Course introduction History of Evolutionary Theory
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Fundamentally, evolution is:
Change through time
Charles Darwin was:
Well-read, well-connected, tried medical school and was hired as a naturalist aboard the HMS Beagle and published the Origin of Species
What was a common hobby among people in the 1800
Natural history
What are two pre-Darwinian western world views
Stasis and “the earth is young”
What does the stasis theory suggest
The fixity of species (Christianity) - all life forms were created by God exactly as they exist in the present world and Great Chain of Being (Aristotle) - all life forms can be placed in a hierarchy from simple to complex with humans at the top
What is the Earth is young theory?
Created by Archbishop James Ussher - analyzed Genesis and estimated that the earth began Sunday October 23rd, 4004 B.C (from the bible)
What is the chronological order in the Chain of Being?
Divine being, angels, humans, animals, plants and minerals
How did the Scientific Revolution contribute to evolution
Began a slow process of changing how we think about the world and it’s inhabitants, development of the Scientific Method, discovery of the New World (North and South America) challenged fundamental views about the planet and exposure to new plants and animals increased awareness of biological diversity
Who was Carolus Linnaeus
First tried to classify organisms and wrote “Systema Naturae” and was considered the father of taxonomy
What impact did Linaeus’s “Systema Naturae” have on evolution?
Created binomial nomenclature (Genus species -ex: Homo sapiens), recognized 42 species of primate in only 3 genera: Homo, Simia or Lemur and placed humans among other “species”
Who was Erasmus Darwin
Charles Darwin’s grandfather, physician, natural historial, poet and wrote “Zoonomia” which suggested that species may have evolved from a common ancestor
Who was Georges Cuvier
First real palaeontologist, established vertebrate paleontology and comparative anatomy as disciplines, ended the debate about whether extinction could occur using fossil evidence and began the long and ongoing study of the earth’s fossil record
Who was Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Early advocate of evolution of species, posited that as the environment changes animals change subsequently through the use/disuse of structures and inheritance of acquired characteristics
Who created the Giraffe hypothesis?
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck
Although Lamarck’s Giraffe theory was false:
He deserves credit for the first cohesive evolutionary theory, complete with mechanism (we now know the mechanism to be incorrect)
Who was Thomas Malthus
Political economist/demographer, wrote an essay on the Principle of Population, suggested that populations grow exponentially in times of plenty; but eventually are checked by famines diseases etc and also suggested that social ills are caused by the overproduction of children and moral irresponsibility of lower class
What is a quote from Thomas Malthus about population
“The increased of population is necessarily limited by the means of subsistence”
What are Malthus’s impacts on biology
Direct influence on Darwin: plant and animal populations produce more offspring than can survive and there will be competition to survive
Who was Charles Lyell
Developed principle of Uniformitarianism - same geologic processes that influence the Earth today (ex: erosion) influenced it in the past and he also indicated that the Earth was very old - at the time the prevailing view was that the earth was only ~6k years old
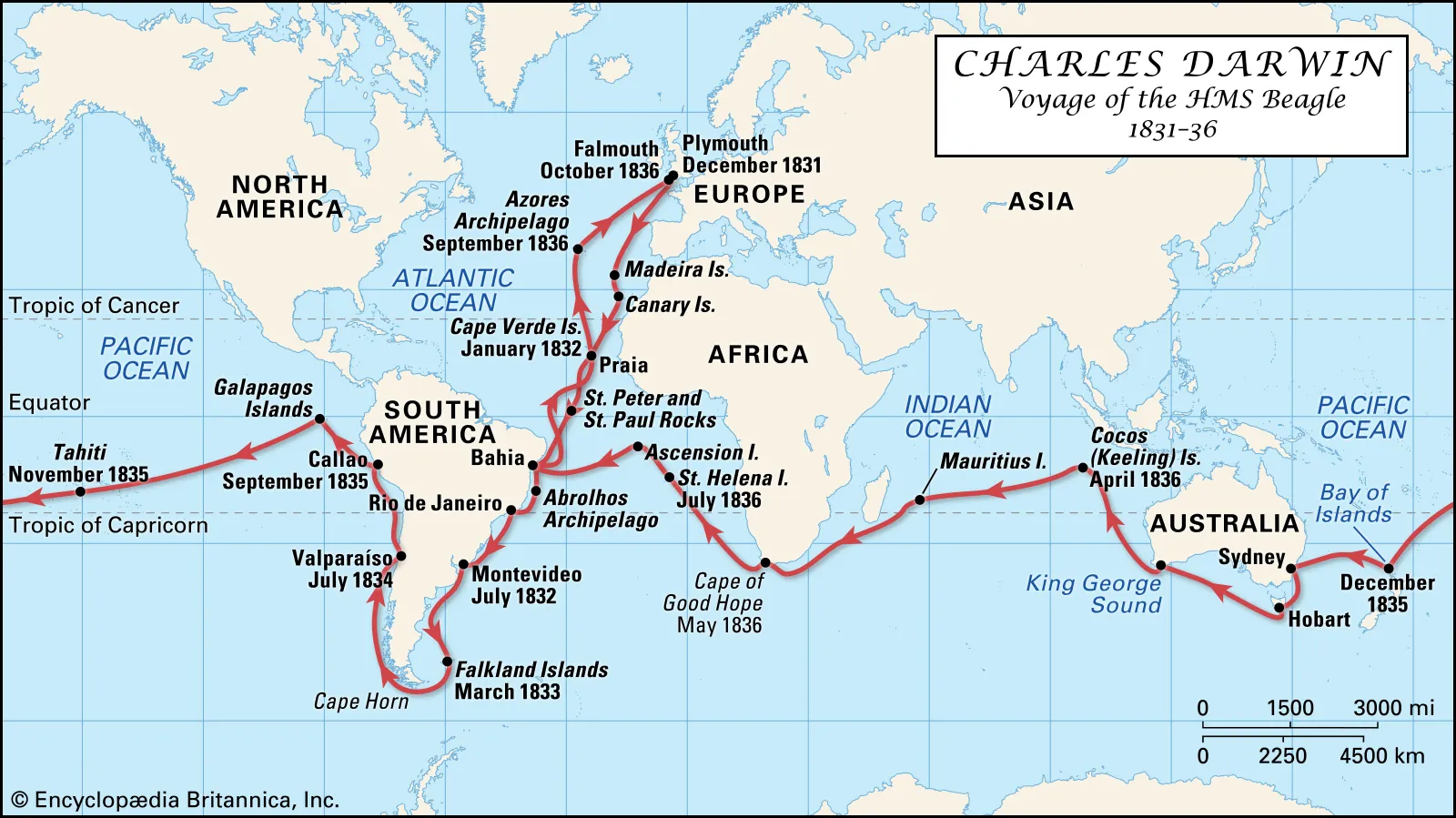
Darwins voyage on the beagle:
Who was Alfred Russel Wallace
A correspondent of Darwin later in life, ship naturalist (Brazil, Malaysia, Indonesia) and independently developed idea of natural selection
How did Wallace and Darwin collaborate
Wallace sent Darwin a draft and Lyell brokered agreement between Darwin and Wallace for simultaneous presentation at the Linnaean society
How did Lyell influence Darwin
Earth old enough for significant changes to have taken place
How did Lamarck influence Darwin
Biological change over time
How did Malthus influence Darwin
Organisms compete over limited resources
What were some of Darwin’s own influences on his studies
His identity and background, general reading and correspondence and his own experiences as a naturalist