Senses
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
General Senses
touch, temperature, pressure, and pain
Special Senses
taste, small, vision, hearing, and balance
5 kinds of receptors
chemoreceptors
pain receptors
thermoreceptors
mechanoreceptors
photoreceptors
chemoreceptors
changes in concentration of chemicals (taste and smell)
pain receptors
tissue/skin damage
thermoreceptors
changes in temperature
mechanoreceptors
changes in pressure /movement (touching, hearing, balance)
photoreceptors
changes in light (sight)
how does a sensation arise?
sensory receptor is set off, the brain projects the sensation back to the source through sensory projection adaptation
how is a sense of pain produced?
prostiglandins are released, the more released the more pain coming with it
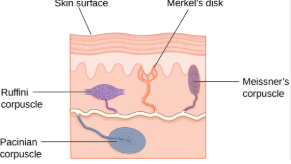
types of pressure and touch receptors
free nerve endings
Meissner’s corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles
merkels disk
hair follicle receptors
ruffinis corpuscles
free nerve endings
pain, Temp, touch, pressure
meissners corpucles
detect light touch
merkels disk
internal pressure and light touch
hair follicle receptor
detect movement of hair
ruffins corpuscles
deep pressure and streching of skin
pacinian corpuscles
deep pressure and vibrations
make sure you know what they look like/where they are in skin
what is the path of light through the eye?
cornea, ah, pupil, lens, vh, retina, photo receptors stimulated, optic nerve
What is the path of sound through the ear?
external auditory meatus, tympanic membrane, malleus, incus, Staples, oval window, vestibule, cochlea, hair cells stimulated, cochlear nerve
static equilibrium
position of the head (up or down)
dynamic equilibrium
movements of the 3 planes