ORAL COM (Communication models, its types, and Communication barriers)
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Physical Barrier
-most obvious barriers to effective communication
-physical limitations can interfere with the process, like noise in the area, faulty technology like poor signal, or speaker lagging in a presentation, class, etc.
Physiology Barrier
-within the body (blindness, deafness, muteness, disabled, dyslexia)
-feeling or any pain that interrupts understanding
Emotional barriers/Psychological Barriers
-based on emotions or psychological and mental problems (phobia, stage fear, depression, and speech order)
-due to a lack of trust, fear, and vulnerability
Cultural Barriers
-due to globalization, any large organization has people from several parts of the world with different cultures
-poor pronunciation in a language, sentence structure, or wrong style or words
-when receiver's culture is different than sender's culture
Kinship
the state of being related to others; societal organizations
Sexuality and Gender
encourage/discourage intimacy and different forms
Religion
religious beliefs and practices are features of all known societies
Cultural taboos
prohibited practices; some normal acts that offend others
Dress codes
accepted way of dressing in a particular social group
Food & Eating habits
what and when you eat
Aristotle's Communication Model
-focuses on public speaking
-Makes use of ethos (credibility, speaker), logos (logic, message), and pathos (emotions, audience)
-no noise or disruption mentioned
-Linear
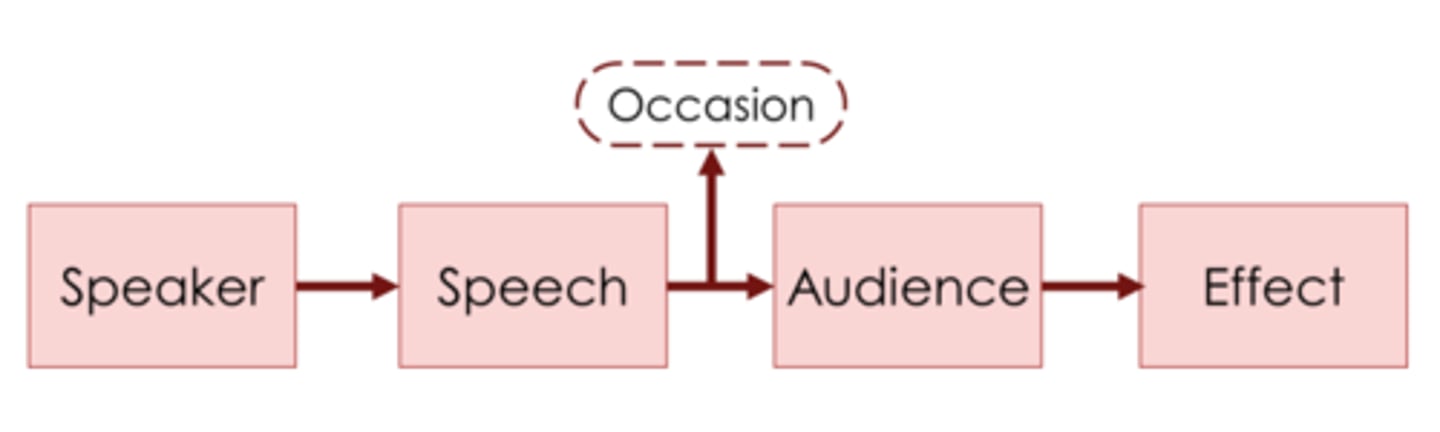
Laswell's Communication Model
-oversimplification of any communication process
-purpose: analyze media propaganda
-medium: tv, radio, news papers
-Linear
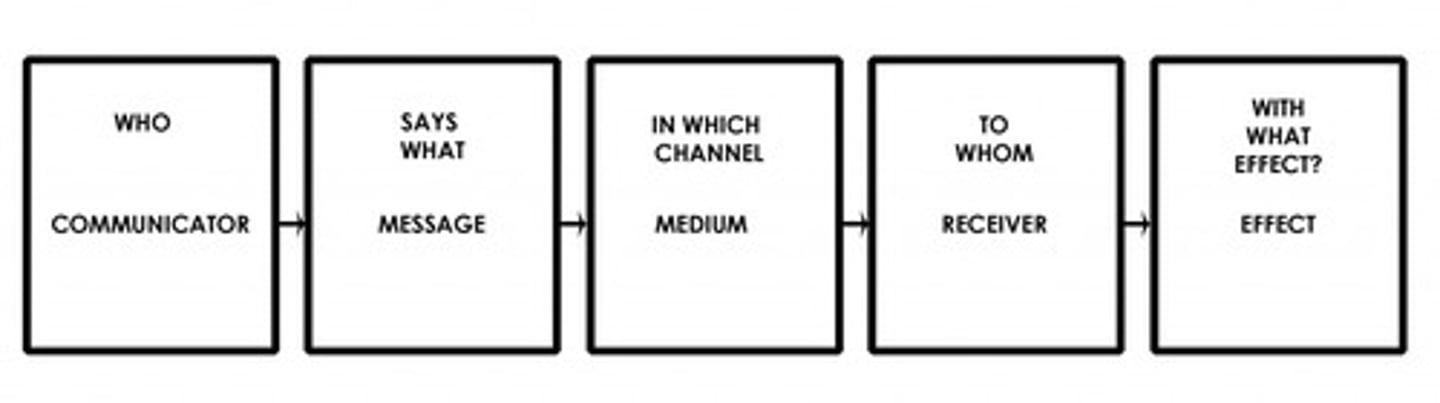
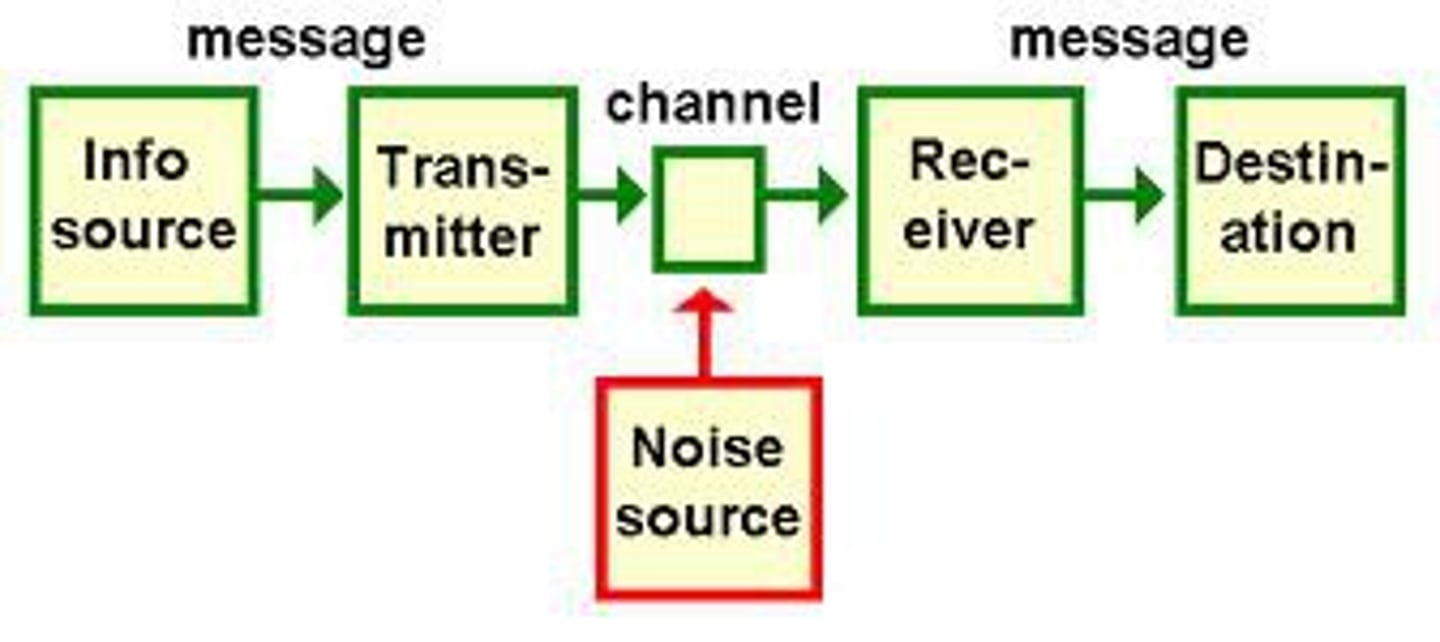
Shannon-Weaver's Communication Model
-technology based model (use of electronics)
-based on long-distance communication forms
-mother of all models
-Linear
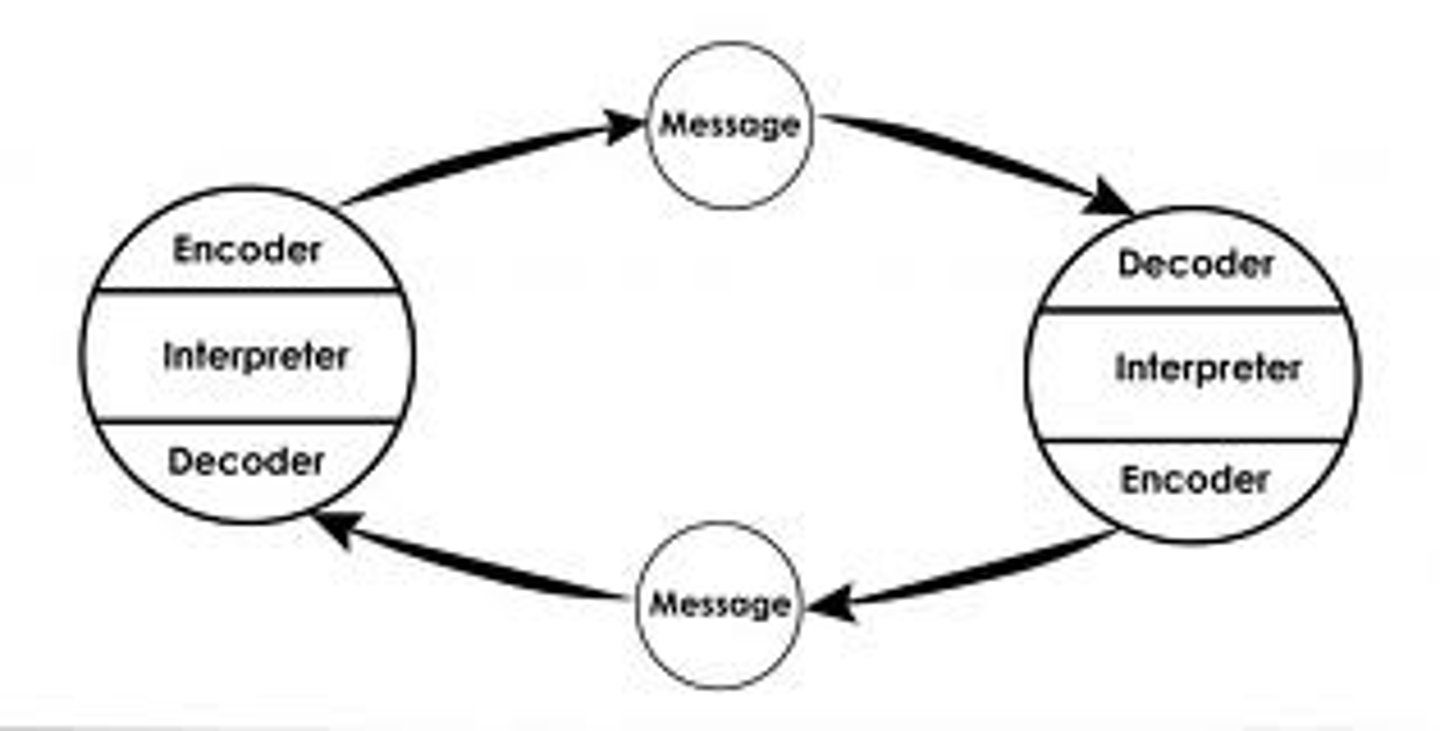
Schramm's Communication model
highlights the dynamic and interactive nature of communication, emphasizing the roles of the source, encoder, message, decoder, receiver, and feedback, while recognizing that shared experiences between communicators enhance understanding and meaning.
-Interactive
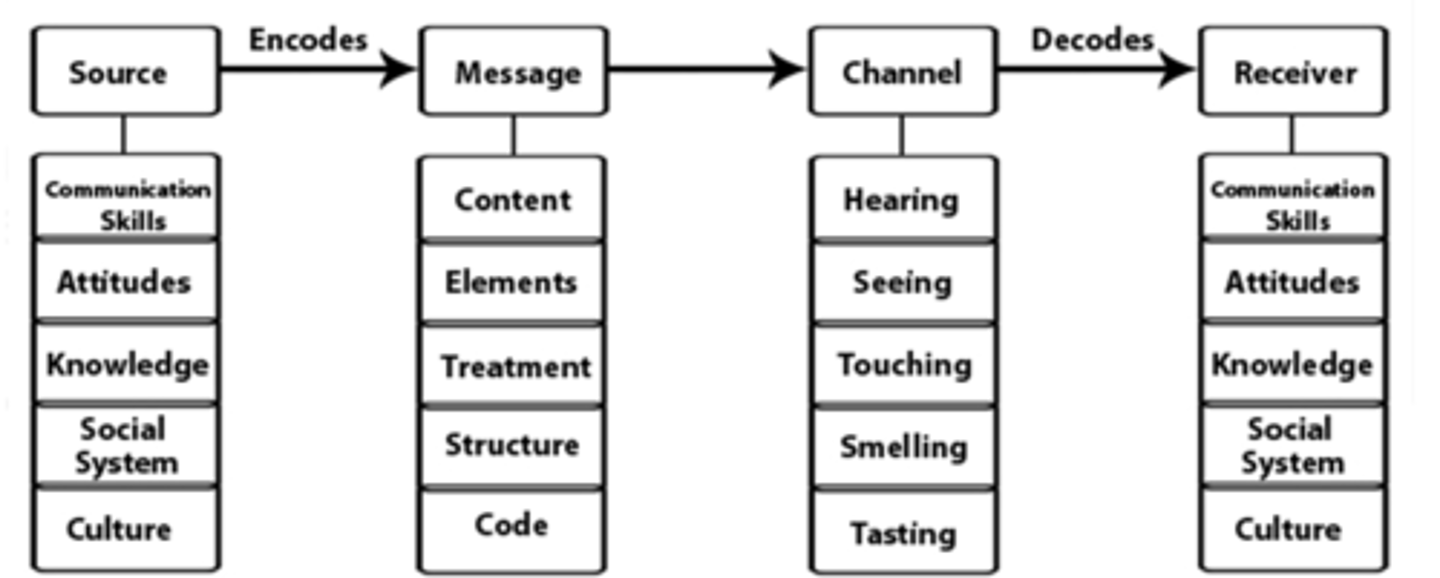
David Berlo's SMCR Model
-emphasizes the importance of four key elements—source, message, channel, and receiver—in effective communication, highlighting how the characteristics of each element influence the overall communication process.
-Linear
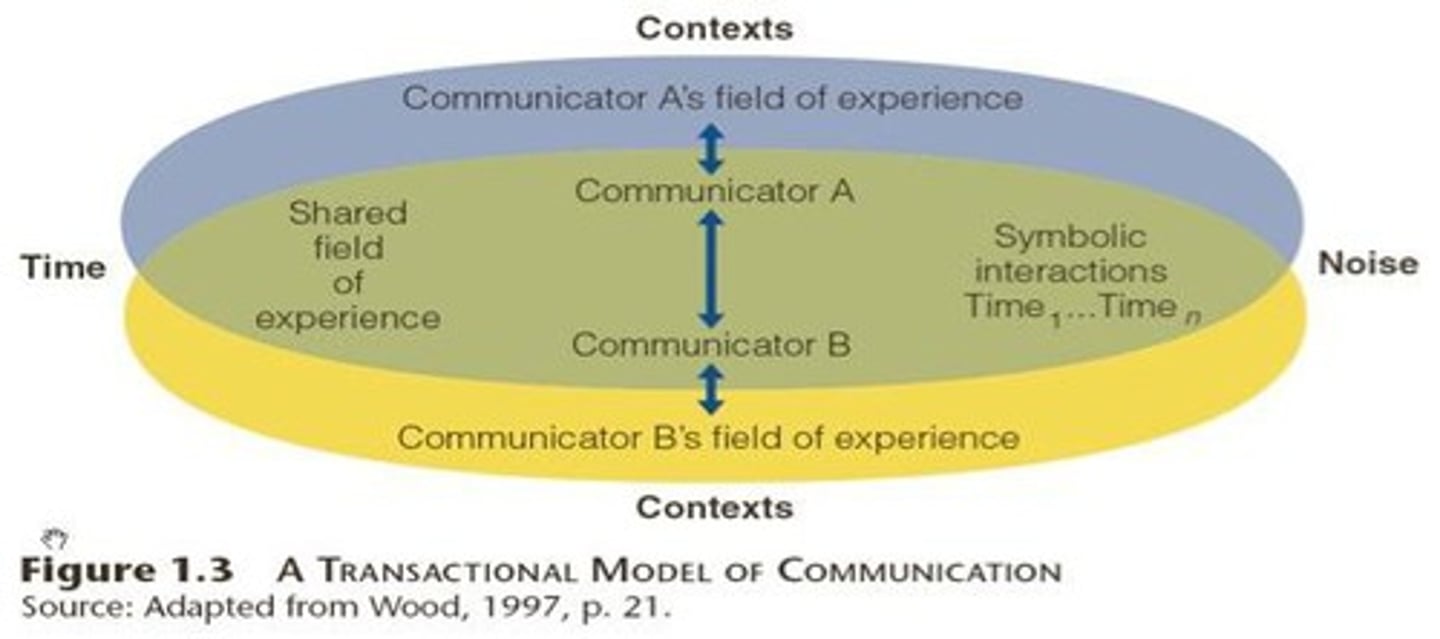
Wood's Communication Model
-emphasizes a transactional approach, highlighting the simultaneous sending and receiving of messages between communicators, and considering the influence of context, noise, and the personal backgrounds of participants on the communication process.
-Transactional
Linear Model of Communication
-no feedback
-Aristotle's, Laswell's, Shannon and Weaver's, David Berlo's
Interactive Model of Communication
-alternating of position (i speak, then you speak after I'm done speaking)
-there's feedback
-Schramm's
Transaction Model of Communication
-can be disrupted while speaking simultaneously
-Wood's
Language Barrier
people who speaks different language that tries to interact
Semantic Barrier
-the difference in meaning attached to words used in communication
-use of ambiguity (Words or phrases that have multiple meanings); Jargon (used by professionals in a particular field can alienate those not familiar with the terminology)
Syntatic barrier
-obstacles in communication that arise from the structure or grammar of a language, which can lead to misunderstandings or confusion
-involves grammar mistakes (verb tense shifts, or different sentence structures), Complex sentences, punctuation misuse, ambiguous mispronounces