AORTIC REGURGITATION QUALITATIVE ASSESSMENT Unit 1
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
what is Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic Regurgitation is the backflow of blood
from the aorta into the left ventricle during
diastole
what can regurgitation result from
Regurgitation can result from disorders of
the aortic valve or aortic root or both
Aortic valve and root abnormalities results
in what?
Aortic valve and root abnormalities results
in malcoaptation
what are the mechanism of AR (These are ways people are born with valve leaflet problems that cause AR by preventing proper closure (malcoaptation)
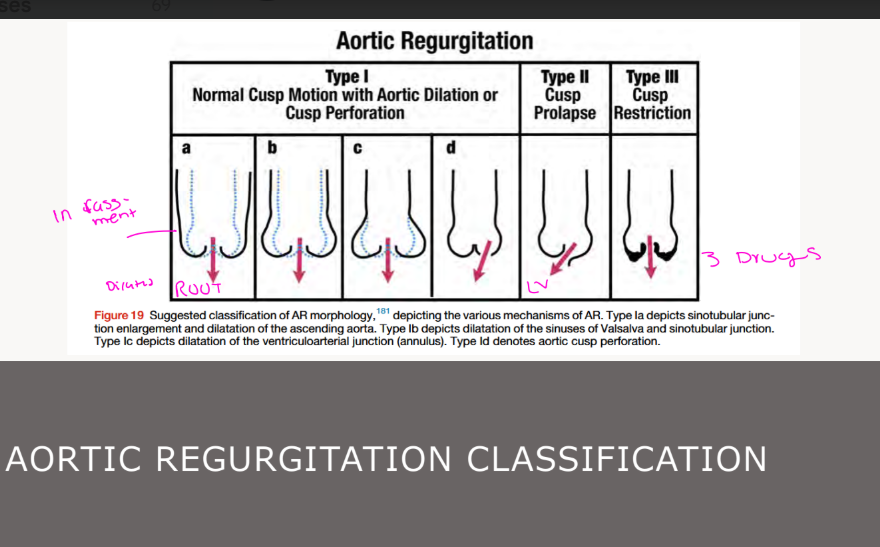
What are the congenital leaflet abnormalities of AR (5) ?
Bicuspid
• Unicuspid
• Quadricuspid
• Aortic Valve Prolapse
• Ventricular Septal Defects with prolapse
What are the AV leaflet abnormalities (5)
ACQUIRED LEAFLET ABNORMALITIES
Senile calcification
• Infective Endocarditis
• Rheumatic disease
• Toxin induced Valvulopathy: Anorectic drugs,
Carcinoid
• Aortic leaflet perforation
Mechanisms AR
CONGENITAL/GENETIC AORTIC ROOT what disorder and give example
Annuloaortic ectasia from connective
tissue disorders
• Connective tissue disorders: Loeys Deitz,
Ehlers-Danlos, Marfan Syndrome, osteogenesis
imperfecta
Aortic Root Abnormalities
ACQUIRED AORTIC ROOT what are the different types of disease
Idiopathic aortic root dilatation
• Systemic hypertension
• Autoimmune disease: systemic lupus,
ankylosing spondylitis, Reiter’s syndrome
Etiology of Aortic Regurgitation
Aortitis syphilitic,
Takayasu’s arteritis •
Aortic dissection •
Trauma
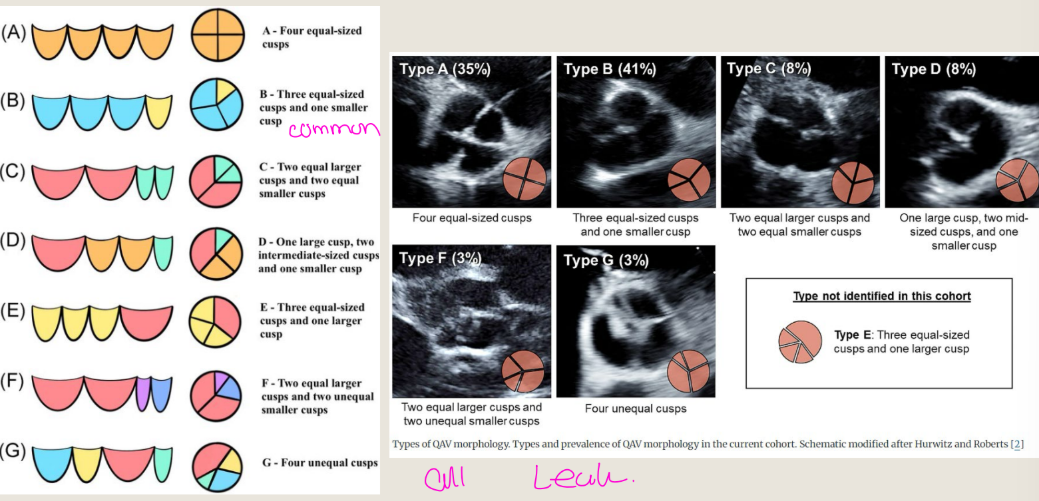
what are the congenital leaflet abnormalities
quadricuspid,
aortic valve prolapse, and VSDs
what is A quadricuspid aortic valve (QAV)
A quadricuspid aortic valve (QAV) is a rare congenital
heart defect where the aortic valve has four cusps
instead of three
how does a A quadricuspid aortic valve (QAV) how does it result from
It's a result of an error during the development of
the aortic valve during pregnancy
Regurgitation is caused by? for Quadricuspid AV
Regurgitation is caused by the inadequate
closing of the four cusps at the end of systole
There are 7 variations that may occur... what are they
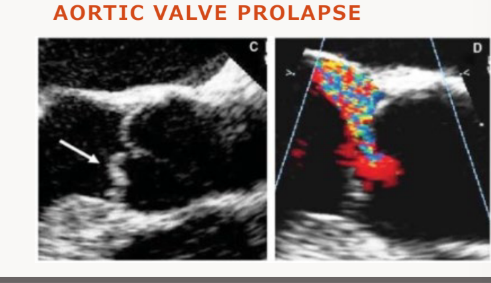
Aortic Valve Prolapse define and what is it highly associated with?
Aortic valve prolapse is a condition where the aortic valve's cusps move down
below the line that connects the valve leaflets to the annulus Highly associated with eccentric AR
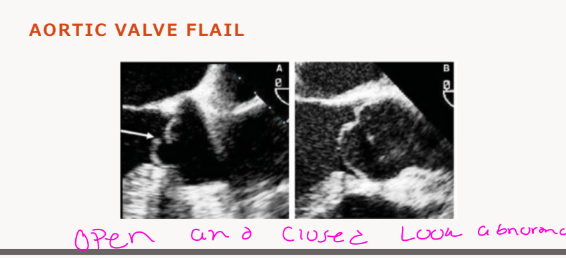
what is Aortic Valve Flail
Diastolic fluttering of the aortic cusp echoes,
abnormal systolic aortic leaflet movement, and
abnormal diastolic fluttering echoes in the left
ventricular outflow tract
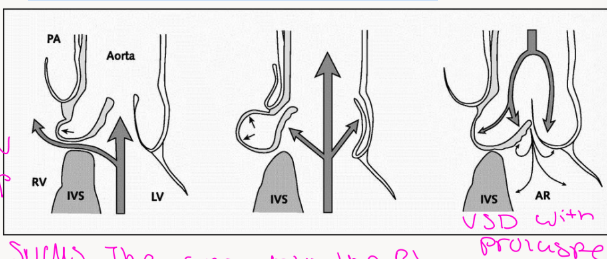
VSD with Aortic Prolapse
Define in systole and what effect is this known as?
In early systole (left), blood ejected from the
left ventricle will be shunted through the
ventricular septal defect
The unsupported right coronary cusp and
right aortic sinus are driven into the right
ventricle. This limits left to right shunting of
VSD flow
This is known as the Venturi effect
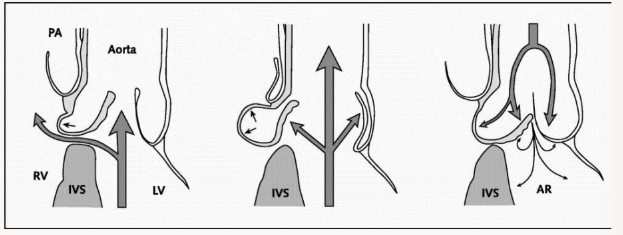
VSD with Aortic Prolapse
in diastole
This is best evaluated in what view
In diastole (right), the intra-aortic pressure
forces the aortic valve leaflet to close, but
the unsupported right coronary cusp is
pushed down into the left ventricular
outflow tract away from the opposed
coronary cusp, resulting in regurgitation
This is best evaluated in PLAX
whats the most frequent concomitant valve disease
Mixed aortic stenosis (AS) and aortic regurgitation (AR) is
the most frequent concomitant valve disease
Aortic Regurgitation with
Aortic Stenosis This valve disease ranges from
This valve disease ranges from mild AS with severe AR to
mild AR with severe AS
Patients with moderate mixed AS/AR have outcomes
Patients with moderate mixed AS/AR have outcomes
similar to those with isolated severe AS
Aortic Regurgitation with Aortic Stenosis
Coexistent with what overload
Patients with severe mixed AS/AR have what affects to there heart
Coexistent pressure and volume overload
Patients with severe mixed AS/AR have
smaller LV dimensions and volumes then a
severe aortic regurgitation patient
Rheumatic aortic valve disease
is a condition that occurs when
the aortic valve of the heart is?
Rheumatic heart disease is the most common heart disease in people what age
its especially common in what sex and which countries
Rheumatic aortic valve disease
is a condition that occurs when
the aortic valve of the heart is
permanently damaged by
rheumatic fever
Rheumatic heart disease is the
most common heart disease in
people under 25
It's especially common in women
from low- and middle-income
countries
Rheumatic AV includes what’s on the commissures of the cusps? you may see what during opening in PLAX? what is Rheumatic AV disease associated with?
Rheumatic AV includes symmetric
fibrosis, retraction and partial fusion of
the commissures of the cusps
May see doming during opening in PLAX
Associated aortic regurgitation, aortic
stenosis, and rheumatic mitral valve
disease
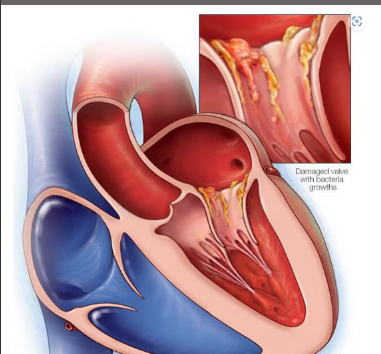
Valve Endocarditis- what kind of condition is this, what does it do to the blood stream, without quick treatment what can endocarditis do, what are the treatment options,
Endocarditis is a life-threatening condition that occurs
when the endocardium becomes inflamed
Bacterial germs get into the bloodstream and attach to
damaged areas in the heart
Without quick treatment, endocarditis can damage or
destroy the heart valves
Treatments for endocarditis include medications and
surgery
Aortic Leaflet can Perforation from?
Aortic leaflets can
perforate from blunt
force trauma or from
mitral valve repairs
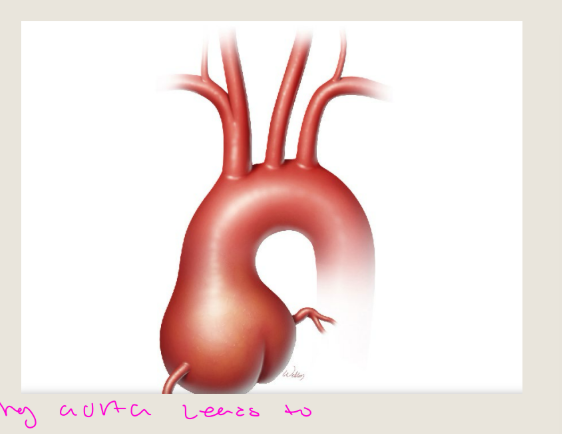
what is Annuloaortic ectasia is a
condition that causes, what is it highly associated with ?what syndrome
Annuloaortic ectasia is a
condition that causes the
ascending aorta and aortic
annulus to widen, or dilate
Highly associated with
connective tissue disorders
like Marfan’s Syndrome
Your connective tissue supports many different
parts of your body, such as, if you have a connective tissue disease these connecting structures are affected how
Your connective tissue supports many different
parts of your body, such as your skin, eyes, and
heart
It is like a "cellular glue" that gives your body
parts their shape and helps keep them strong
When you have a connective tissue disease, these
connecting structures are negatively affected
Connective Tissue Disorders, They fall into three main categories: what are they
Autoimmune diseases
Genetic disorders
cancers (sarcomas)
Marfan syndrome is caused by?
Most people with this syndrome get it how?
Marfan syndrome is caused by a defect in
the gene that enables your body to produce
a protein that helps give connective tissue
its elasticity and strength
Most people with Marfan syndrome inherit
the abnormal gene from a parent who has
the disorder
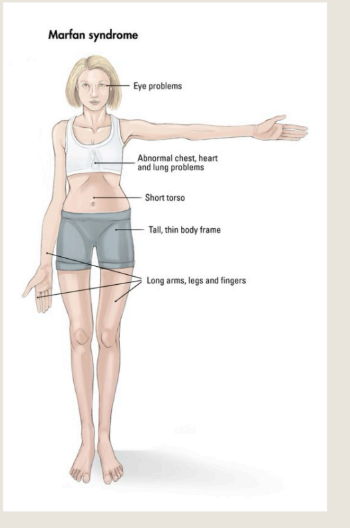
Marfan syndrome affects which groups of people
Marfan syndrome affects men
and women equally and
occurs among all races and
ethnic groups
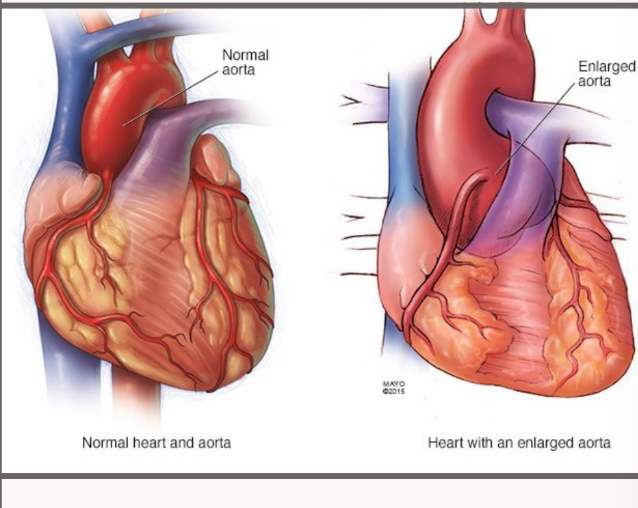
what is the most specific MFS
finding, whats the shape and what should be measured
Aortic root dilatation is the most specific MFS
finding
“Onion shape” AORTIC ROOT
The aortic sinus, the sinotubular junction, aortic
annulus, and ascending aorta should be measured
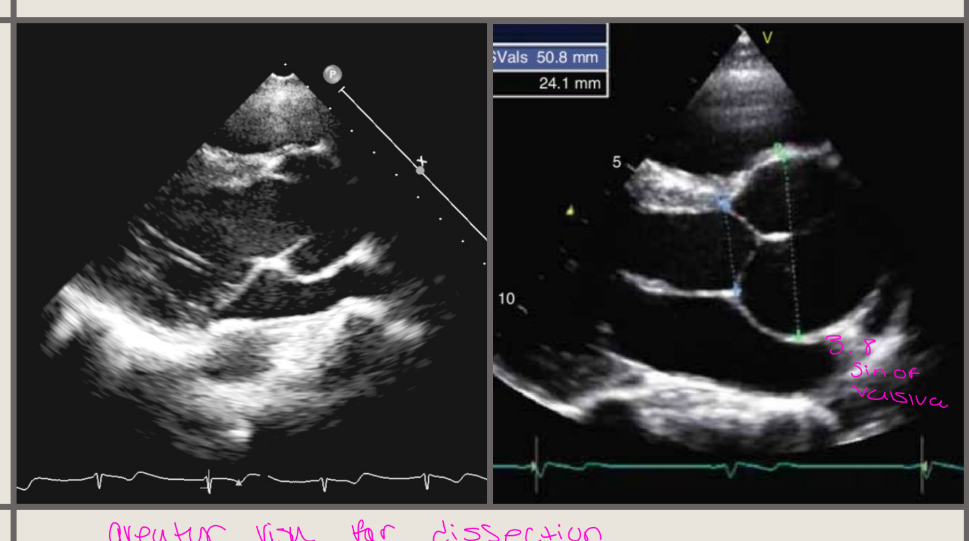
In Marfans syndrome what is frequenctly observed in MFS PT and what may progress and the regurgitation flow is often what
Mitral valve involvement is frequently observed in
MFS patients
MVP may progress to MV Flail
The regurgitation flow is often extremely eccentric
as well
Acquired Root Dilatation may occur in
______parts of the aorta?
Idiopathic describes
Acquired Root Dilatation may occur in different parts of the aorta.
Idiopathic describes a disease of unknown cause
What is systemic Hypertension is what condition that occurs when what? the aorta will experience what
Systemic hypertension is a
chronic condition that occurs
when blood pressure in the
arteries is too high. Aka high
blood pressure or hypertension
The aorta will experience
effacement of the ST junction
and dilatation of the ascending
aorta
what is Autoimmune Diseases and what can it cause
An autoimmune disease occurs when the body's
immune system mistakenly attacks its own
healthy cells, tissues, and organs
It can cause inflammation of the aorta which may
cause complications like aneurysms and
dissections
Aortic Dilatation
from Trauma
Aortic Dissection what do we always look ?
Always look for the presence and
severity of aortic regurgitation
AORTIC
Regurgitation
CHRONIC what happens to the LV volume and what else
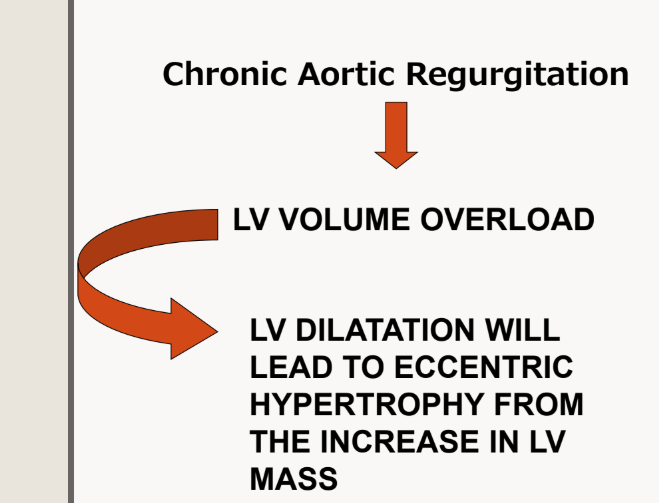
For chronic AR the LV is being filled by ___ sources which are?
The left ventricle is being
filled by 2 sources...the
left atrium and the aortic
regurgitation
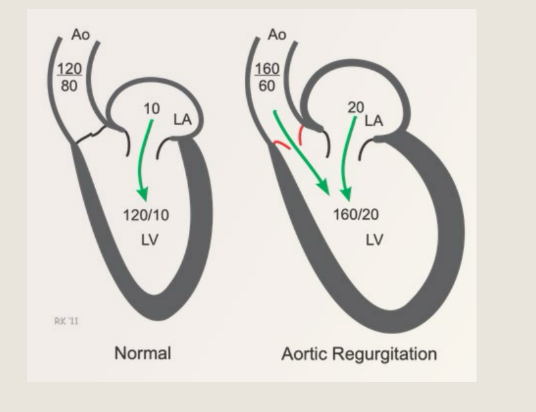
for chronic AR what happens to the SV, CO, and function
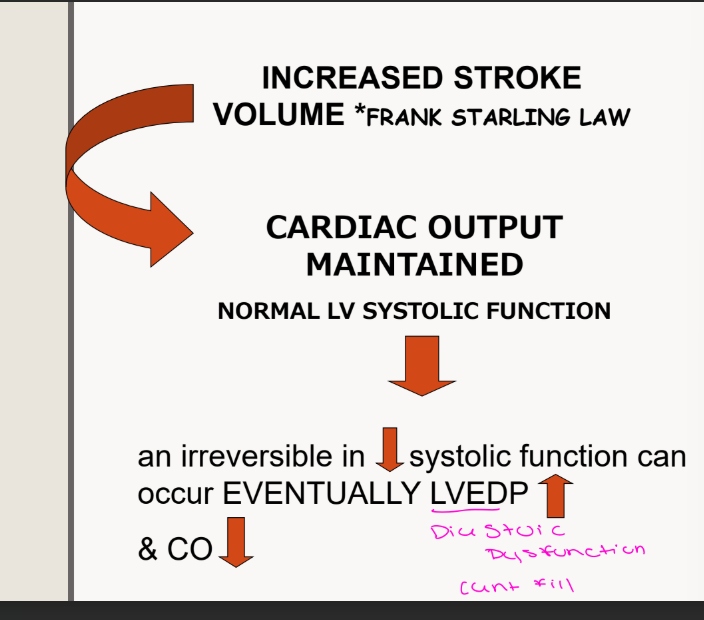
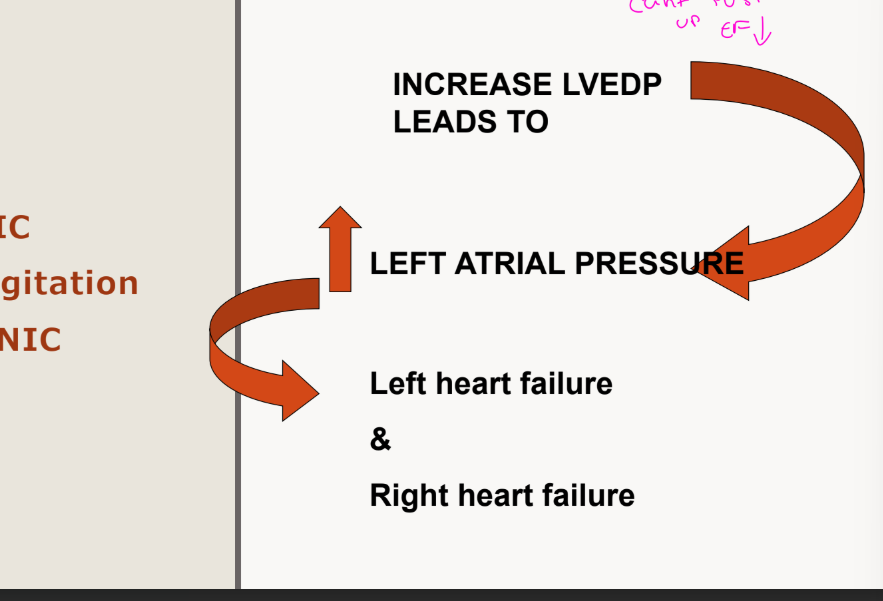
For chronic AR increase LVEDP leads to?
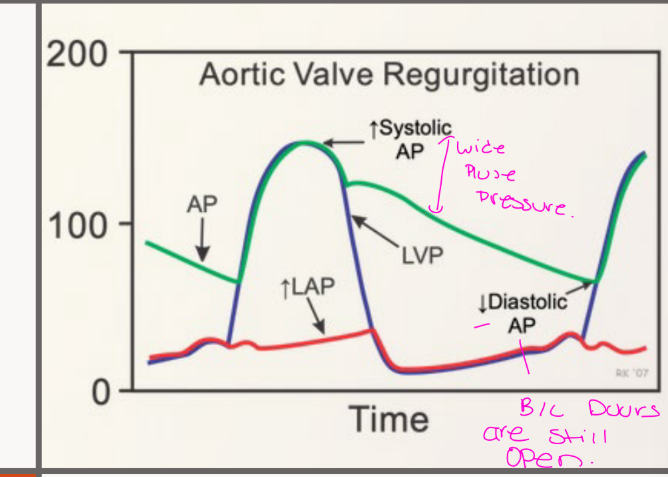
Pressure Changes for chronic AR, changes in what
Changes in the aortic
pressure, LVP and LAP
can be observed with
aortic regurgitation
what are the Clinical
Presentation for chronic AR
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic
It’s a slow progressive disease that
leads to dyspnea and decrease
exercise capacity
Most cases are trace to mild
With severe aortic regurgitation...
what are the chronic AORTIC Regurgitation Patient Symptoms (5)
Fatigue
Syncope (uncommon)
Shortness of Breath
Palpitations
Chest pain
AORTIC Regurgitation Physical Examination (pressures)
Wide pulse Pressure
• Bounding Peripheral pulses
• Displaced hyperdynamic left
ventricle impulse
AR physical examination
what are the Murmurs
what S sounds and this will indicate what
and what are other associated murmus
Murmurs
Early, high pitched, blowing, diastolic
decrescendo murmur
– Left sternal border
S3 S4 gallop *heart failure
Other associated murmurs
– Austin-Flint murmur (severe)
– Mid to late diastolic rumble at the cardiac apex
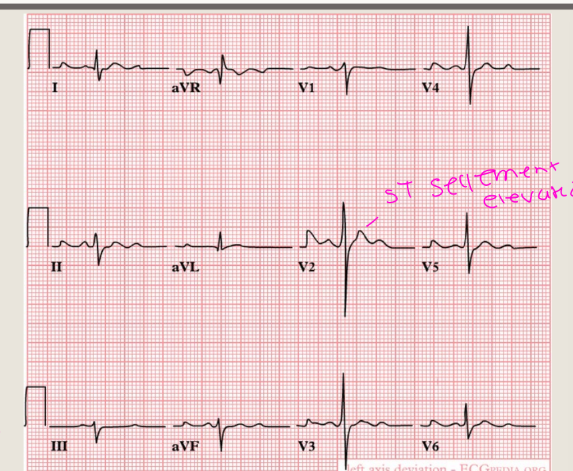
what are the ECG
Changes for AR??????
Shows LV hypertrophy
with ST segment
elevation, left atrial
enlargement, and
possibly ventricular
tachycardia
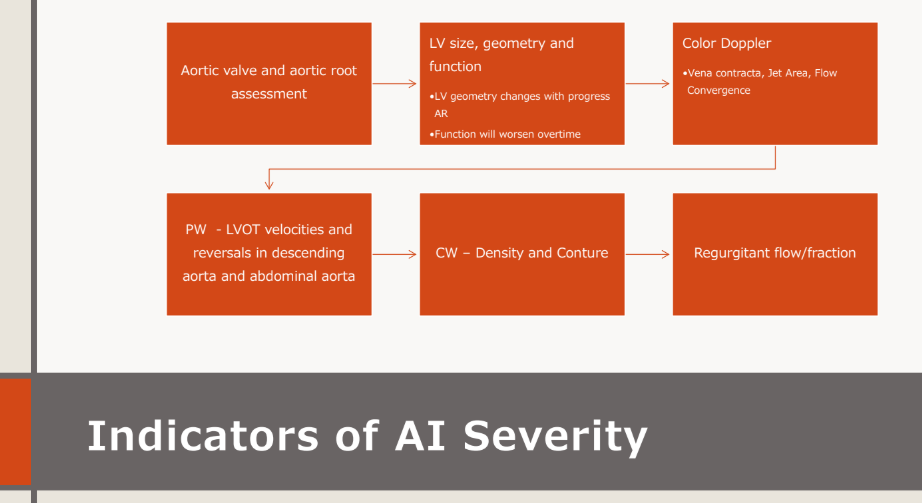
what is the CHRONIC AORTIC
REGURGITATION
QUALITATIVE
ASSESSMENT….indicators of AI severity
Interrogation
of Aortic
Regurgitation
combines... (AR assessment)
Color flow imaging
• Spectral Doppler Assessment
• And Indirect signs
Assessment begins in what view
Color doppler shows the presence of what
measure what
Assessment begins in PLAX
Color Doppler shows the presence of
aortic regurgitation
Measure the LVEDD for LV dilatation
Aorta measurements including Sinus of
Valsalva, ST junction, and proximal aorta
Valve etiology
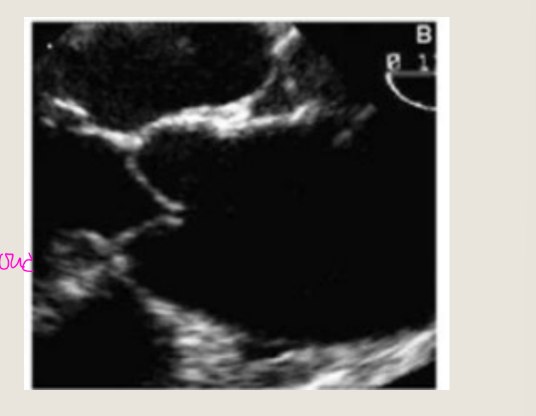
what is this showing
Austin-Flint murmur (severe)
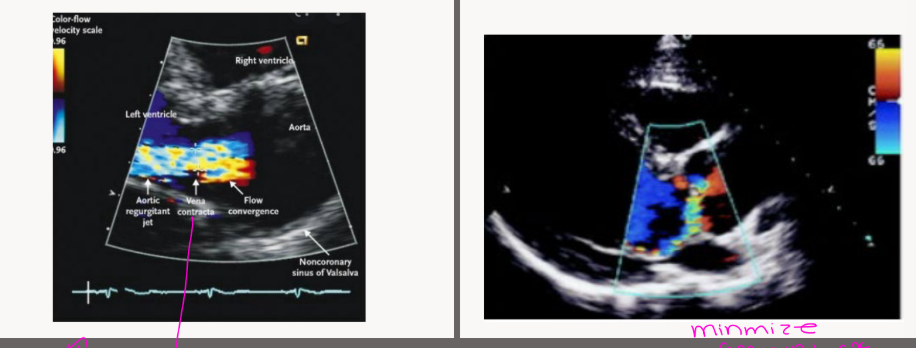
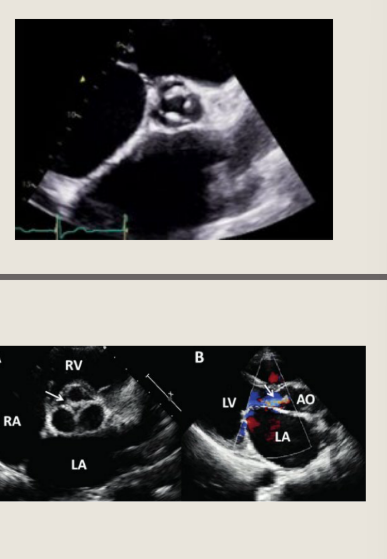
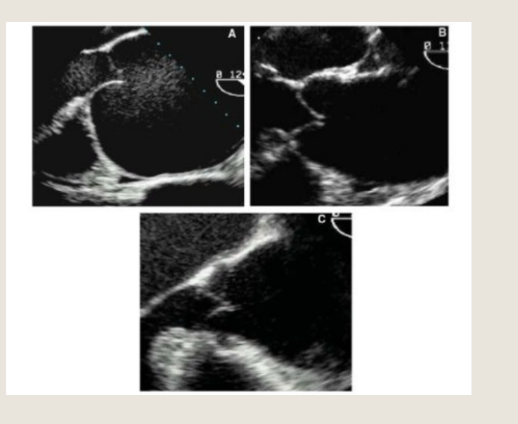
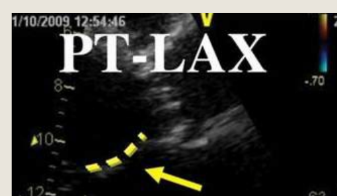
which one is central VS eccentric AR
Central is the 1st pic
eccentric is the 2nd pic
AR via color flow may be unreliable due to what
Unreliable due to
diastolic blood pressure
and acute AR
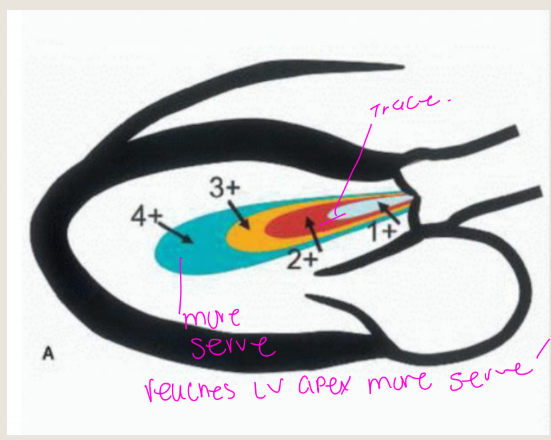
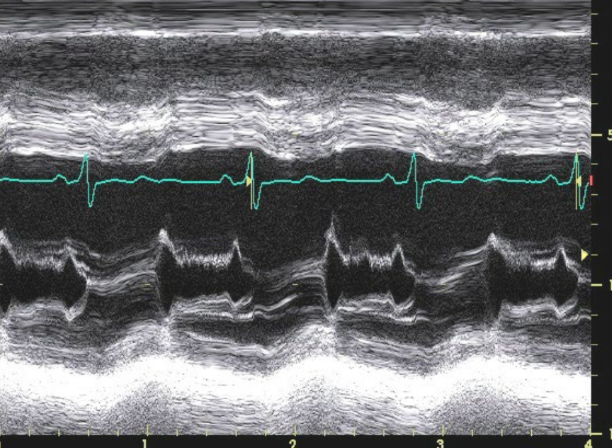
what is this showing
Doming of the anterior leaflet
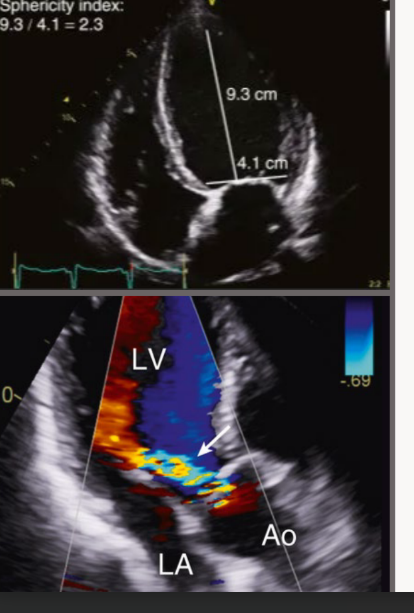
Chronic AR significant compensatory are what and seen in which view with what
Significant compensatory LV dilation and
increased sphericity of the LV are seen in the
apical four-chamber view with chronic severe
AR
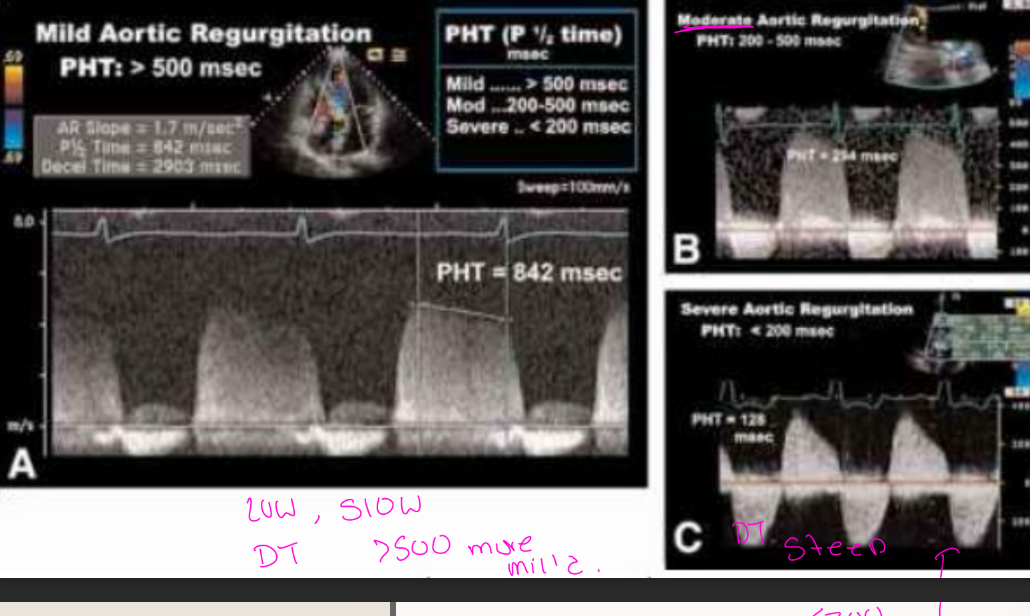
CW Doppler
Density proportional to what
Density of signal increase as what increase
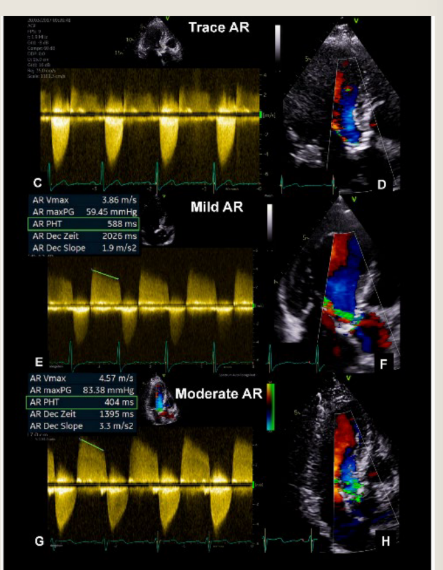
how does Mild regurgitation show up
how does Severe Regurgitation show up
Sensity proportional to RBC’s
Density of signal increase as RV increase
Mild R
Faint Doppler signal
Difficult to obtain
Severe R
Dense Doppler signal
Shape of CW Doppler reflects?
Severe AR may become asymmetrical
reflecting
Shape of CW Doppler reflects pressure
changes
Severe AR may become asymmetrical
reflecting rapid equalization of pressure
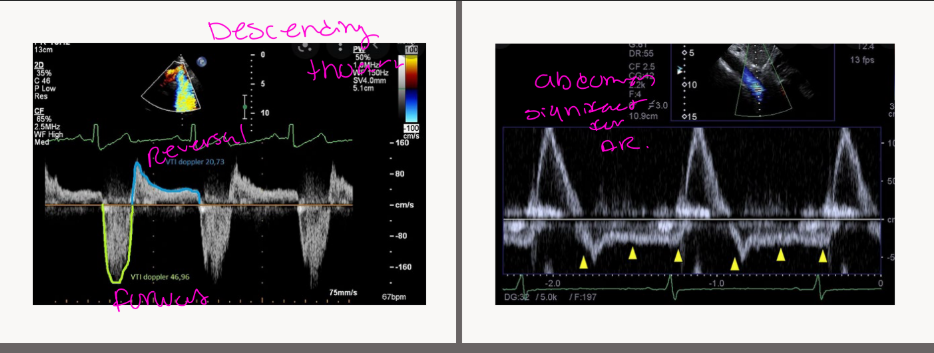
ECHO FEATURES
Left atrium dilated *chronic
– Increased diastolic filling pressures
Pulsatile aorta
- Flow reversal in aorta (descending
and abdominal)
Evidence of pulmonary hypertension
- Elevated TR velocity
- Dilated IVC/hepatic veins
PW DOPPLER
INTERROGATION
OF REVERSALS
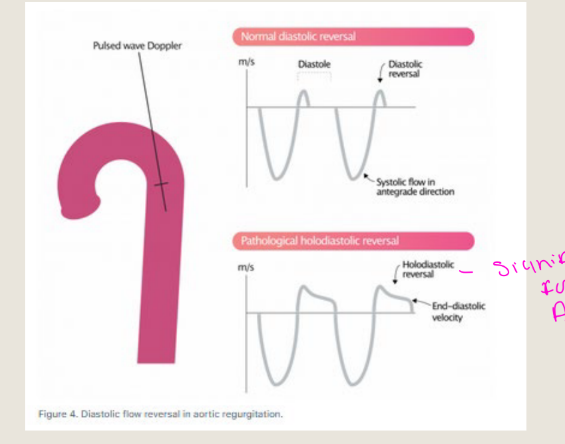
REVERSALS IN THE AORTA