ch 4 lecture
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
Tissue
A group of similar cells that usually have a similar embryological origin and are specialized for a particular function
Histology
The science that deals with the study of tissues
interstitial growth (cartilage)
Chondrocytes grow and divide, laying down more matrix inside the cartilage. This type of growth mainly occurs during childhood and adolescence.
appositional growth (cartilage)
Cartilage grows in diameter when new matrix is added to the surface of the existing tissue
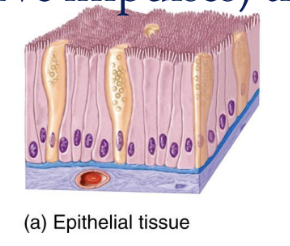
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces, lines hollow organs, body cavities, and ducts; forms glands
Cells are tightly packed together with little or no extracellular matrix
No blood vessels, so this is found directly adjacent to blood vessel rich connective tissue
almost always form surface layers and are not covered by another tissue
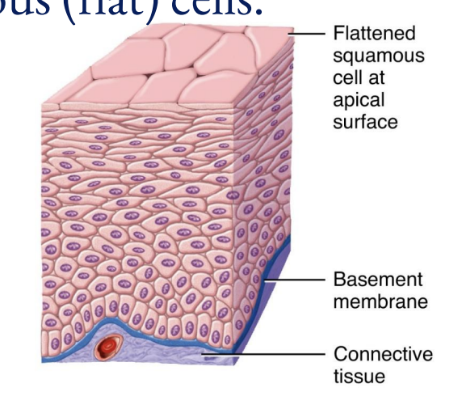
General Features of Epithelial Tissue
Arranged in sheets, in either single or multiple layers
Consists mostly of closely packed cells with little extracellular material
Many cell junctions are present, providing secure attachments among cells
Has an apical surface-free surface and a basal surface attached to a base membrane
Adhere firmly to nearby connective tissue via a thin extracellular layer, the basement membrane
Avascular; exchange of materials between epithelium and adjacent connective tissue is by diffusion
Have a nerve supply
Have a high capacity for renewal (a high mitotic rate)
Major Functions of Epithelial Tissues
Serve as a selective barrier that limits or aids the transfer of substances into and out of the body
Serves as a secretory surface that releases products produced by the cells
Serves as a protective surface that resists the abrasive influences of the environment
Surfaces of Epithelial Cells
Apical, Lateral, Basal
Apical Layer
Most superficial layer
Lateral Layer
Side of cell; the area where epithelial cells adhere to each other to form a sheet-like structure.
Basal Layer
Deepest layer
Basement Membrane Consists of…
Basal lamina (secreted by epithelial)
Reticular lamina (closer to connective tissue-fibroblasts
Roles of Epithelial Tissues
Protection, filtration, secretion, absorption, excretion
Layers of Epithelial Cells
Simple (one)
Stratified (several)
Pseudostratified (one layer that appears as several)
Cell Shapes
Squamous (flat)
Cuboidal (cube-like)
Columnar (rectangular)
Transitional (variable)
Simple Epithelium
Functions in diffusion, osmosis, filtration, secretion, and absorption
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Not all cells reach the apical surface
Apical cells can contain cilia
goblet cells secrete mucus
Stratified Epithelium
Two or more layers
Squamous Cells
Thin; rapid passage of substances
Cuboidal Cells
wide, cube or hexagons; function in either secretion or absorption
Columnar Cells
Taller than wider, function for secretion and absorption
Transitional Cells
Change cells from squamous to cuboidal and back (urinary bladder)
Epithelial Tissue Naming Combinations
Simple squamous, simple cuboidal, simple columnar, stratified squamous, stratified cuboidal, stratified columnar, pseudostratified columnar
Simple Squamous Epithelium
composed of a single layer of flat cells resembling tiled floor
Located in the air sacs of lungs, in the lining of blood vessels, the heart, lymphatic vessels, serous membranes
Sites of filtration, diffusion, secretions
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
composed of a single layer of cube shaped cells
located in the surface of ovary, lining of the kidney tubules, smaller ducts of many glands (like thyroid gland)
Function: secretion and absorption
Simple Columnar Epithelium
forms a single layer of column like cells
±cilia, ±microvilli, ±mucous (goblet cells)
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Appears to have multiple layers due to nuclei which are at various depths. In reality, all cells are attached to the basement membrane in a single layer, but some do not extend to the apical surface
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Has an apical surface that is made up of flat cells
The other layers have different shapes, but the name is based on the apical layer
The many layers are ideal for protection against strong friction forces
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
has an apical surface made up of two or more layers of cube-shaped cells
Located in sweat glands, part of the urethra
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Located in parts of the urethra, large excretory ducts of glands (esophageal gland), small areas of anal mucous membrane
Gland
A single cell or mass of epithelial cells adapted for secretion
Endocrine Glands
Ductless; their secretory products (hormones) enter the extracellular fluid and diffuse into the blood
Exocrine Glands
sweat, oil, and digestive glands
secrete their products into ducts that empty at the surface of covering and lining epithelium or directly onto a free surface
Mixed glands
Pancreas, ovaries, testes
Unicellular Gland
single-celled, such as the goblet cell
Multicellular Gland
composed of cells that form a distinctive microscopic structure or macroscopic organ, such as sweat, oil, and salivary glands
Categorization of multicellular glands
ducts and shape of the secretory portion
Ducts
are branched (compound) or unbranched (simple)
Shape of the secretory portion
Tubular (straight) and acinar (rounded)
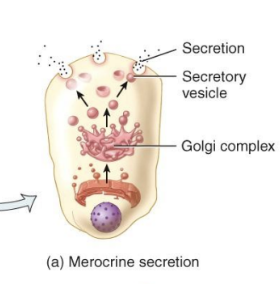
Merocrine Glands
form the secretory products and discharge it by exocytosis
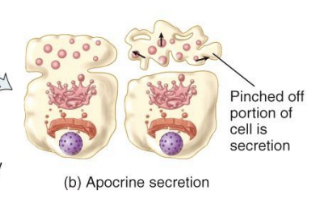
Apocrine Glands
accumulate their secretary product at the apical surface of the secreting cell
that portion then pinches off from the rest of the cell to form the secretion with the remaining part of the cell repairing itself and repeating the process
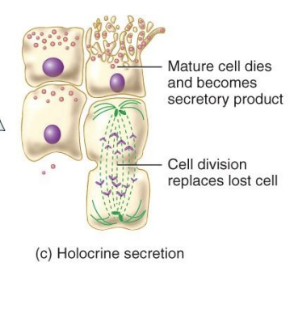
Holocrine Gland
accumulate the secretory product in the cytosol; when the cell dies, it and its products are discharged as the glandular secretion, with the discharged cell being replaced by a new one
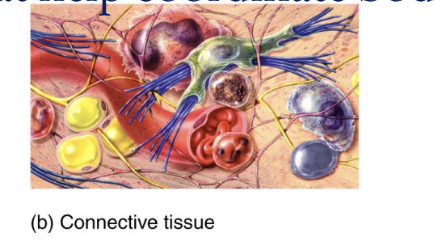
Connective Tissue
protects and supports the body and its organs, binds organs together, stores energy reserves as fat, and provides immunity
Large amount of extracellular material separates cells
Significant networks of blood vessels
the most abundant and widely distributed tissue in the body.
consists of two basic elements: cells and extracellular matrix (formed from ground substance and fibers)
do not occur on free surface
highly vascular(except for cartilage and tendons)
except for cartilage, it contains nerve supply
derived from mesenchyme
4 tissue types
Muscular, Nervous, epithelial, and connective
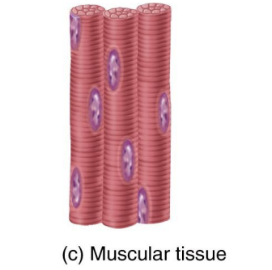
Muscular Tissue
Responsible for movement and generation of force
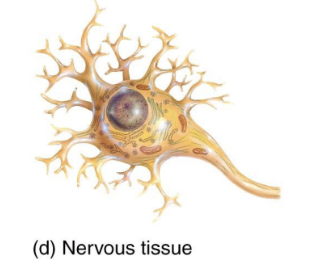
Nervous Tissue
Initiates and transmits action potentials (nerve impulses) that help coordinate body activities.
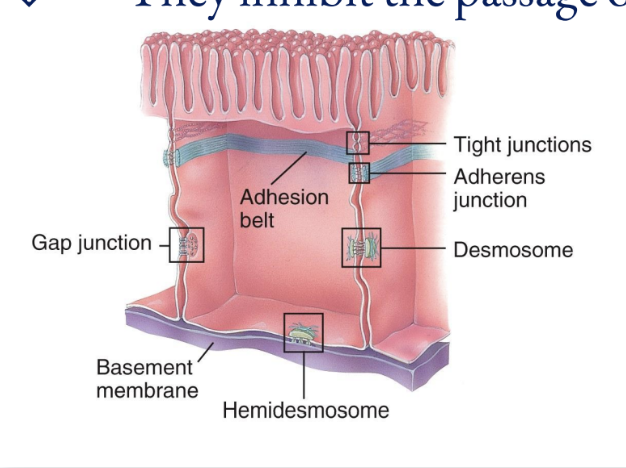
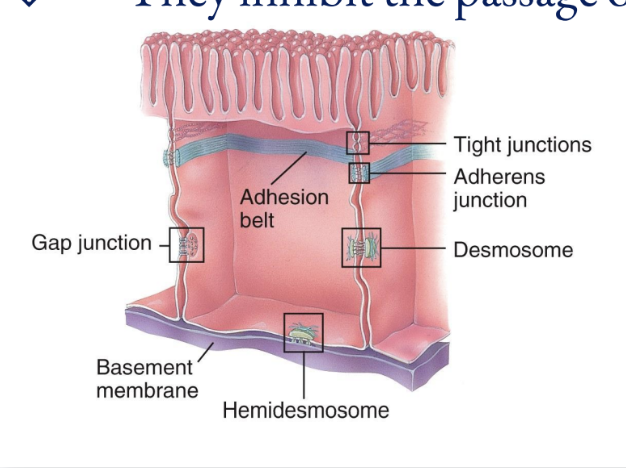
Cell Junctions
Points of contact between adjacent plasma membranes
Cell Junction Functions
Form fluid-tight seals between cells
Anchor cells together or to extracellular material
Act as channels, which allow ions and molecules to pass from cell to cell within a tissue
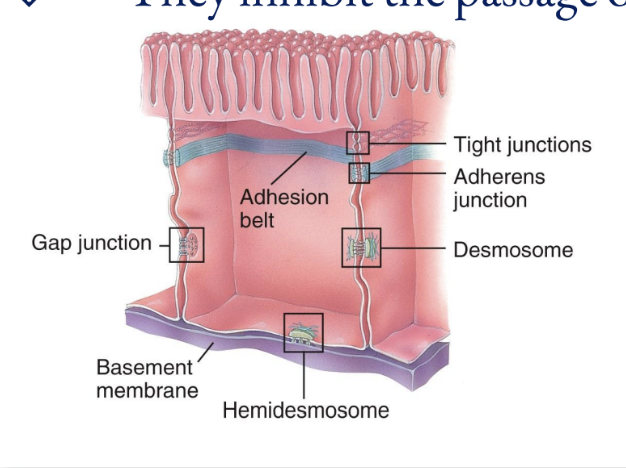
Five most important cell junctions
tight junctions, adherens junctions, desmosomes, hemidesmosomes, and gap junctions
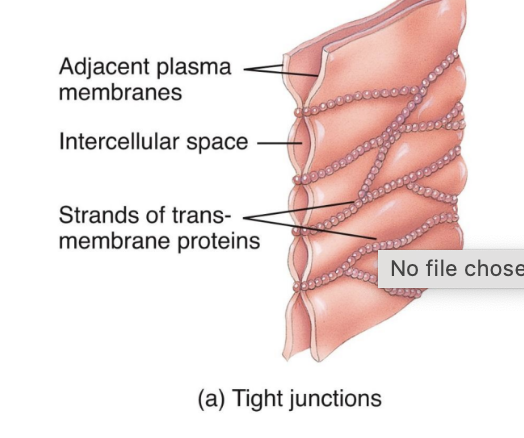
Tight Junctions
Consist of weblike strands
Form fluid-tight seals between cells
Common among epithelial cells that line the stomach, intestines, and urinary bladder
They inhibit the passage of substances between cells
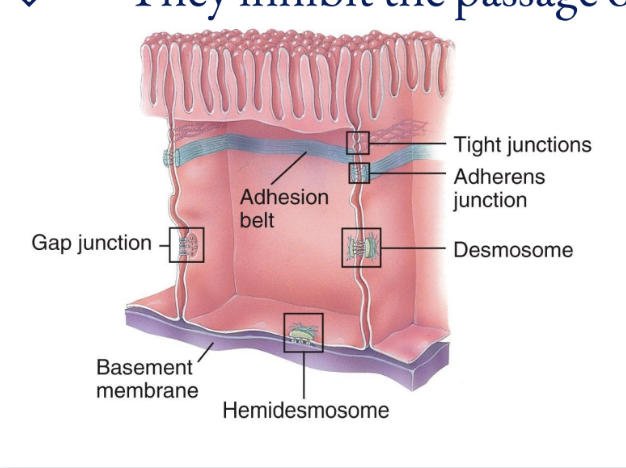
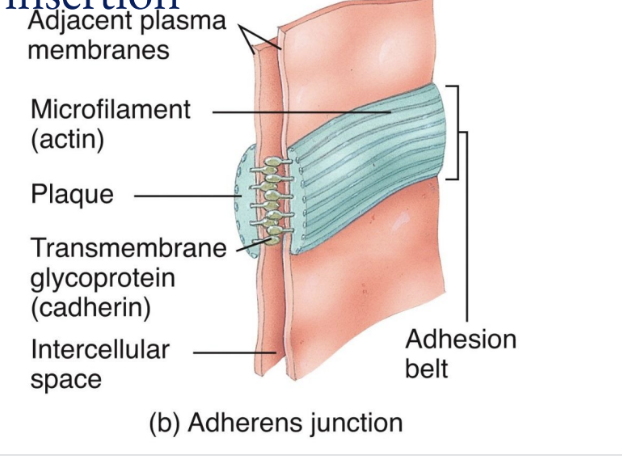
Adherens Junctions
Made up of plaque and anchor cells together
Form the adhesion belt and keep tissues from separating as they stretch and contact
Transmembrane glycoproteins called cadherins join the adjacent cells by insertion
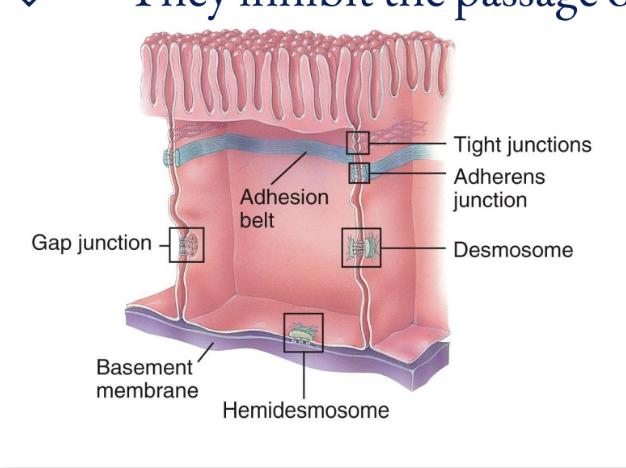
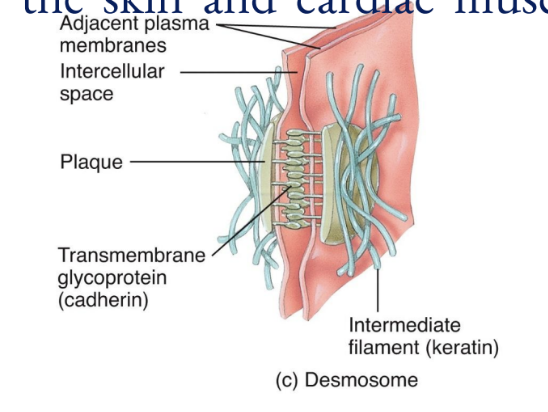
Desmosomes
composed of plaque and are linked by transmembrane glycoproteins that extend across a gap between adjacent cell membranes and link the cytoskeletons of cells together
These spot weld-like junctions are common among the epidermis of the skin and cardiac muscle cells in the heart
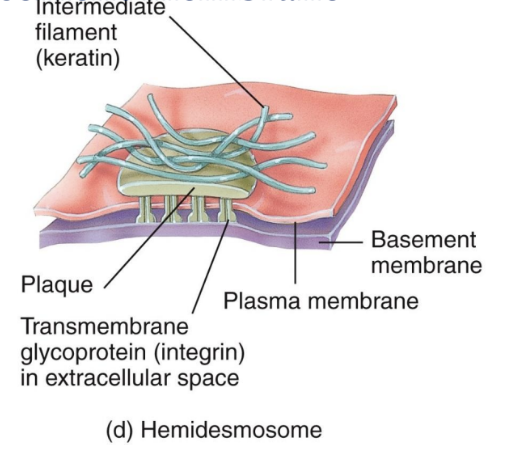
Hemidesmosomes
Half-welds that join cells to the basement membrane
The transmembrane glycoproteins in these are called integrins, which attach to laminin in the basement membrane
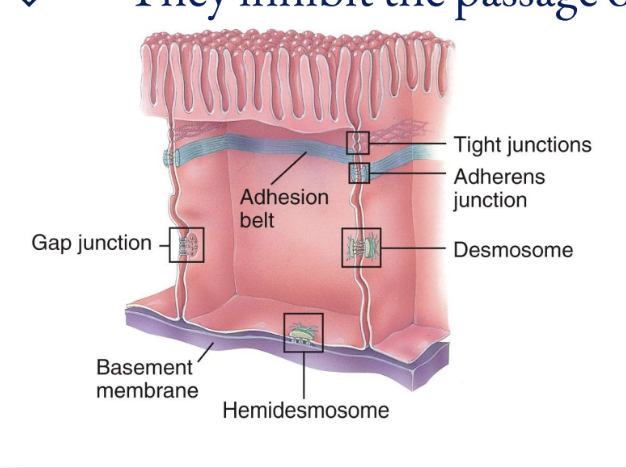
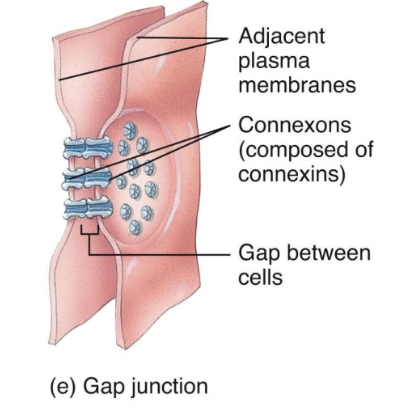
Gap Junctions
Allow cells in a tissue to rapidly communicate through connexins (tiny fluid filled tunnels; transmembrane protein channels that connect cells together)
They are not fused together; only small ions and molecules pass through, proteins cannot
Allow cell communication (nerve or muscle impulses)
Immature cells
end in -blast (ex: fibroblast, chondroblast)
Mature Cells
end in -cyte (osteocyte)
reduced capacity for cell division and matrix formation and are mostly involved in maintaining the matrix
Fibroblasts
secrete fibers and matrix
Macrophages
also called histiocytes; develop from monocytes and are phagocytic (destroy bacteria)
Plasma Cells
develop into antibody- producing B lymphocytes or B-cells
Mast Cells
abundant alongside blood vessels and produce histamine)
Adipocytes
fat cells which store energy in the form of fat; found below skin and around organs
Leukocytes
white blood cells
Elastic Fibers
Stretchable but strong fibers made of the proteins elastin and fibrillin
found in skin, blood vessels, lung tissue
Eosinophils
White blood cells that migrate to sites of parasitic infection and allergic responses
Neutrophils
white blood cells that migrate to sites of infection and destroy microbes by phagocytosis
Ground Substance
the material between cells and fibers
made of water and organic molecules
supports cells and fibers, binds them together, and provides medium for exchanging substances between blood and cells
Collagen Fibers
strong, flexible bundles of the protein collagen; the most abundant in your body
reticular fibers
made up of collagen and glycoproteins
provide support in blood vessel walls and form branching networks around various cells
ECM
located in the spaces between connective tissue cells
composed of fibers and ground substance
Three types of fibers embedded in the matrix between cells of connective tissues
collagen fibers, elastic fibers, reticular fibers
Collagen Fibers
composed of the protein collagen, are very tough and resistant to stretching, yet allow some flexibility in tissue; they are found in bone, cartilage, tendons, and ligaments
Elastic Fibers
composed of the protein elastin, provide strength and stretching capacity and are found in skin, blood vessels, and lungs
Reticular Fibers
consisting of collagen and glycoprotein, provide support in the walls of blood vessels and form a strong, supporting network around fat cells, nerve fibers, and skeletal and smooth muscle fibers
Embryonic Connective Tissue
present in the embryo or fetus
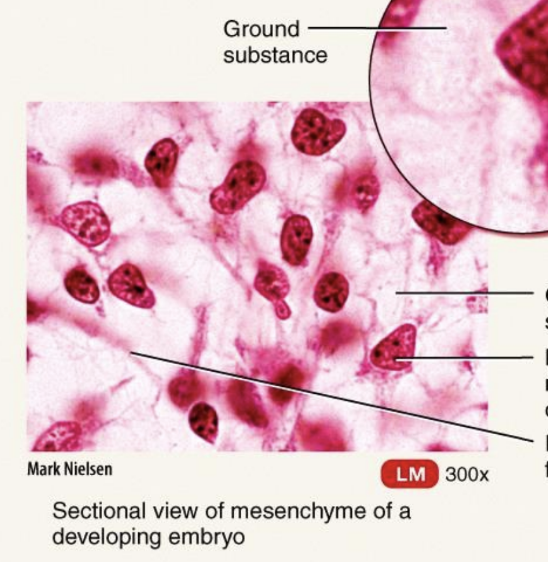
Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mesenchyme
irregularly shaped mesenchymal cells embedded in semifluid ground substance that contains delicate reticular fibers
Located exclusively under the skin and along developing bones of embryo; some in adult connective tissue, especially along blood vessels
Forms almost all other types of connective tissue
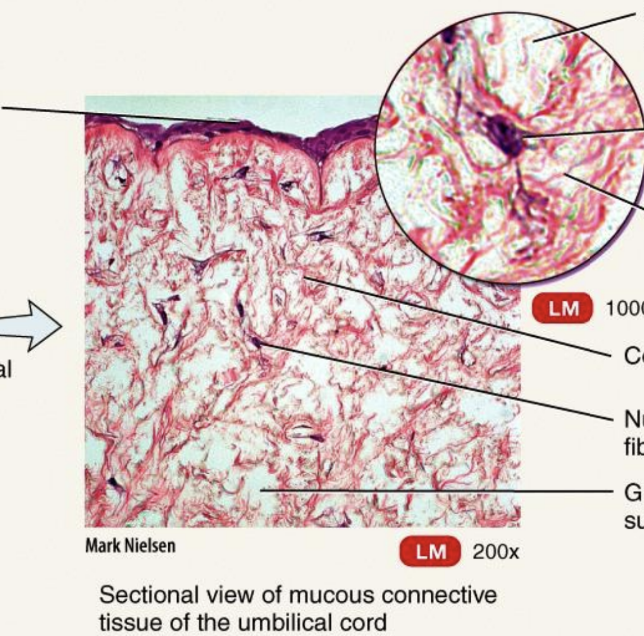
Embryonic Connective Tissue: Mucous Connective Tissue
widely scattered fibroblasts embedded in viscous, jellylike ground substance that contains fine collagen fibers
located in the umbilical cord of fetus
Function: support
Mature Connective Tissue
exists in the newborn, has cells differentiated from mesenchyme, and does not change after birth
Five Types: Loose connective tissue, Dense connective tissue, Cartilage, Bone tissue, Liquid connective tissue
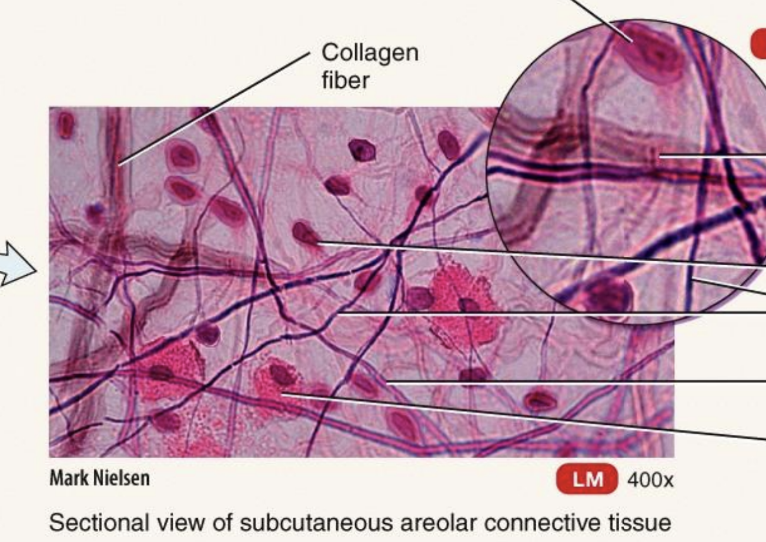
Mature Connective Tissue; loose connective tissue: Areolar Connective Tissue
one of the most distributed connective tissues; consists of fibers (collagen, elastic, reticular) arranged randomly and several kinds of cells embedded in a semifluid ground substance
Located in and around nearly every body structure; in subcutaneous layer deep to skin; papillary region of dermis of skin; lamina propria of mucous membranes; around blood vessels, nerves, and body organs
Function: support, strength, elasticity
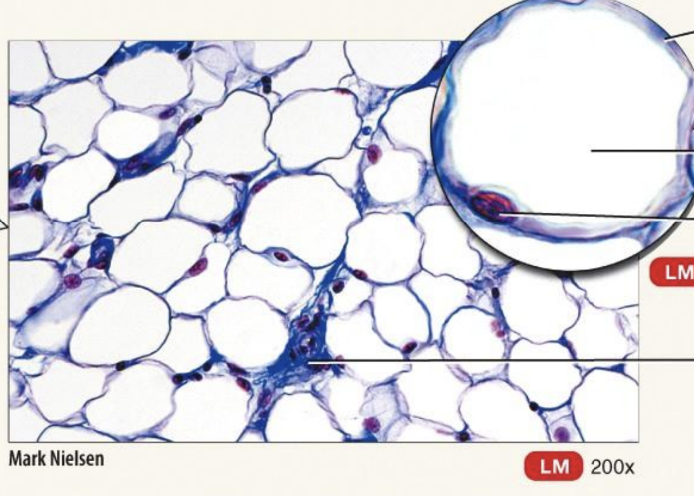
Mature Connective Tissue; loose connective tissue: adipose tissue
cells derived from fibroblasts, called adipocytes, that are specialized for storage of triglycerides as a large, centrally located droplet.
White Adipose Tissue: in adults
Brown Adipose Tissue: darker due to very rich blood supply and numerous pigmented mitochondria
Located wherever areolar connective tissue is located
Reduces heat loss through skin; served as an energy reserve; supports and protects organs
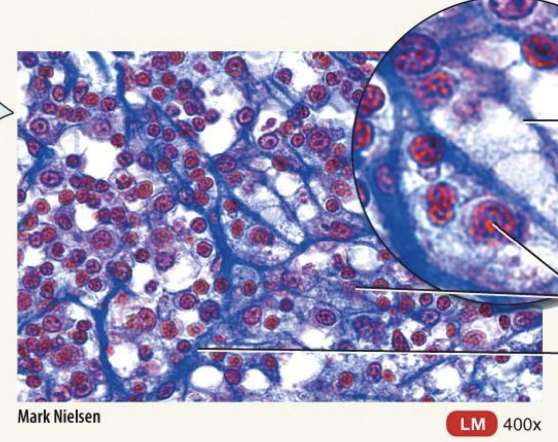
Mature Connective Tissue; loose connective tissue: Reticular Connective Tissue
the fine interlacing network of reticular fibers and reticular cells
located in the stroma of the liver, spleen, lymph nodes; red bone marrow; reticular lamina of basement membrane; around blood
Forms stroma of organs; binds smooth muscle tissue cells; filters and removes worn-out blood cells in spleen and microbes in lymph nodes
Dense regular connective tissue
consists of bundles of collagen fibers in a regular and orderly, parallel arrangement that confers great strength
Forms tendons, ligaments
Provides strong attachment between various structures
Dense irregular connective tissue
contains fibers that are irregularly arranged and is found in parts of the body where tensions are exerted in various directions
It usually occurs in sheets, such as the dermis of the skin
It is also found in heart valves, the perichondrium, the tissue surrounding cartilage, and the periosteum
Provides tensile(pulling) strength
Elastic Connective Tissue
consists of elastic fibers and fibroblasts
It is quite strong and can recoil back to its original shape after being stretched
It is found in lung tissue and elastic arteries, allows stretching of various organs
Cartilage
consists of a dense network of collagen fibers and elastic fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate
Its strength is due to its collagen fibers; its resilience due to the chondroitin sulfate
surrounded by a dense irregular connective tissue membrane called the perichondrium
Unlike other connective tissues, this has no blood vessels or nerves (except in the perichondrium),due to secretion of antiangiogenesis factor (a substance that prevents blood vessel growth)
function: support, shock absorption, smooth movement of joints (no friction), and flexibility.
three types: hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic
Perichondrium
a dense, fibrous membrane that covers cartilage and helps it grow, repair, and maintain its function
Hyaline Cartilage
the most abundant but weakest type of cartilage and has fine collagen fibers embedded in a gel-type matrix. It affords flexibility and support. At joints, it reduces friction and absorbs shock.
articular cartilage is a type
surrounded by a perichondrium
Fibrocartilage
contains bundles of collagen fibers in its matrix
It does not have a perichondrium.
Combining strength and rigidity, it is the strongest of the three types of cartilage
the least flexible type of cartilage
makes up intervertebral discs, menisci of knee
Elastic Cartilage
contains a threadlike network of elastic fibers within the matrix.
A perichondrium is present. It provides strength and elasticity and maintains the shape of certain organs.
Growth of Cartilage
accomplished by interstitial (endogenous) growth (expansion from with) and appositional (exogenous) growth (from without)
Bone Tissue
Bone is composed of bone or osseous tissue
consists of a matrix containing mineral salts and collagenous fibers and cells called osteocytes, the periosteum, red and yellow bone marrow, endosteum
Bone supports, protects, helps provide movement, stores minerals, and houses blood-forming tissue
Bone is classified as either compact or spongy, depending on how the matrix and cells are organized
The basic unit of compact bone is the osteon or haversian system, consisting of four parts
Spongy bone has trabeculae rather than osteons
Four parts of bone tissue
lamellae
lacunae
canaliculi
central (haversian) canal
Lamellae
“Little plates”
concentric rings of matrix that consist of mineral salts that give bone its hardness and collagen fibers that give bone its strength
Lacunae
small spaces between lamellae that contain mature bone cells called osteocytes
Canaliculi
minute canals containing processes of osteocytes that provide routes for nutrient and waste transport
A central (haversian) canal
contains blood vessels and nerves
Liquid Connective Tissue: Blood
vascular tissue
consists of a liquid matrix called plasma and formed elements suspended in the plasma
formed elements include erythrocytes, leukocytes, and thrombocytes
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that function in transporting respiratory gases
Leukocytes
white blood cells
involved in phagocytosis, immunity, and allergic reactions
Thrombocytes
Platelets that function in blood clotting
Lymph
Interstitial fluid flowing in lymph vessels