Triangles of the Neck: Key Biology Terms & Definitions
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
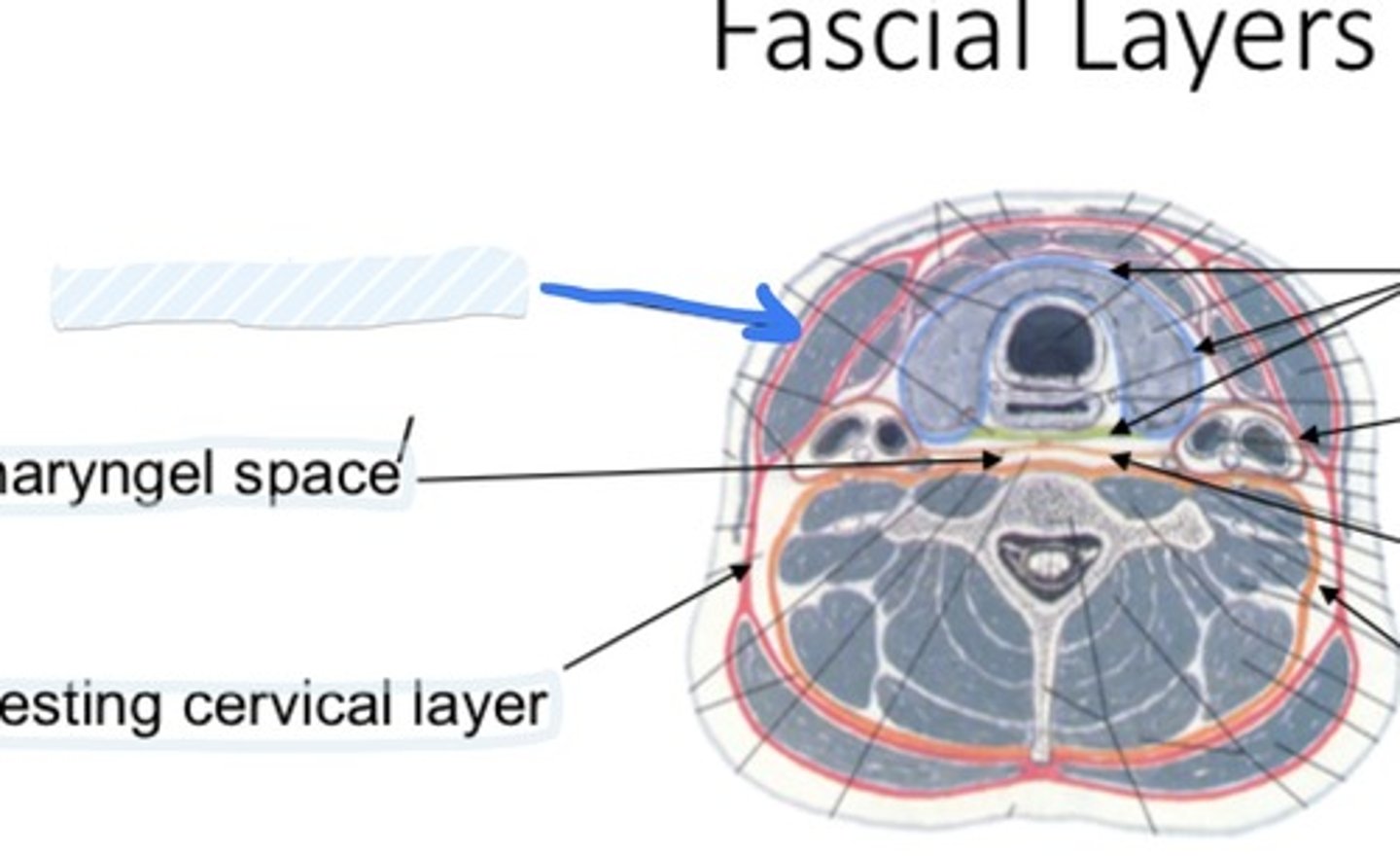
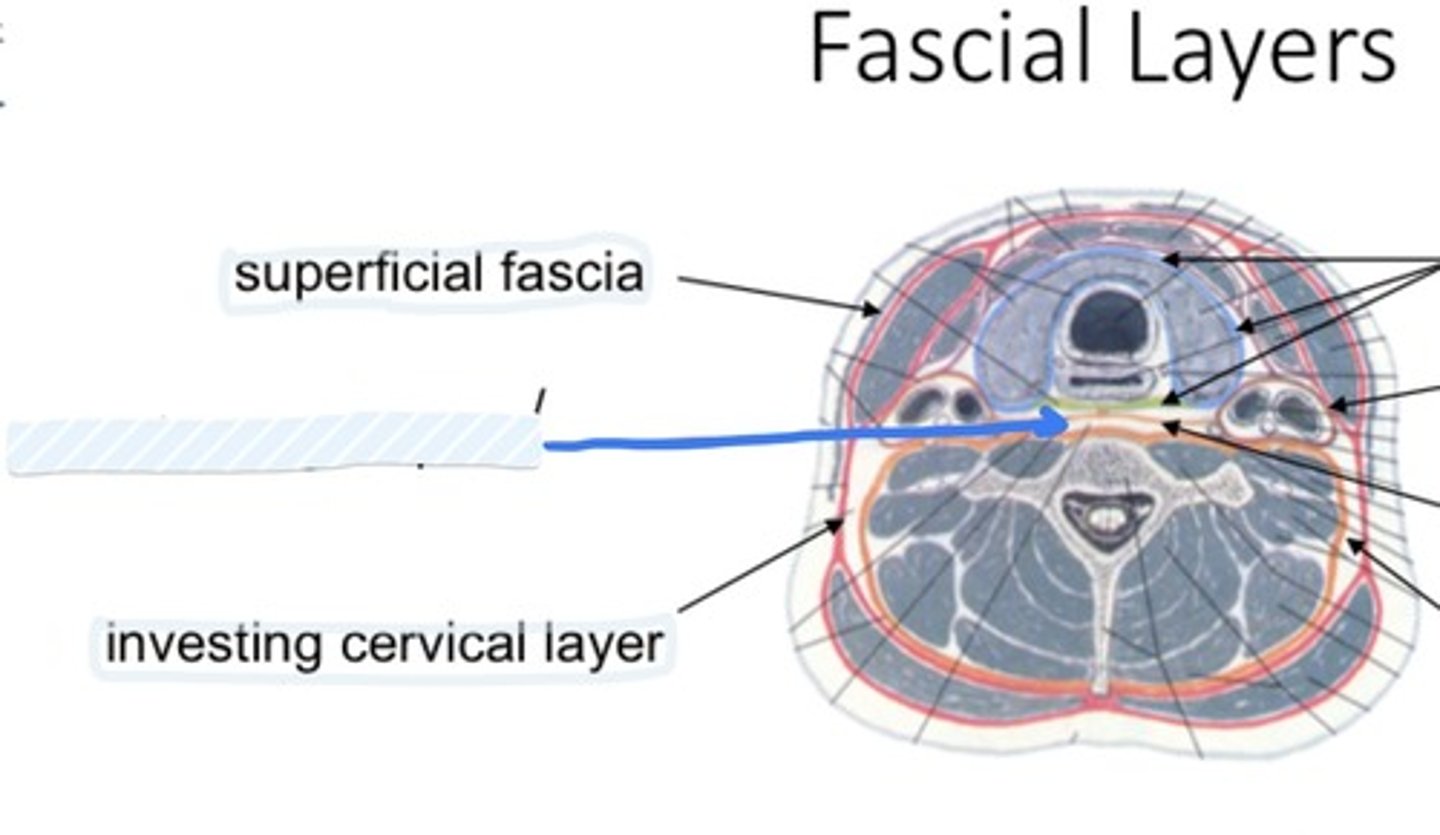
Superficial fascia
Retropharngeal space
Investing cervical layer
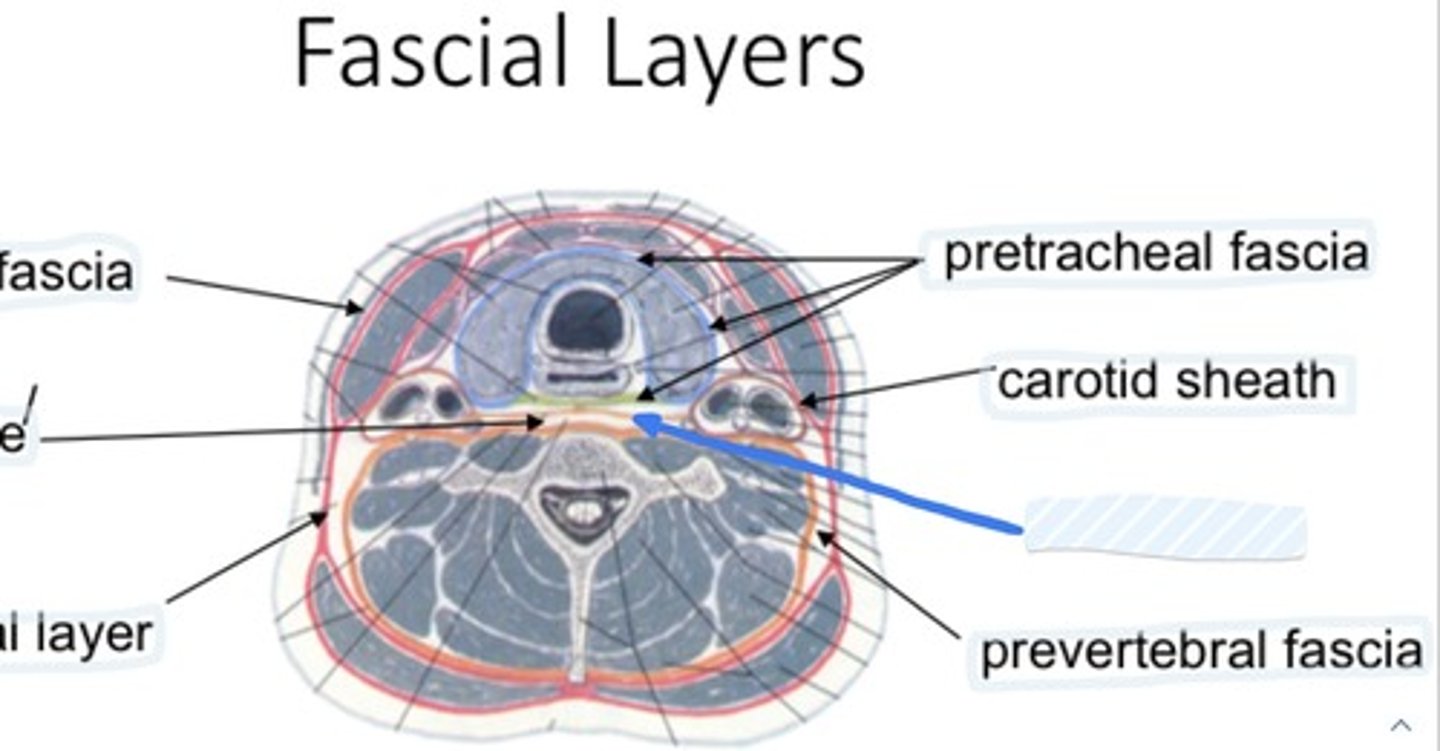
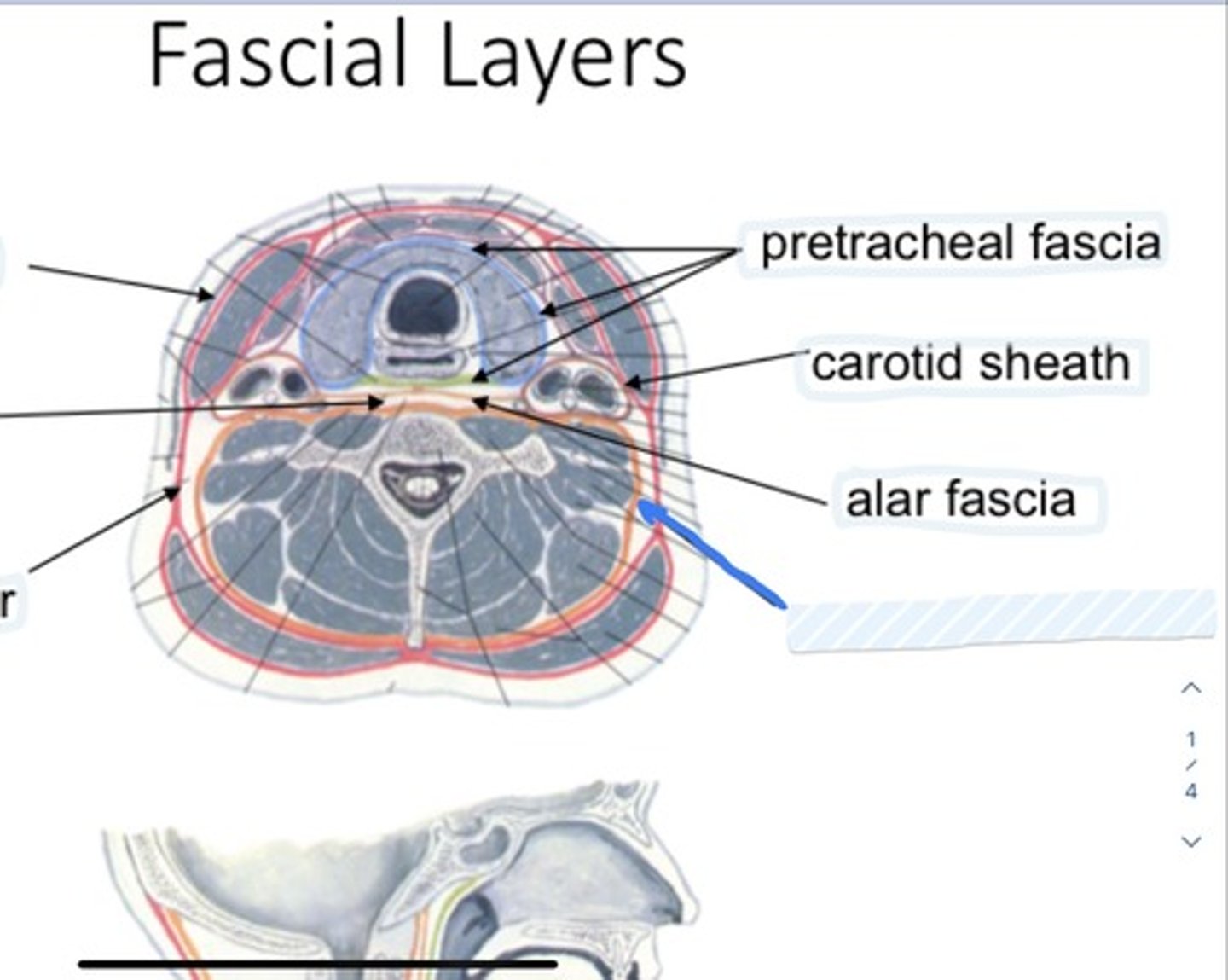
Pretracheal fascia
Carotid sheath
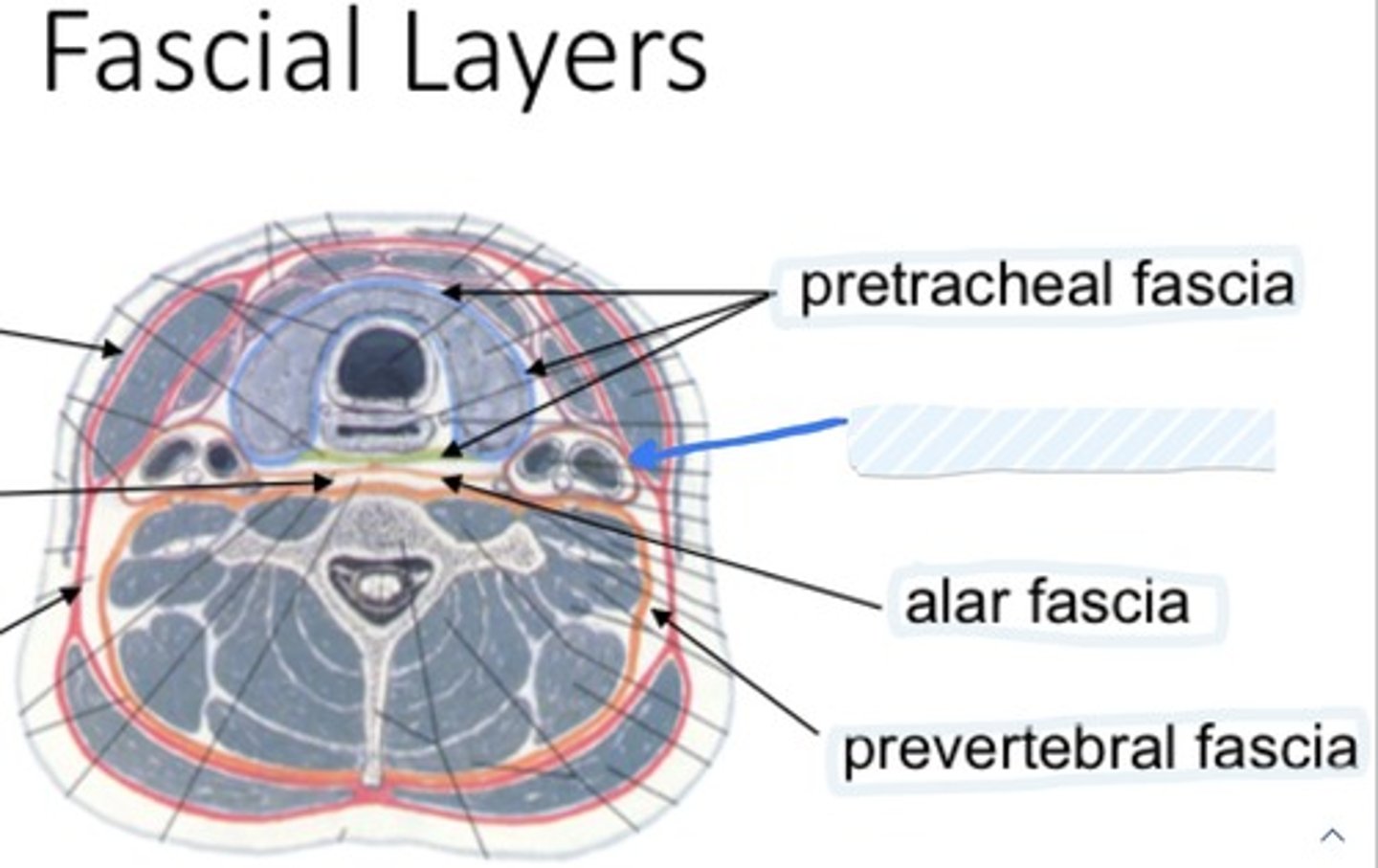
Alar fascia
Prevertebral fascia
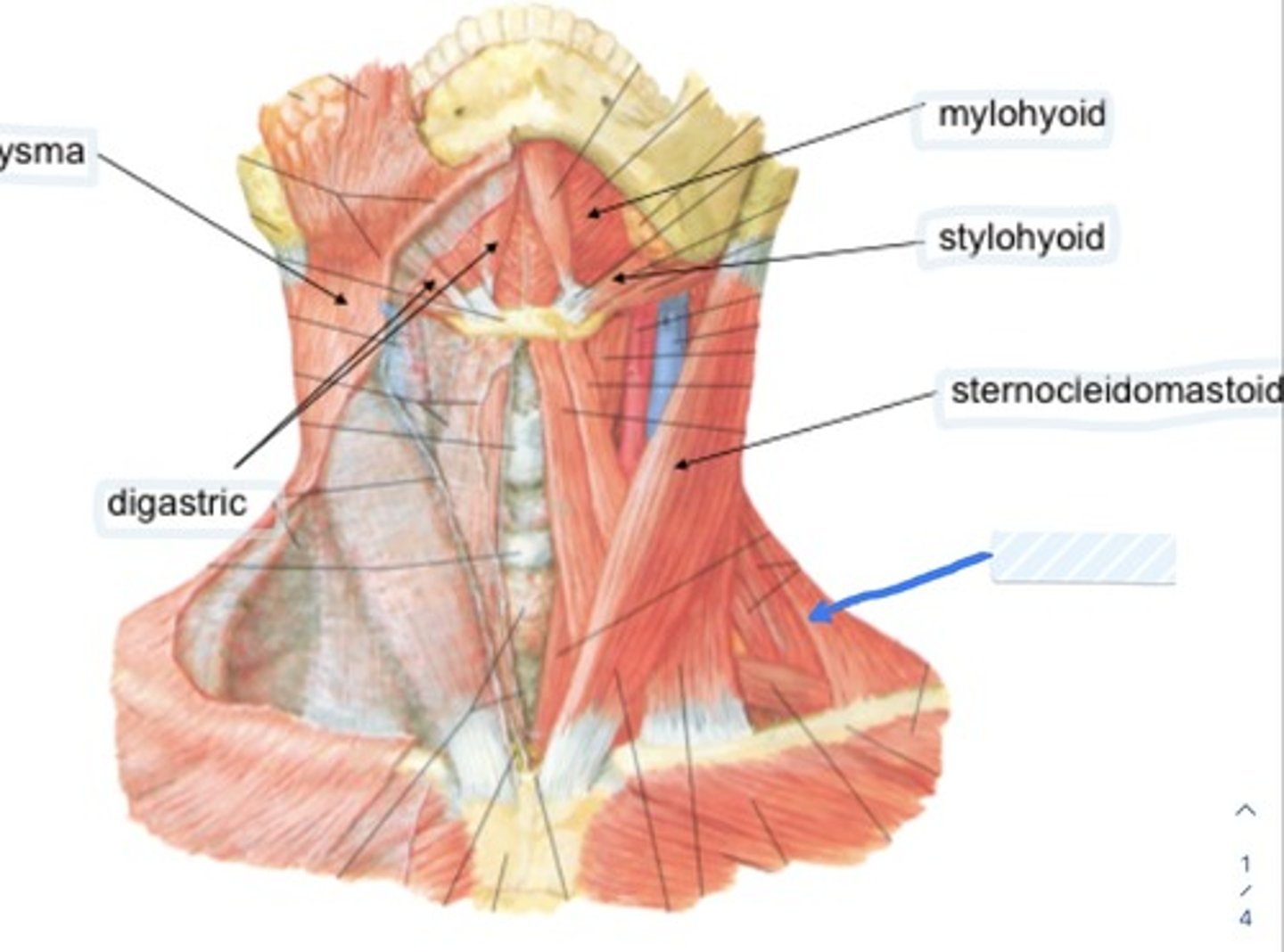
Platysma
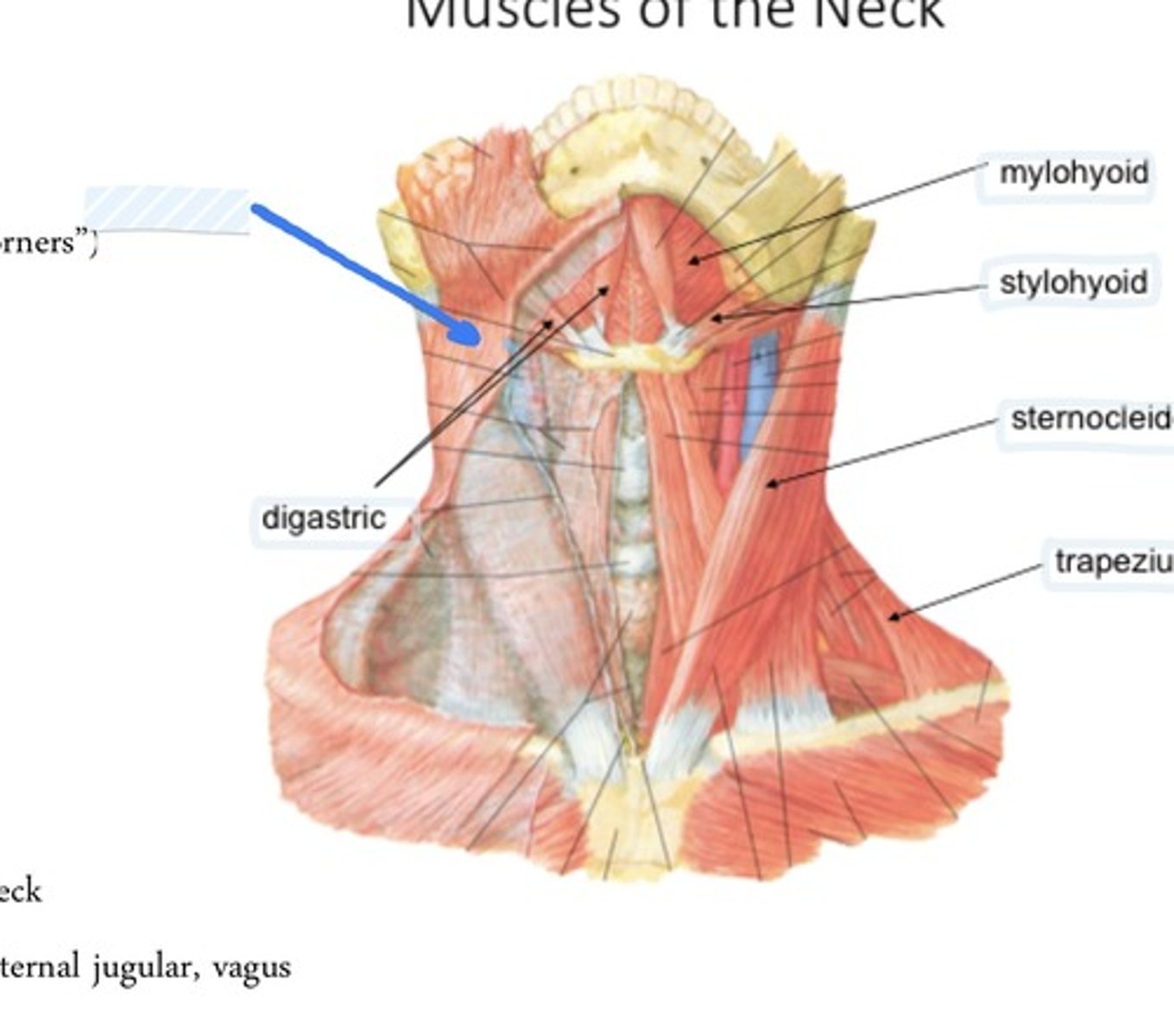
Digastric
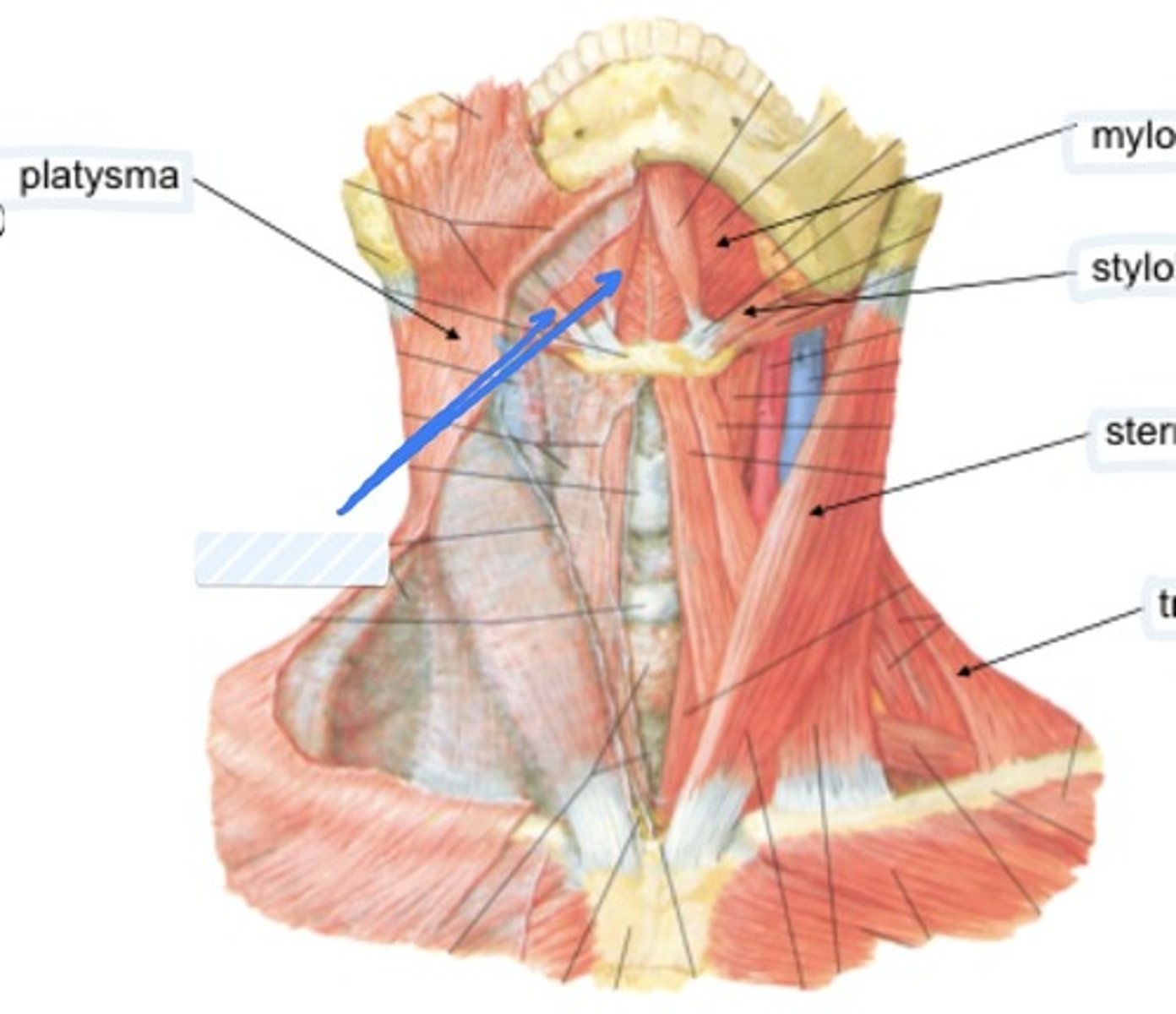
Mylohyoid
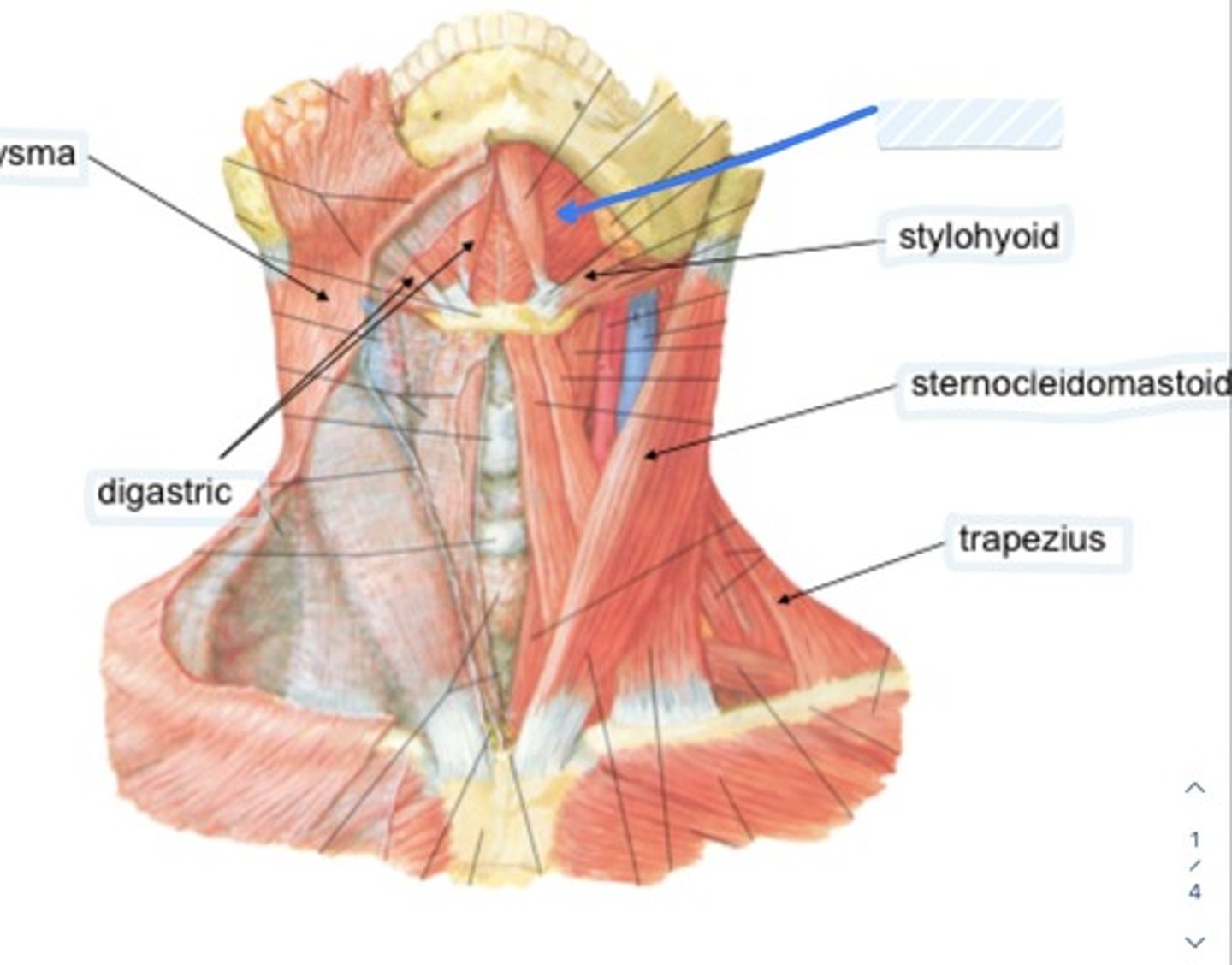
Stylohyoid
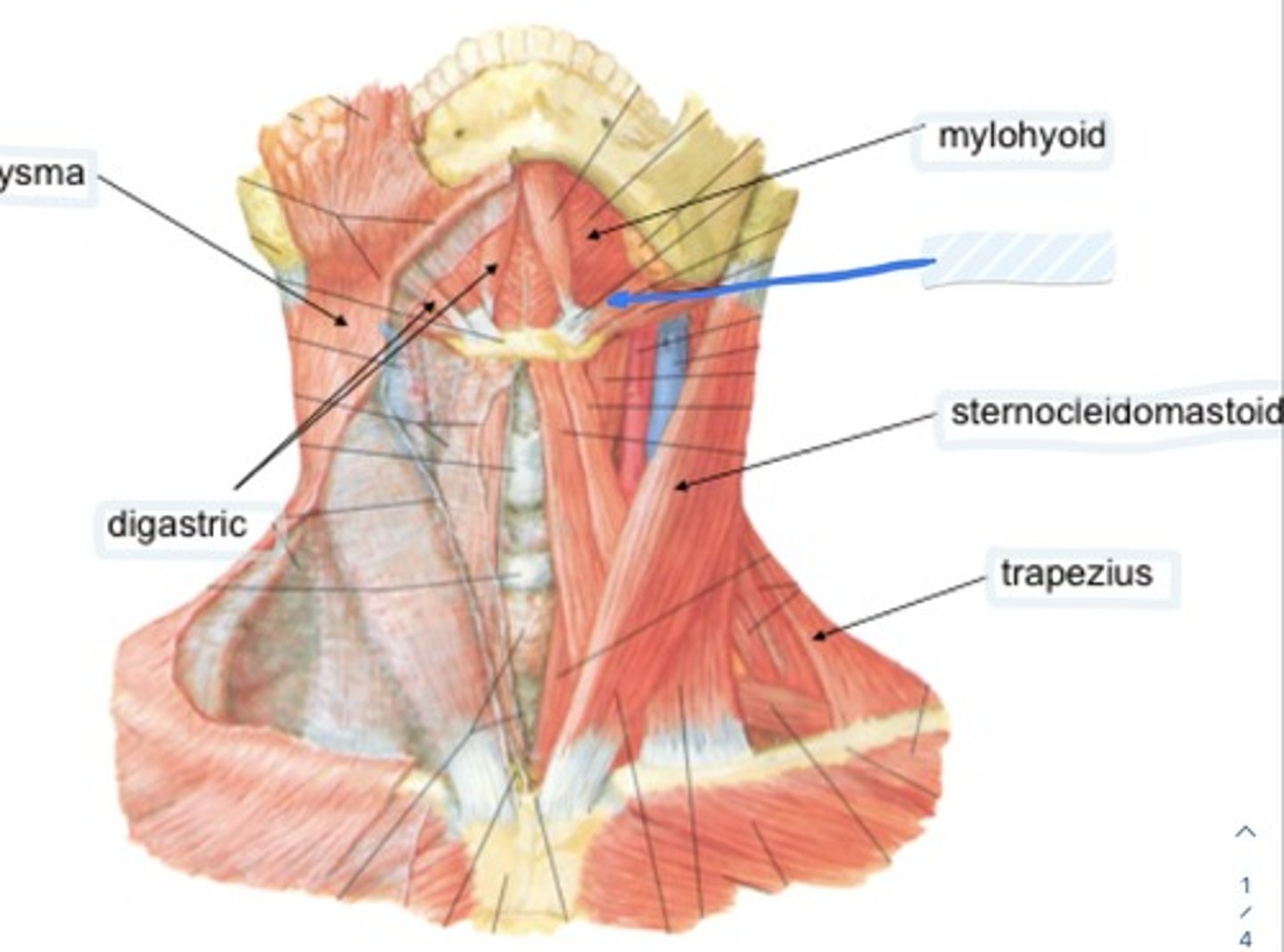
Sternocleidomastoid
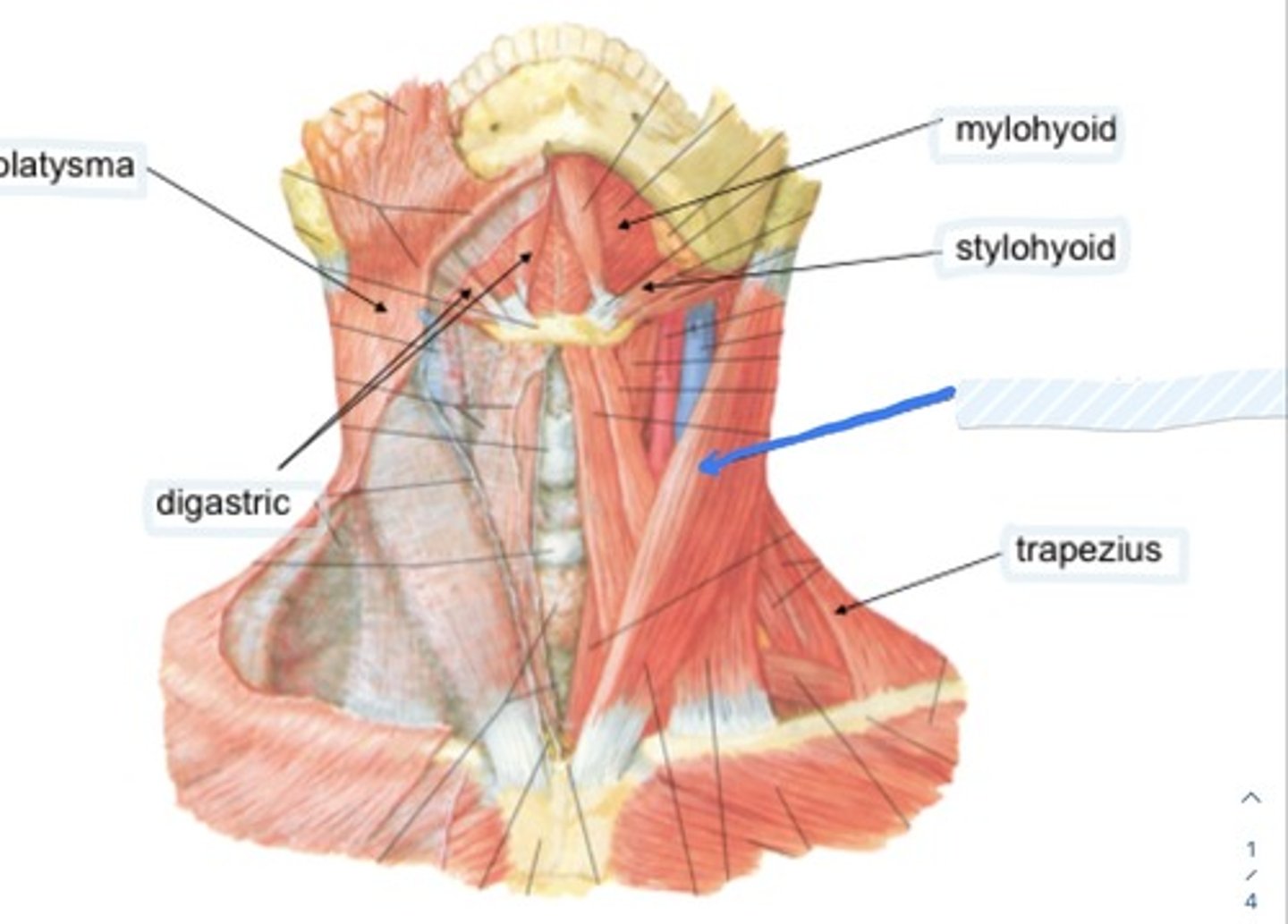
Trapezius
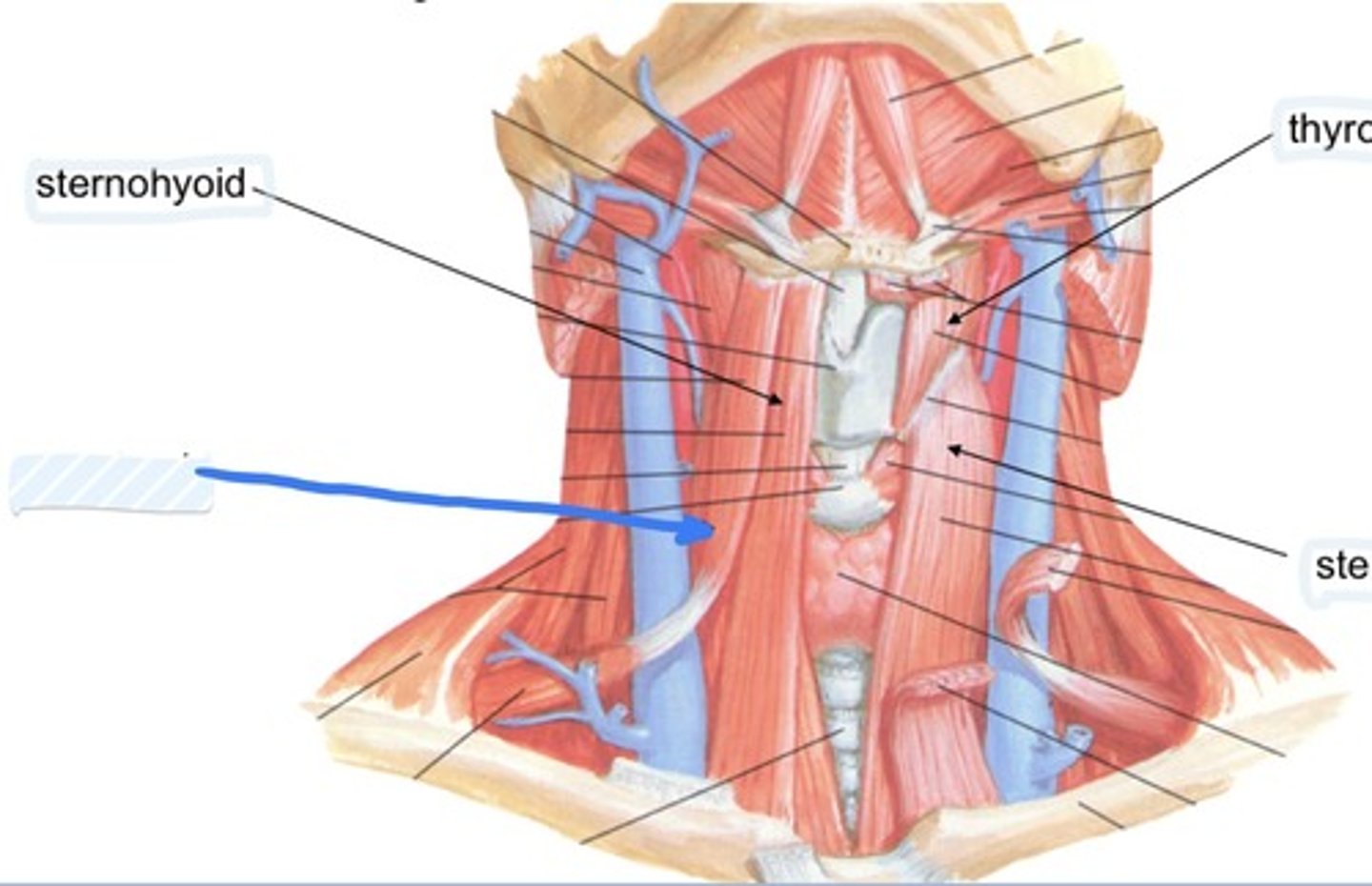
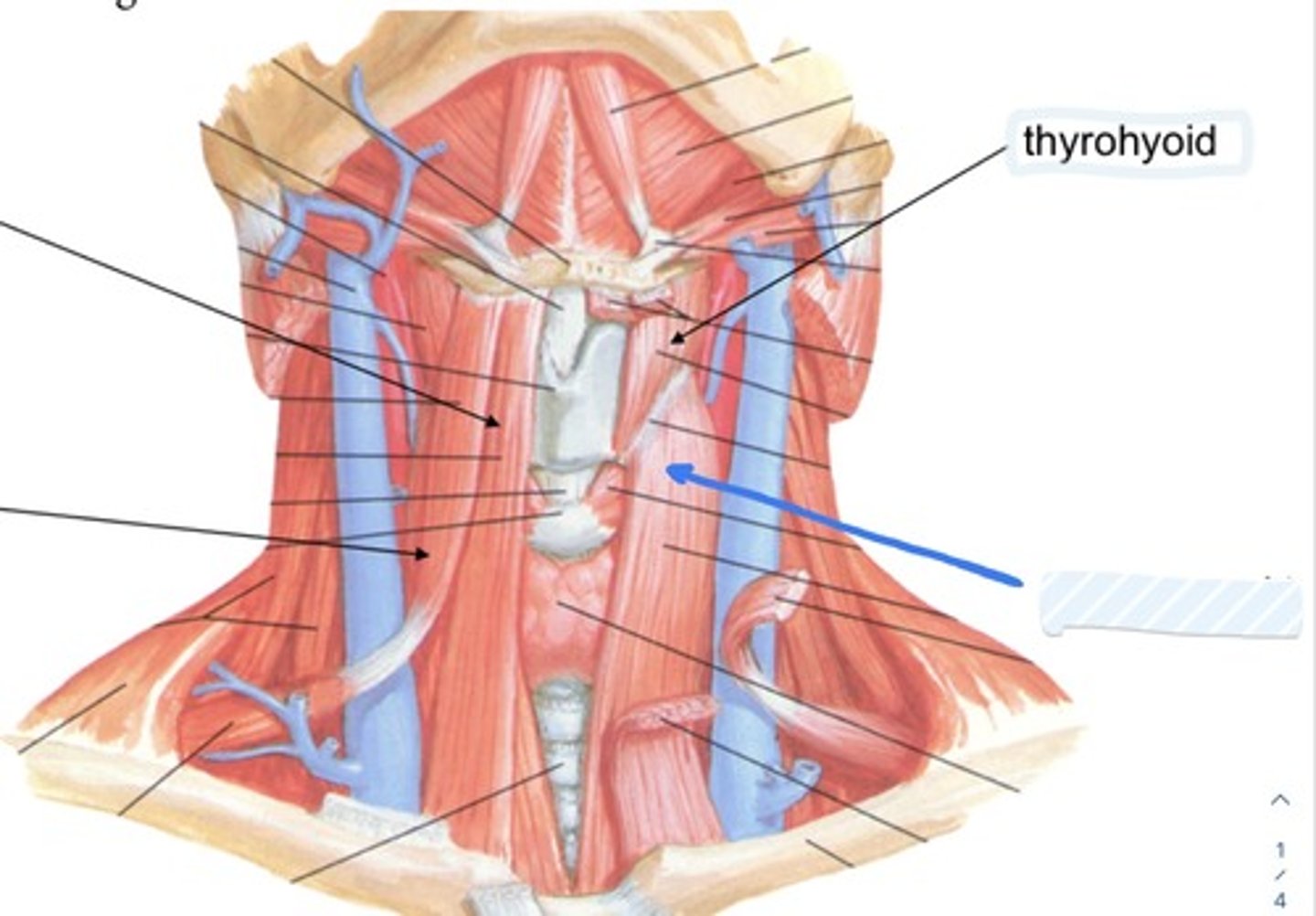
Sternohyoid
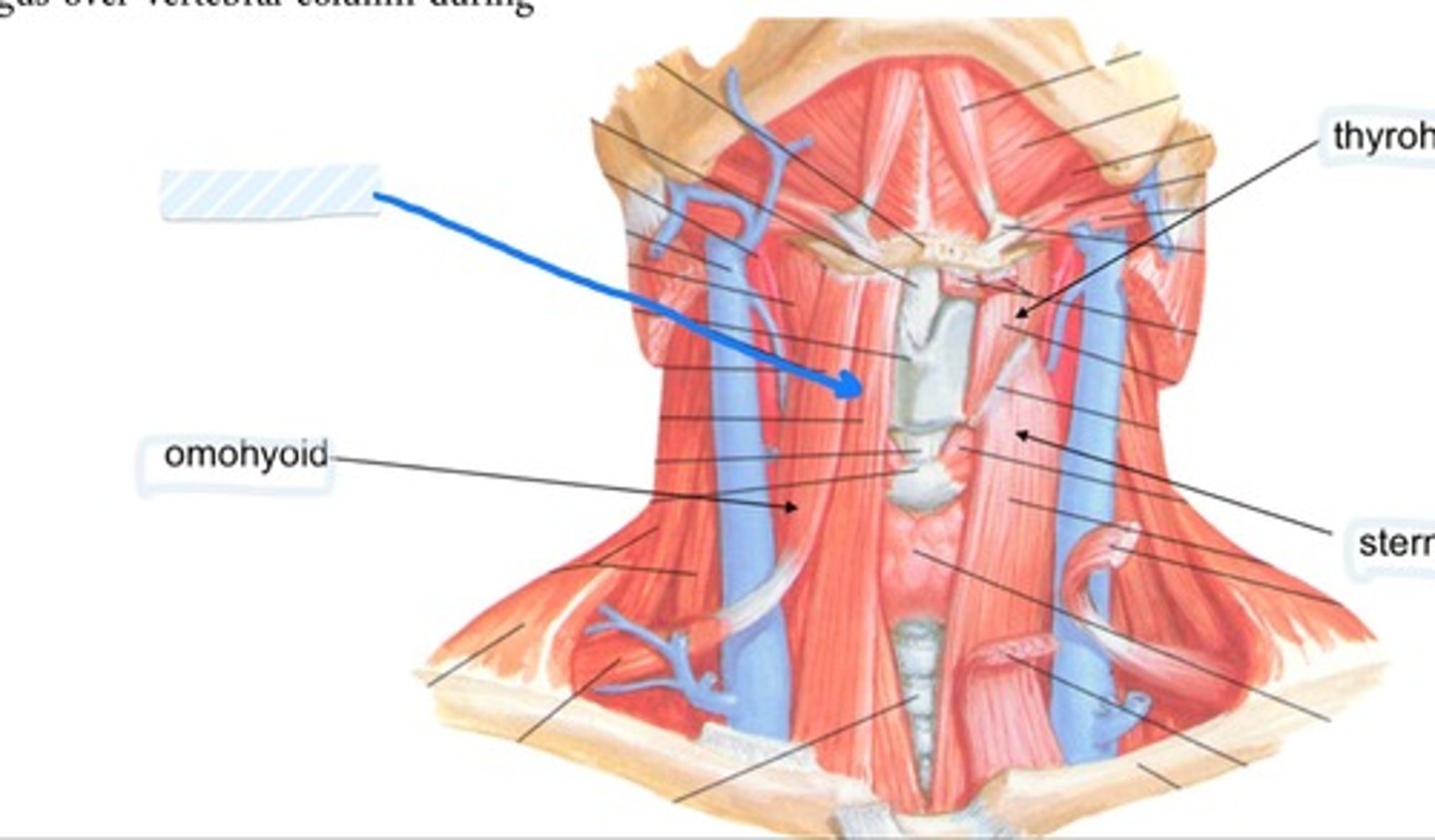
Omohyoid
Thyrohoid
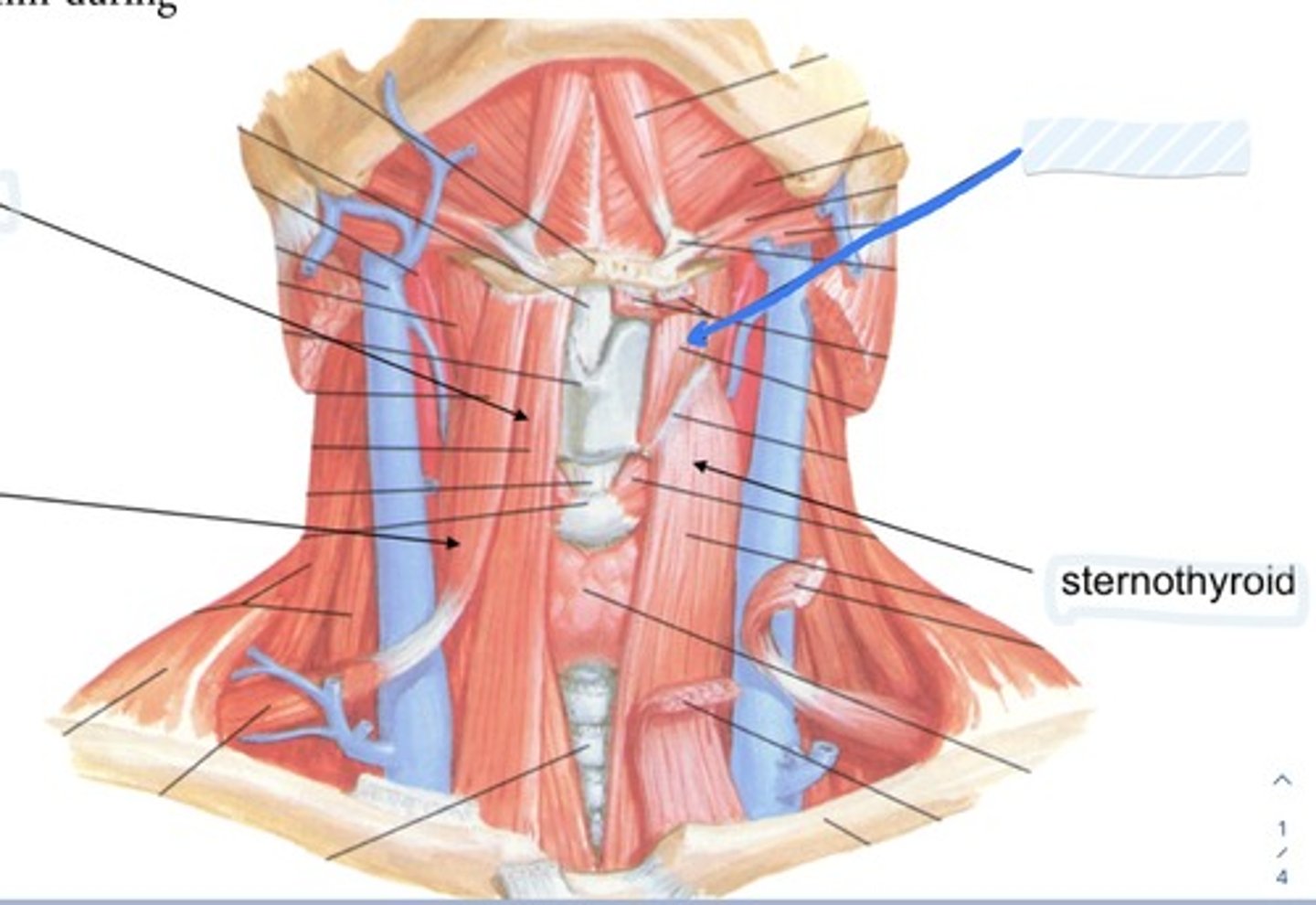
Sternothyroid
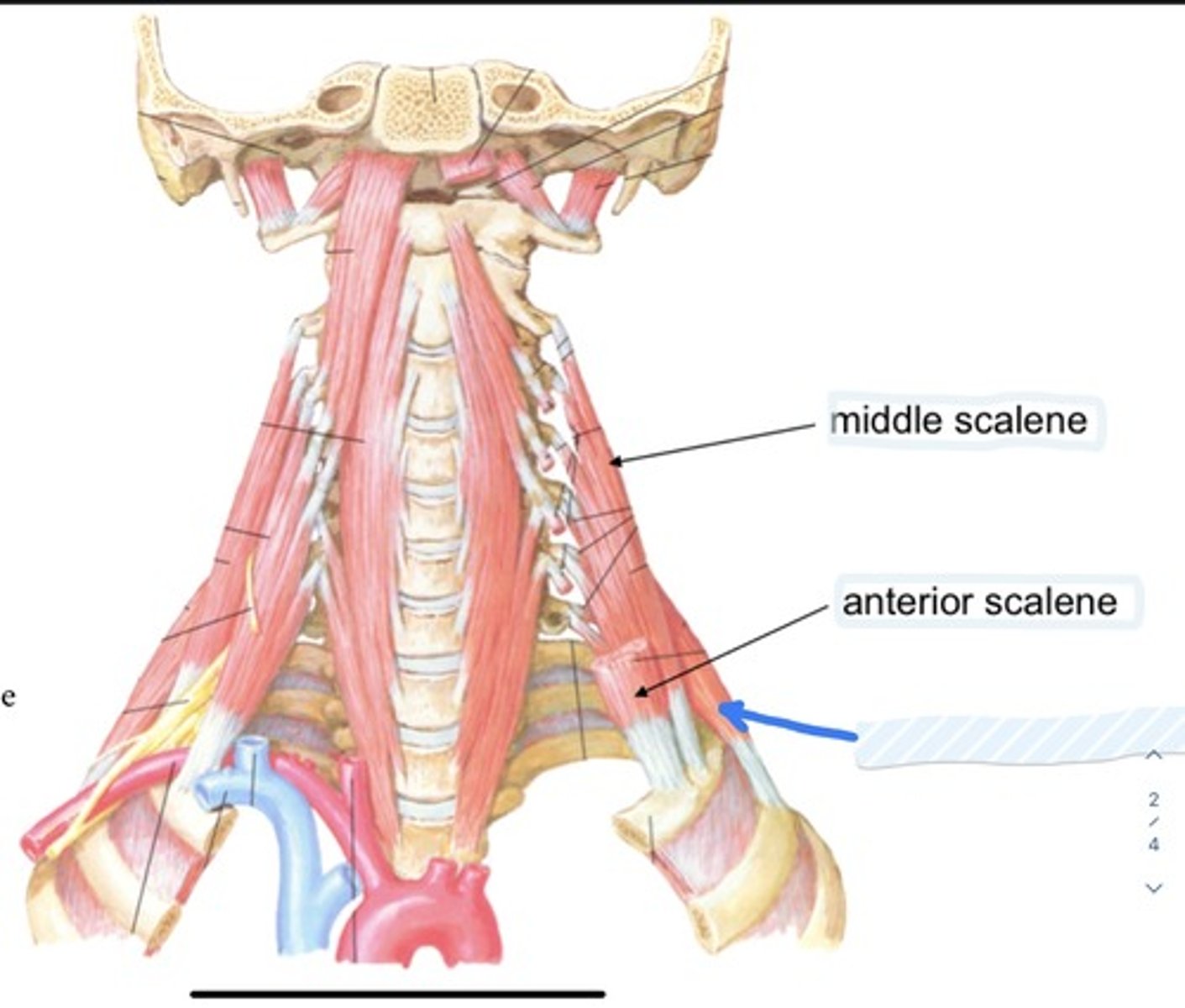
Middle scalene
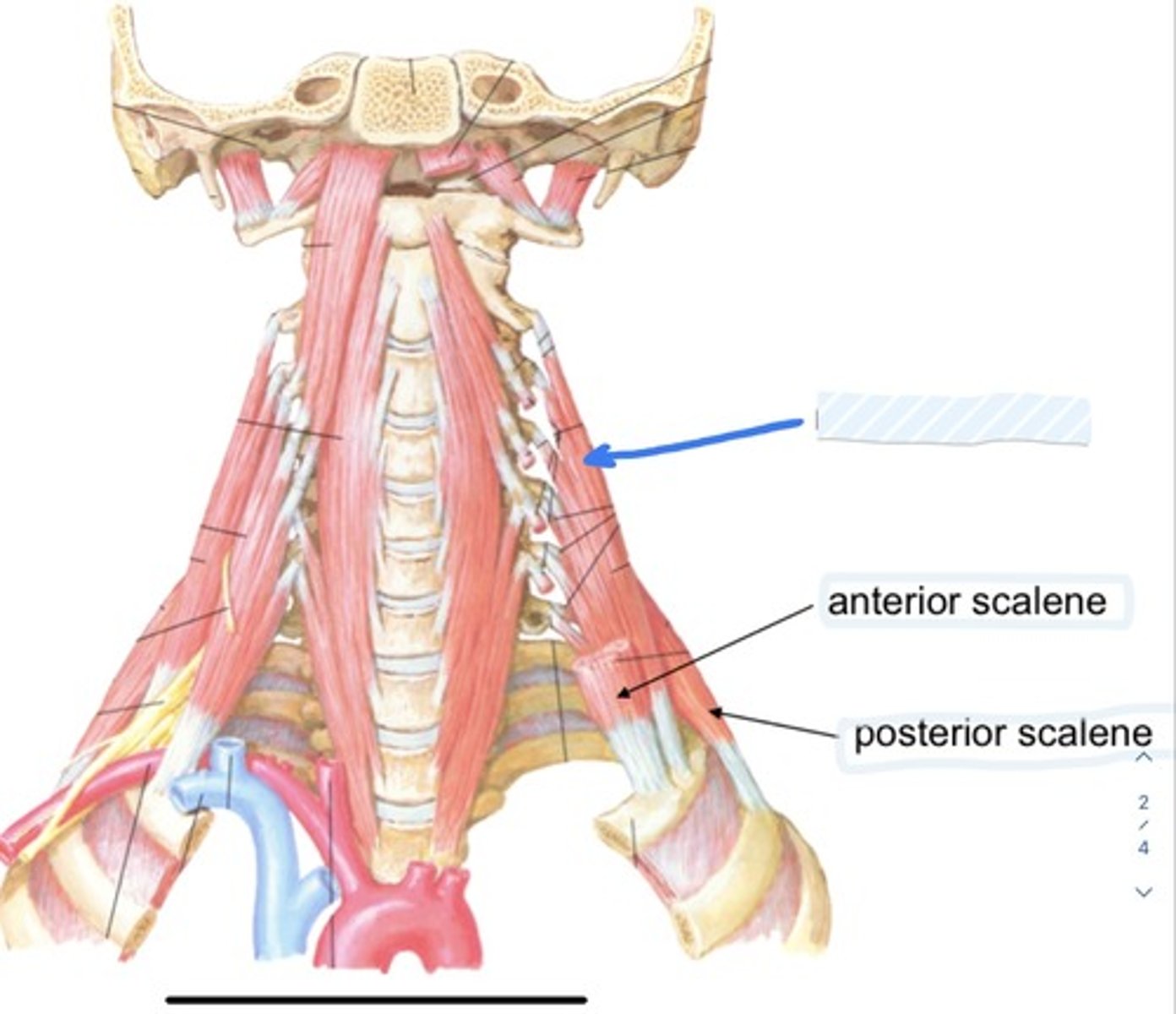
Anterior scalene
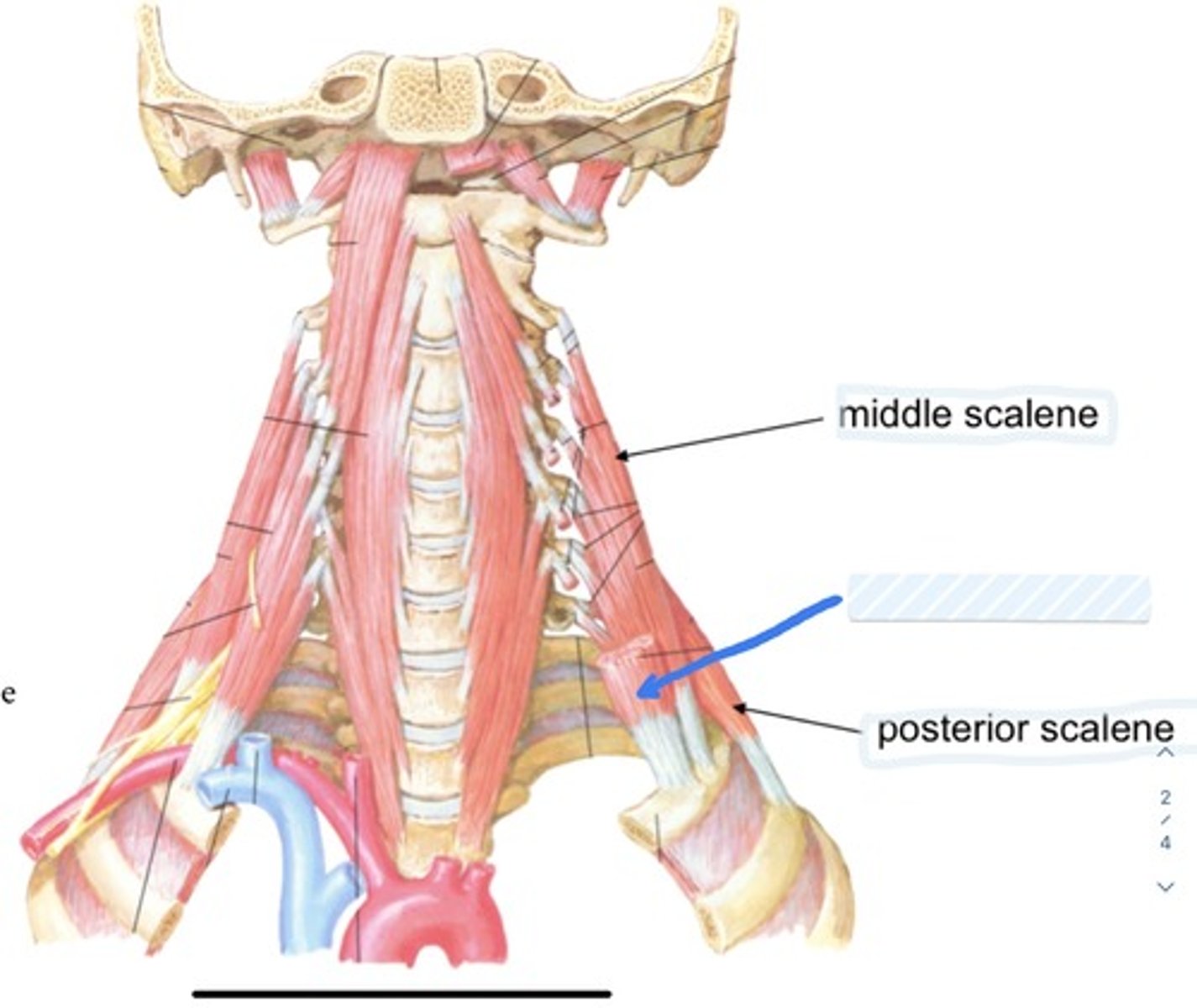
Posterior scalene
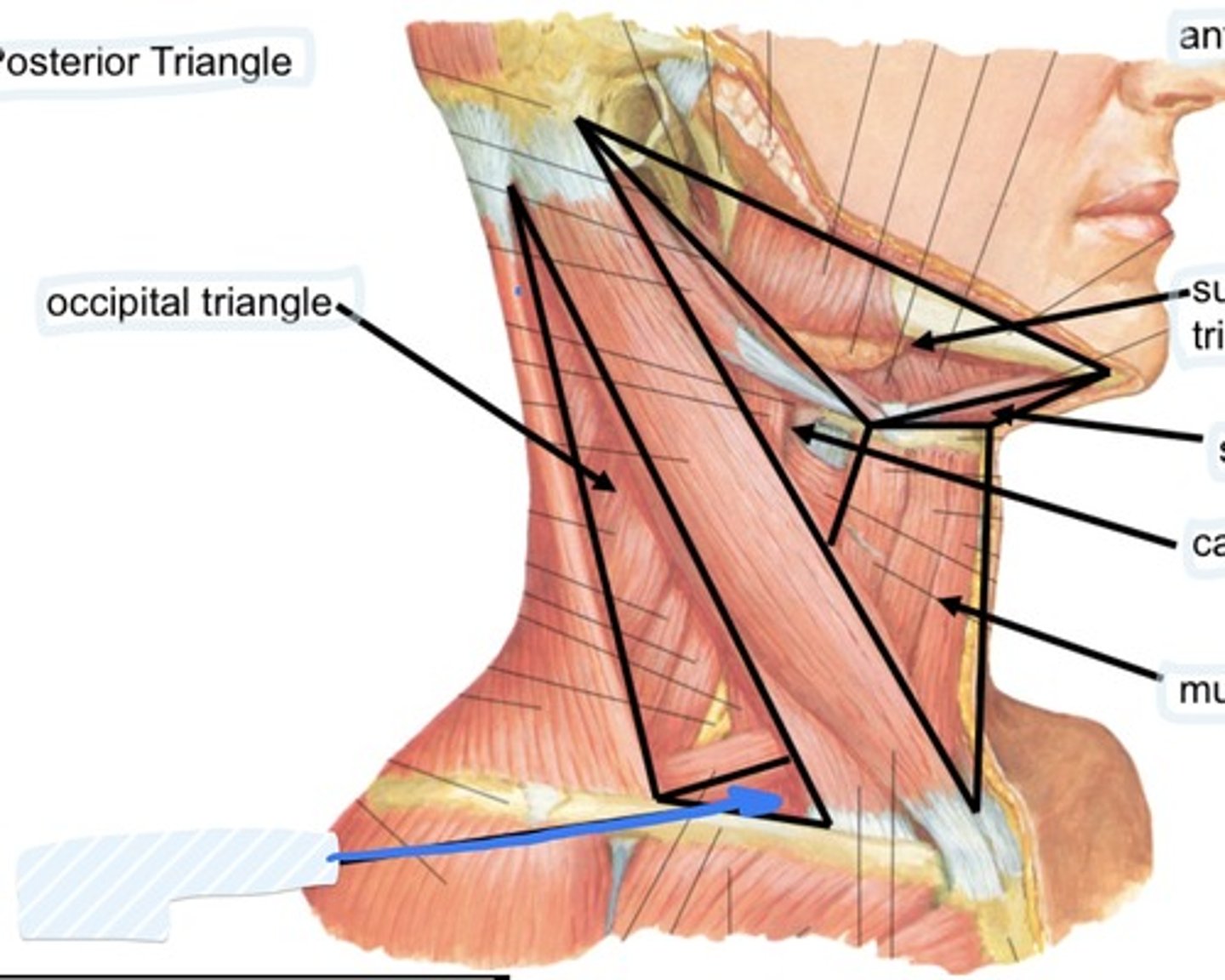
Occipital triangle
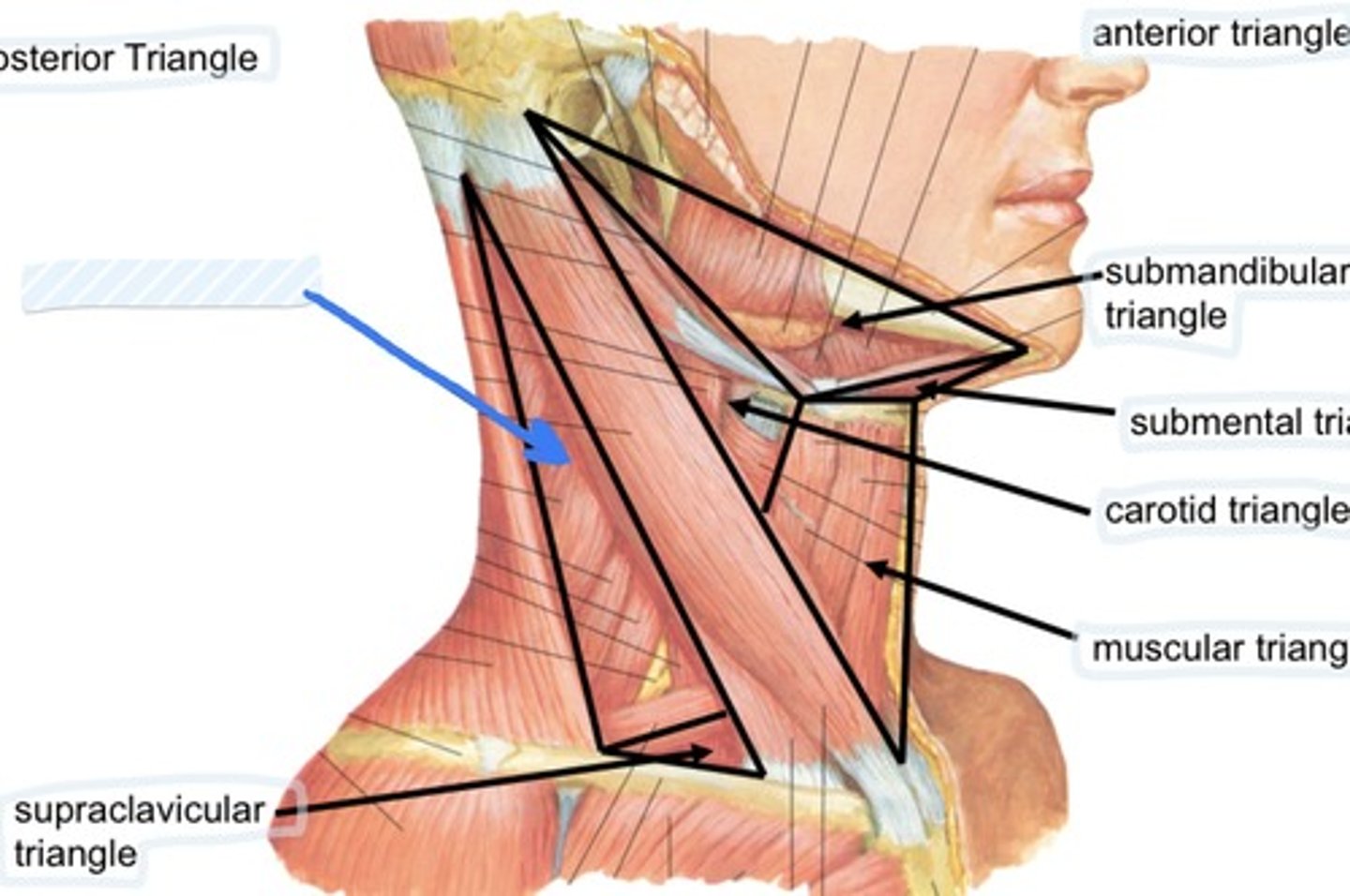
Supraclavicular triangle
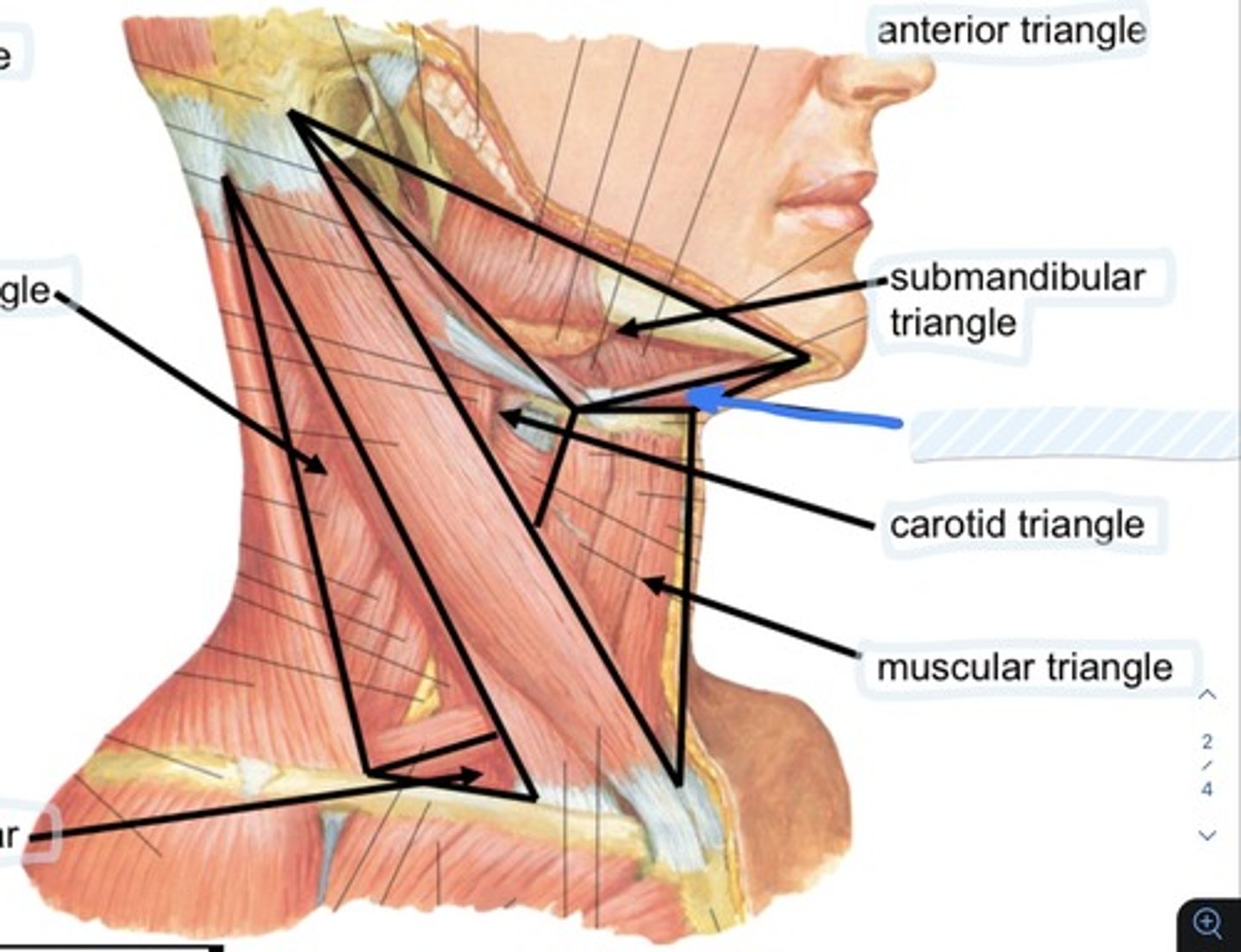
Submandibular triangle
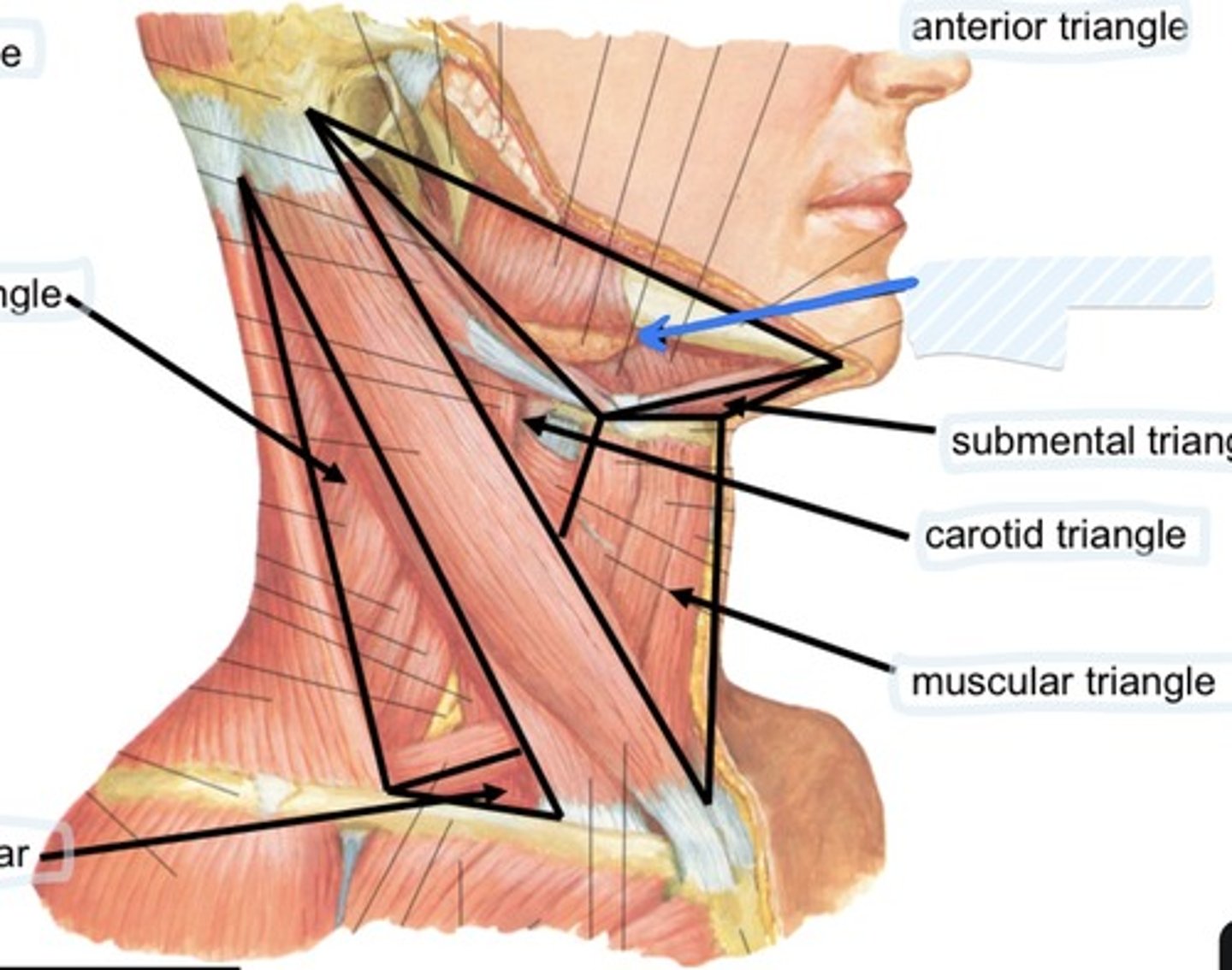
Submental triangle
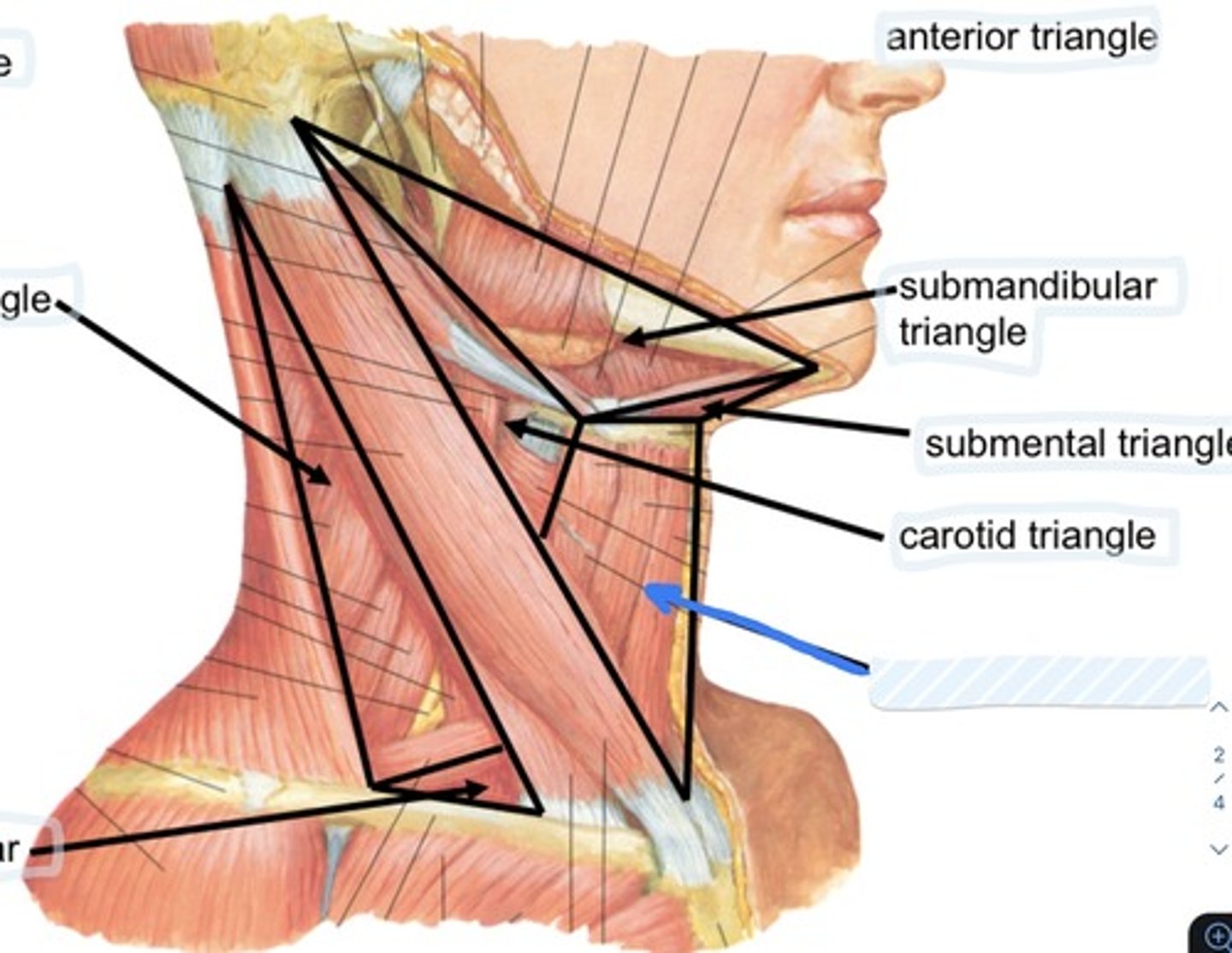
Carotid triangle
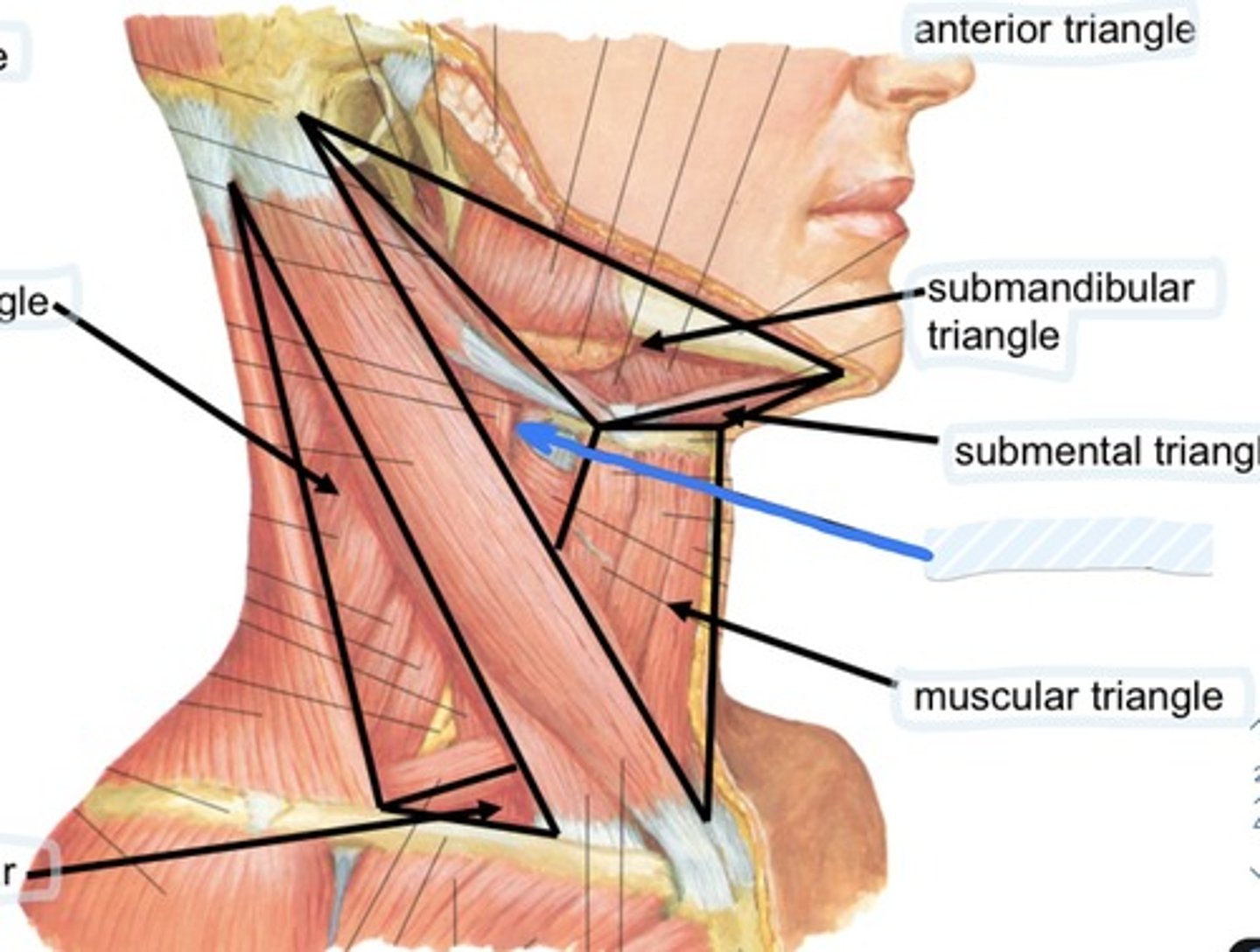
Muscular triangle
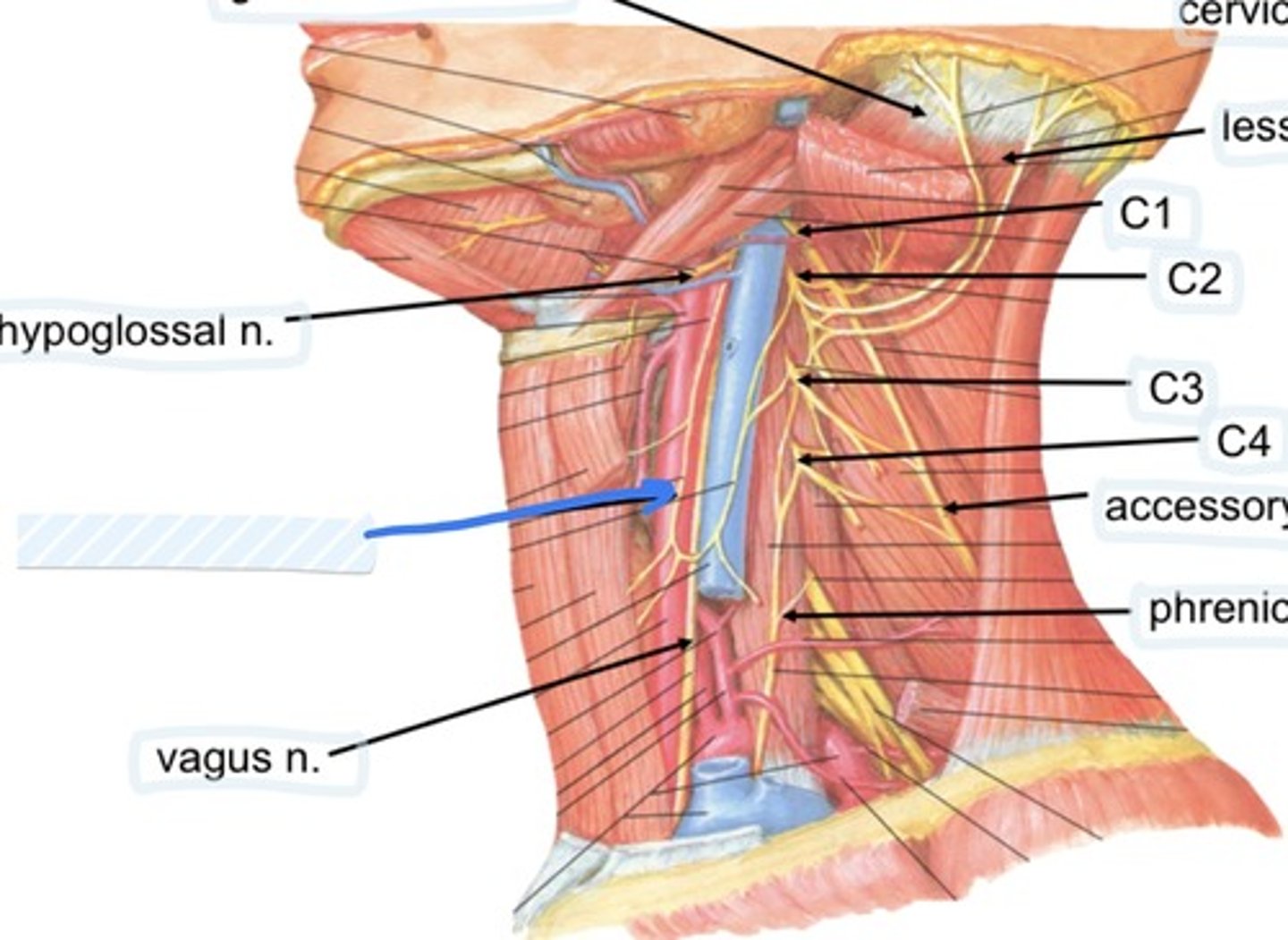
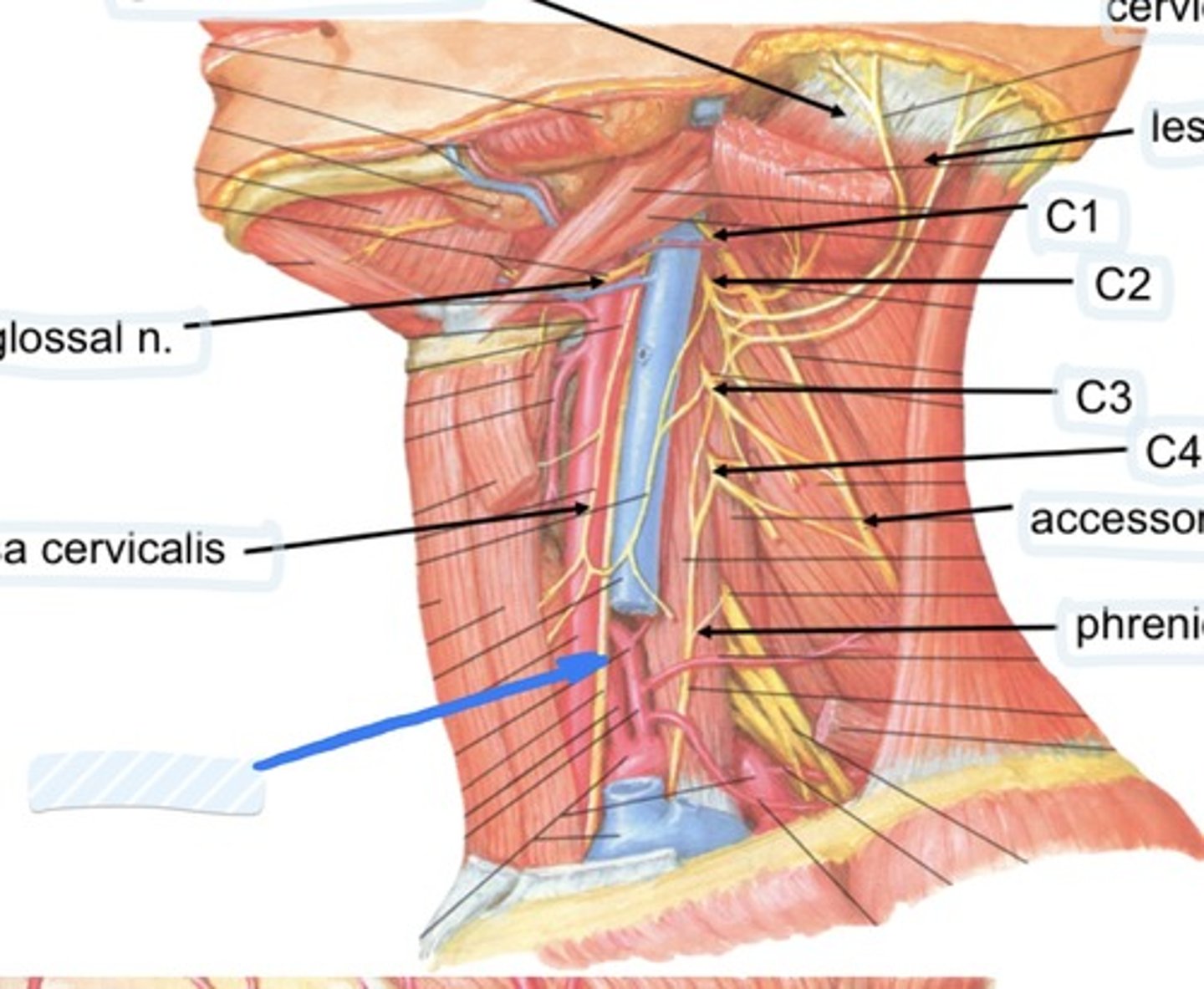
Hypoglossal n.
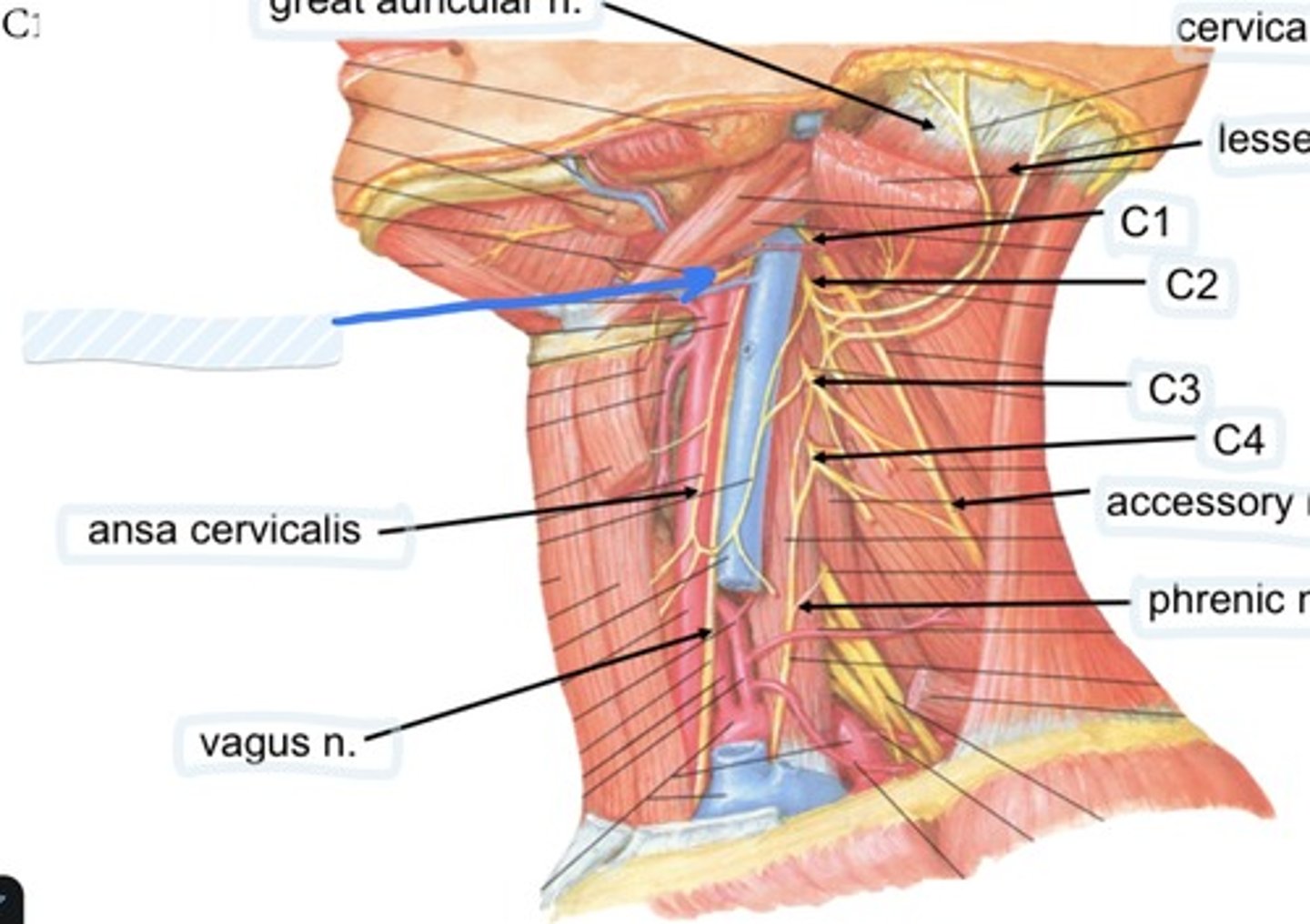
Ansa cervicalis
Vagus n.
Great auricular n.
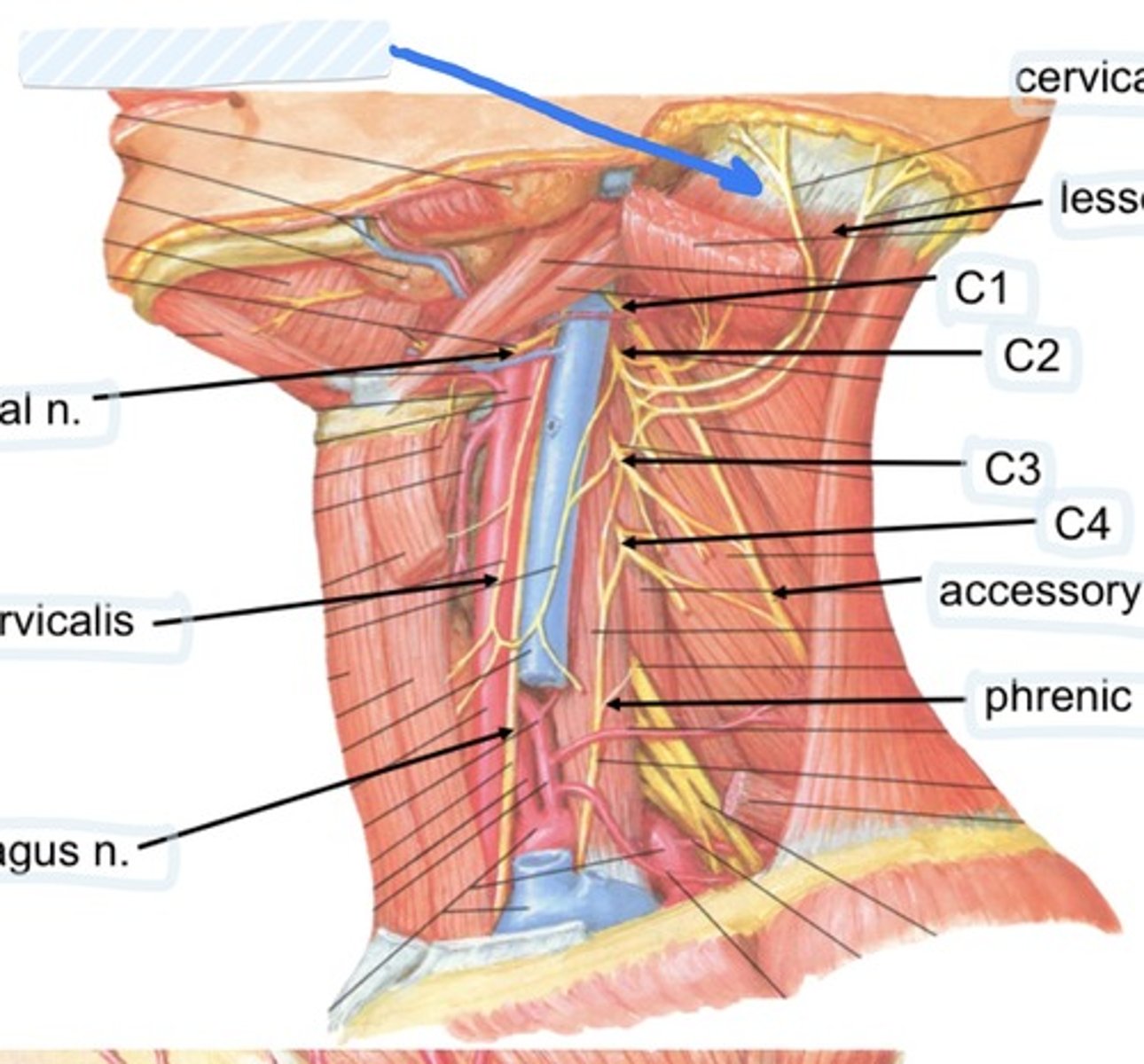
Cervical plexus
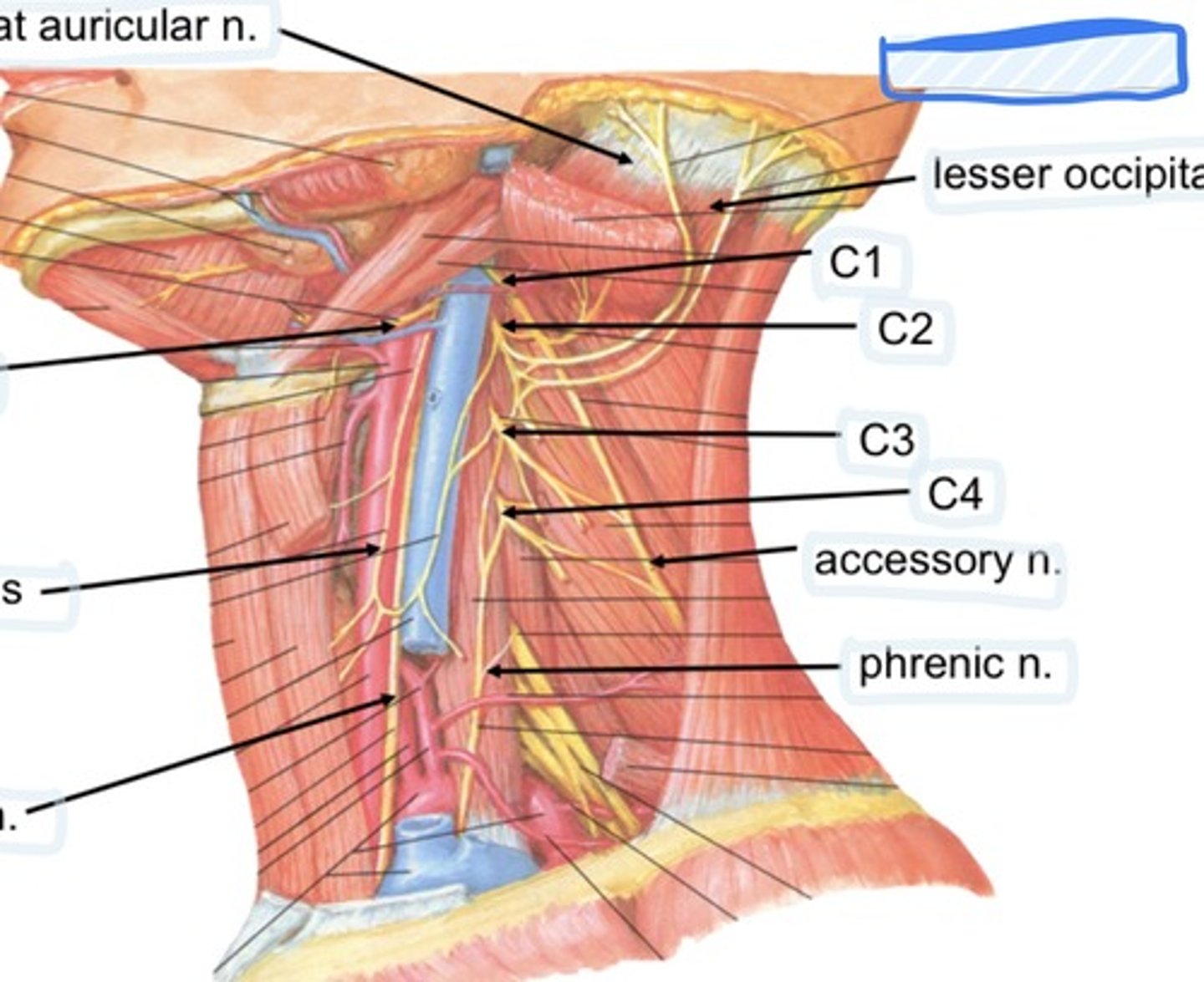
Lesser occipital n.
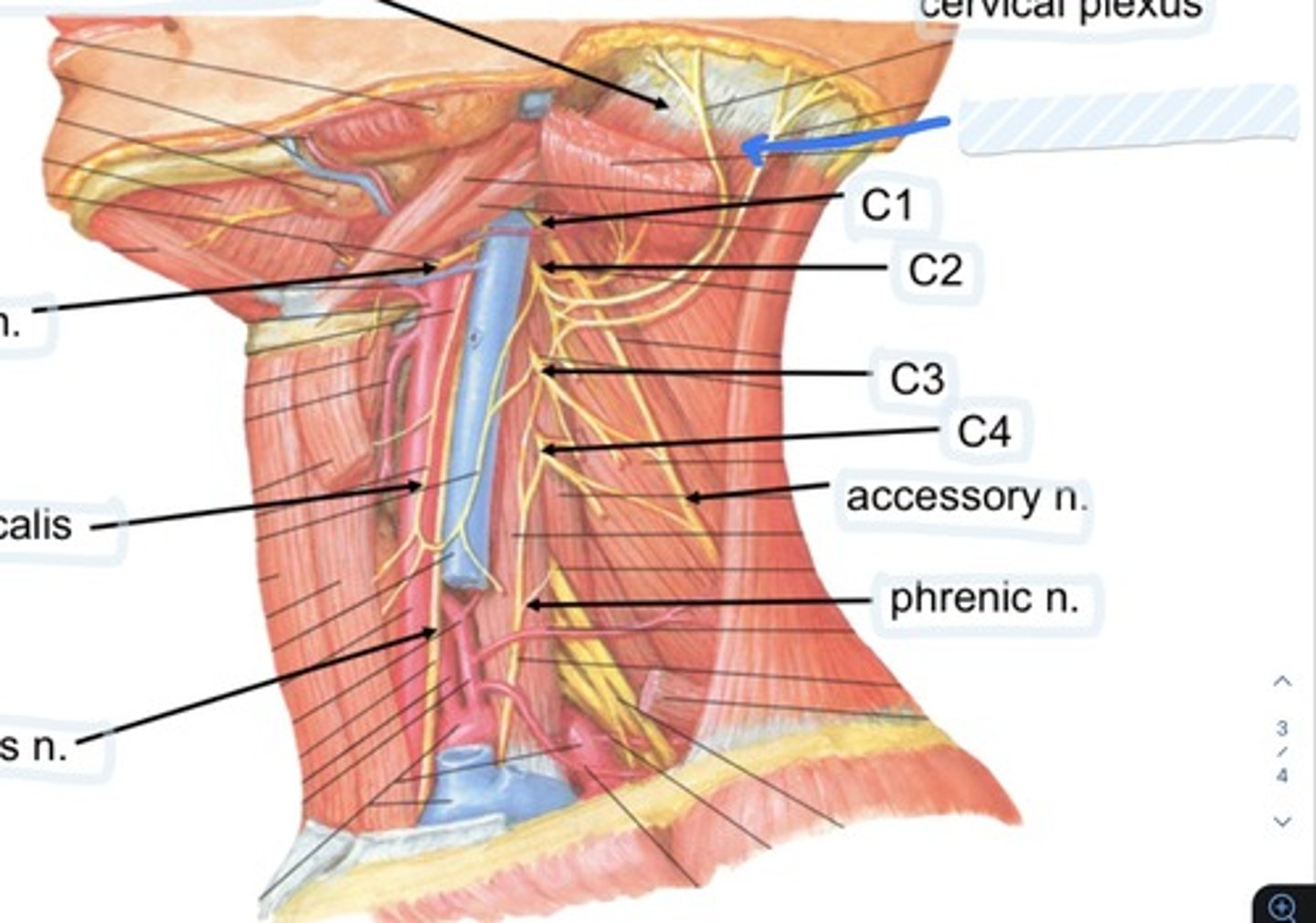
C1
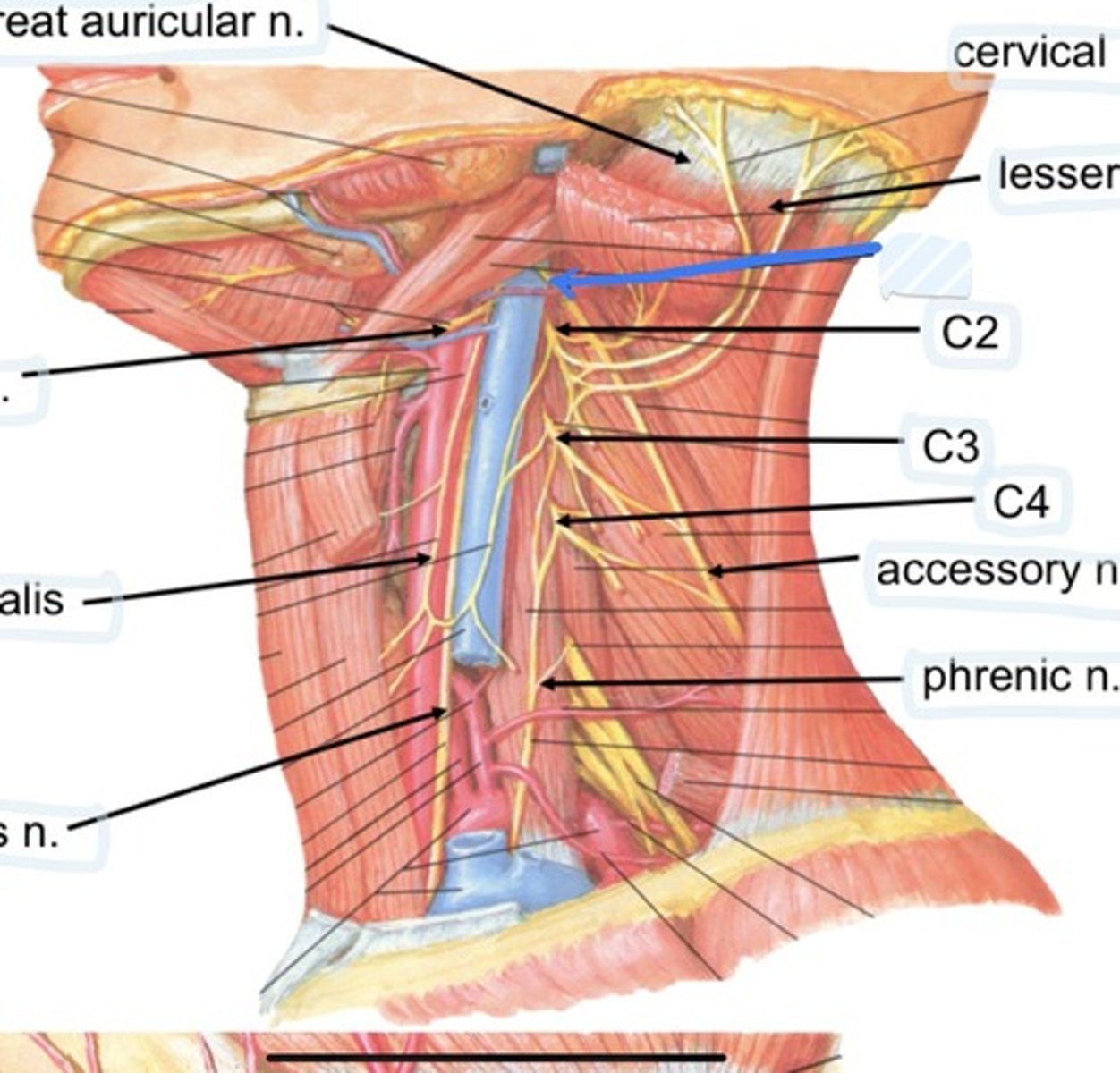
C2
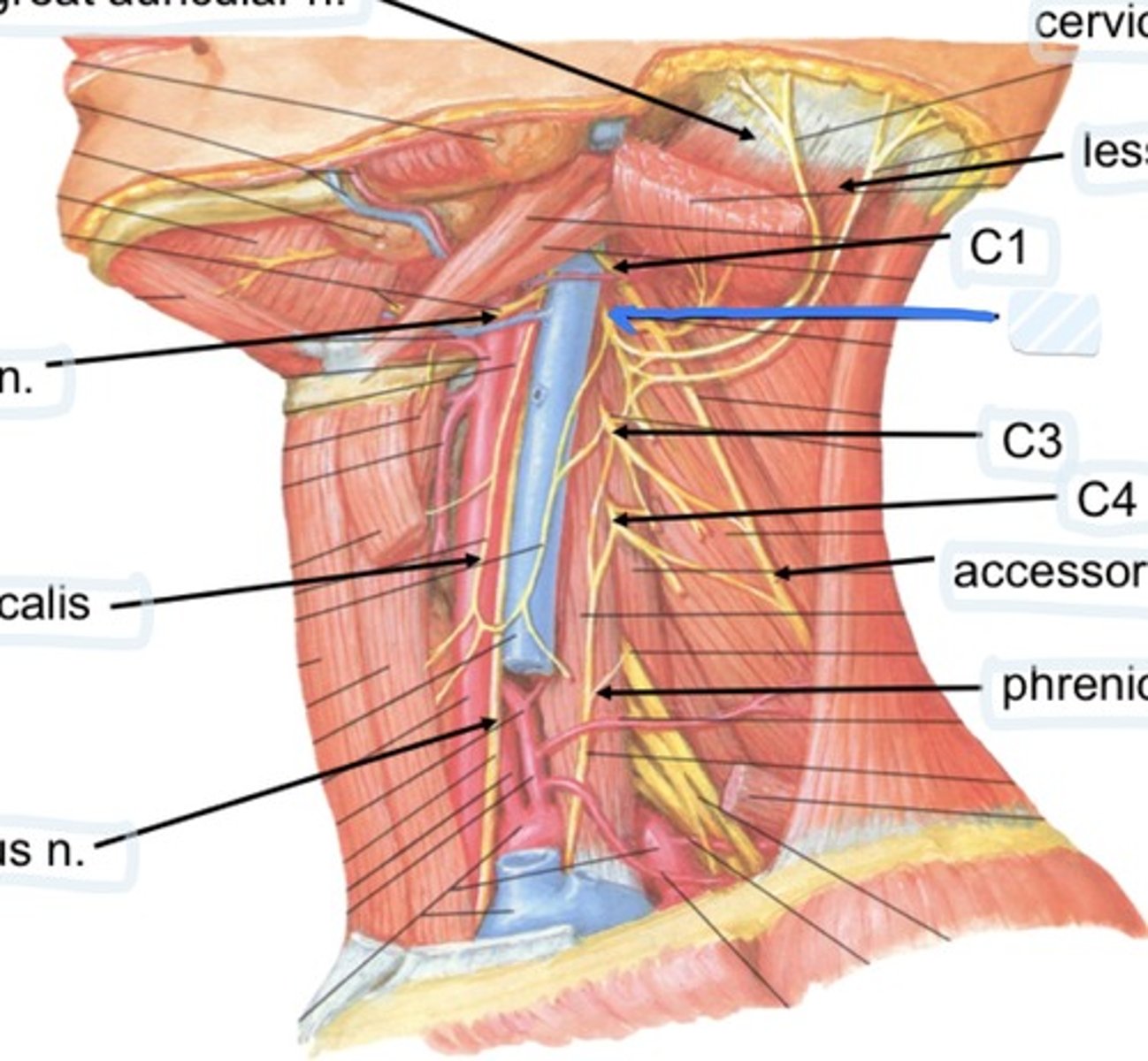
C3
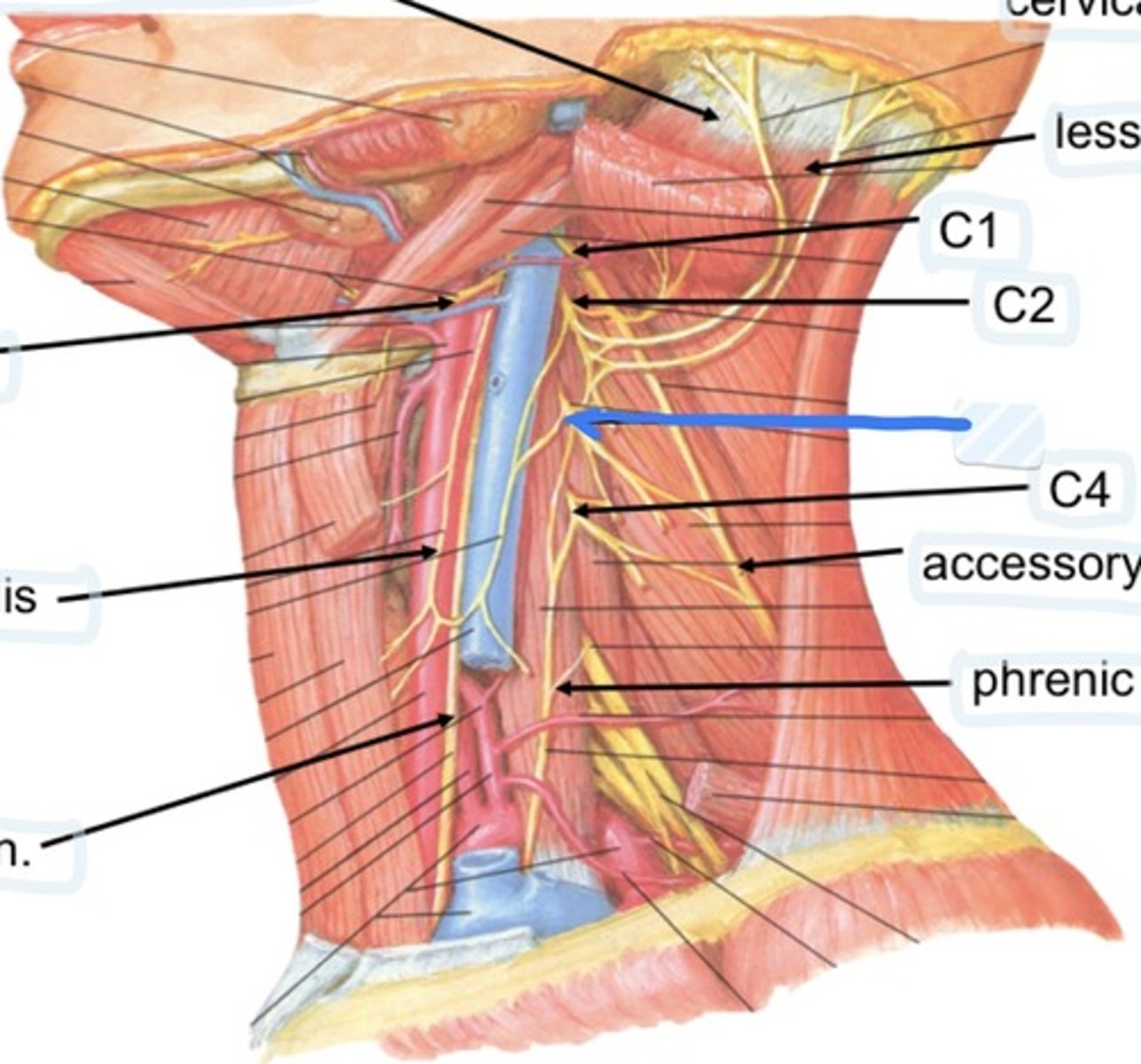
C4
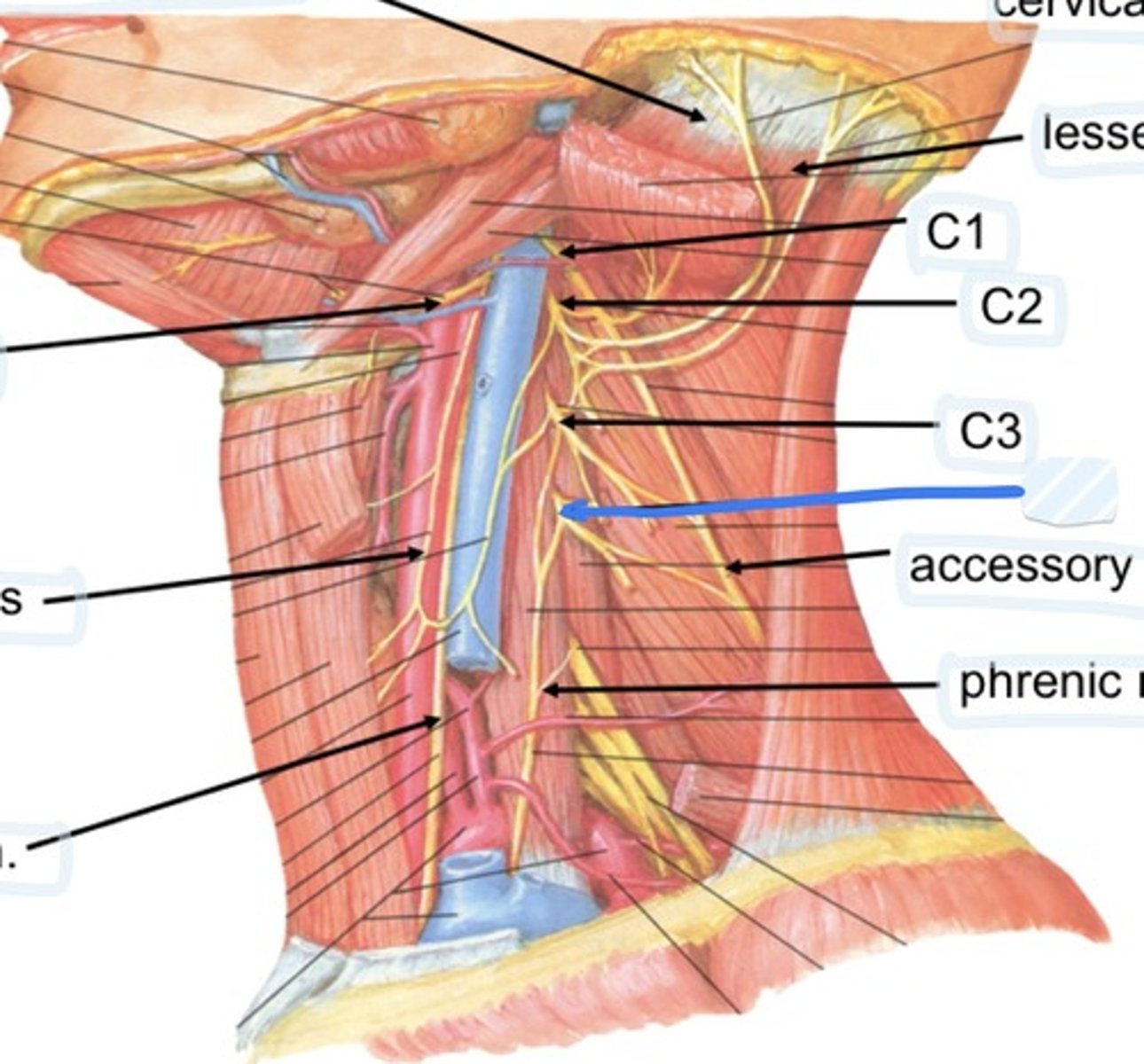
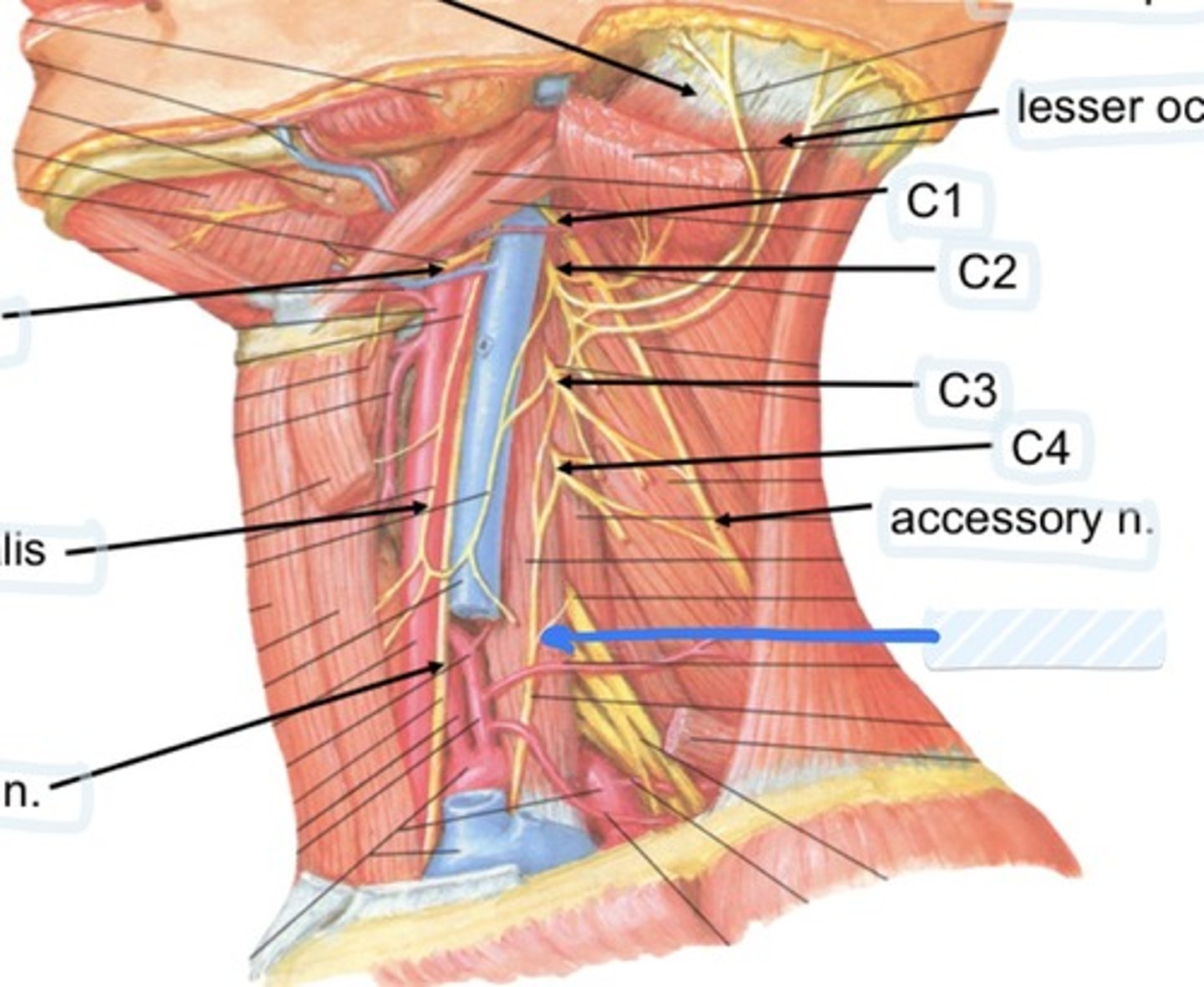
Accessory n.
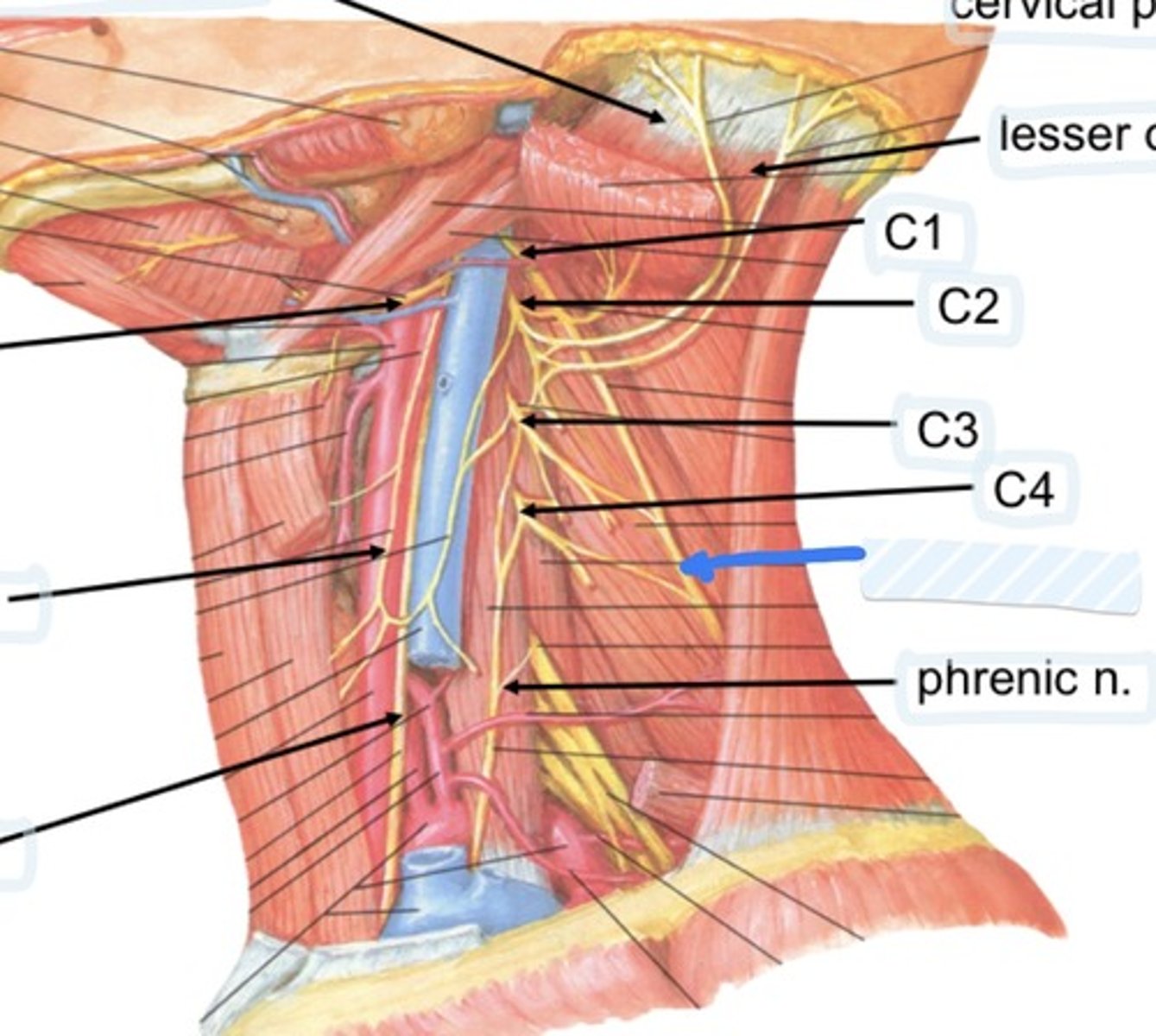
Phrenic n.
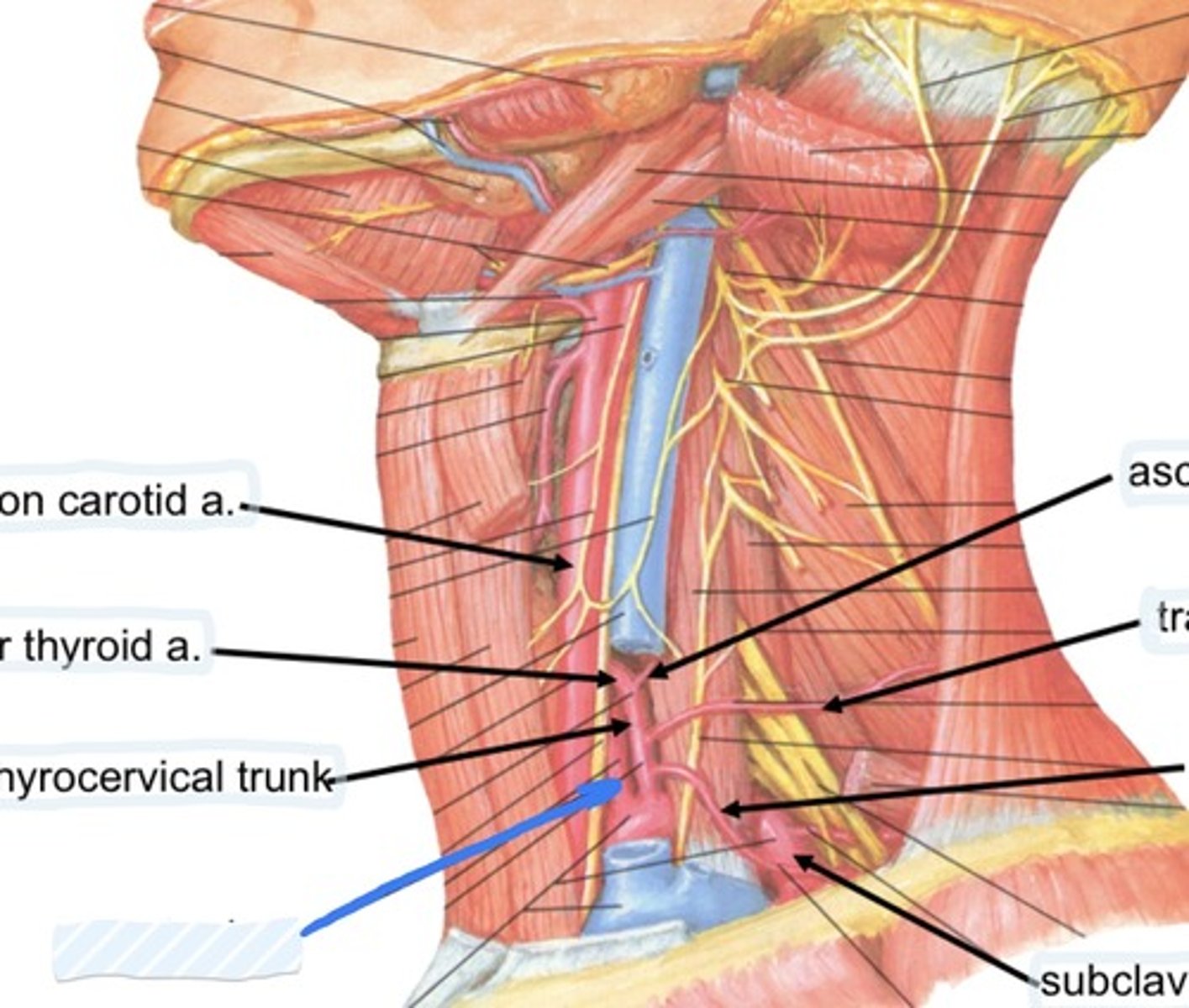
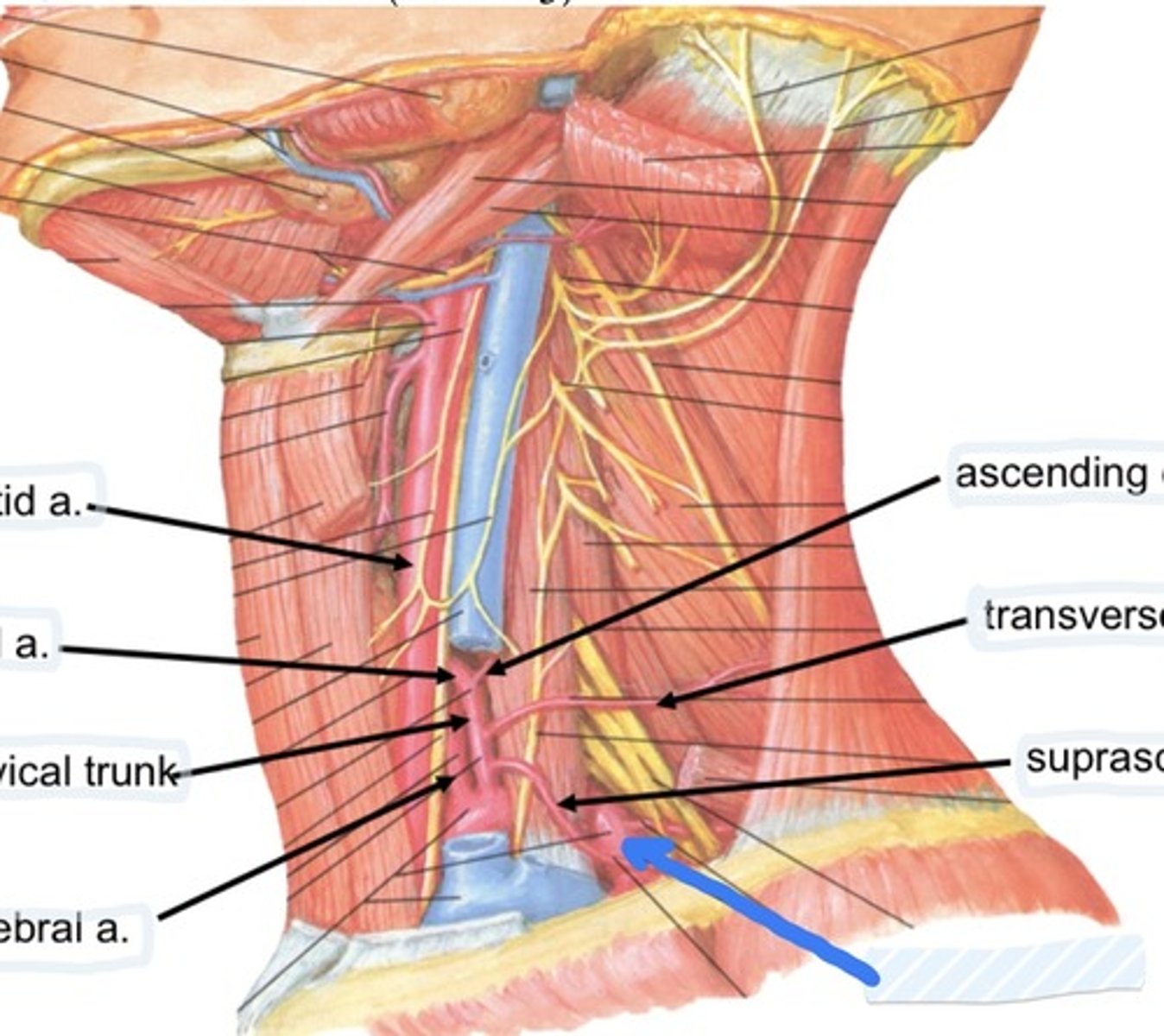
Common carotid a.
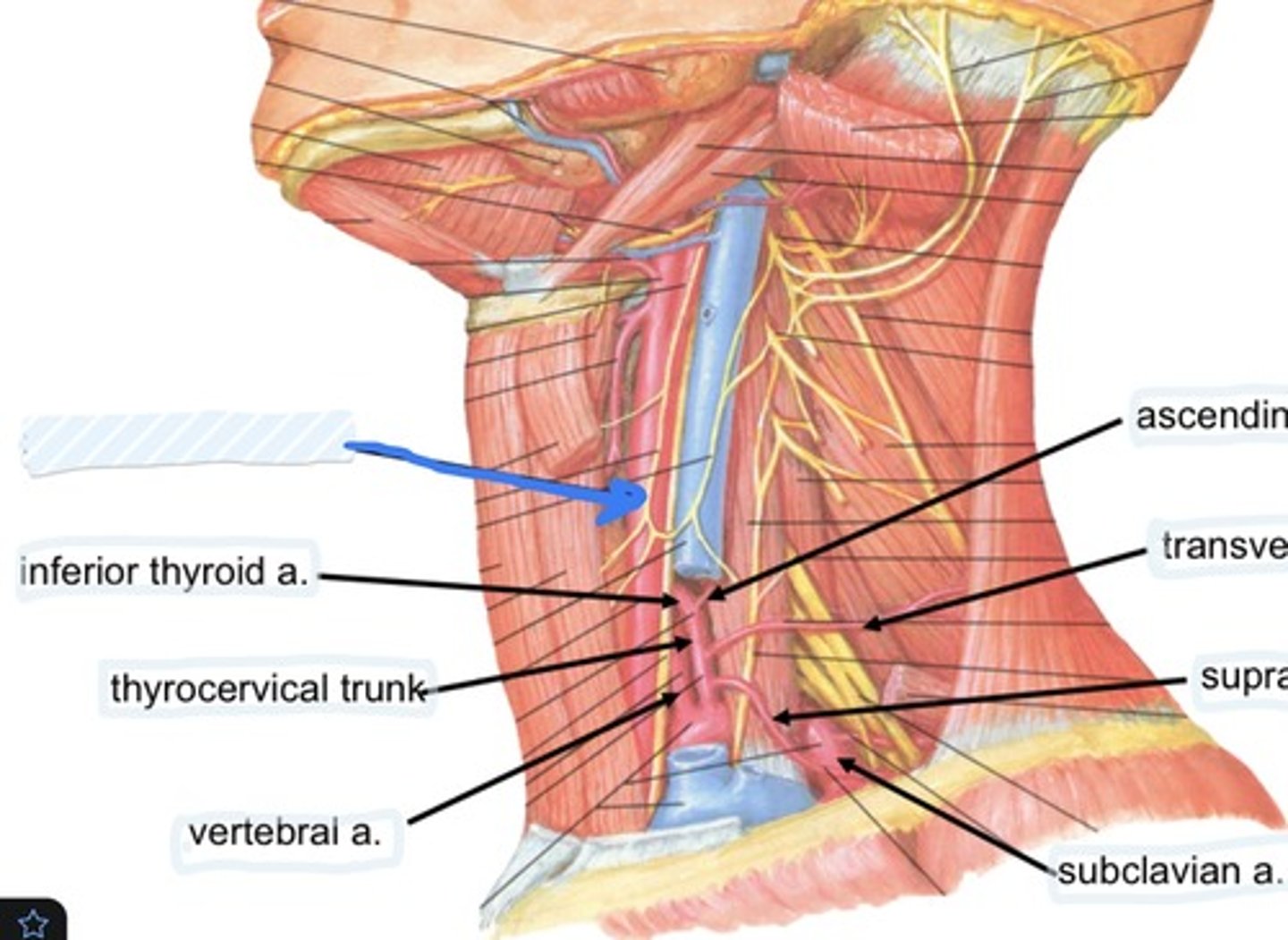
Inferior thyroid a.
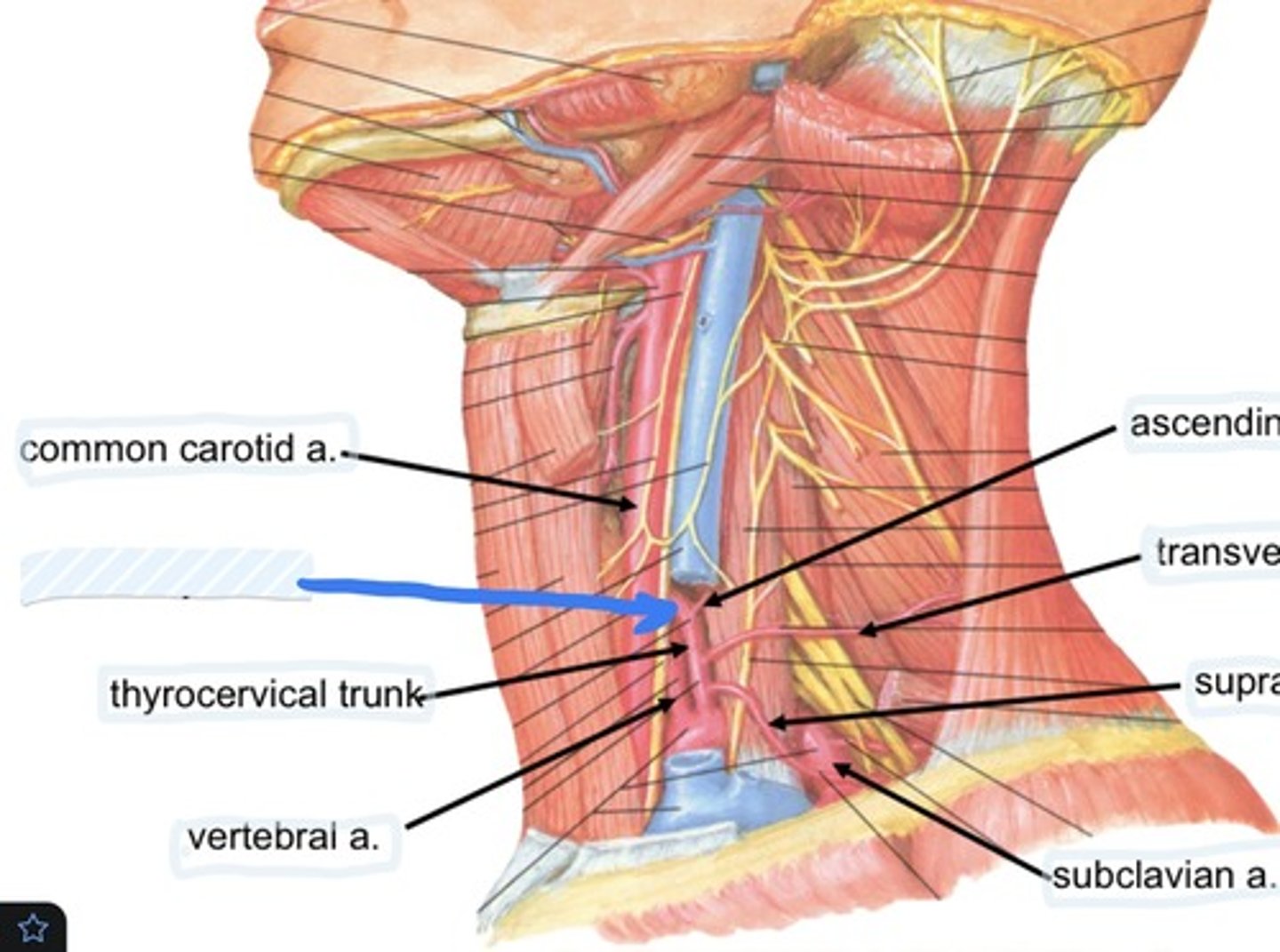
Vertebral a.
Ascending cervical a.
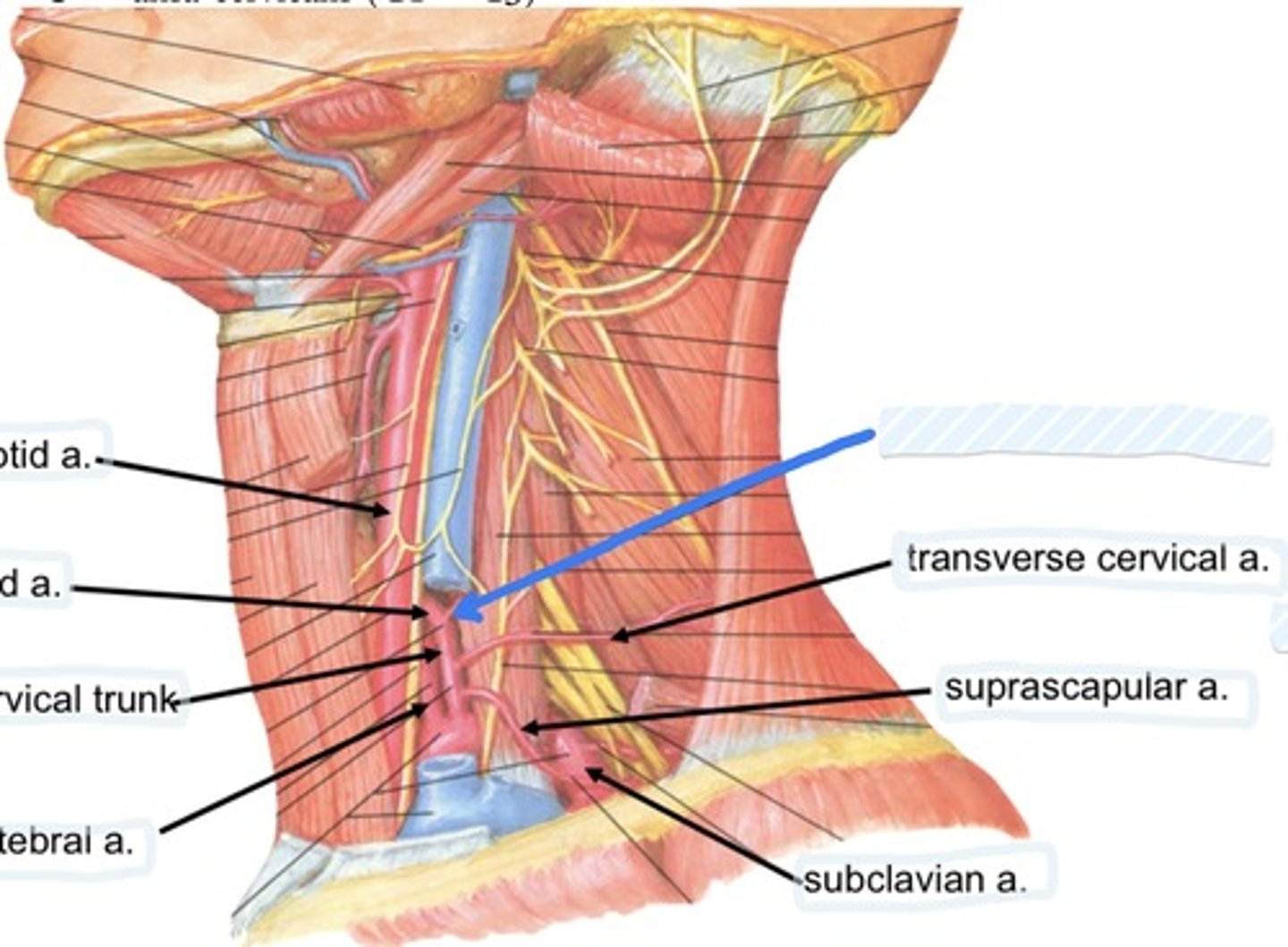
Transverse cervical a.
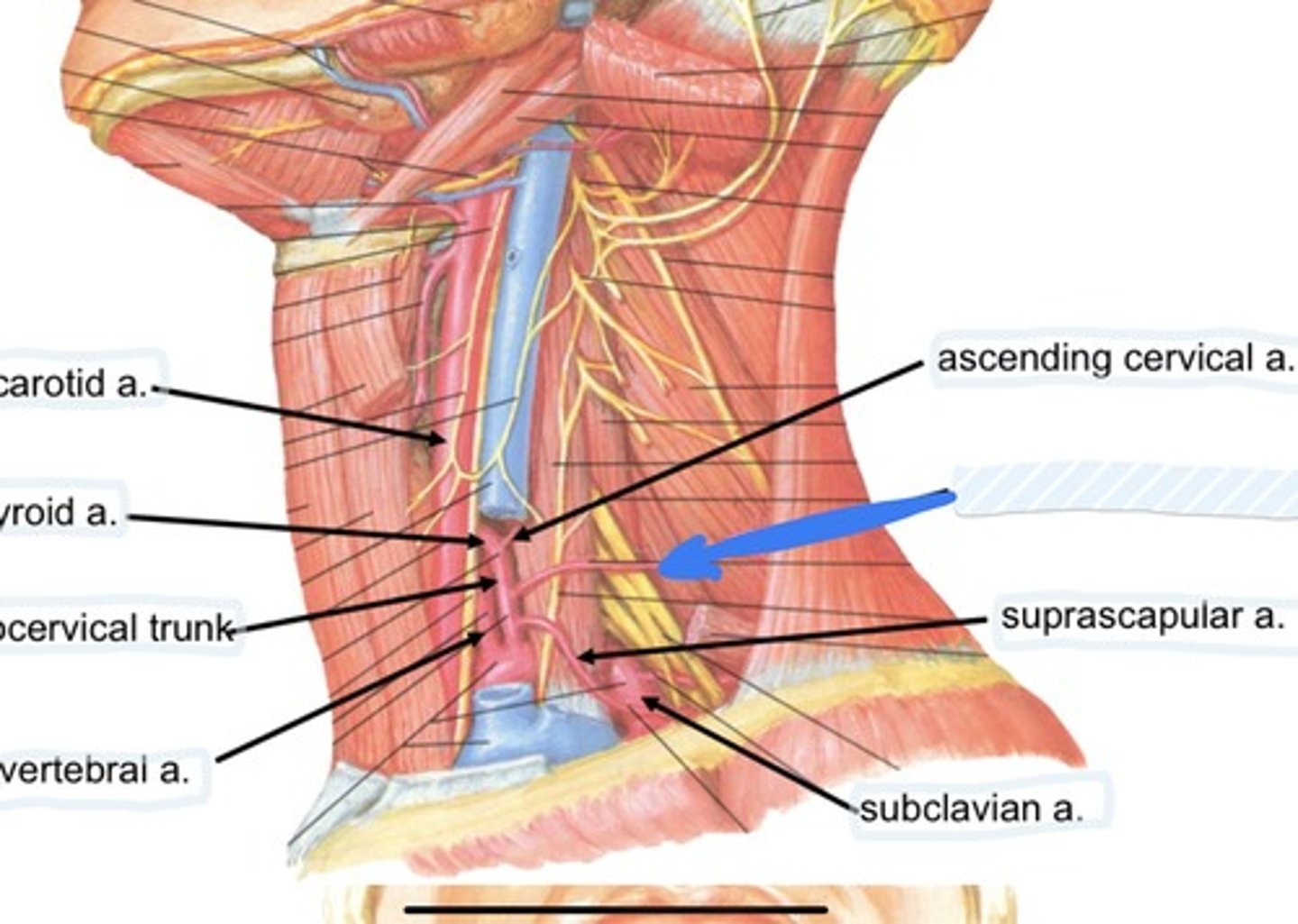
Suprascapular a.
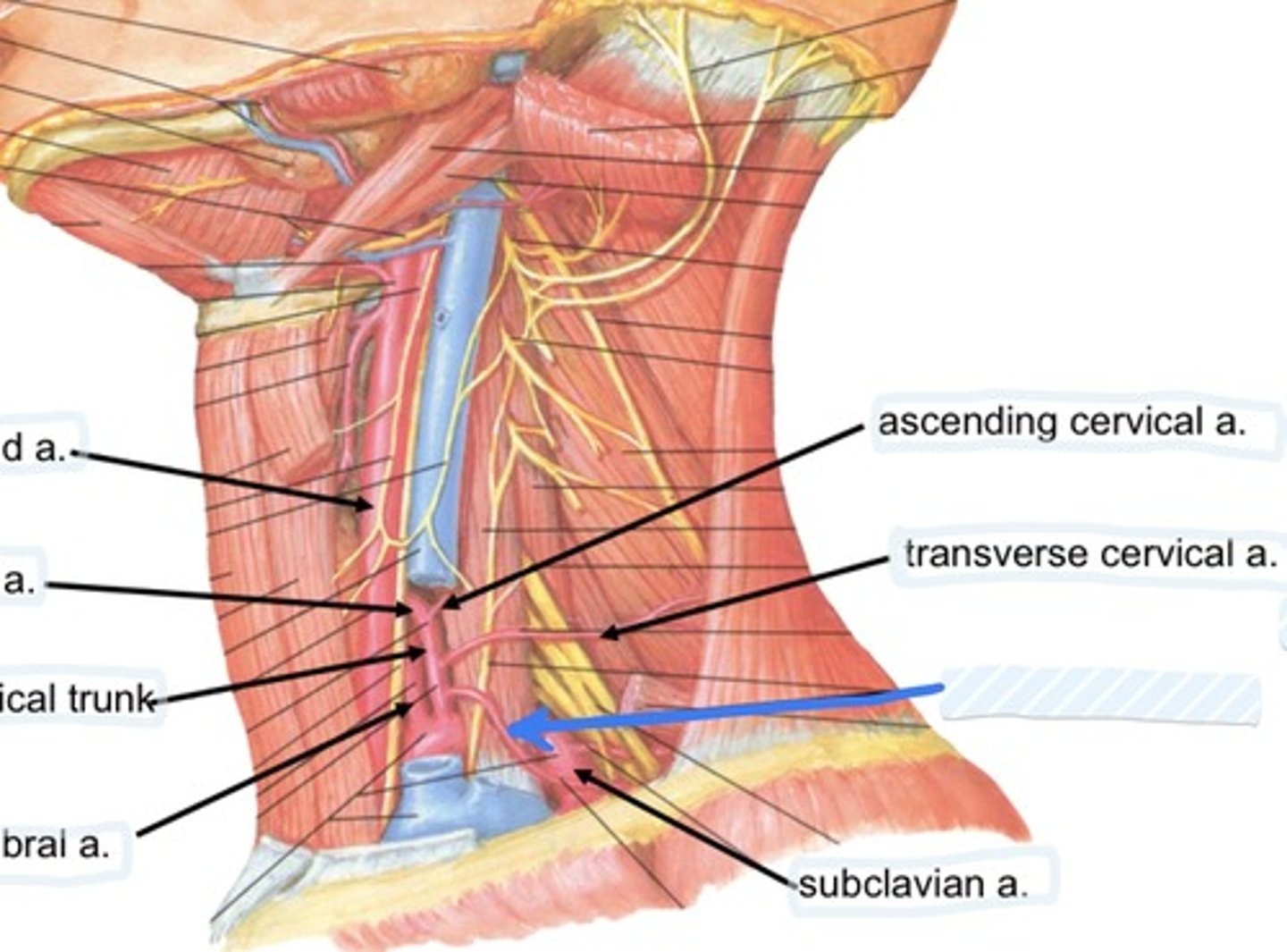
Subclavian a.
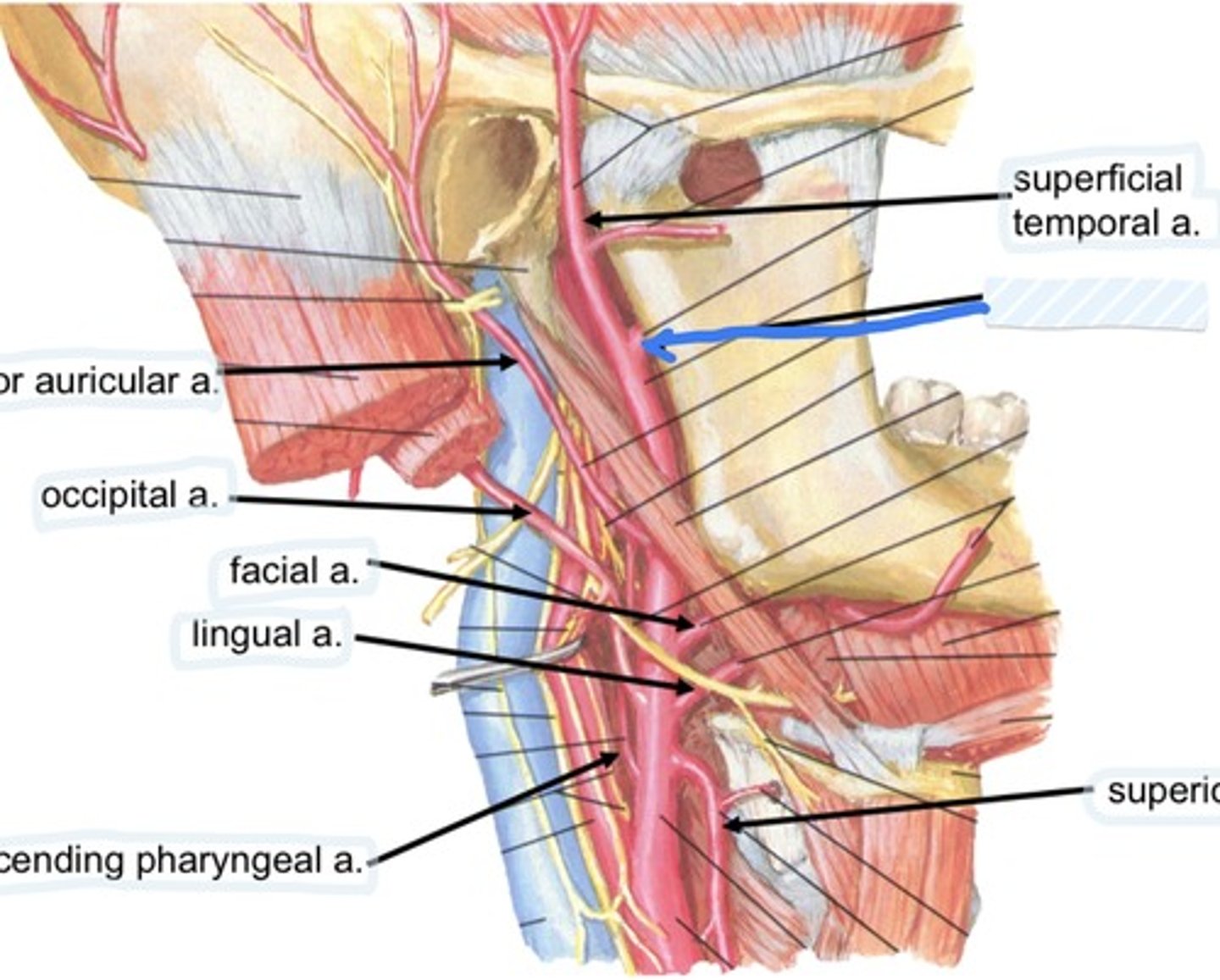
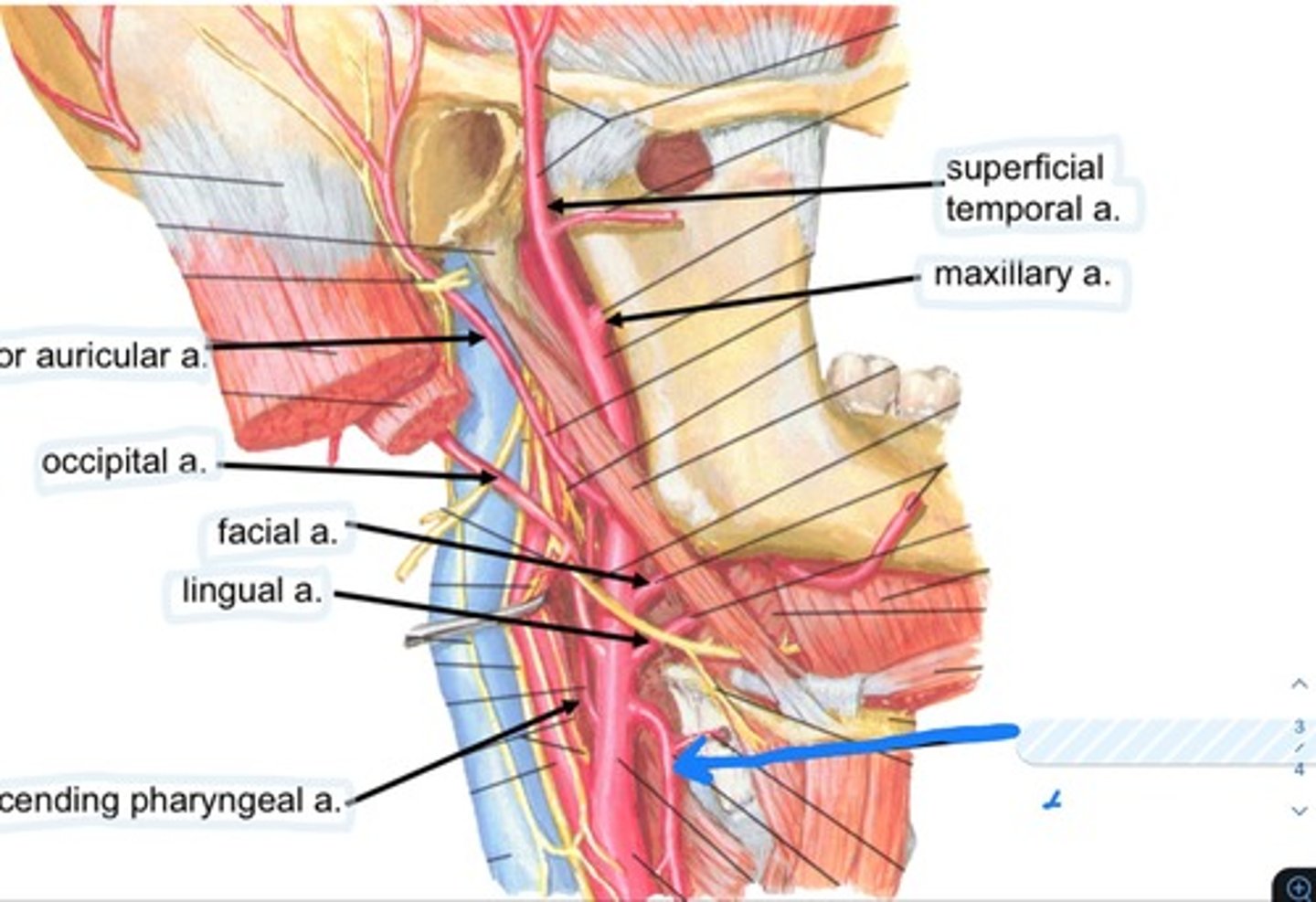
Occipital a.
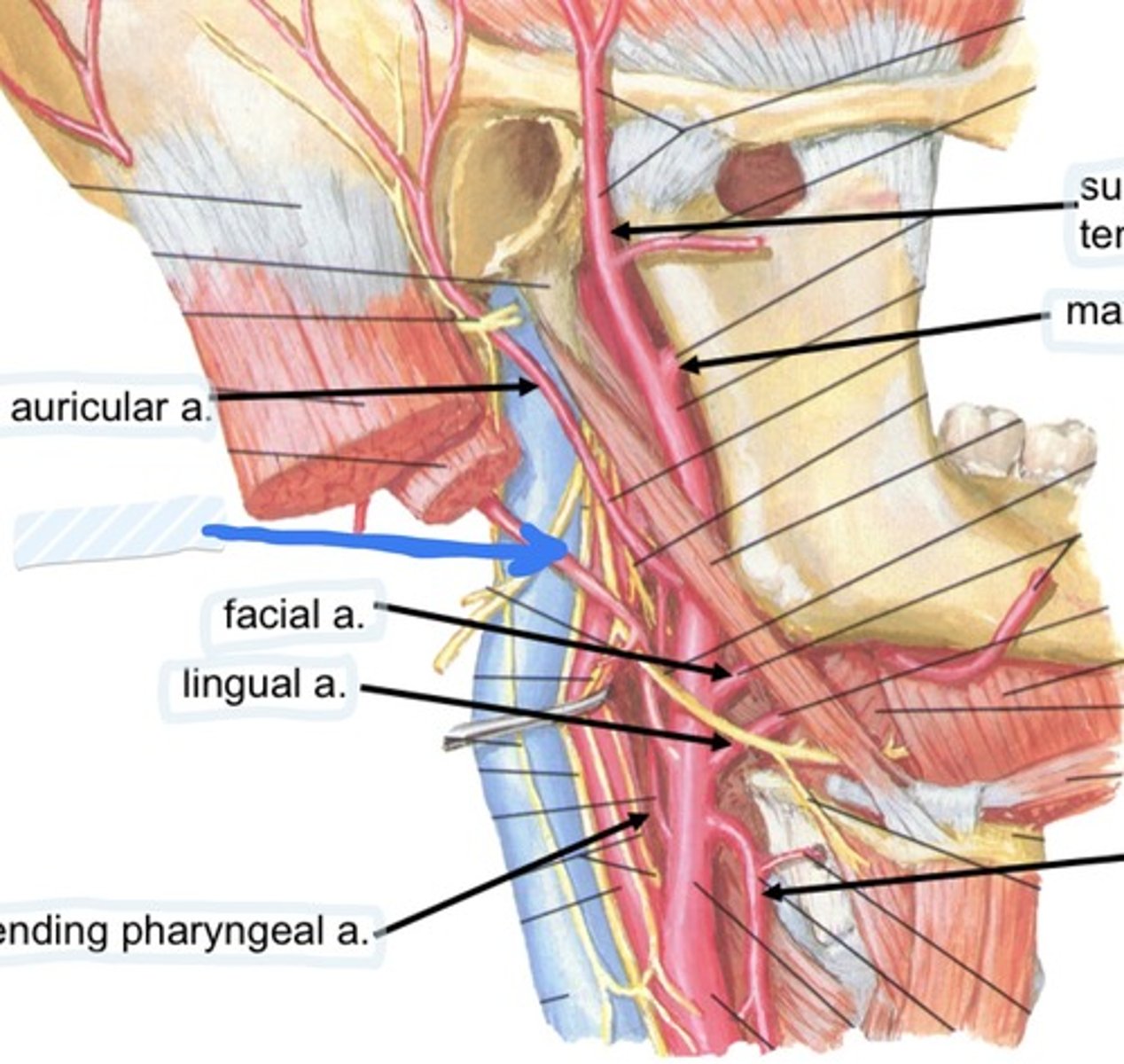
Facial a.
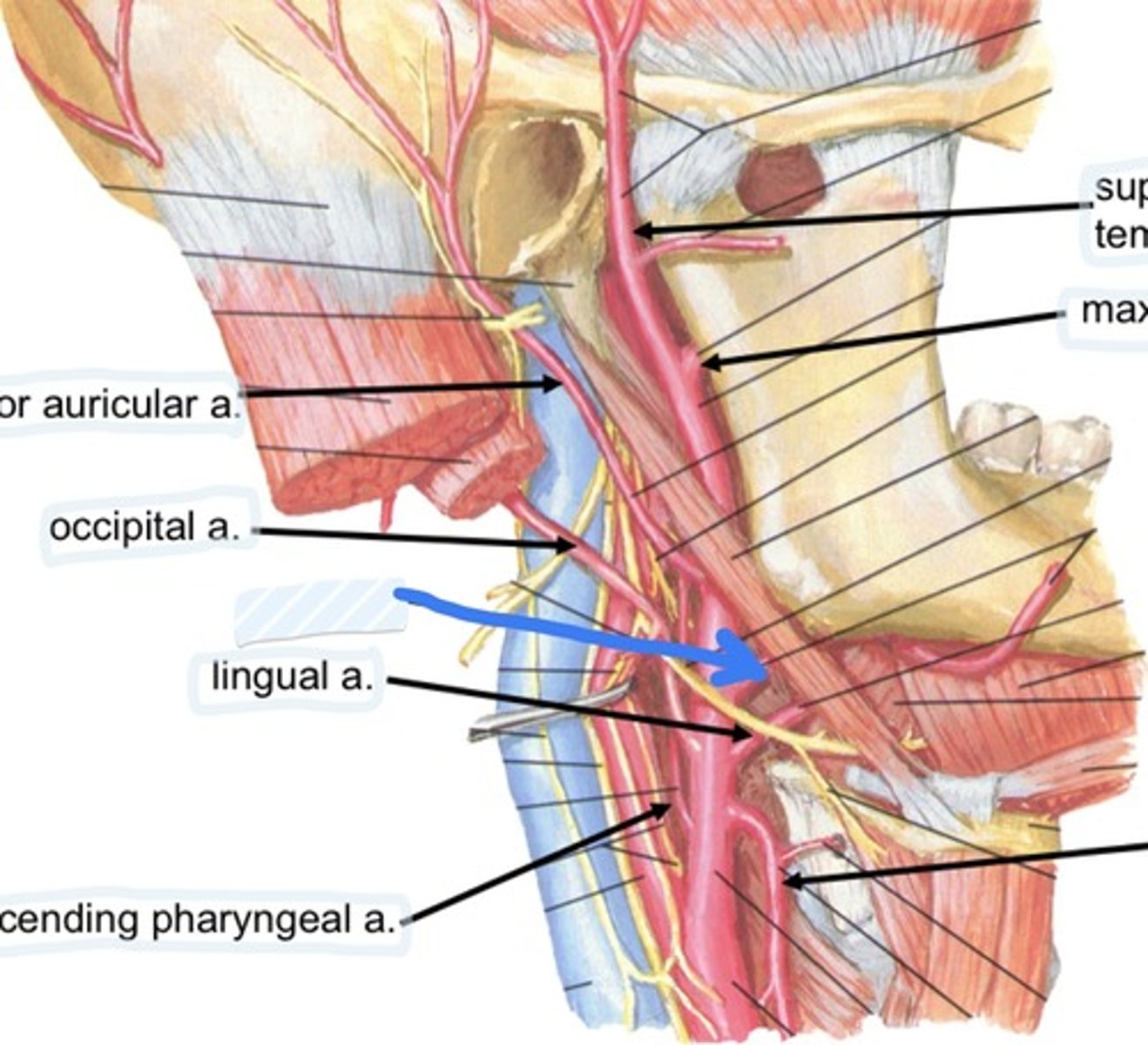
Lingual a.
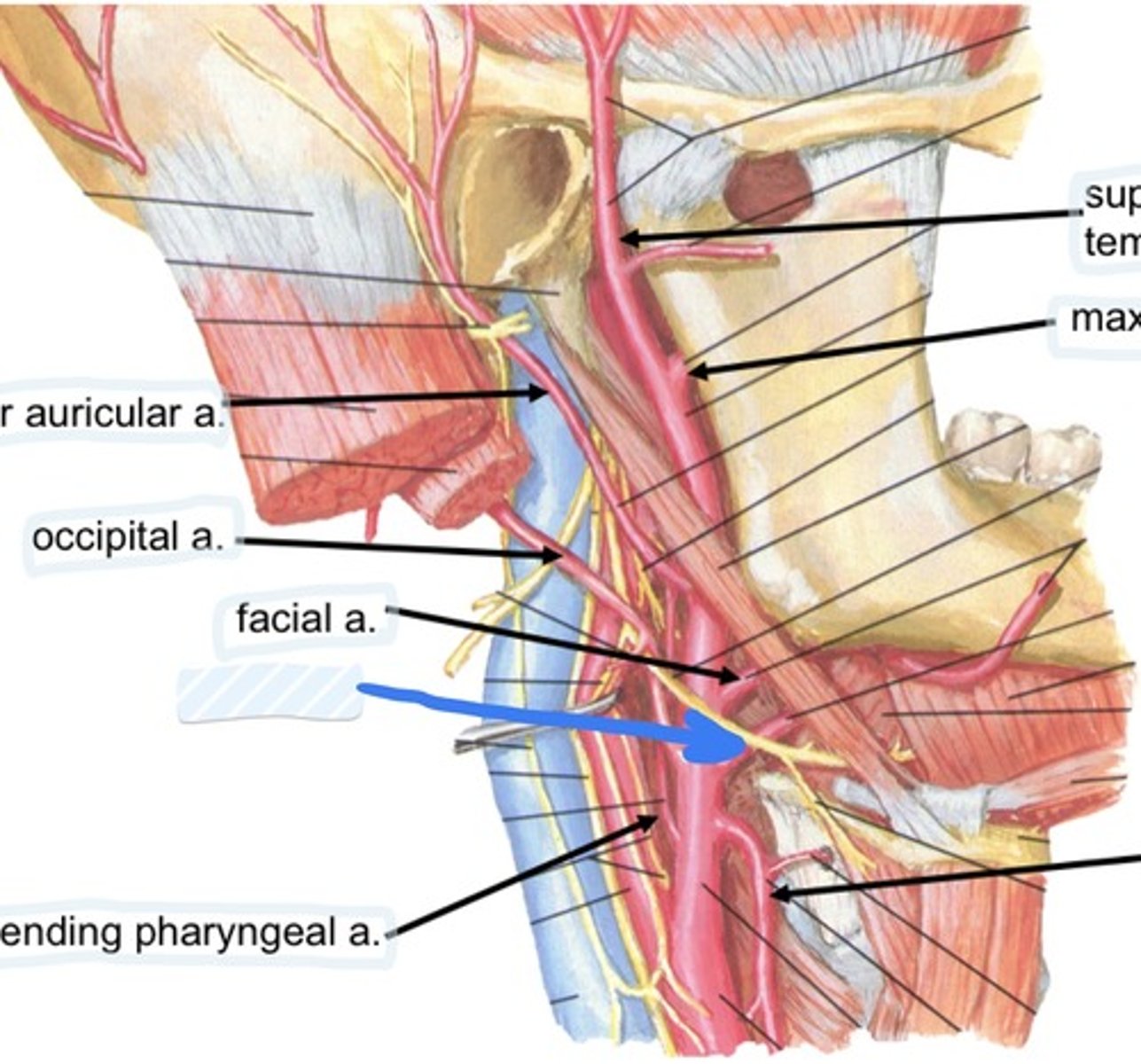
Ascending pharyngeal a.
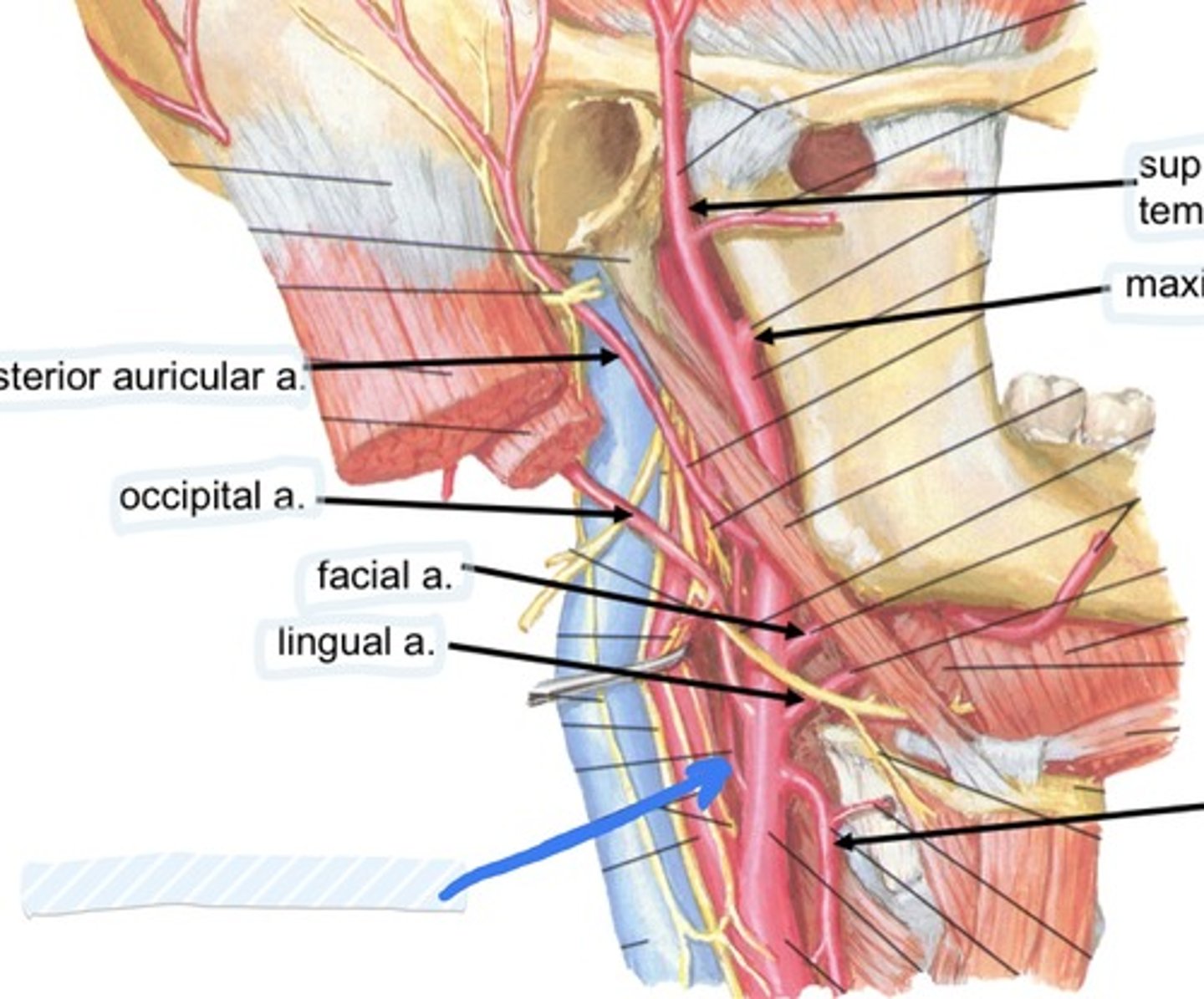
superficial temporal a.
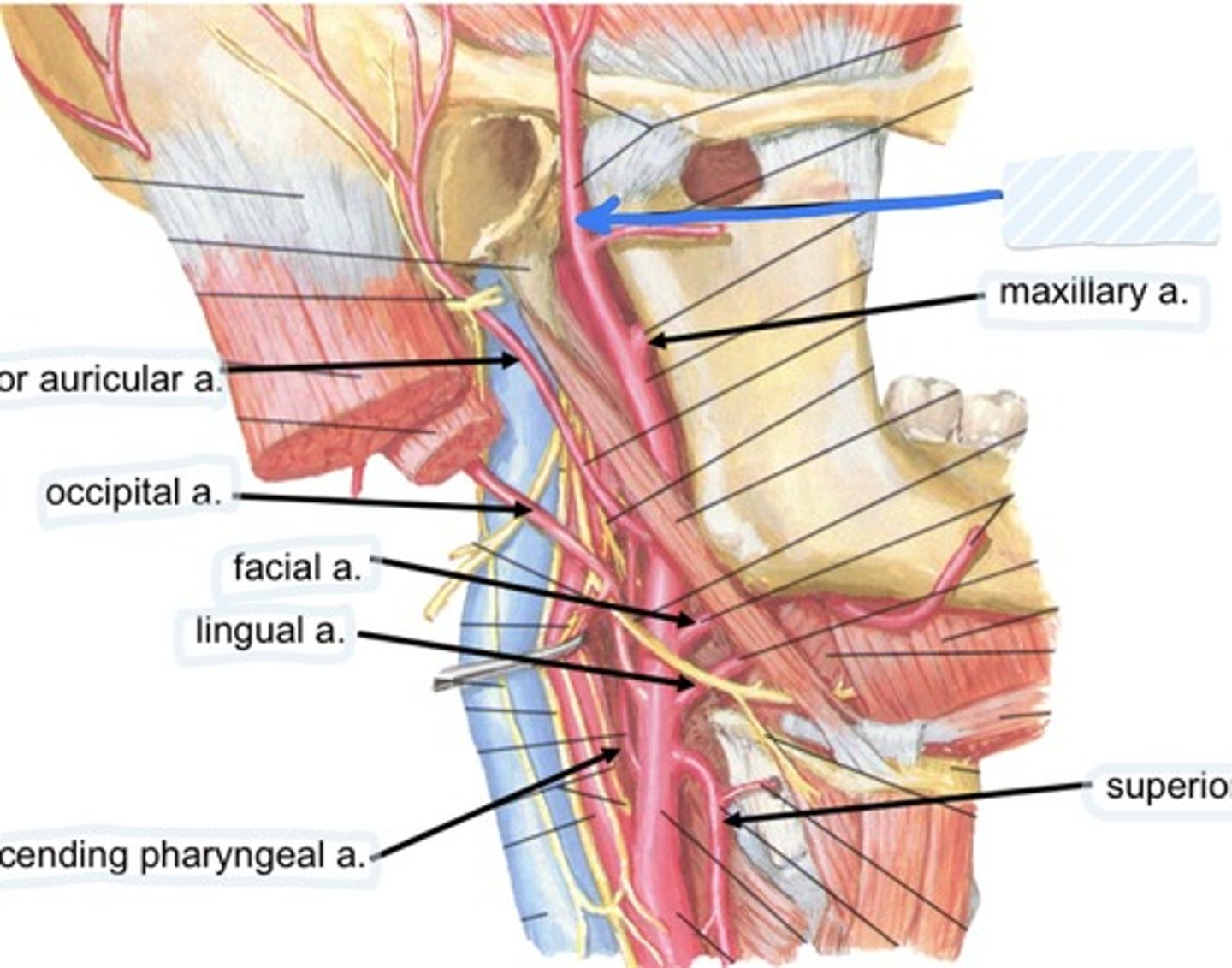
Maxillary a.
Superior thyroid a.
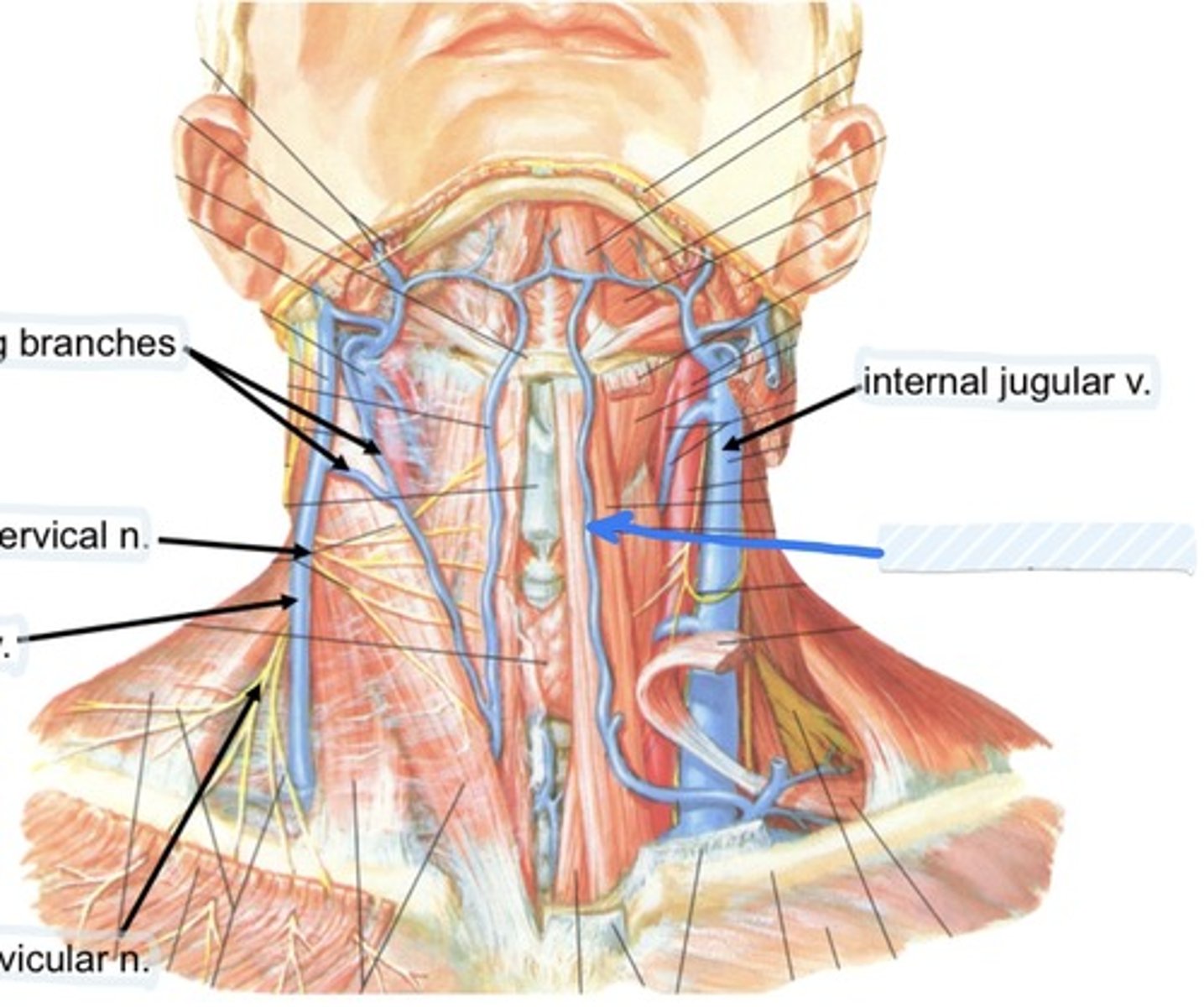
Communicating branches
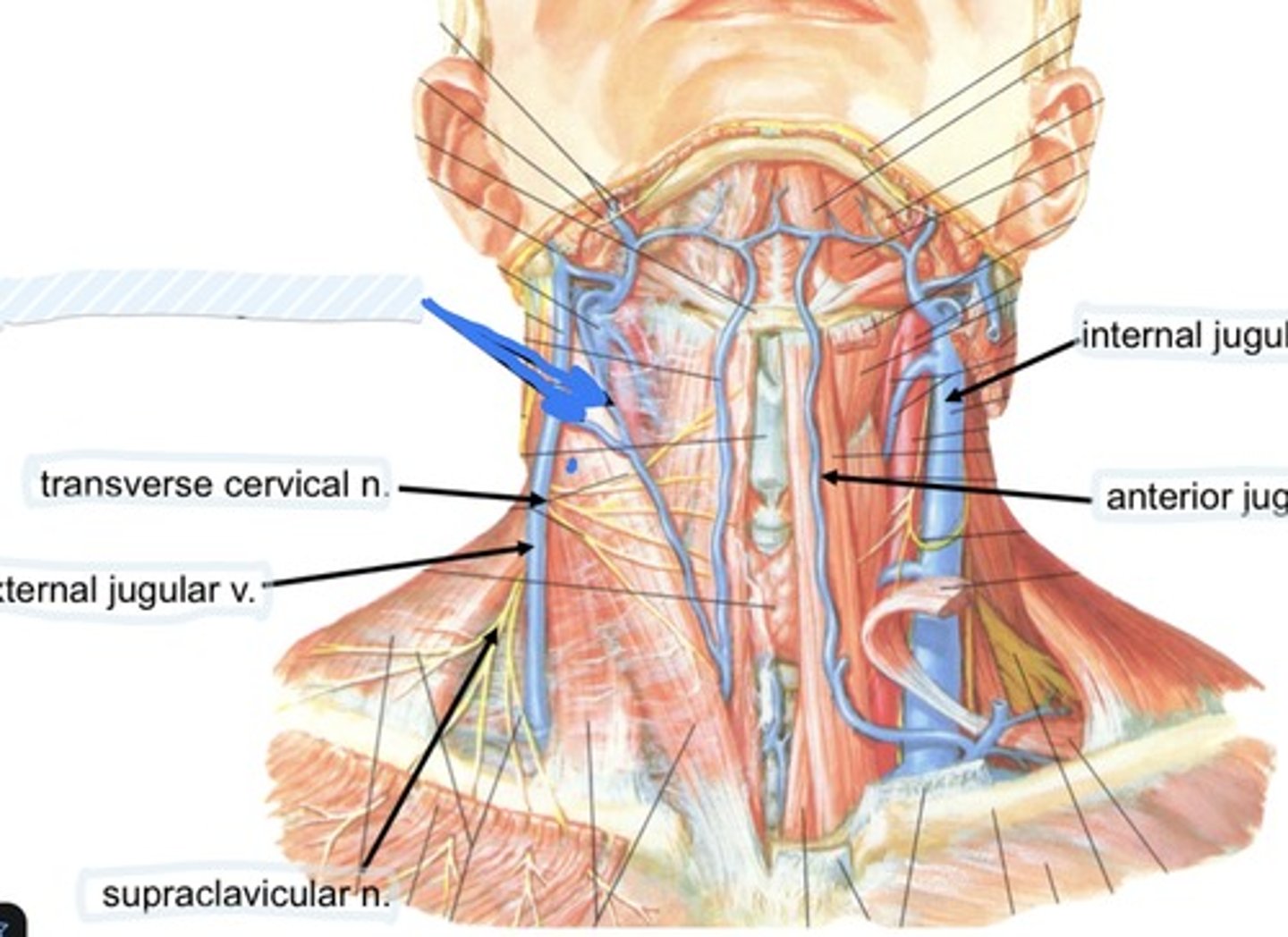
transverse cervical n.
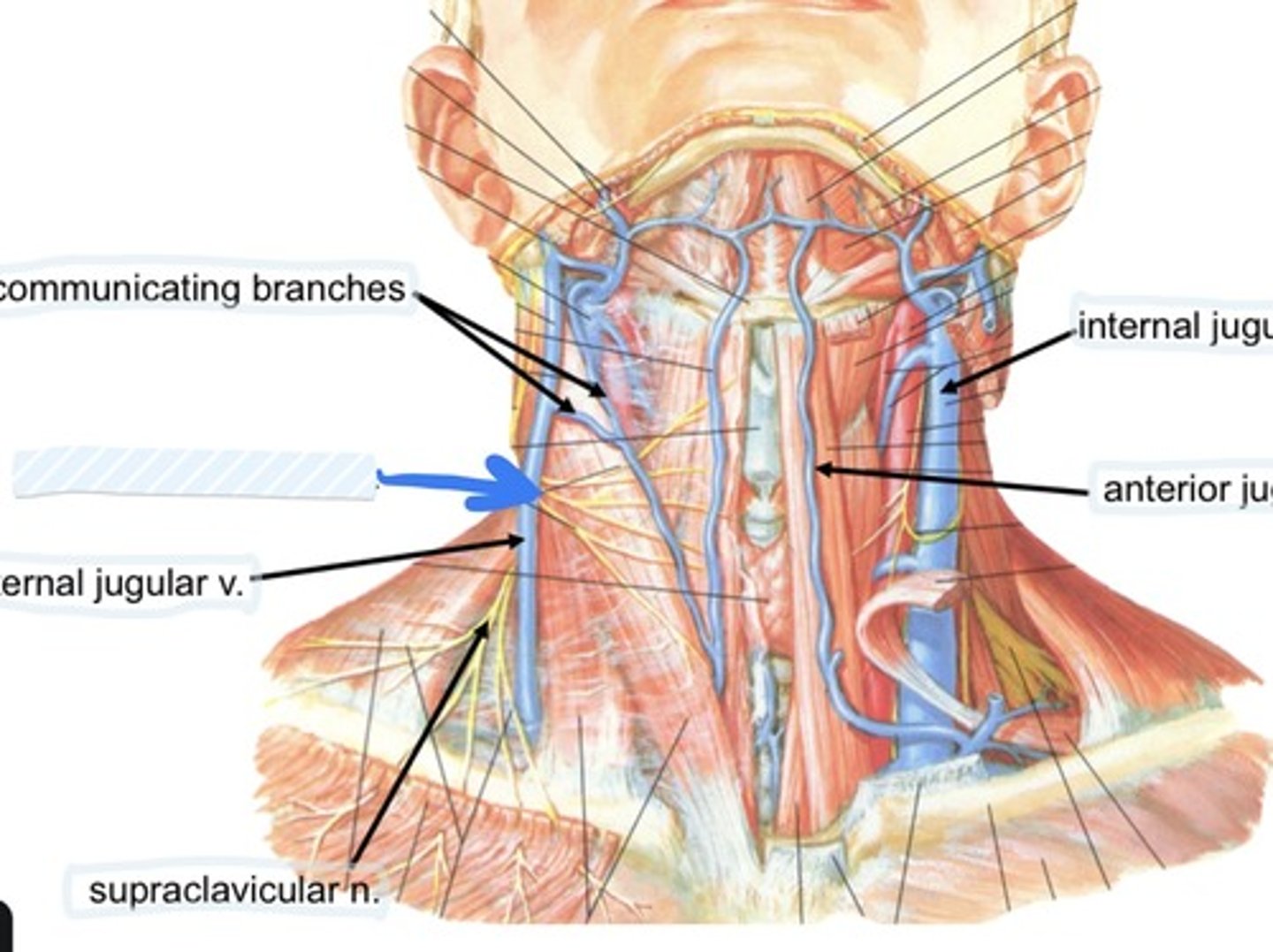
External jugular v.
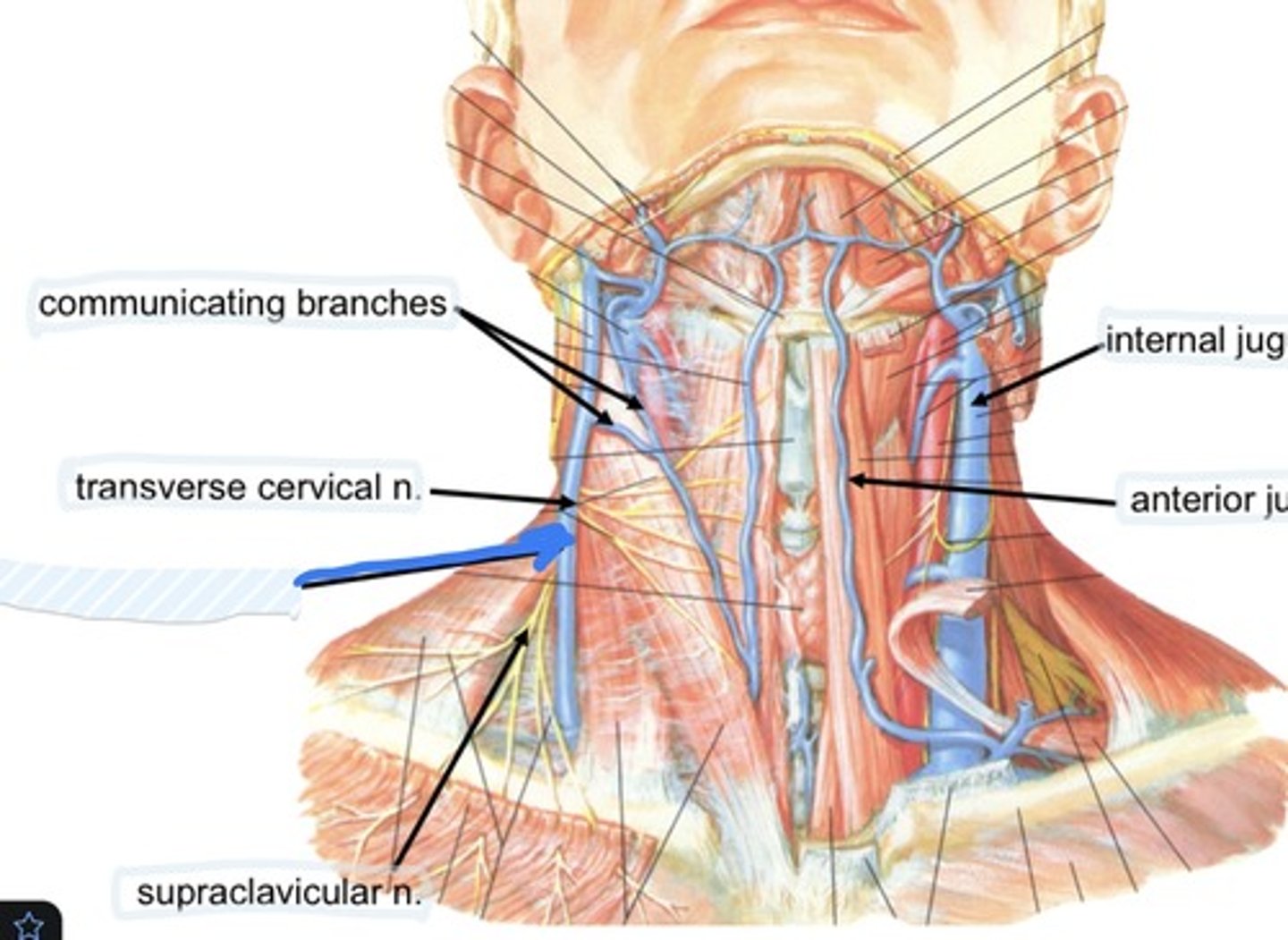
Supraclavicular n.
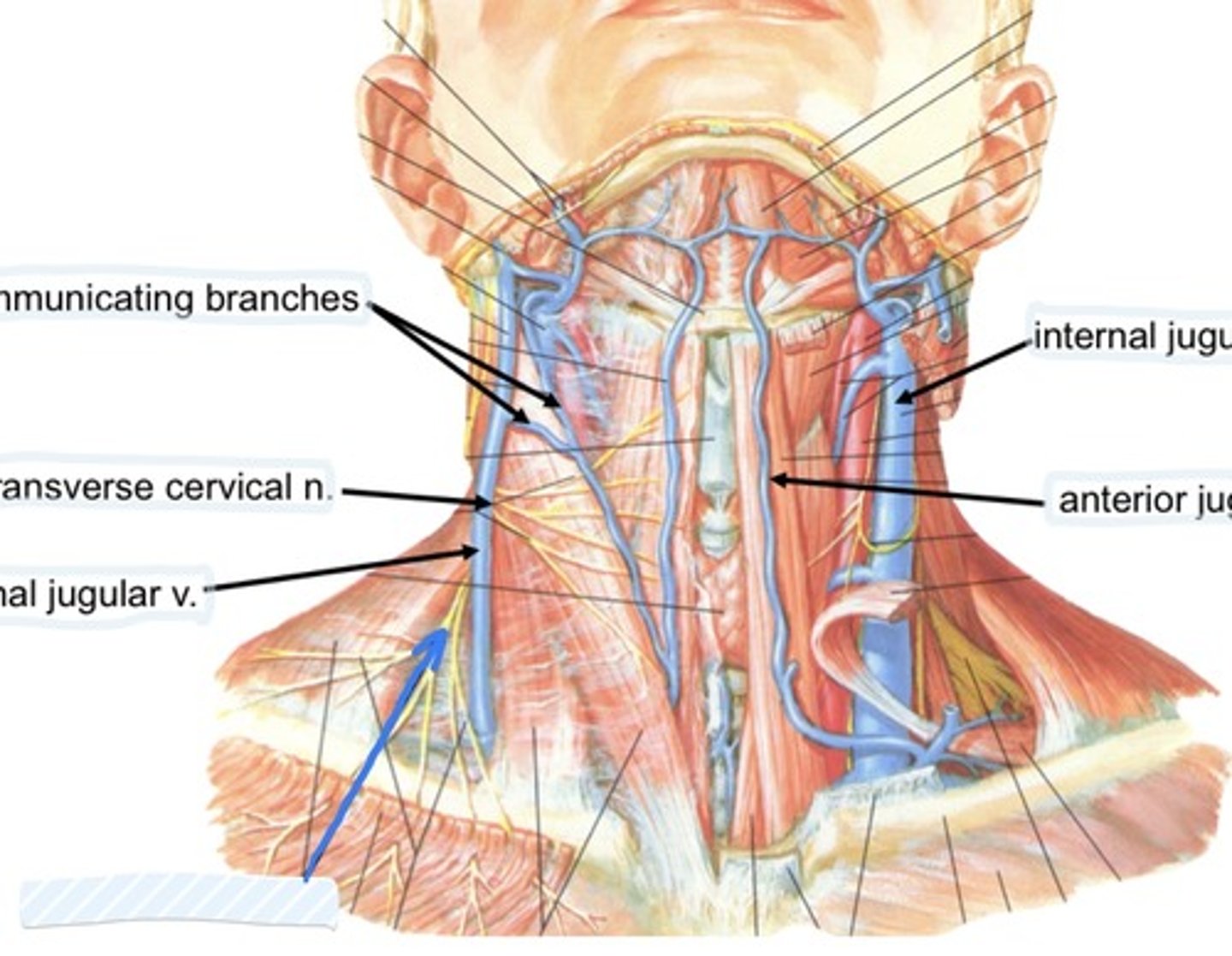
Internal jugular v.
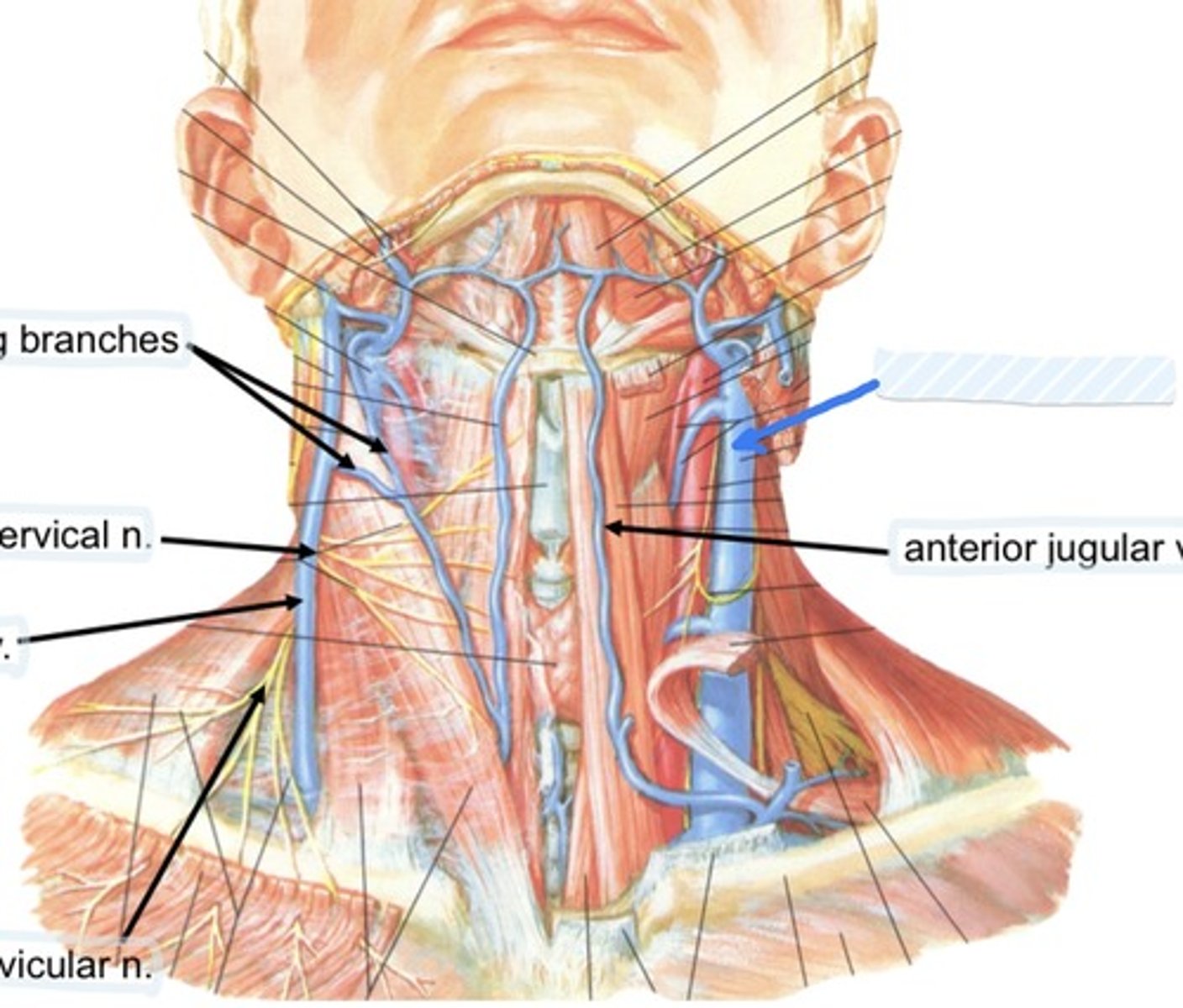
Anterior jugular v.
Platysma
Sits in superficial fascia tissue and has no bony insertion
Investing cervical, pretracheal, prevertebral
Name the 3 types of deep cervical fascia
Investing cervical layer
The most superficial of the deep layers
Investing cervical layer
envelops the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid
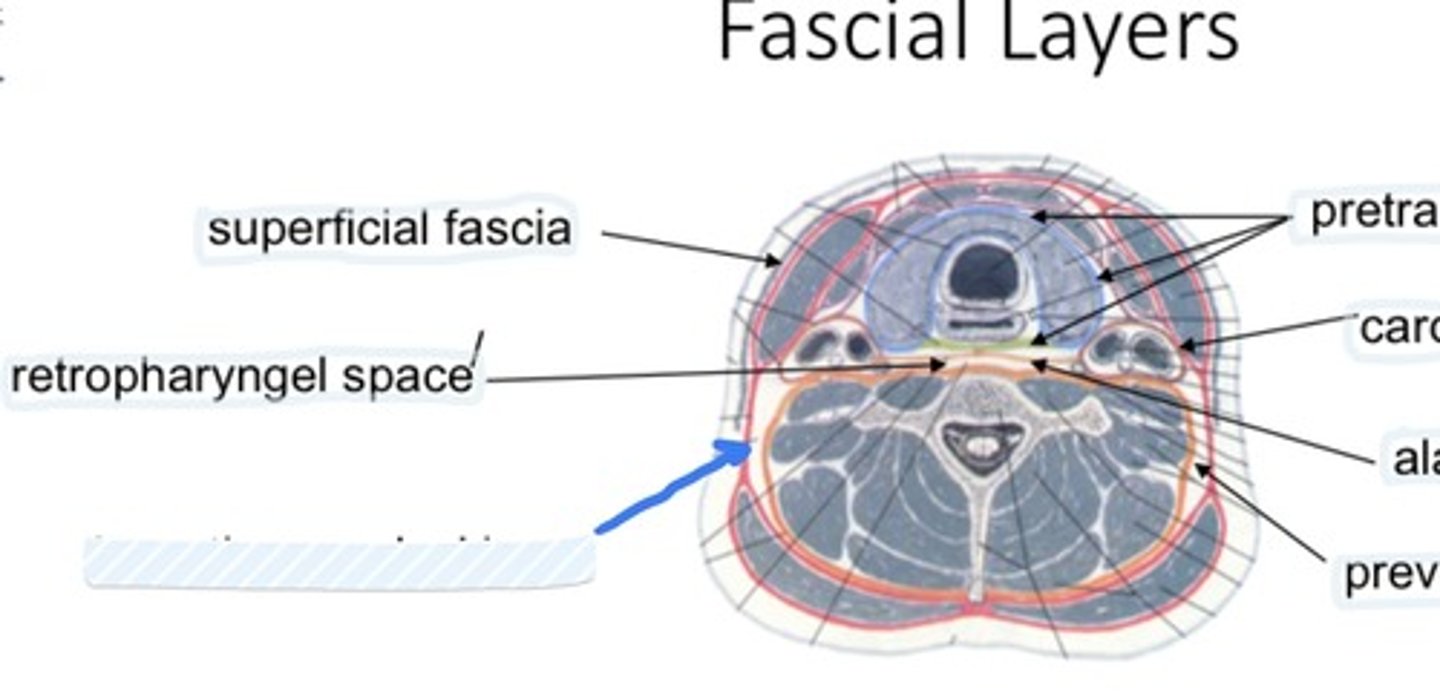
Pretracheal layer
Envelops the infrahyoid muscles, thyroid gland, trachea, esophagus
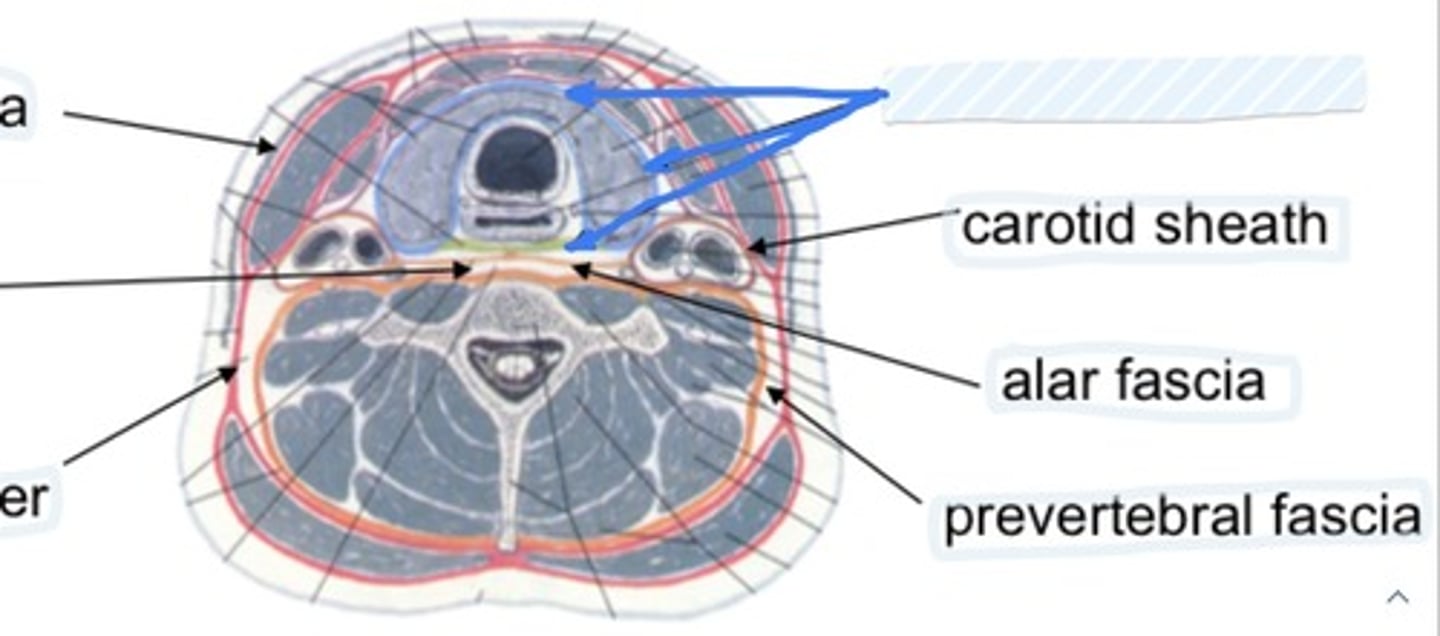
Prevertebral layer
Envelops the vertebral column and associated muscles
Carotid sheath
Contains common/internal carotid arteries, internal jugular, vagus nerve, carotid sinus nerve, lymph nodes
Alar fascia
Joins the carotid sheaths
Alar fascia
Allows movement of pharynx/esophagus over vertebral column during swallowing
Platysma
Broad, paper thin sheet in superficial fascial plane that diffuses into subcutaneous fascia of thorax
Sternocleidomastoid
Contains sternal and clavicular heads
Mastoid process
Insertion of sternocleidomastoid
Sternum
Origin of Sternocleidomastoid
Sternocleidomastoid
Function is flexion and ipsilateral rotation of neck
Trapezius
Function is to elevate, retract, and depress the scapula
Accessory n.
Innervation of Sternocleidomastoid and trapezius
Suprahyoid muscles
Work to elevate the hyoid bone and depress the mandible
Mandible
Origin of mylohoid m.
Geniohyoid muscle
Styloid process to hyoid bone
Mylohyoid
Forms support of the base of the tongue
Digastric m.
Intertendon between bellies anchored to hyoid through fibrous sling from pretracheal fascia becase of angle of pull, elevates hyoid, depresses mandible
Infrahyoid muscle
Depresses hyoid
Trapezius, sternocleidomastoid, and clavicle
Define the posterior triangle
Omohyoid
What muscle divides the posterior triangle
Occipital triangle and supraclavicular triangle
The omohyoid divides the posterior triangle into
Sternocleidomastoid, mandible, and midline
Define the anterior triangle
Occipital triangle
part of external jugular vein, posterior branches of cervical plexus of nerves, accessory nerve, trunks fo brachial plexus, transverse cercical artery, cervical lymph nodes
Supraclavicular triangle
subclavian artery (3rd part), part of subclavian vein, suprascapular artery, supraclavicular lymph nodes
Submandibular triangle
submandibular gland, submandibular lymph nodes, hypoglossal nerve, mylohyoid nerve, parts of facial artery and vein
Submental triangle
suprahyoid muscles, submental lymph nodes, venous system to anterior jugular vein
Carotid triangle
carotid sheath and contents, external carotid artery, hypoglossal nerve, ansa cervicalis, accessory nerve, thyroid gland, larynx, pharynx, lymph nodes, branches of cervical plexus
Muscular triangle
sternothyroid, sternohyoid muscles, thyroid and parathyroid glands
Vagus n
contained in carotid sheath of carotid triangle, between carotid artery and internal jugular vein
Spinal accessory n
Found in occipital triangle; accepts branches from C2-C4
Hypoglossal n
Found in submandibular triangle, along with branch of C1
C3-C5
Phrenic nerve runs from spinal levels
C1-C4
Cervical plexus runs from
Vagus n
Controls most muscle of tonation
Hypoglossal n
Controls the intrinsic m. of tongue under the tongue
Suprascapular a., transverse cervical a., and interior thyroid a.
3 branches of the thyrocervical trunk are
Communicating branches
Collateral drainage of veins in the neck