K1.3 experimental methods
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
lifetime of a species - symbol + definition

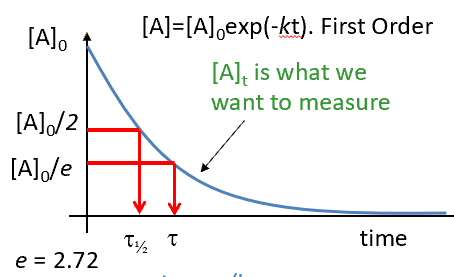
lifetime for first order reactions

graph showing half life and lifetime for first order reaction
techniques used to measure lifetimes of minutes/hours
conventional techniques - titrations, conductivity, pressure, volume change
techniques used to measure lifetimes of 10s of seconds
automated conventional techniques (titrations, conductivity, pressure, volume change)
techniques used to measure lifetimes of seconds
mixing problems - monitoring requires fast response, spectroscopic techniques
techniques used to measure lifetimes of milliseconds
discharge flow or flash photolysis
techniques used to measure lifetimes of microseconds
flash photolysis - spectroscopic monitoring
techniques used to measure lifetimes of nanoseconds - femtoseconds
specialised flash photolysis - approaching timescales of bond formation
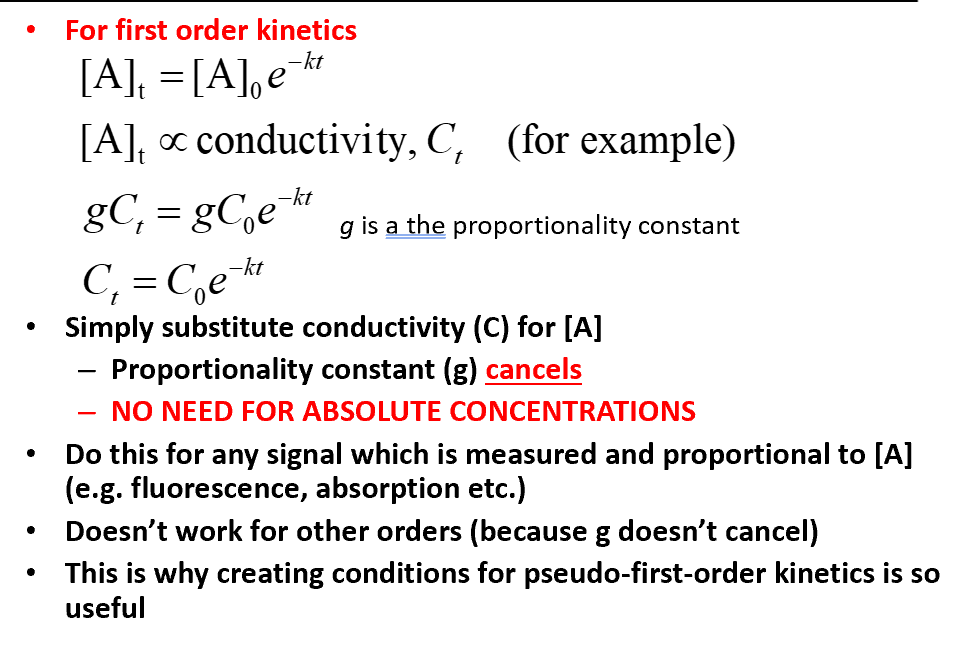
relationship between concentration and conductivity for first order kinetics and how this is useful
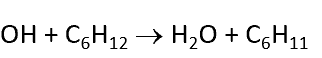
discharge flow labelled diagram including discharge and what is injected
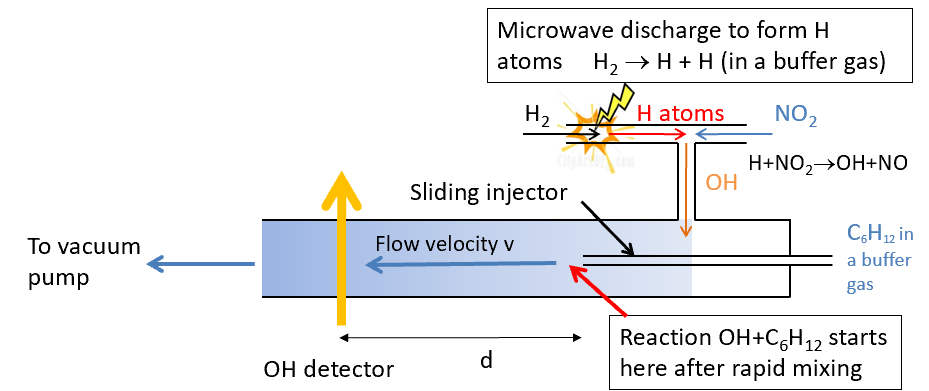
how is reaction time changed?
by moving the injector back and forward (vary the distance and t=d/v)
how is flow velocity calculated and what does this allow you to find
v (cm s-1) is calculated from volumetric flow rate (cm3 s-1)/flow tube area (cm2)
allows t to be calculated (t=d/v)

how is the reaction monitored
measure the OH signal (usually detected by laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy) and hence monitor the reaction via the loss of OH
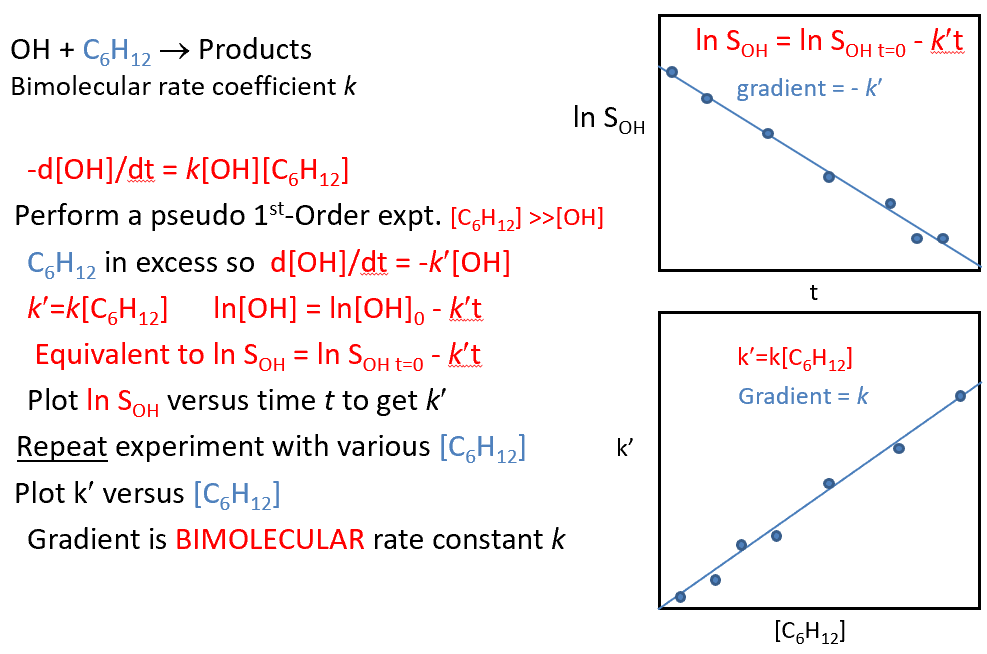
phase and kinetics for discharge flow method
gas phase reaction. most of the mixture is an unreactive buffer gas, eg He/Ar/N2 and the total pressure is a few Torr
make reaction pseudo-first-order such that d[OH]/dt = -k’[OH] and k’ =k[C6H12]
[C6H12] >> [OH]
![<p>gas phase reaction. most of the mixture is an unreactive buffer gas, eg He/Ar/N<sub>2 </sub>and the total pressure is a few Torr</p><p>make reaction pseudo-first-order such that d[OH]/dt = -k’[OH] and k’ =k[C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>]</p><p>[C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>12</sub>] >> [OH]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3c8c9bad-7260-4796-8e84-2921c9e0c5d2.png)
explain the laser-induced fluorescence detection of OH
Laser induces electronic excitation of OH at 308nm
There is then spontaneous emission (like radioactive decay) and the intensity of this is proportional to OH concentration.
This is detected by a sensitive detector called a photomultiplier (PMT)
how is the bimolecular rate coefficient obtained from pseudo-first-order data
discharge flow possible detection methods and what they are used to detect
laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy (LIF) for OH, H, CN, IO
resonance fluorescence (RF, using a lamp) for H, N, O, Br, Cl, F
mass spectrometry
laser-magnetic resonance (older method), 3CH2
resonance-enhanced multi-photon ionisation, CH3, HCl
pros of discharge flow method
relatively cheap
flexible method of radical generation
fast timescale possible
variety of detection methods available
discharge flow cons
limited range of timescales (10-4s) and pressures (only up to a few Torr)
Gas-phase only
Surface reactions can change kinetics
Temperature control is challenging
what technique is used for ultrafast reactions
what timescale is this
give an example equation
how are the reactants generated
how is the reaction monitored
what type of technique is this
when half life < 10-4 s flow methods are too slow as reagents don’t move along the tube before they have reacted and mixing times are long
flash photolysis is used instead: A(radical) + B(molecule) → products
premix reactant B and something A can be made from then generate A radicals with a flash of light
monitor radical A as it reacts with B and decays in time
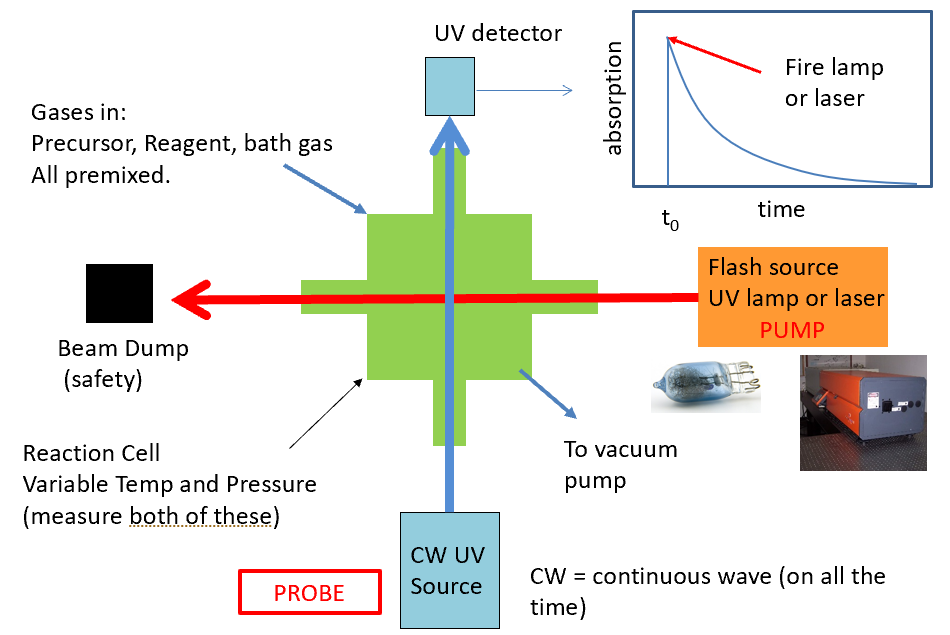
example of a pump and probe technique
flash photolysis with absorption spectroscopy diagram and example graph