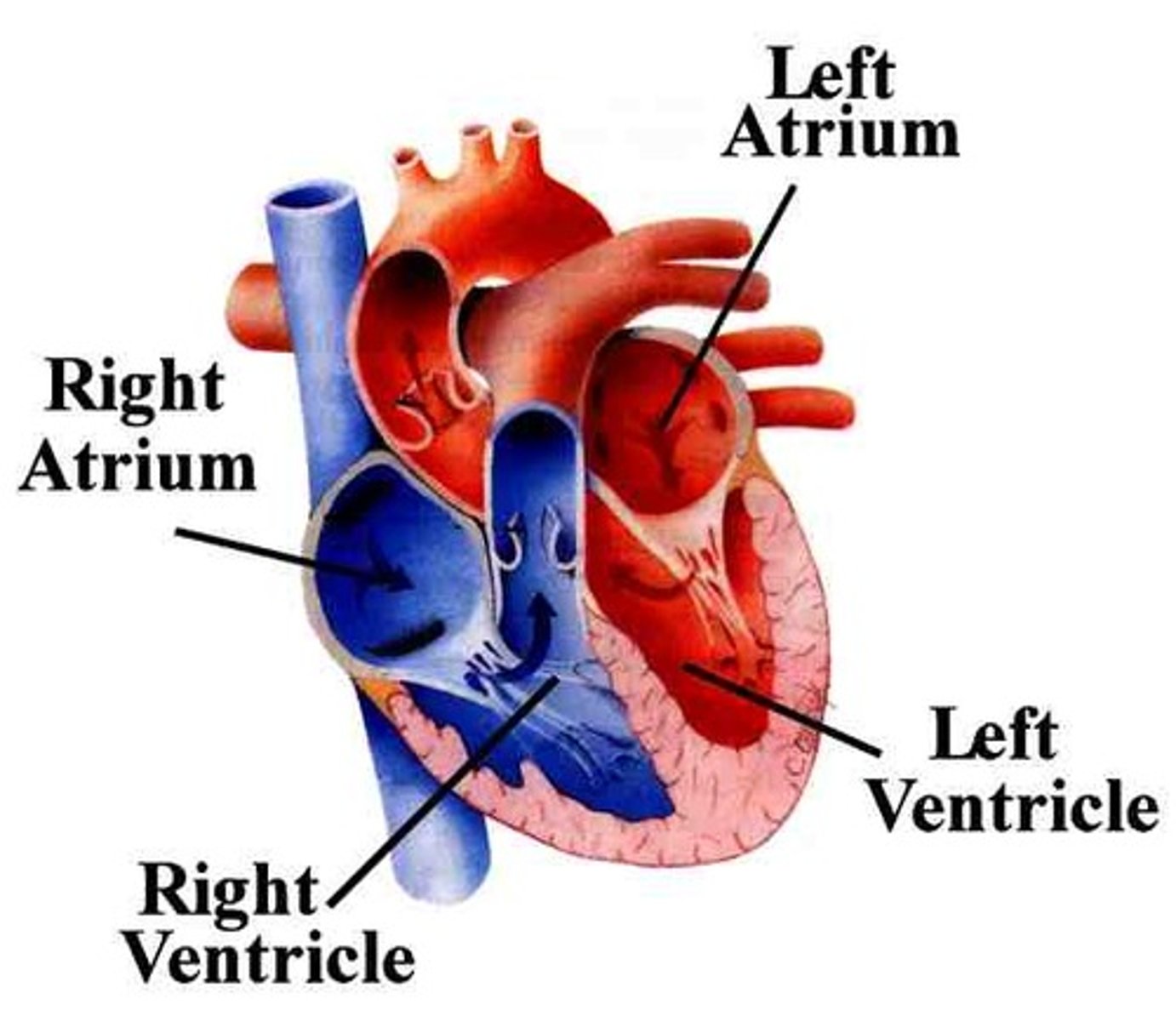
Atria
Upper chambers of the heart that receive blood, the right atrium receives blood from the vena cava and the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary vein
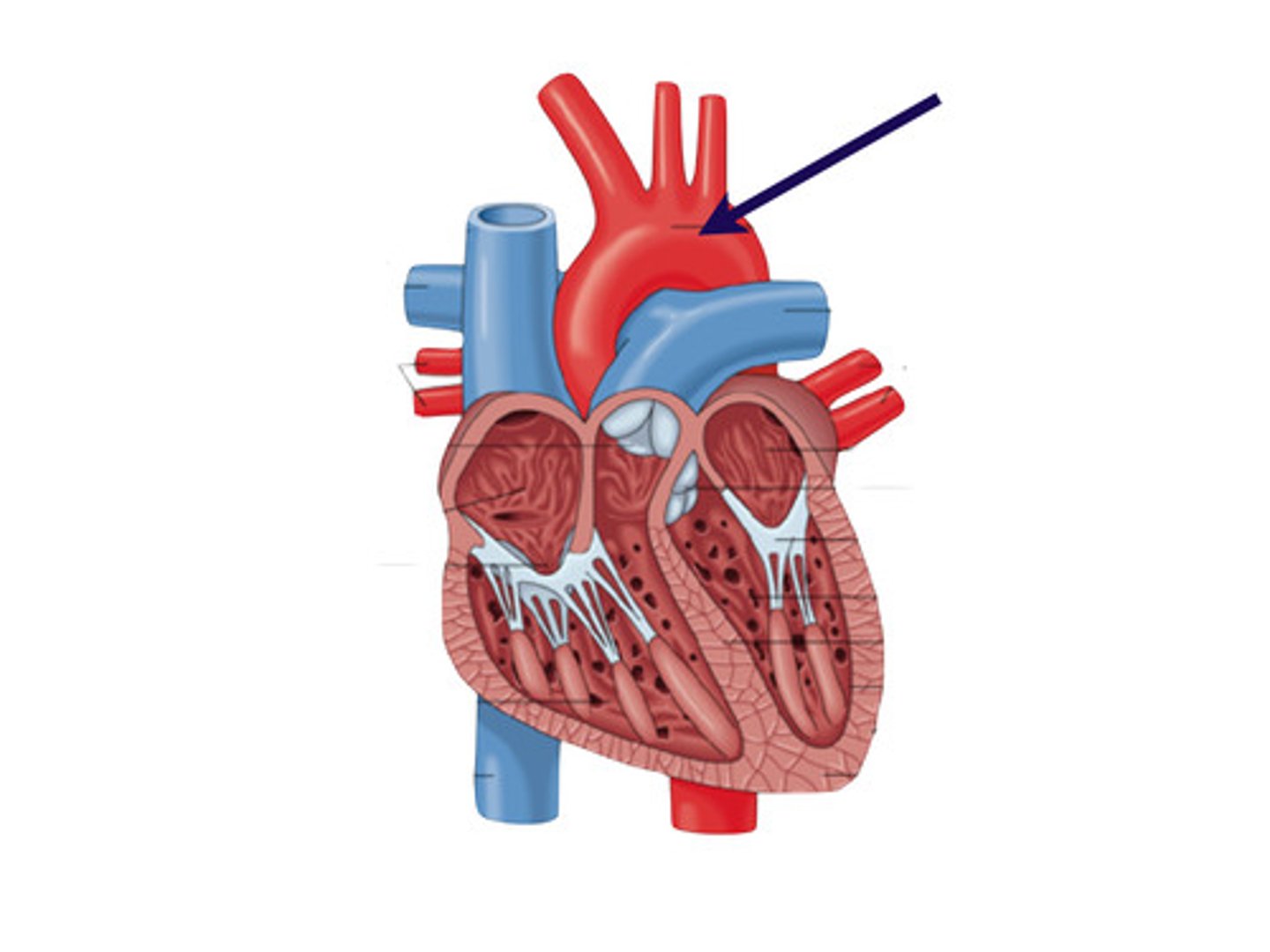
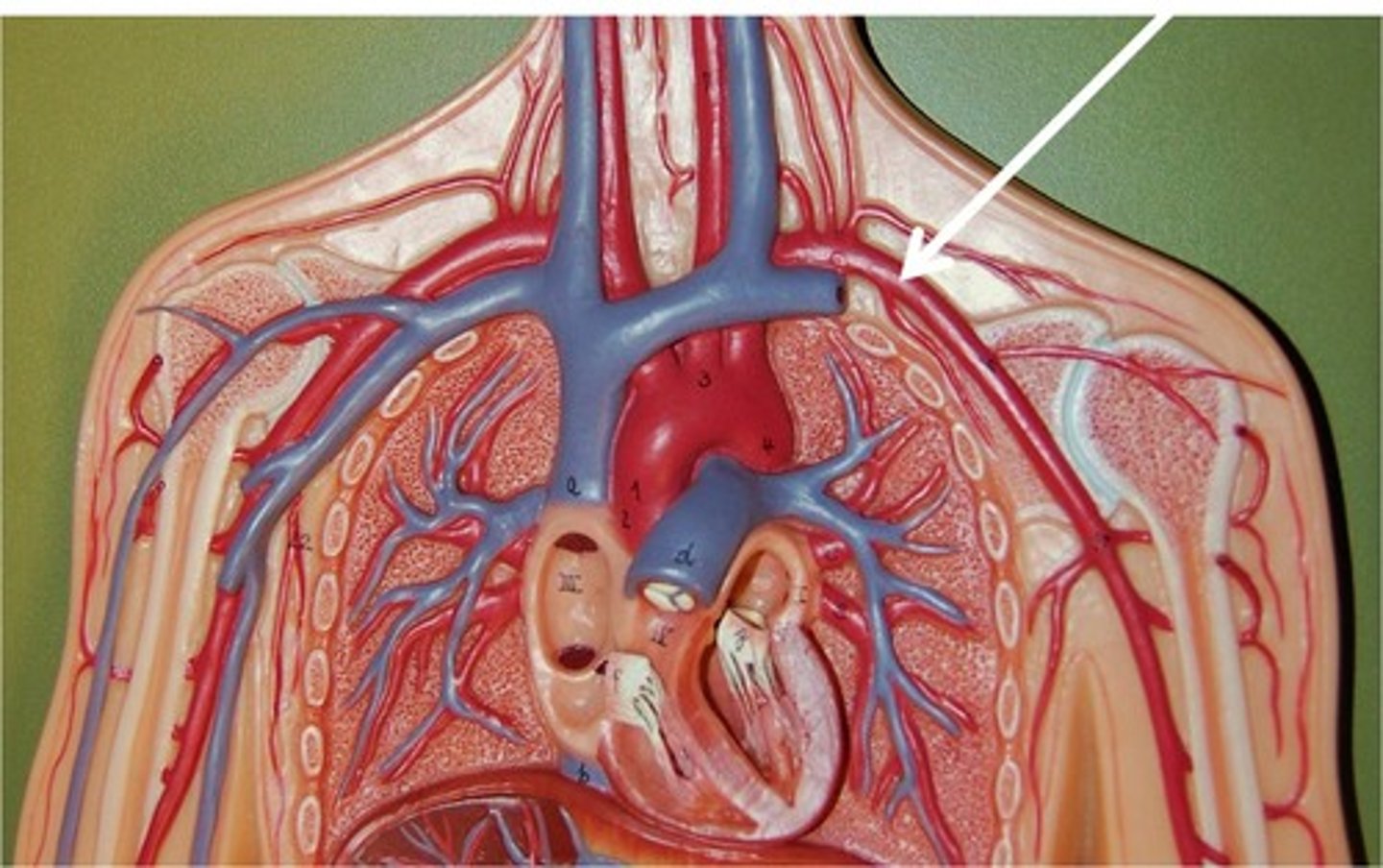
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, carries oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle
Vena cava
The largest vein in the body, carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart, specifically to the right atrium

Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
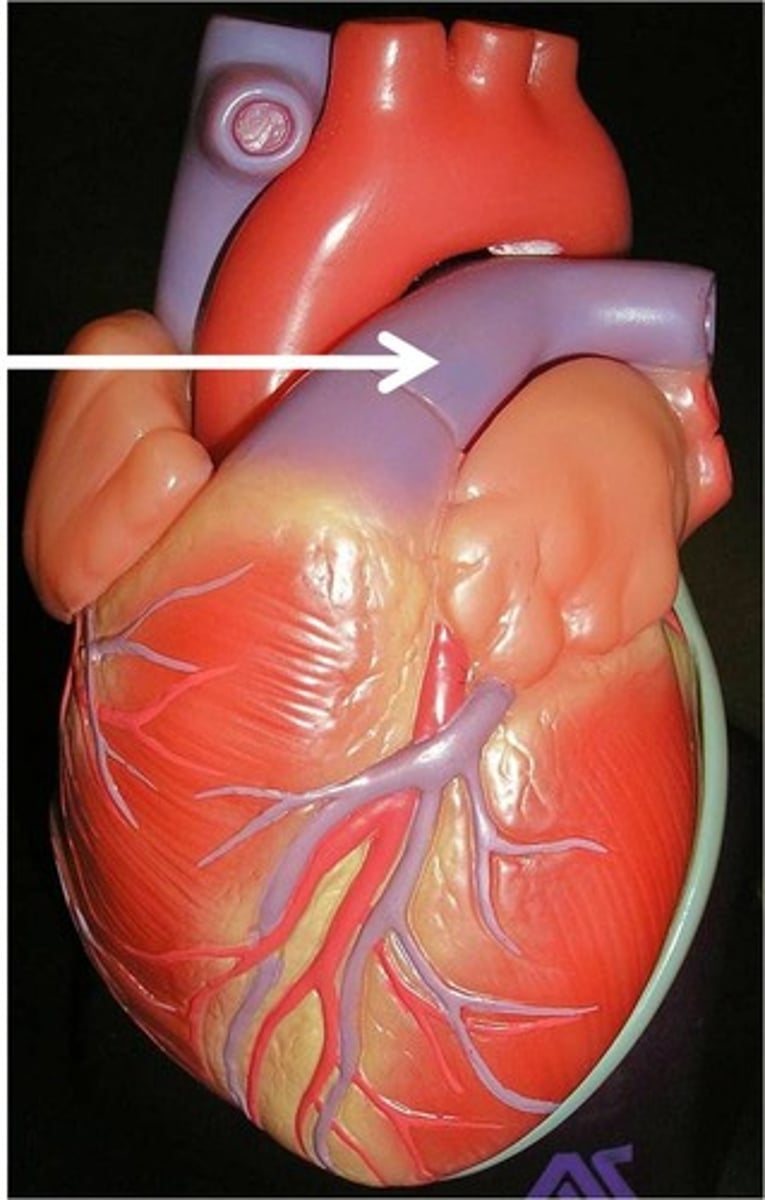
Pulmonary vein
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
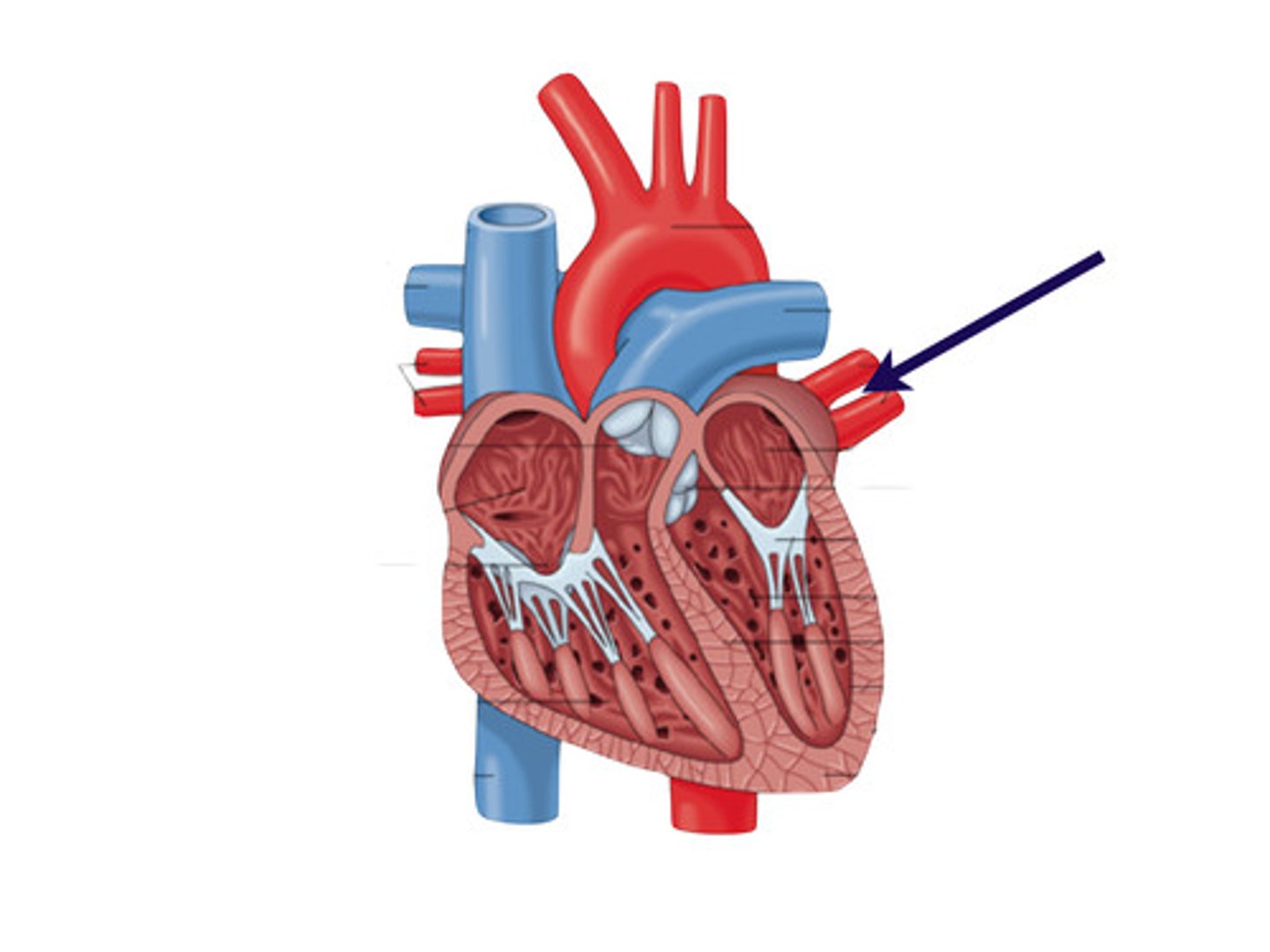
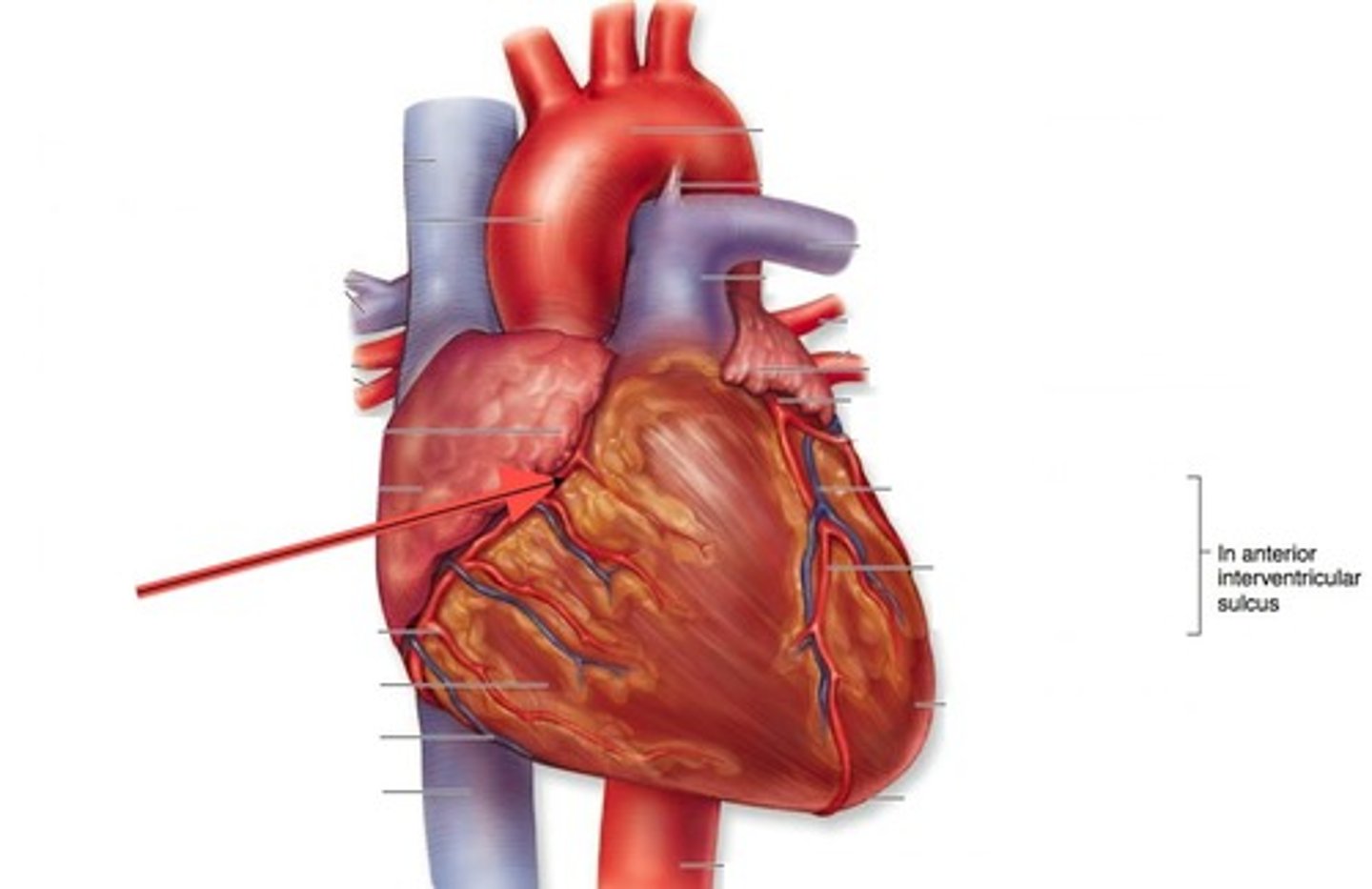
Coronary arteries
Blood vessels that supply the muscle of the heart
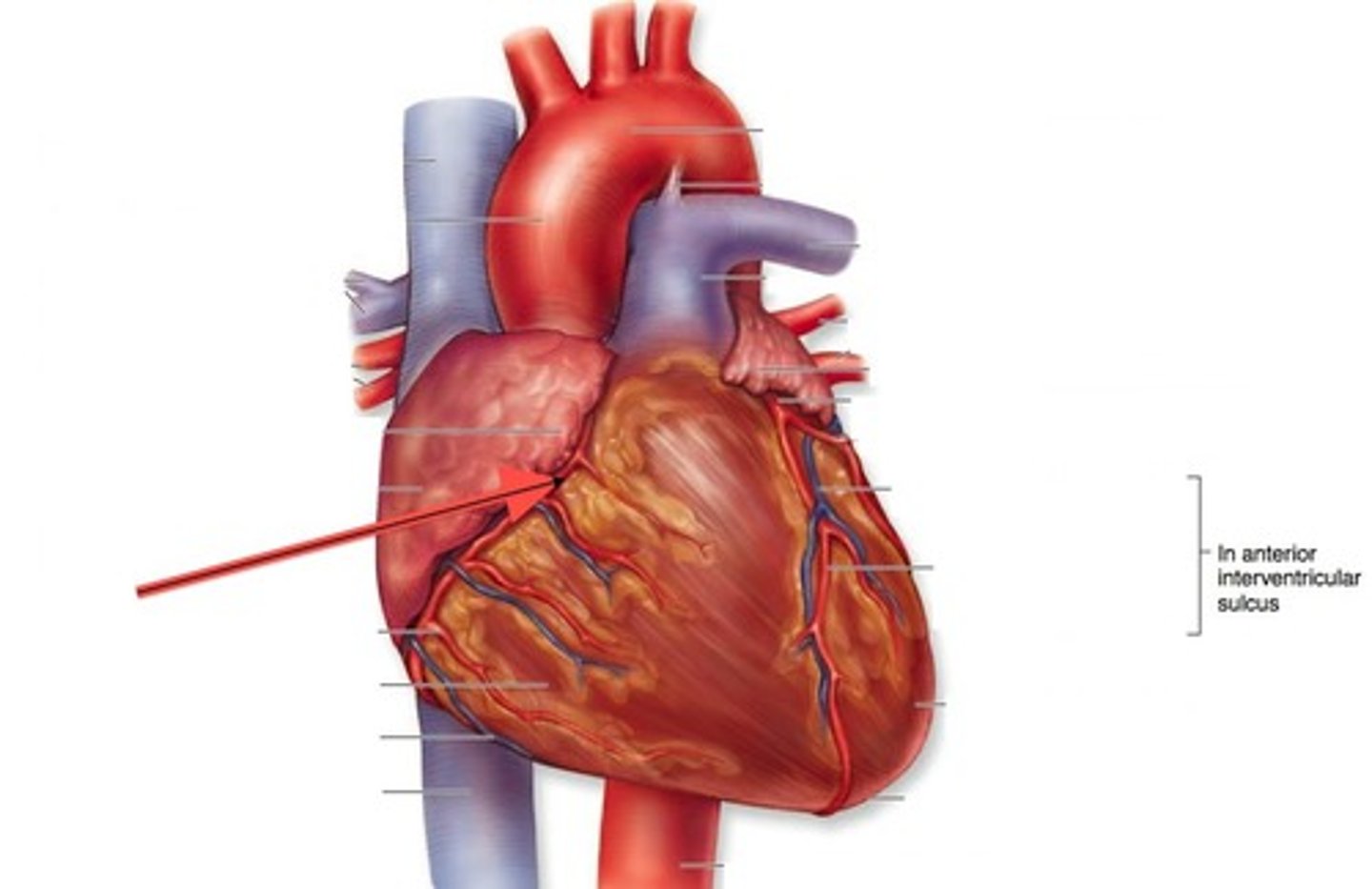
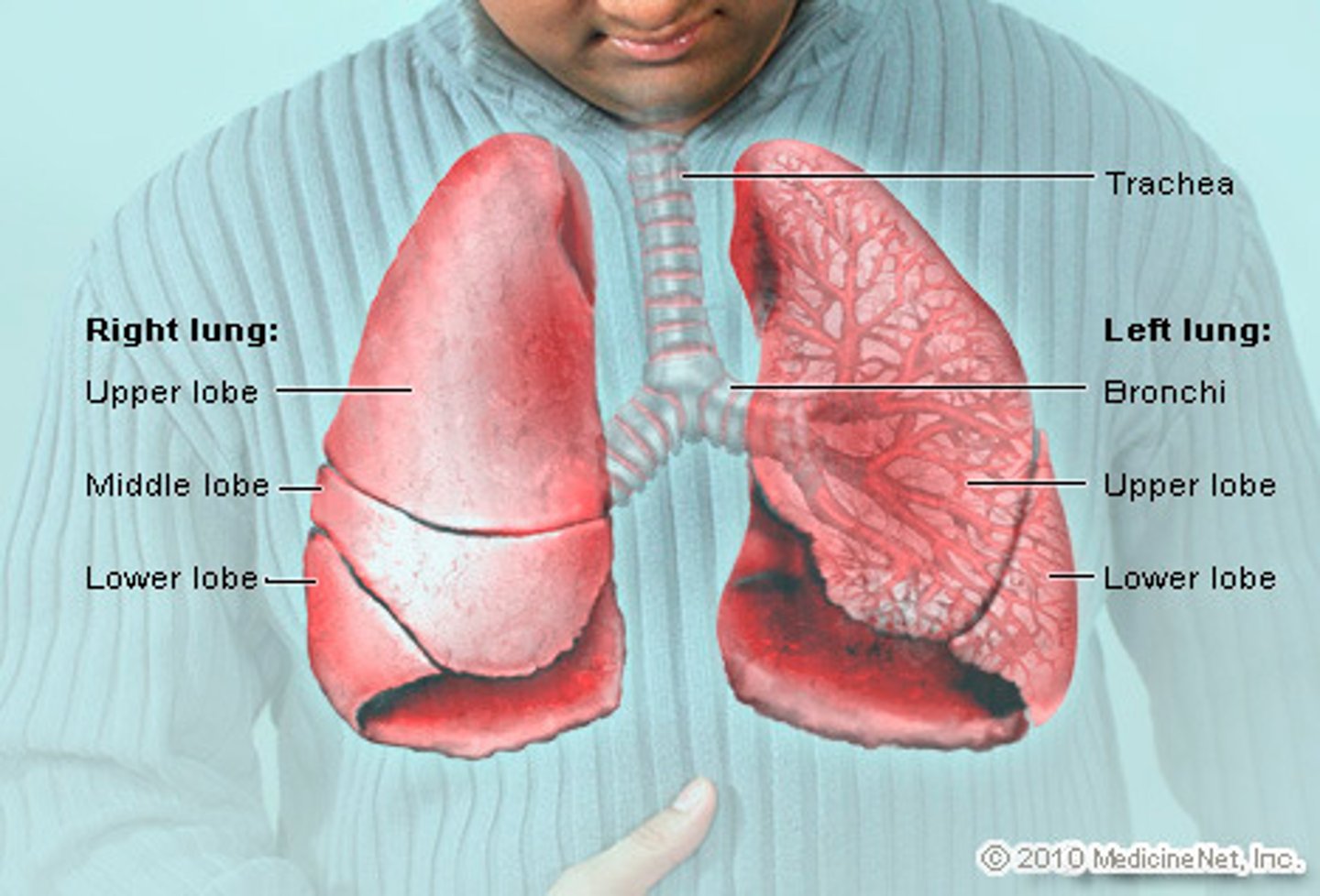
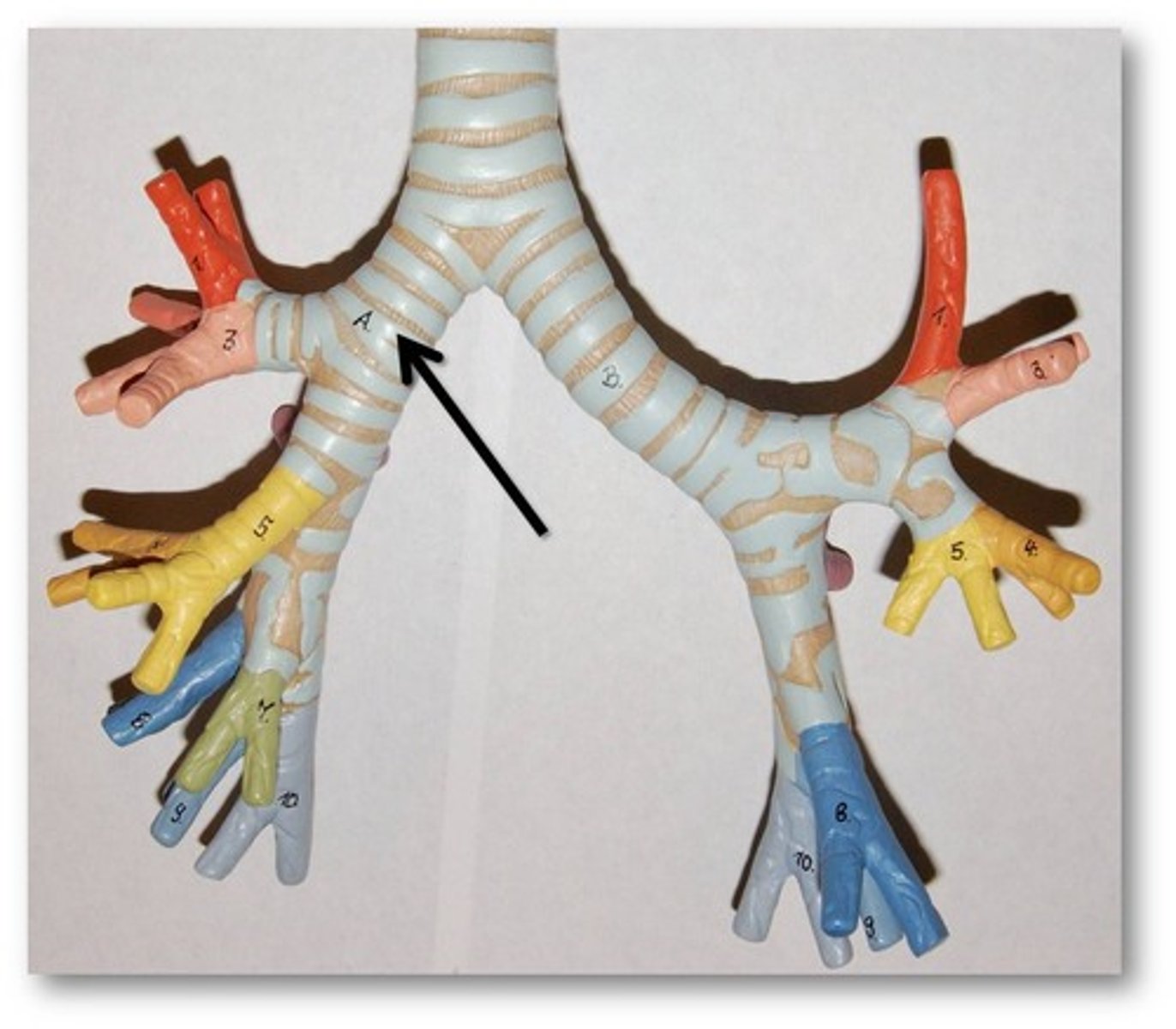
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
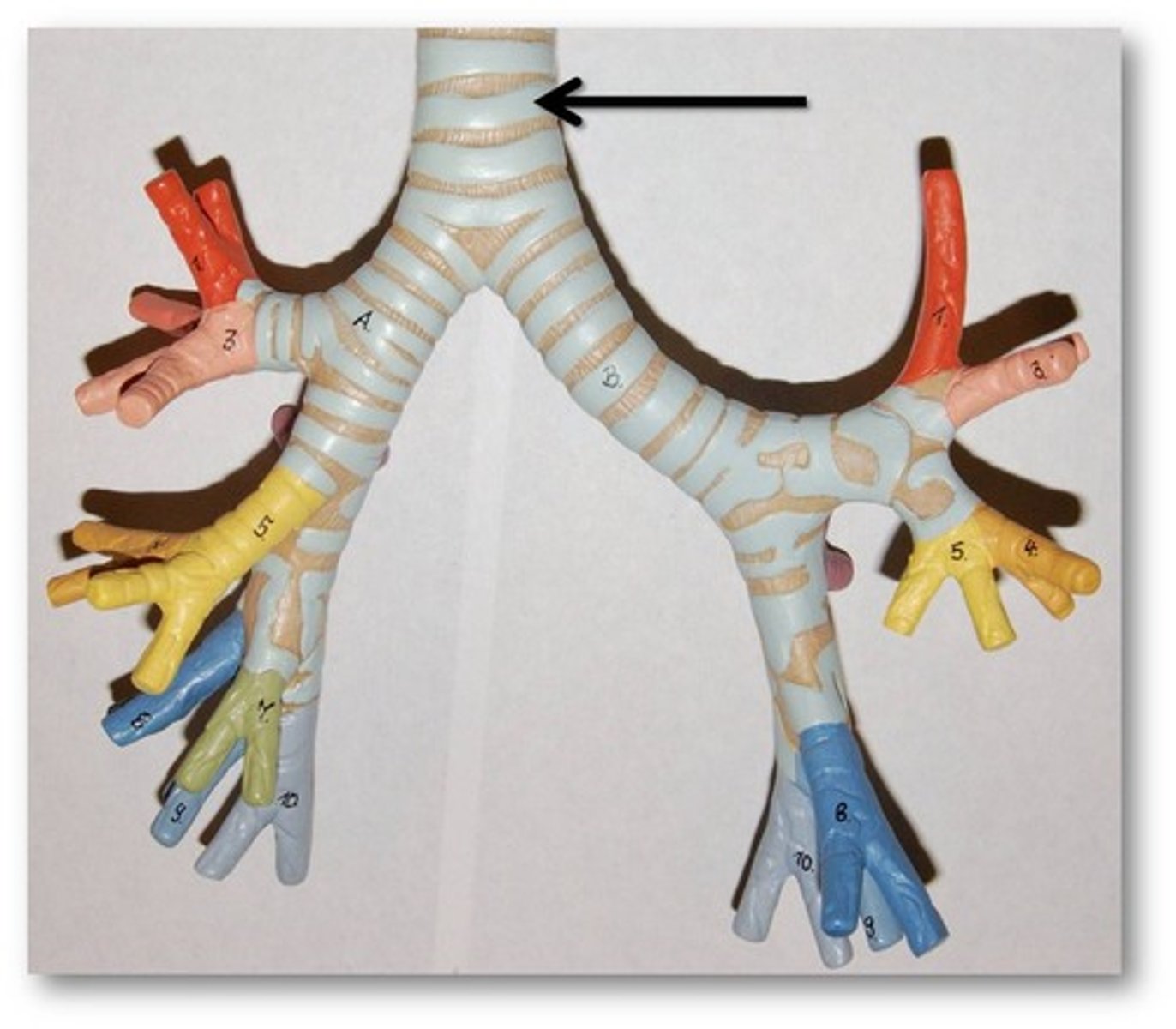
Bronchi
Two short branches at the lower end of the trachea that carry air into the lungs
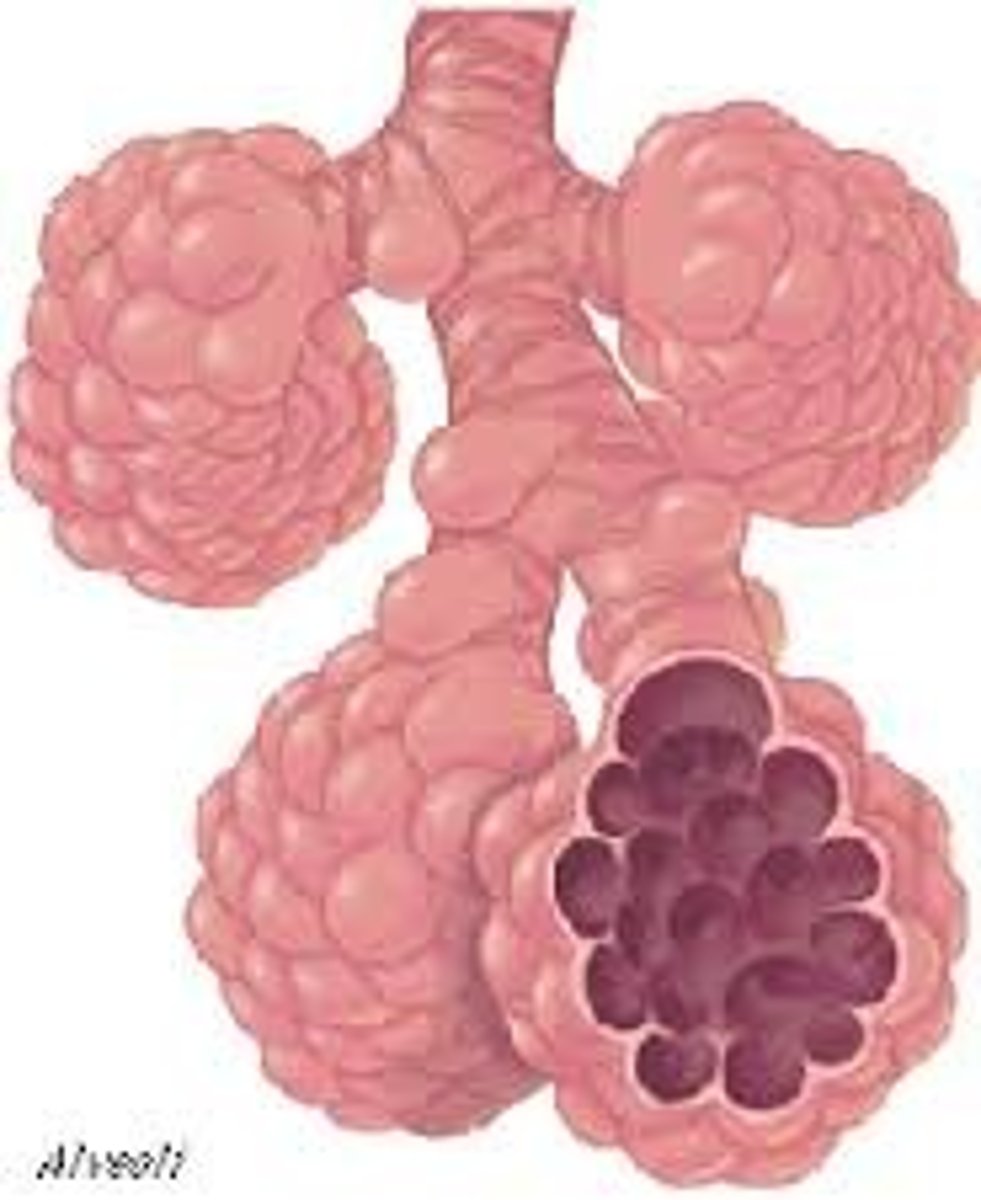
Alveoli
Tiny sacs of lung tissue where gaseous exchange takes place with the blood
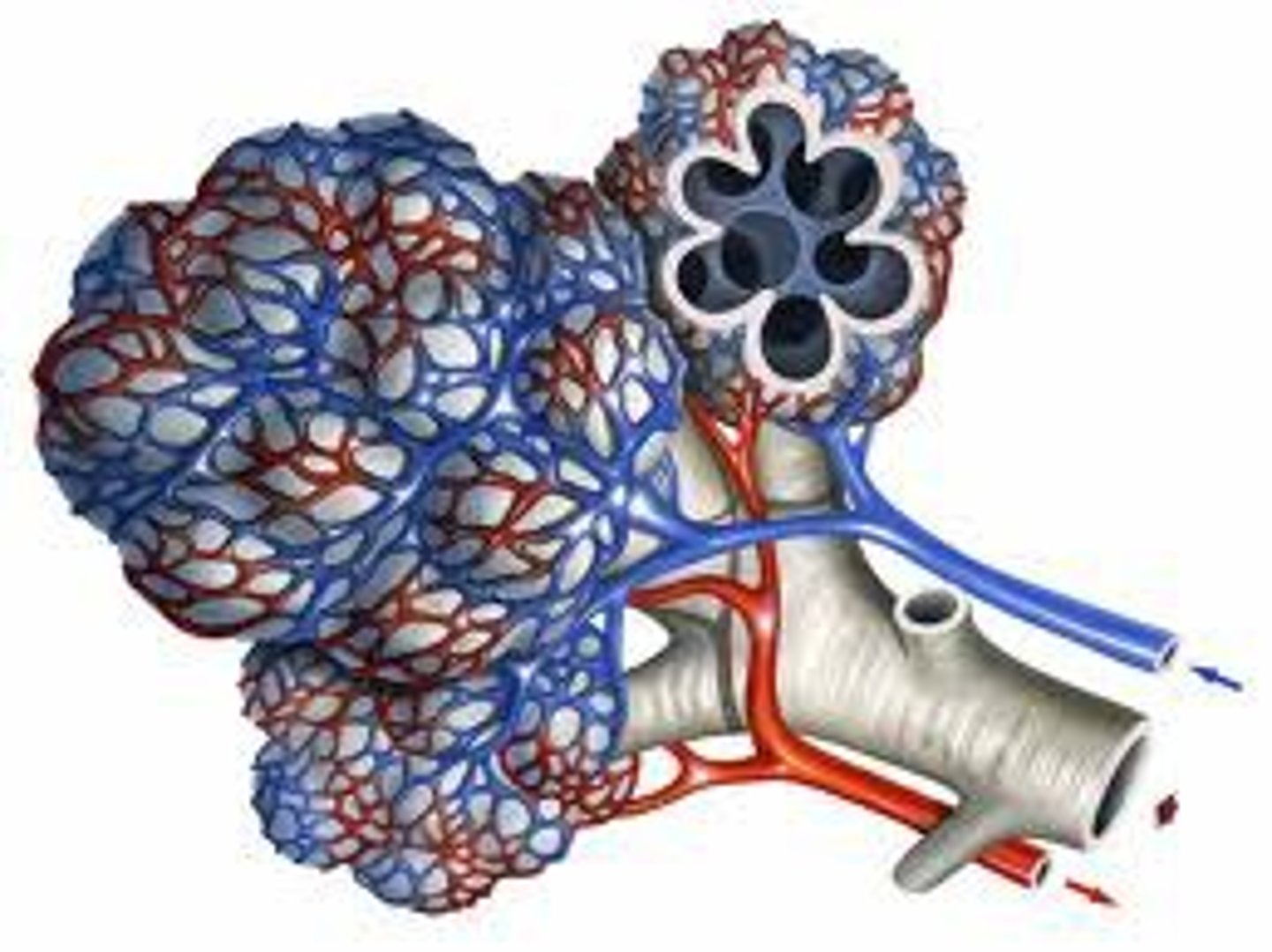
Capillary network
An interconnecting network of capillaries surrounding the alveoli
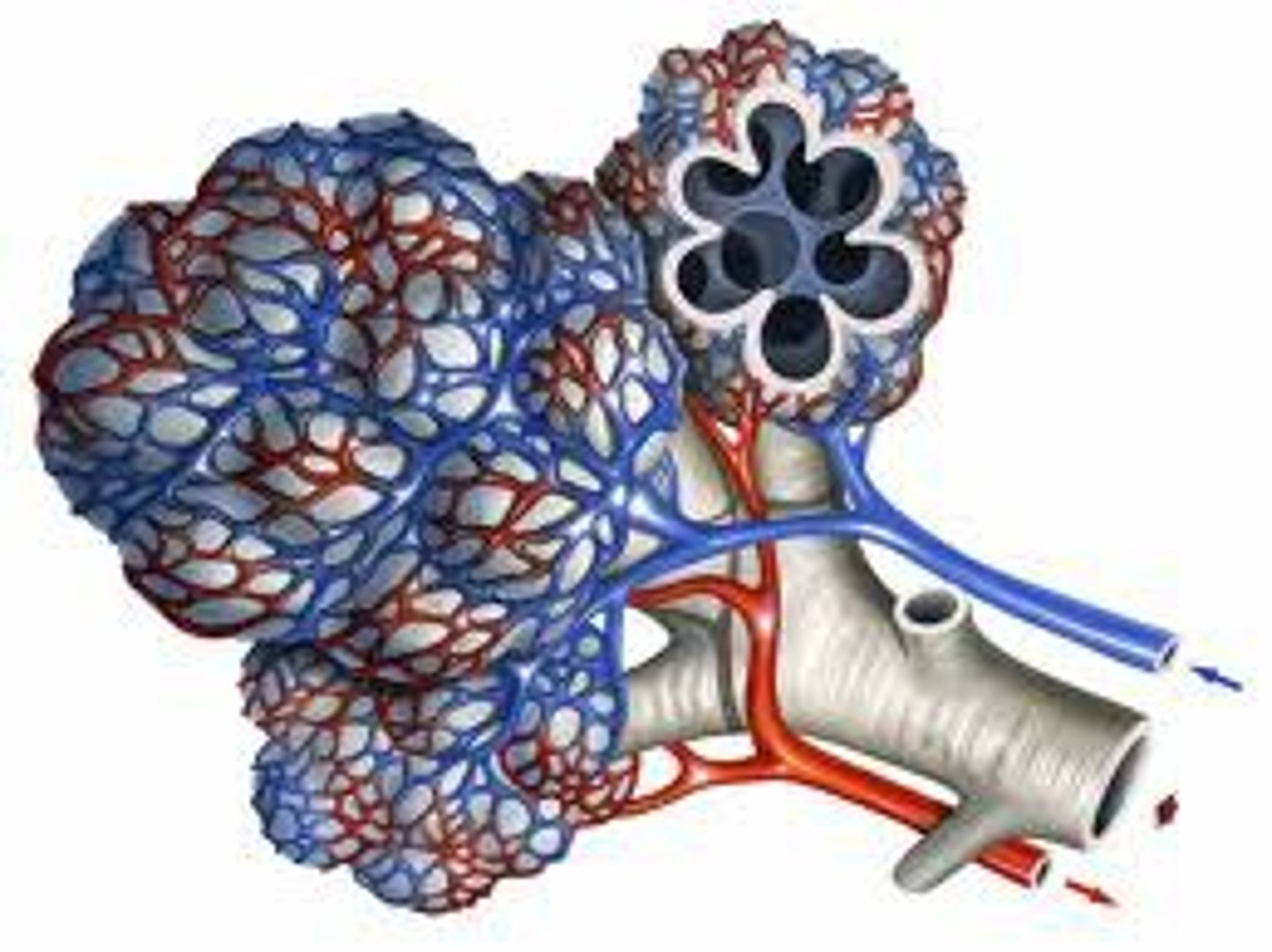
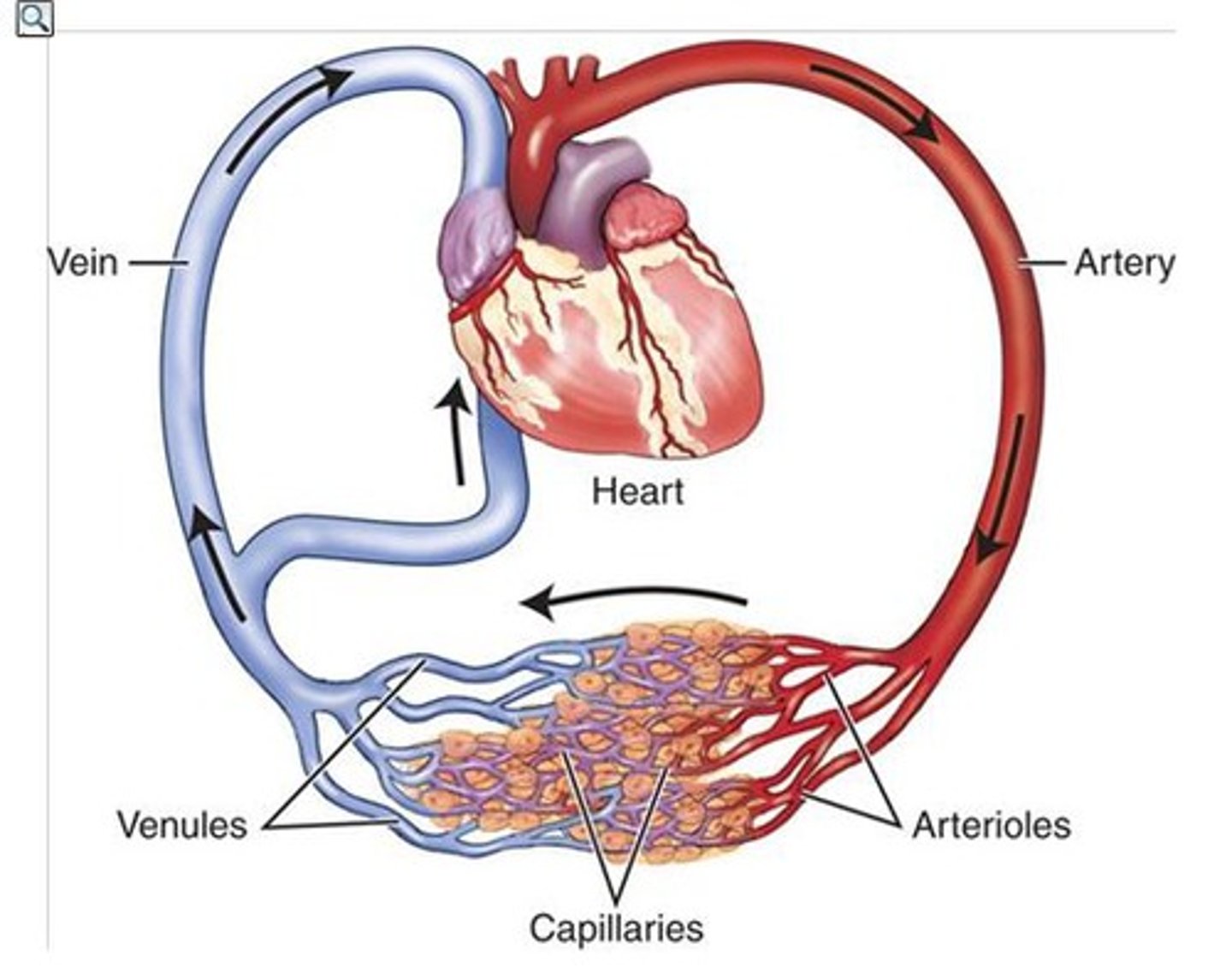
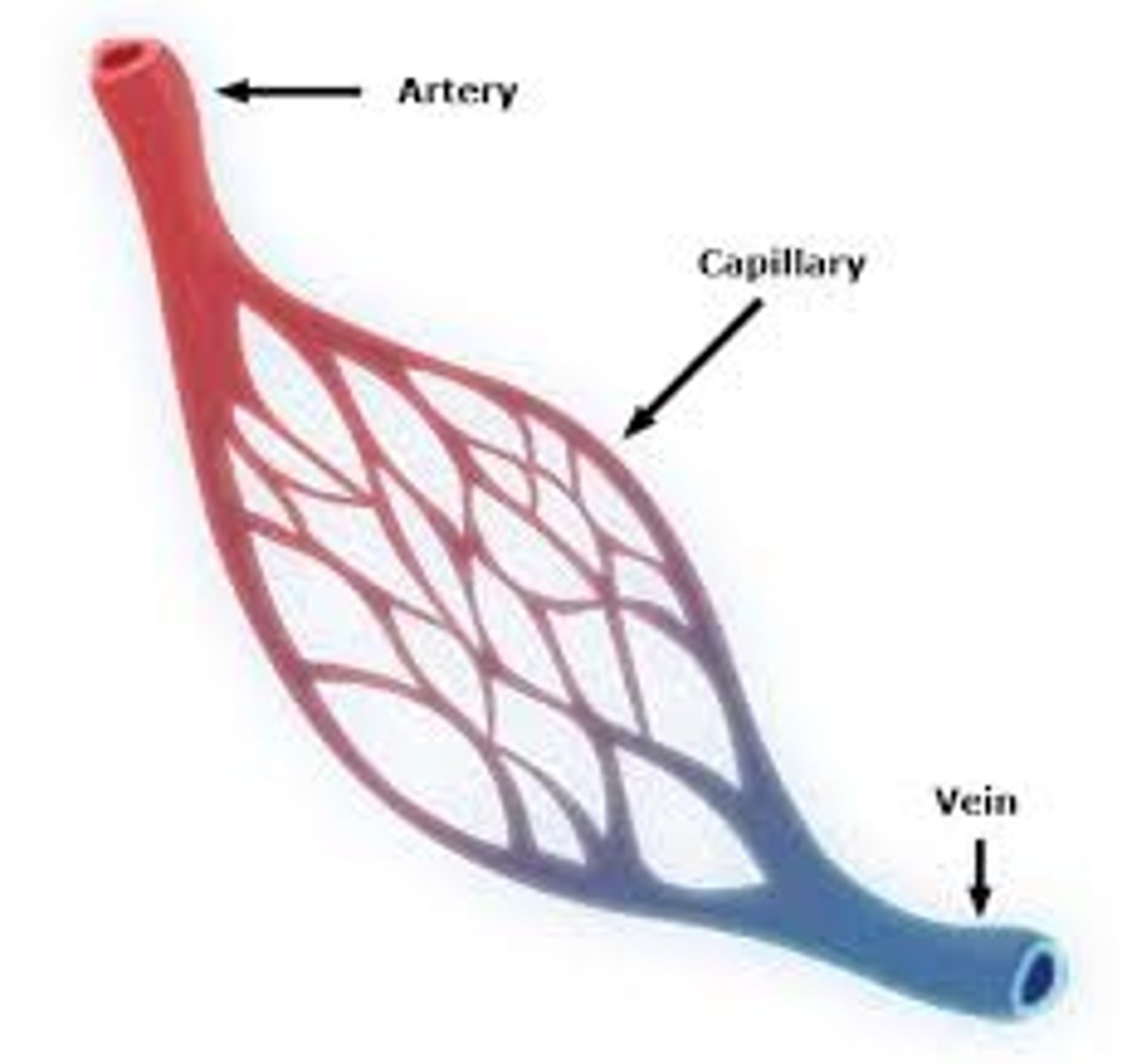
Arteries
Blood vessels they carry blood away from the heart
Veins
Blood vessels that carry blood back to the heart

Capillaries
Smallest and thinnest blood vessels where the exchange of molecules takes place

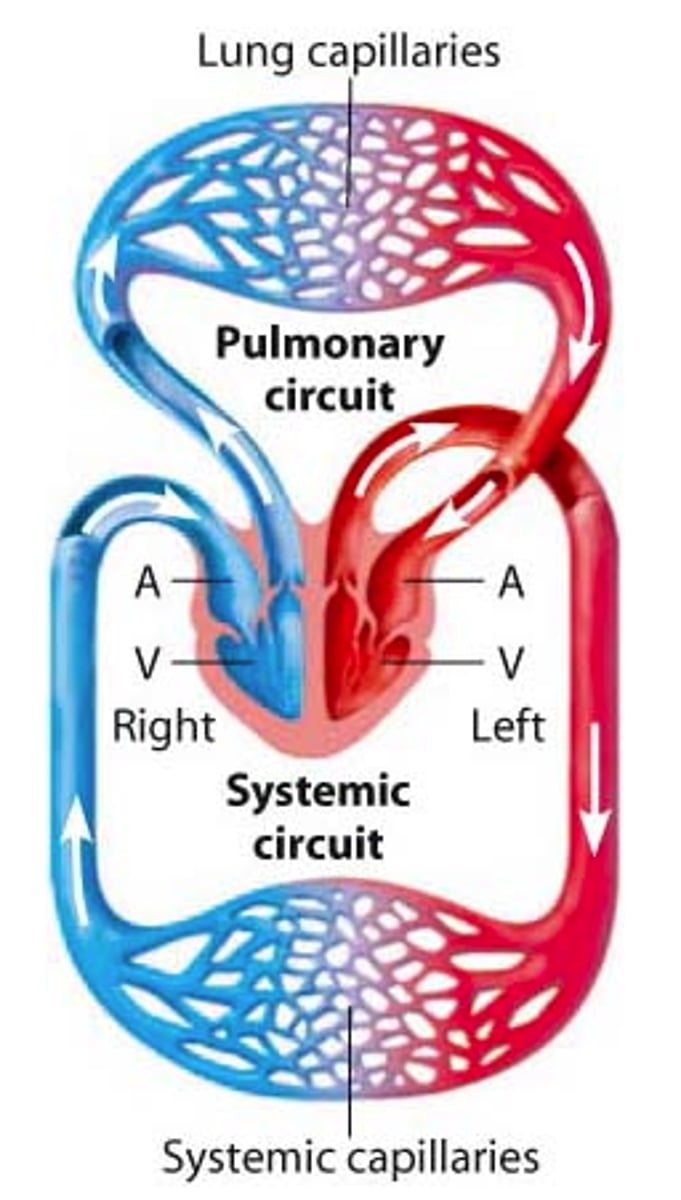
Double circulatory system
The human circulatory system is a double system that has a circuit linking the heart and lungs and a circuit that links the heart to the rest of the body
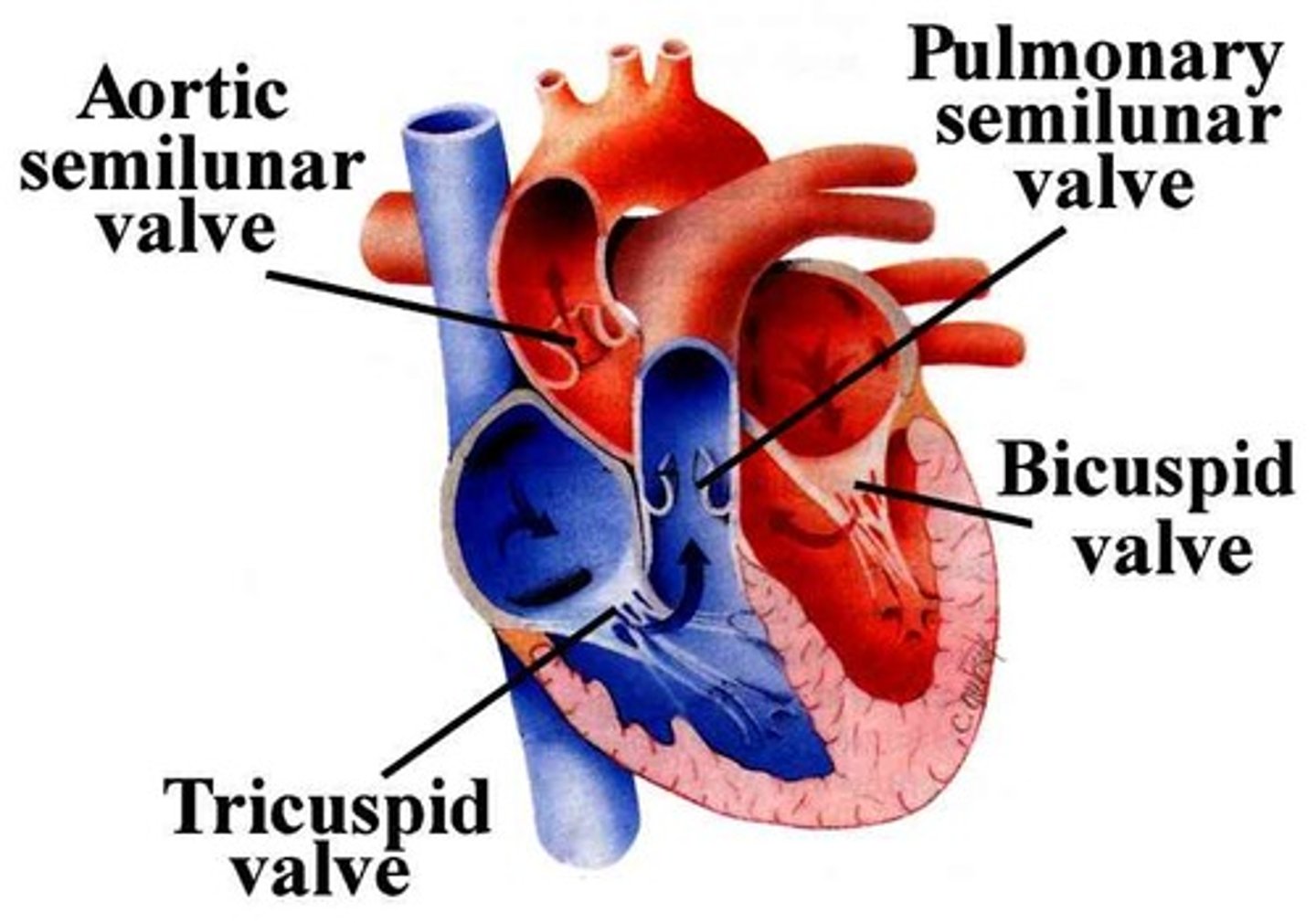
Tricuspid valve
The valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle, its role is to make sure blood flows the correct way through the atrium into the ventricle

Pulmonary valve
The semilunar valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery, it enables a regular flow of blood from the heart to the pulmonary artery and lungs
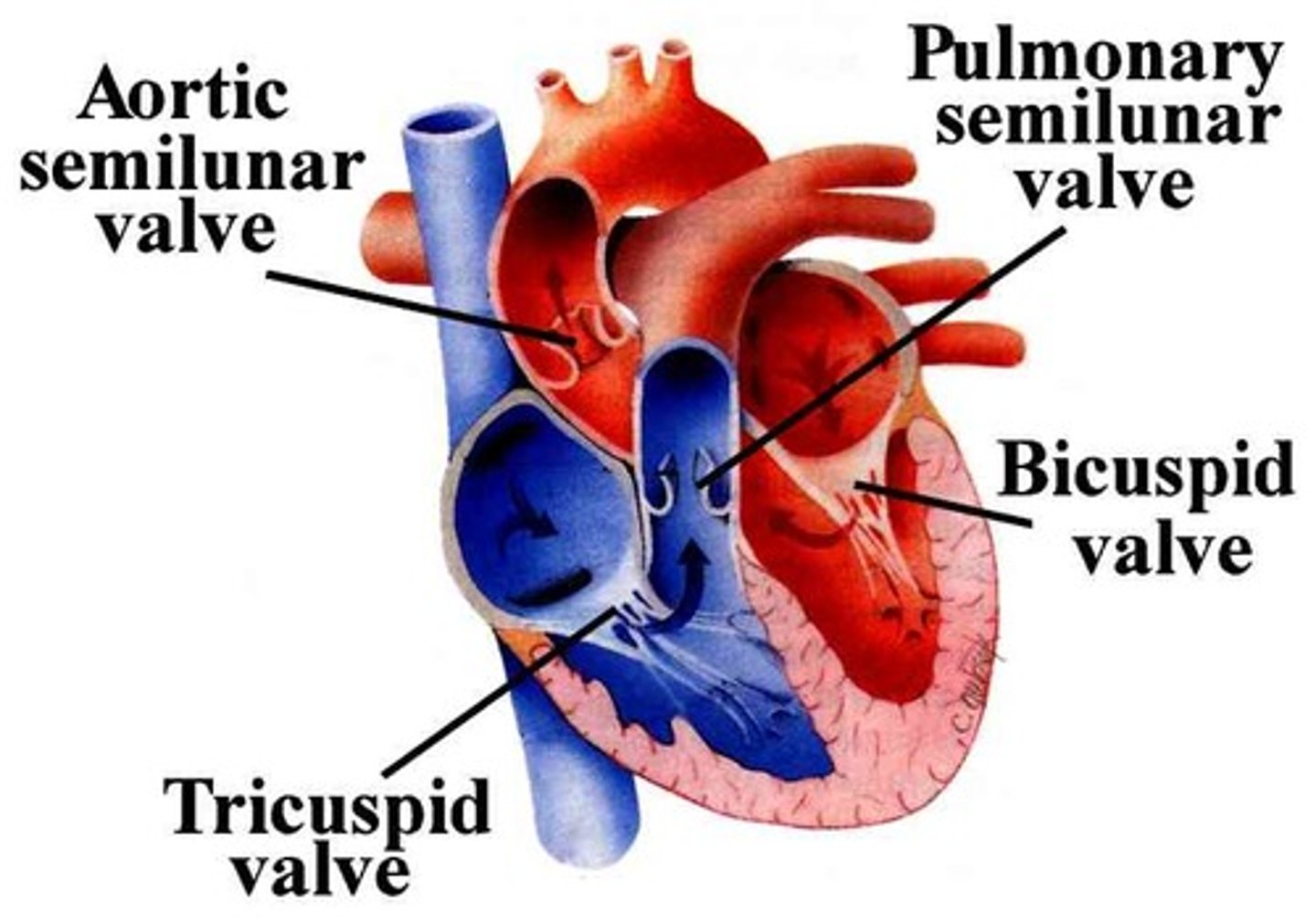
Mitral or bicuspid valve
The bicuspid valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle, its role is to make sure blood flows the correct way through the atrium into the ventricle
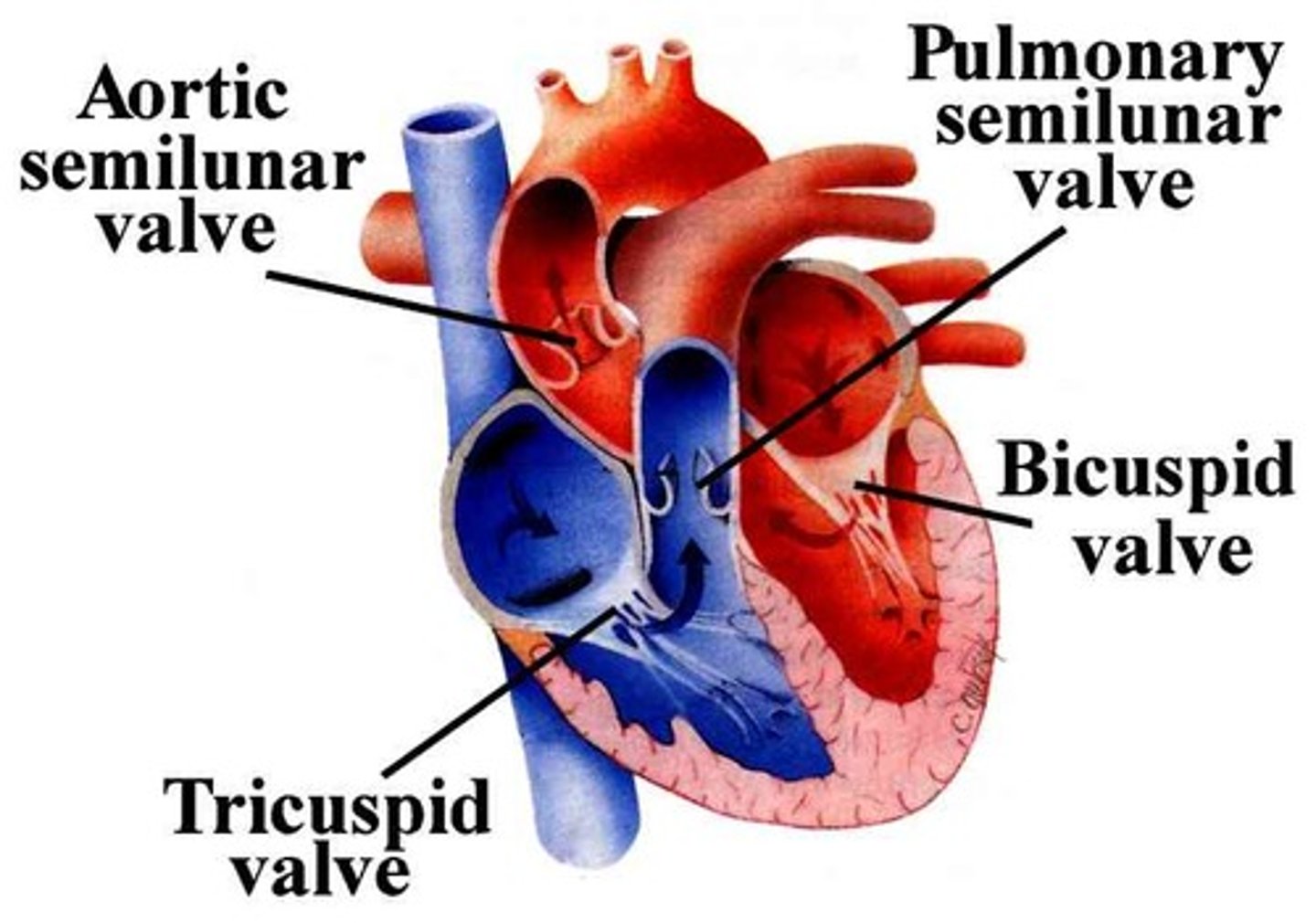
Aortic valve
The semilunar valve separating the aorta from the left ventricle, helps to keep blood flowing in the correct direction so that oxygenated blood can reach the rest of the body via the aorta
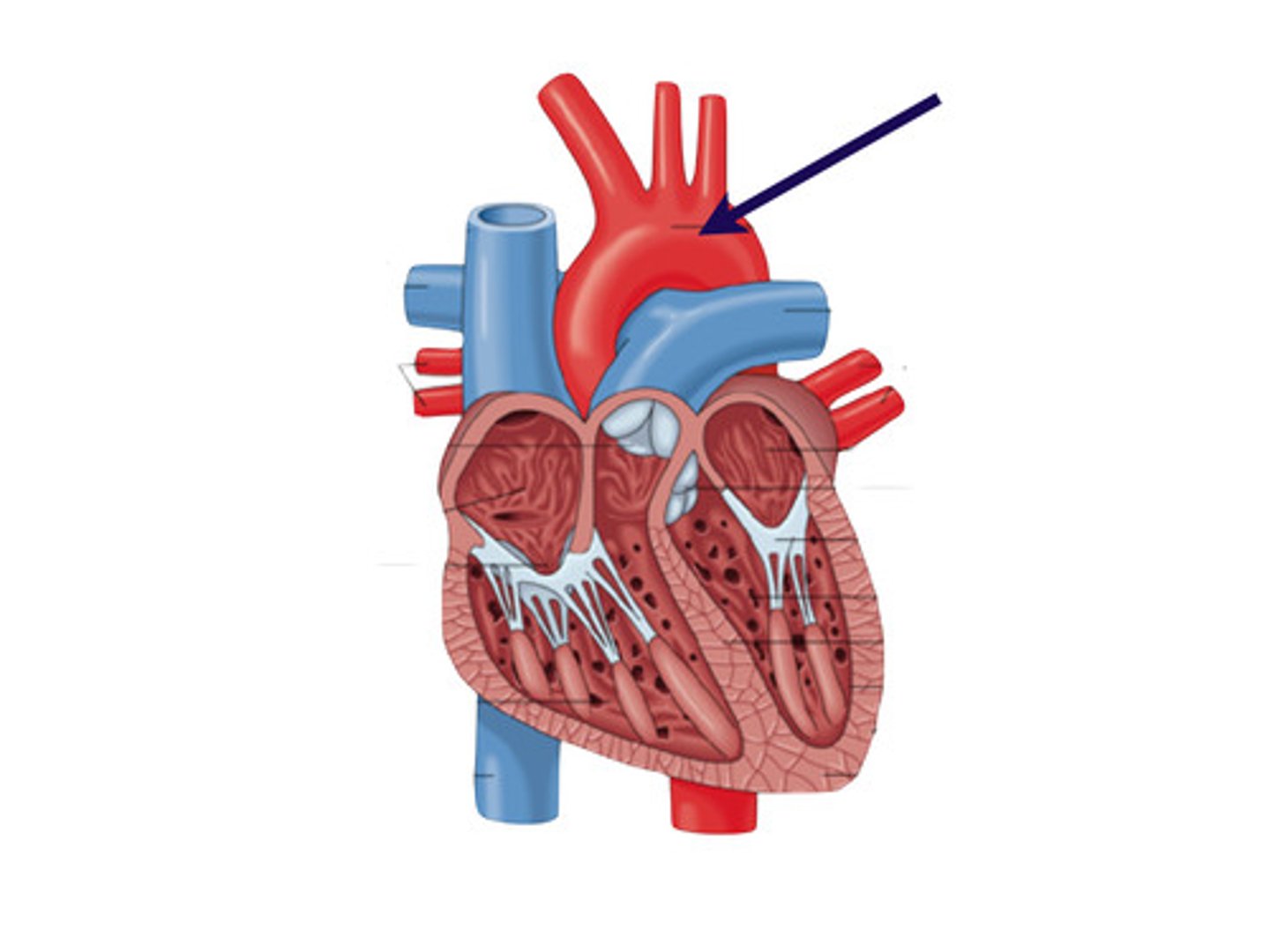
Aorta
The largest artery in the body, carries oxygenated blood to the body from the left ventricle
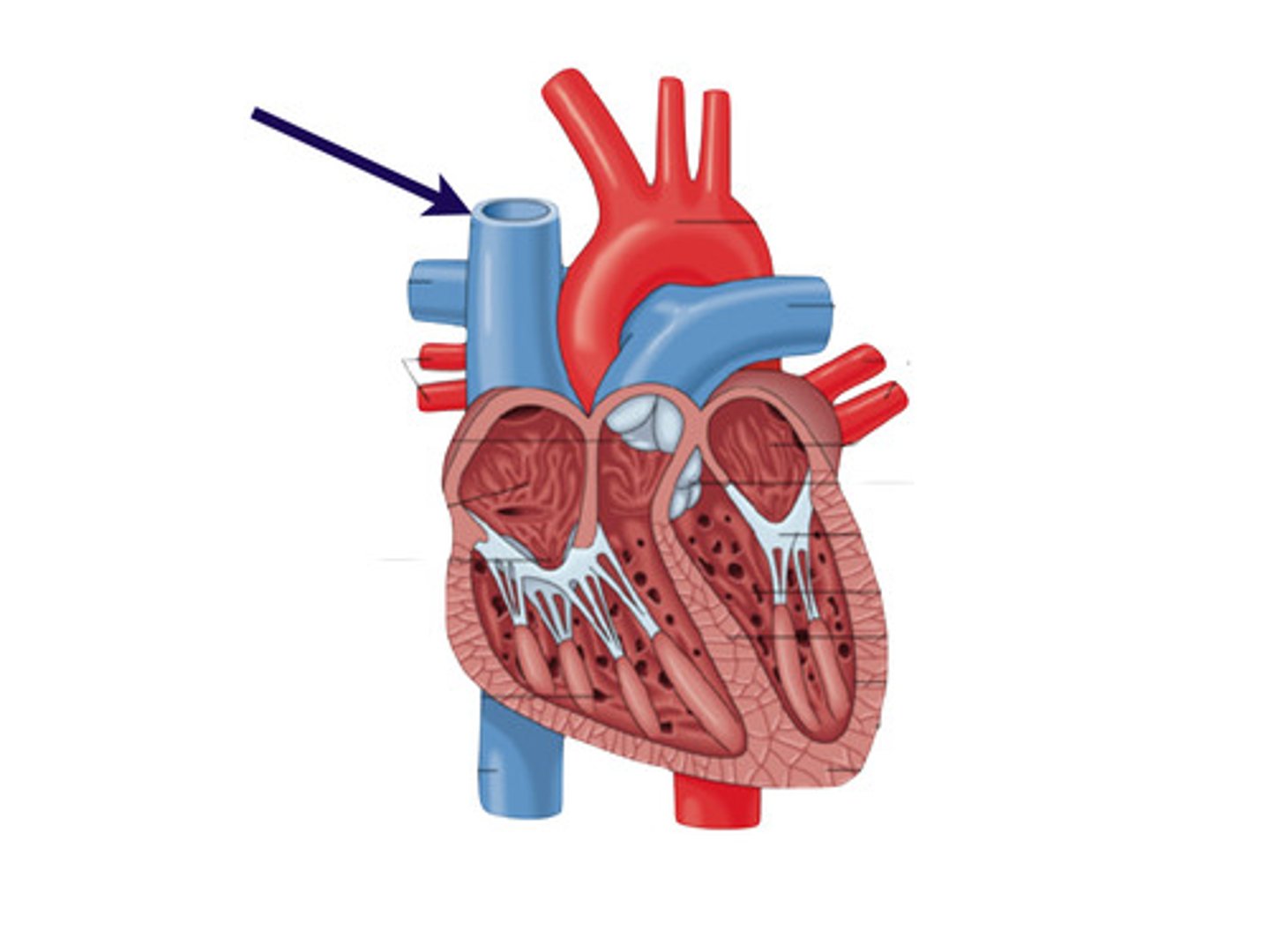
Vena cava
The largest vein in the body, carries deoxygenated blood from the body back to the heart, specifically to the right atrium
Pulmonary artery
Carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
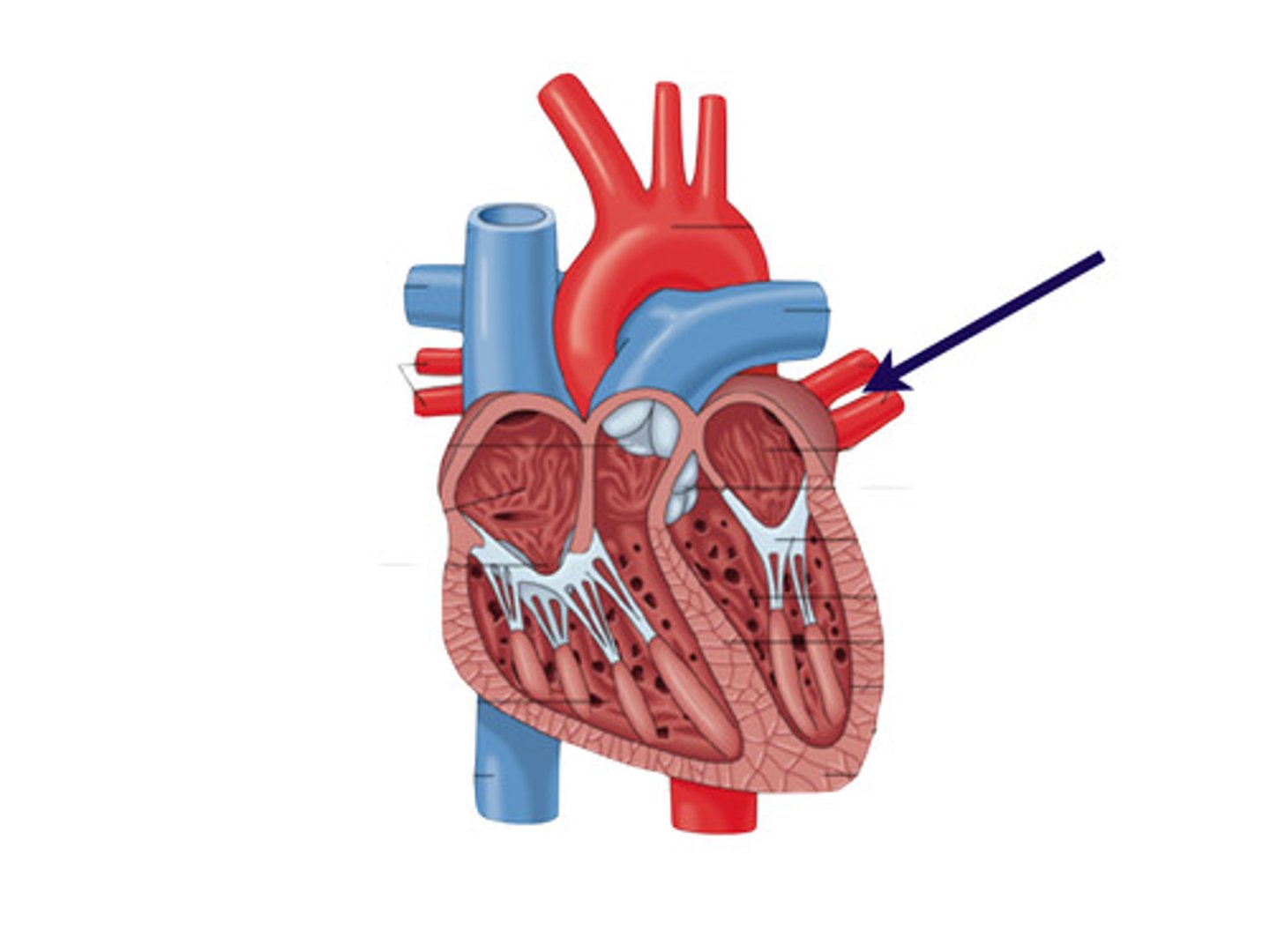
Pulmonary vein
Carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart
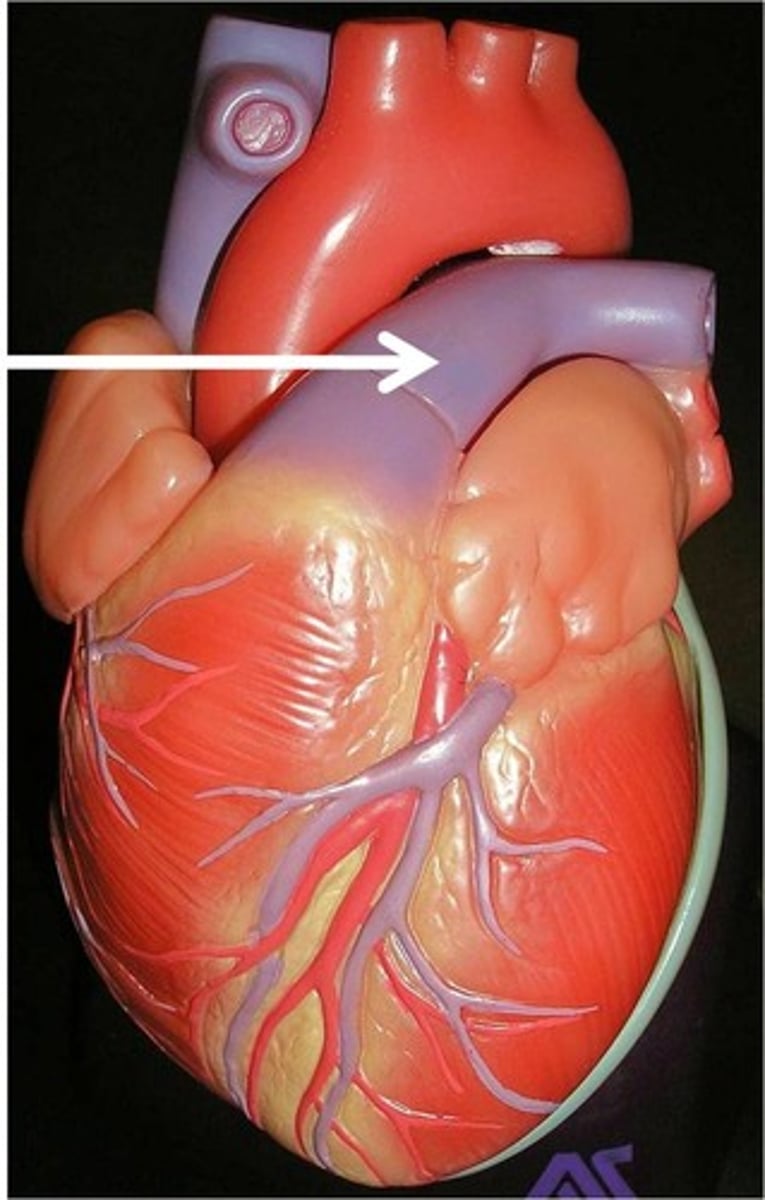
Coronary arteries
Blood vessels that supply the muscle of the heart
Capillary network
An interconnecting network of capillaries surrounding the alveoli
Arteries (with more info about shape and structure)
Blood vessels with thick walls, a narrow lumen and elastic fibres, they carry blood away from the heart

Veins features
Blood vessels with valves to prevent the back-flow of blood, thin walls and a large lumen, they carry blood back to the heart
Capillaries(___ exchange answer)
Smallest and thinnest blood vessels where the exchange of molecules takes place, they consist of a single layer of cells
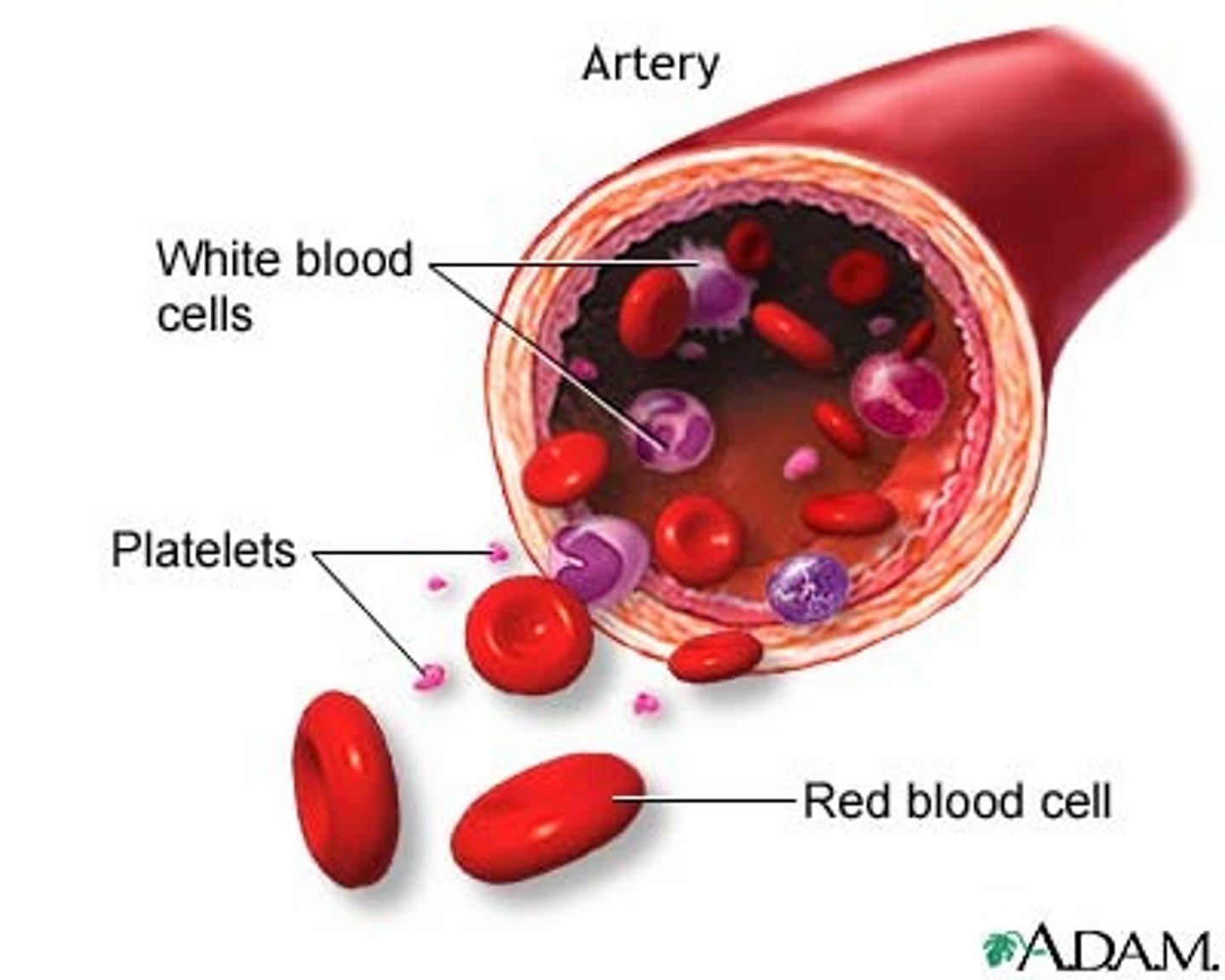
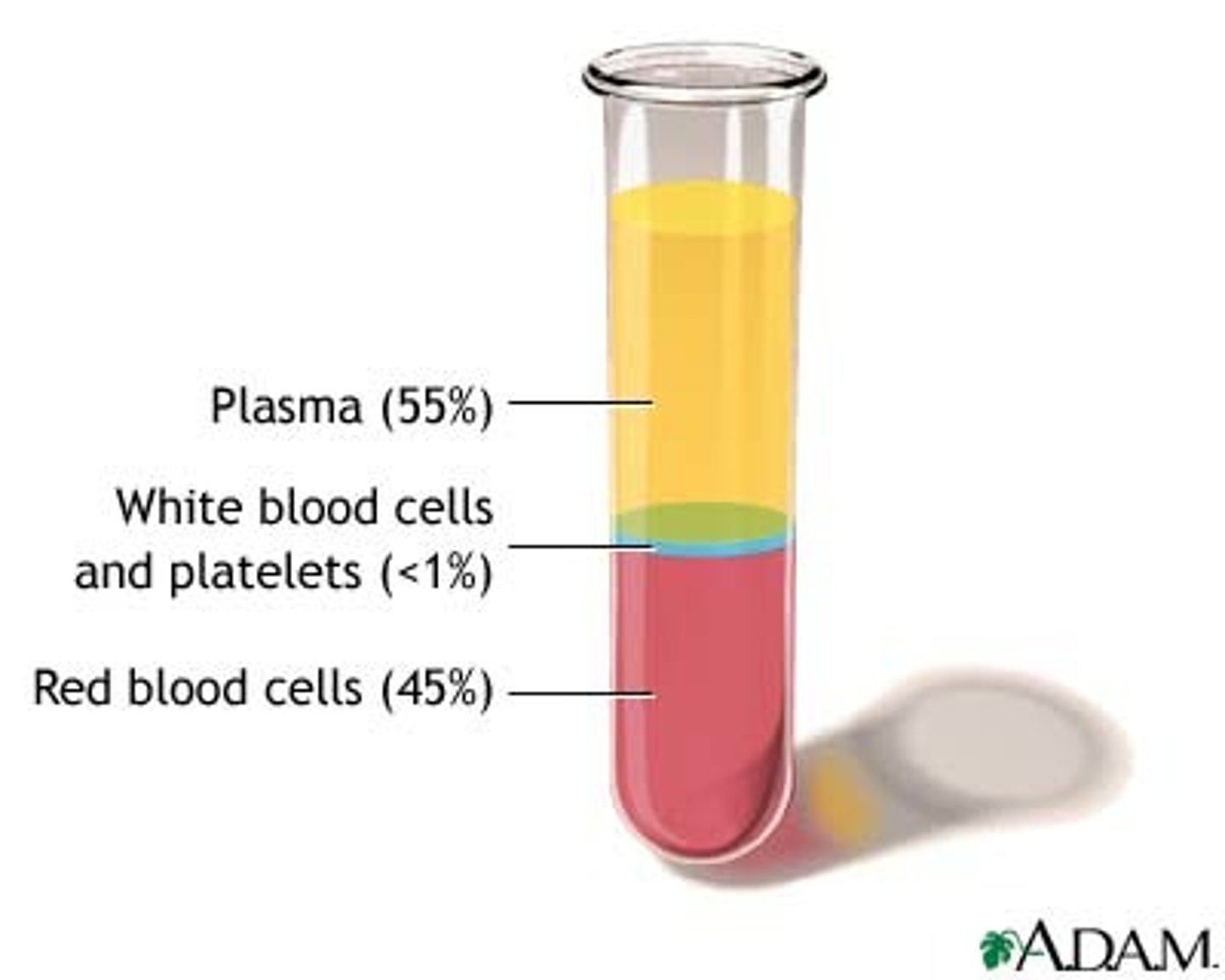
Blood
Connective tissue made of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets
Plasma
The liquid part of blood
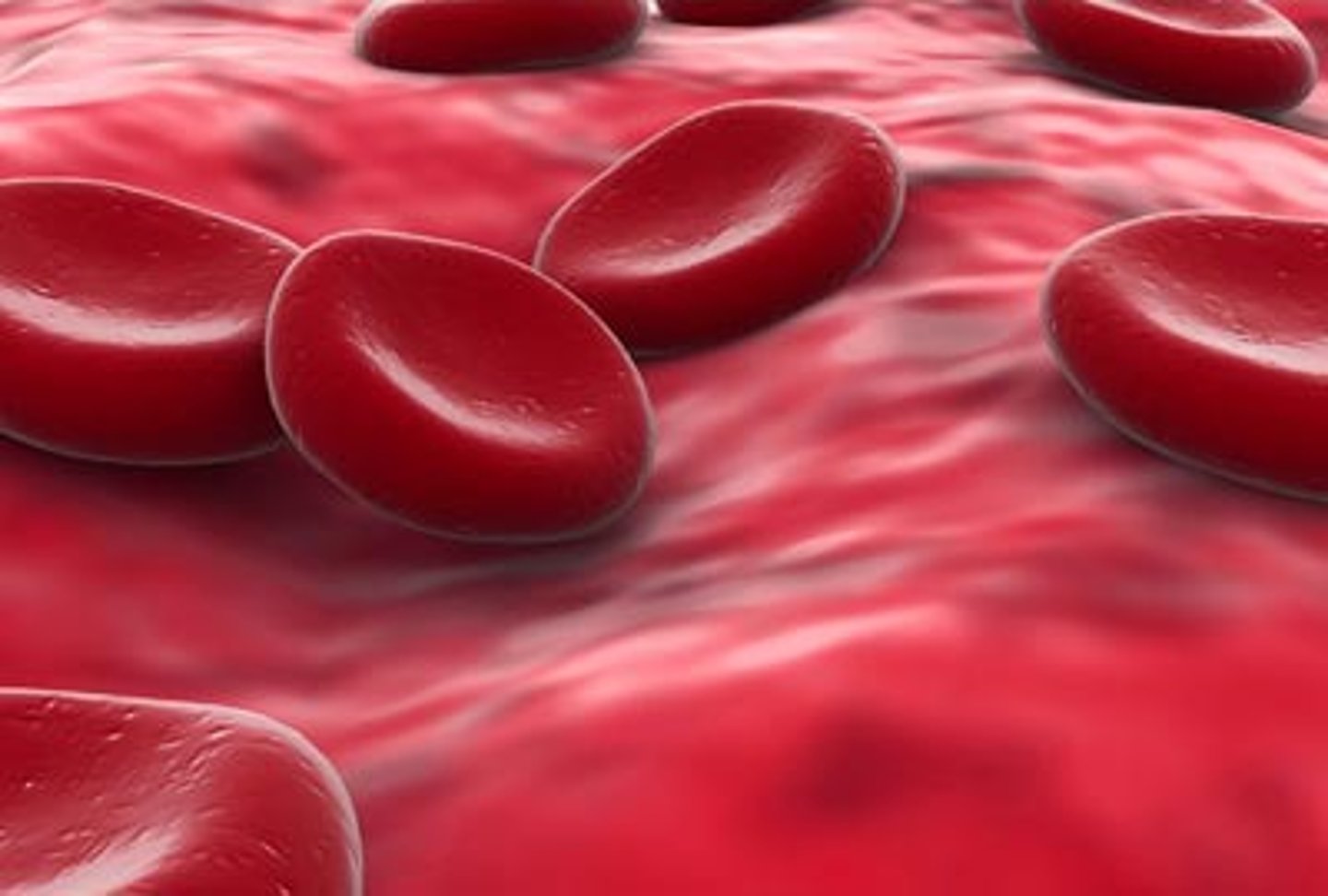
Red blood cells
Blood cells that carry oxygen from the lungs to the body cells, they have lost their nucleus to make space for haemoglobin
Haemoglobin
Protein molecule in the blood responsible for carrying oxygen around the body

White blood cells
Blood cells that help destroy disease-causing microorganisms

Platelets
Particles in the blood needed for blood clotting
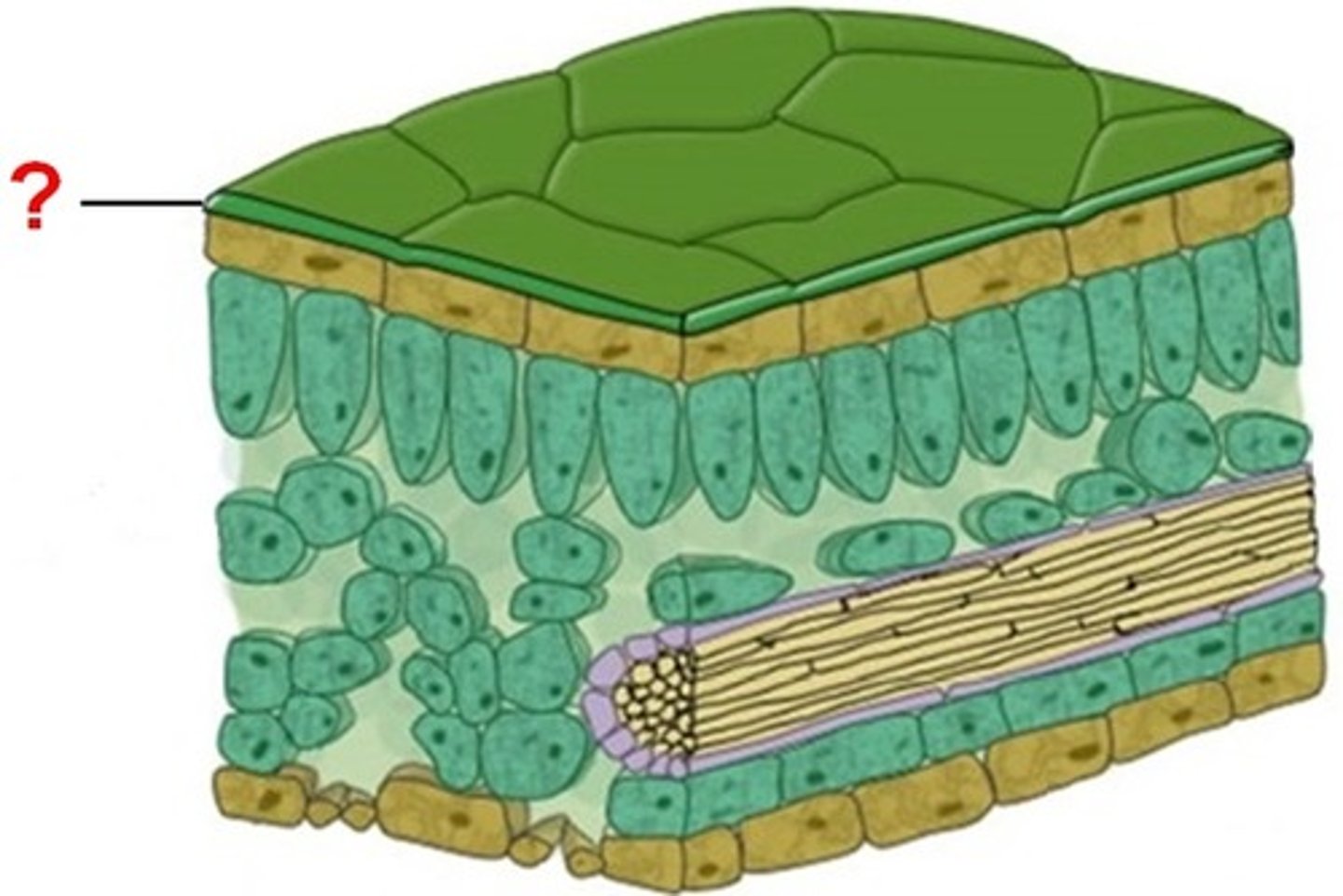
Epidermal tissue
Tissue that covers and protects the plant
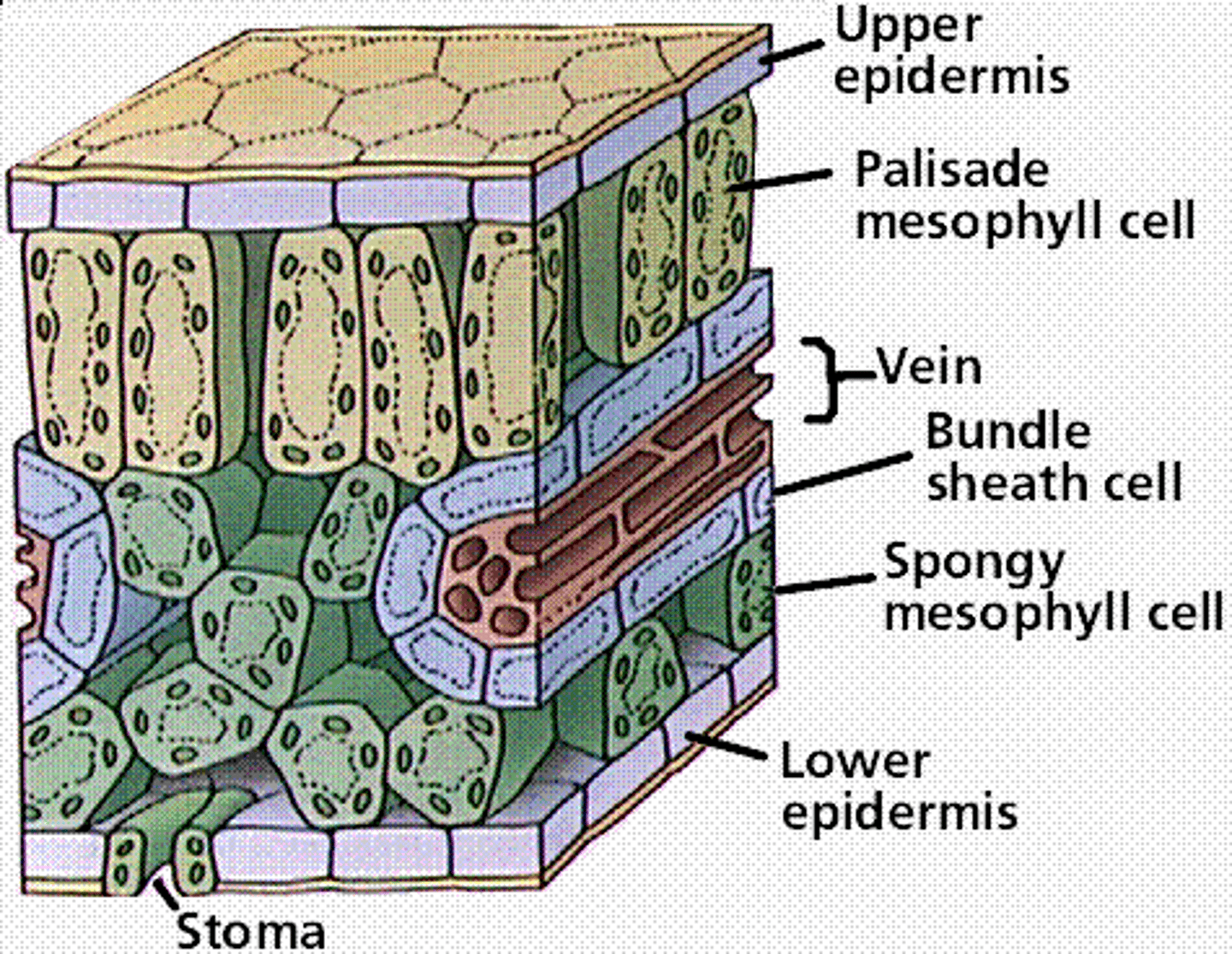
Waxy cuticle
A layer on the surface of the leaf which protects the plant and reduces water loss, thicker on the upper surface
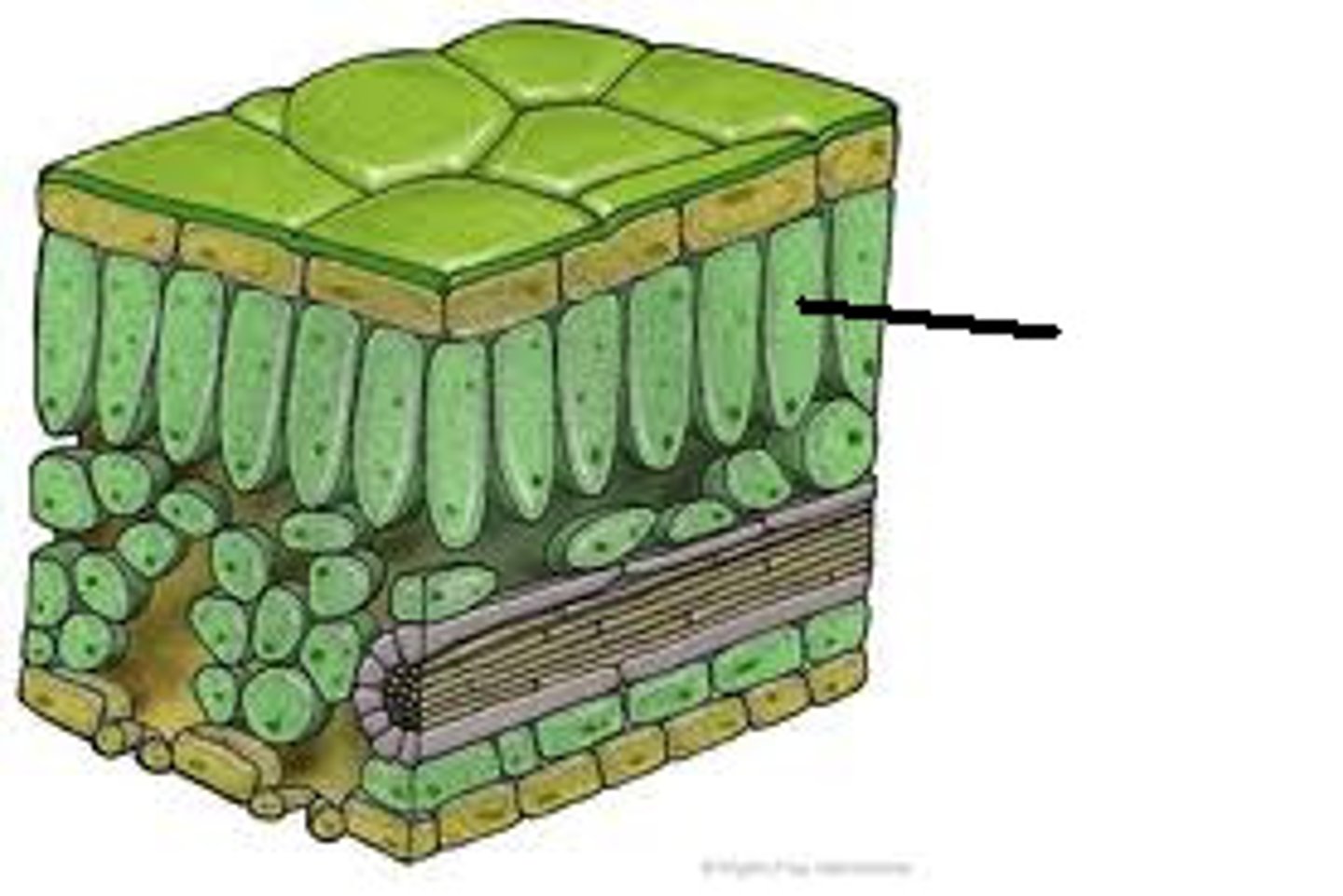
Palisade mesophyll
Photosynthetic tissue below the epidermis in a leaf, palisade cells contain high concentrations of chlorophyll and high quantities of chloroplasts for photosynthesis
Spongy mesophyll
Layer of tissue found beneath the palisade mesophyll that is packed loosely for efficient gas exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen

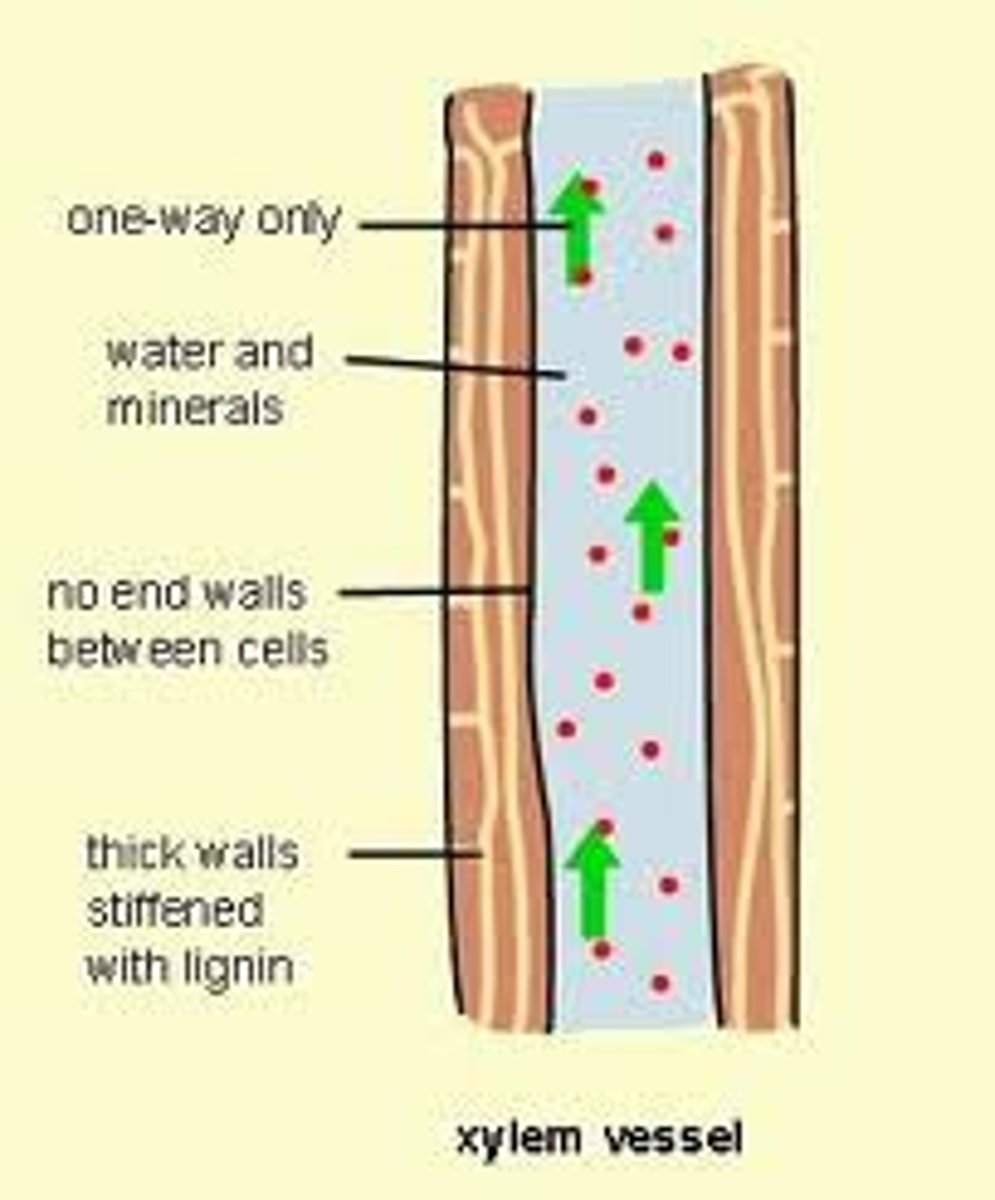
Xylem
Non-living vascular tissue that carries water and dissolved minerals from the roots of a plant to its leaves, the xylem is hollow and nearby cells are lignified or dead so water can move continuously
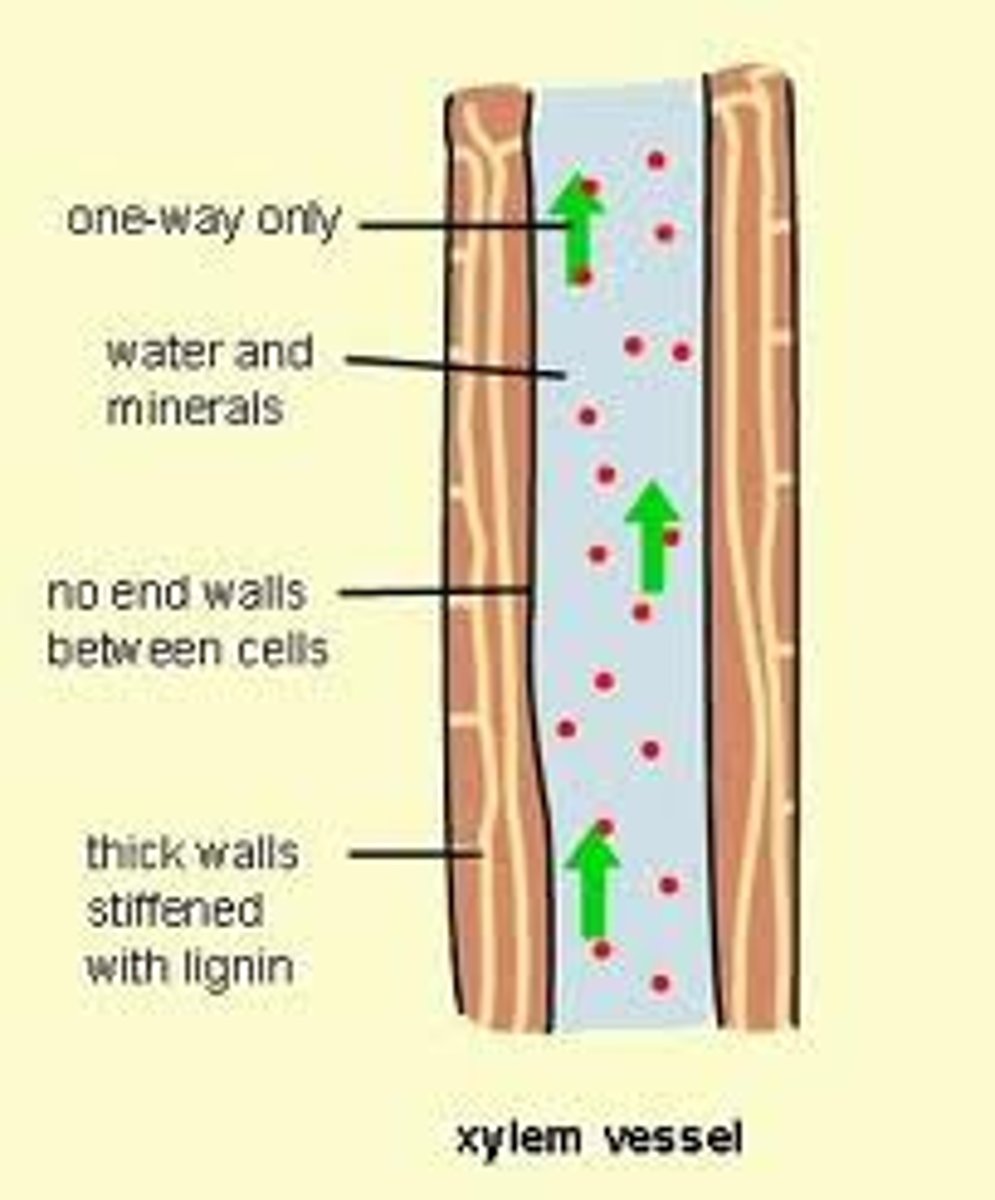
Lignin
A chemical that provides support to xylem cells and prevents the unwanted movement of water into nearby cells
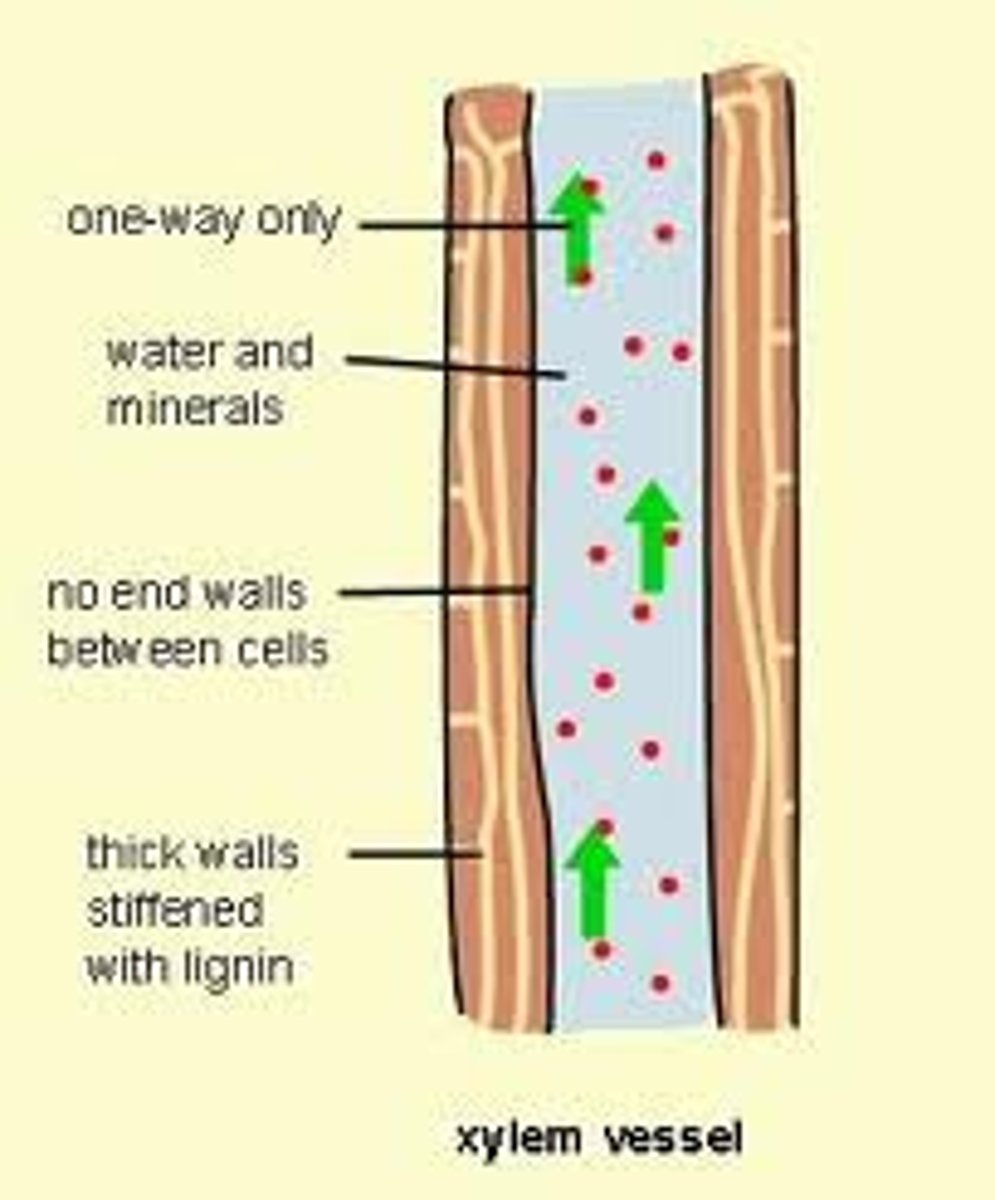
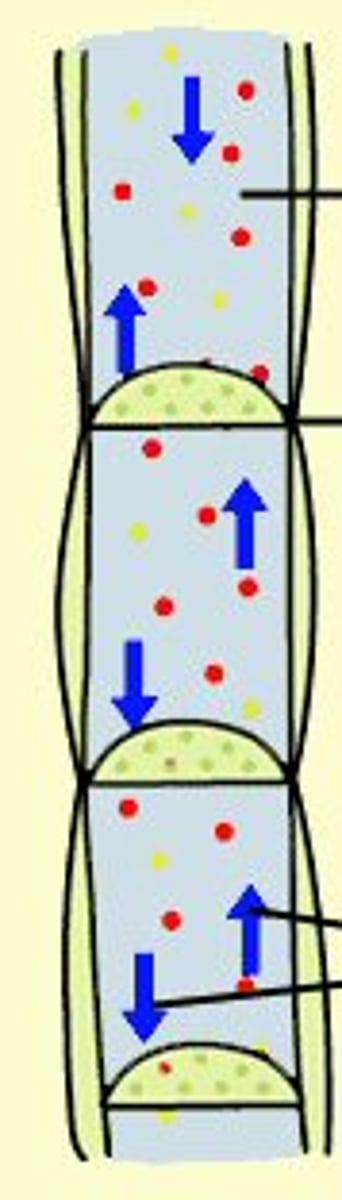
Phloem
Living and elongated vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant, the phloem has sieve plates that act as pores to allow molecules to diffuse between cells
Meristem
Undifferentiated plant tissue from which new cells are formed, found in the shoots and roots

Shoots
The aerial portion of a plant body consisting of stems, leaves and flowers

Roots
Underground plant organs that absorb water and minerals

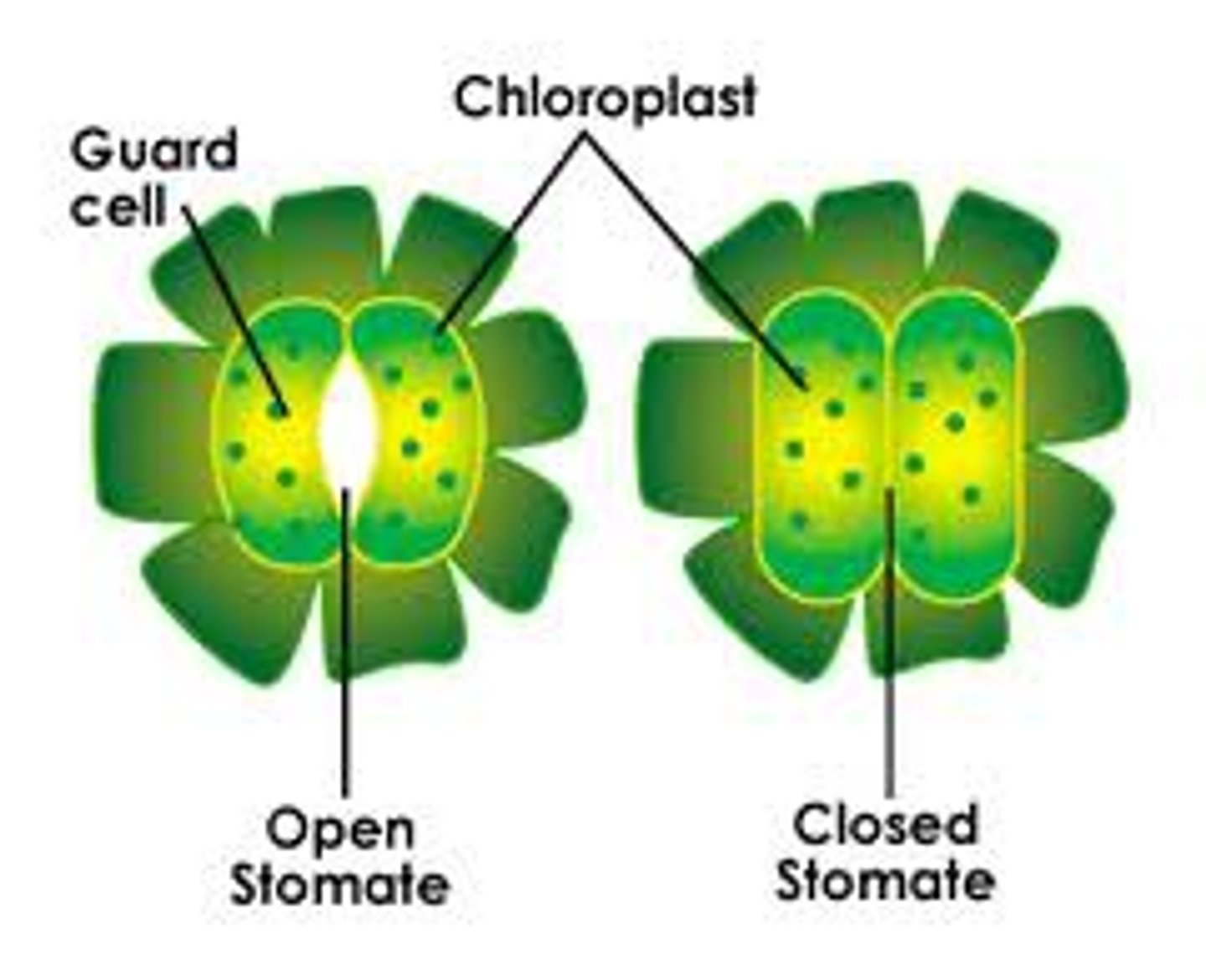
Stomata
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen, carbon dioxide and water can move
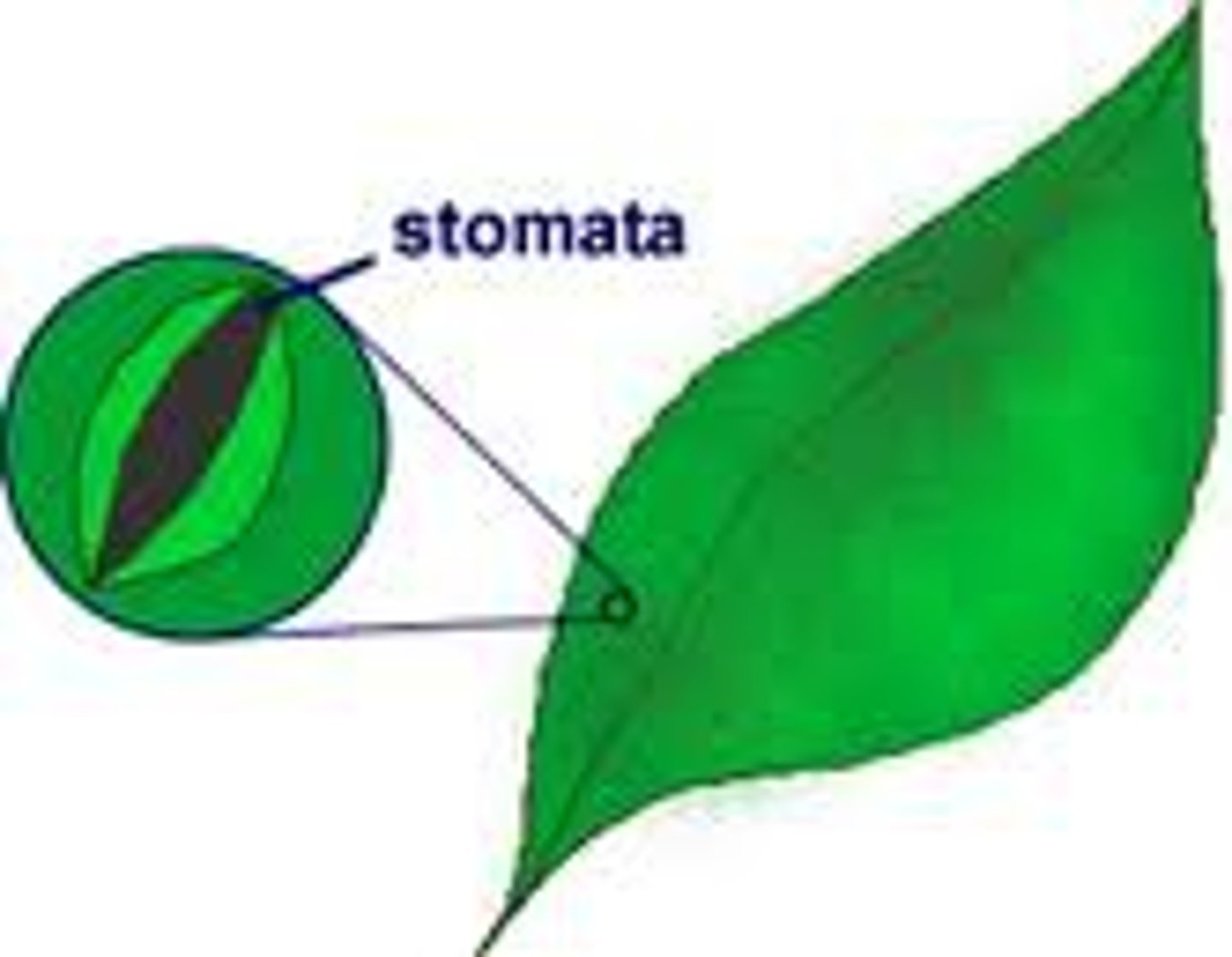
Guard cells
Pairs of cells that surround the stomata and control their opening and closing to optimise gas exchange and reduce water loss

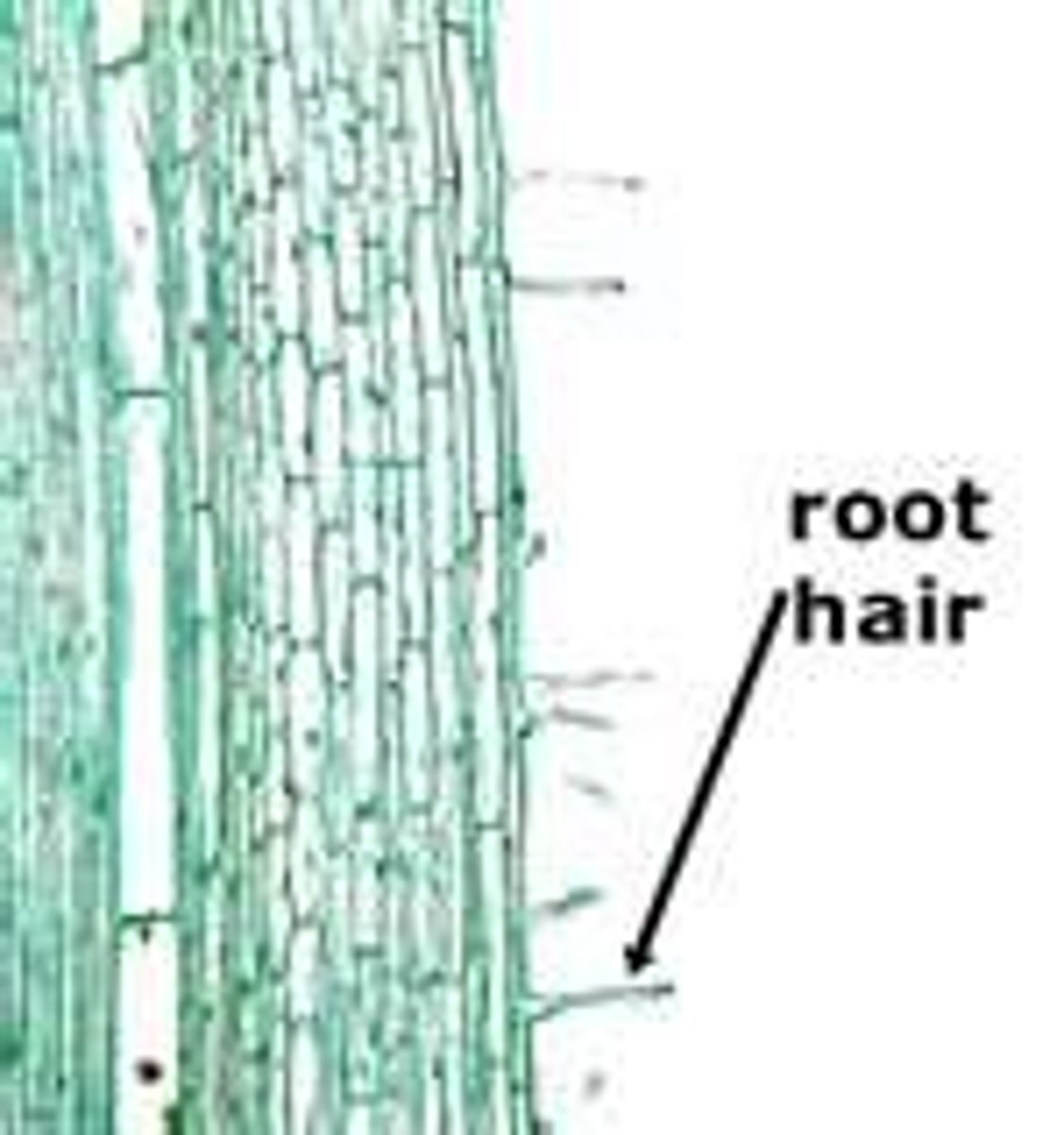
Root hair cell
Cells that absorb water and mineral ions from the soil, via diffusion, osmosis or active transport using structures with a large surface area
Transpiration
The process of the movement of water through a plant and the loss of water from a plant through its leaves
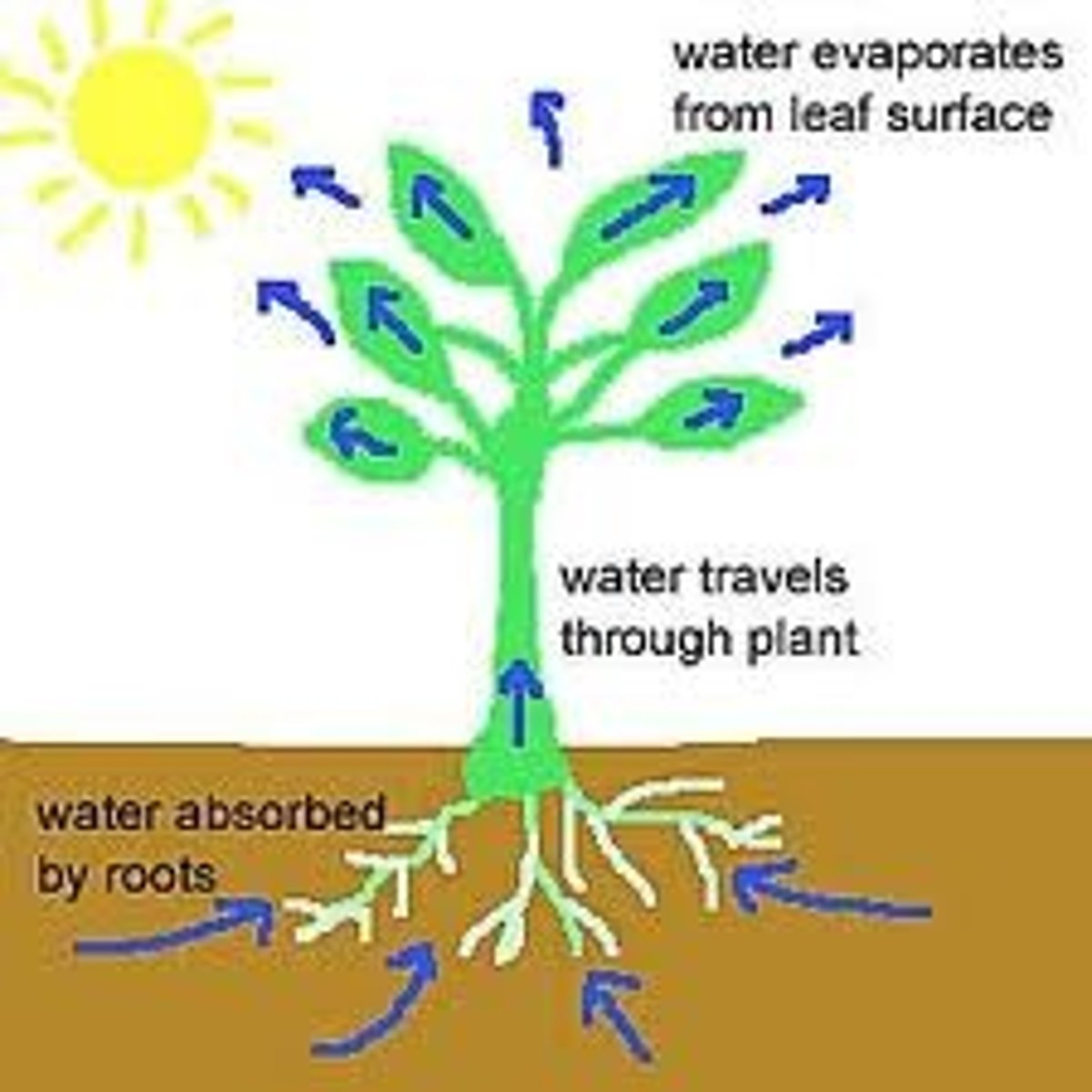
Factors affecting transpiration
Changing temperature, humidity, air movement and light intensity
Rate of transpiration
The rate of water loss from a plant
Effects of factors affecting transpiration
Light, wind and heat will increase the rate of transpiration, humidity will decrease the rate of transpiration
Potometer
A device used for measuring the rate of water uptake of a plant due to photosynthesis and transpiration, a bubble of water will move along the potometer to indicate the rate of transpiration

Translocation
The transportation of sugars and amino acids around the plant via phloem tissue, sugars are prone to translocation as they are made in the leaves and needs to be transported around the plant