Actin Filaments - 30
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Main functions of actin filaments
important in movements involving cell surfaces, forming contractile ring during cytokinesis , muscle contraction, transport of molecules, and forms stable structures like micro villi
Physical properties of actin filaments
Thinner than micro and intermediate filaments, have polarity, more flexible and are shorter than microtubules
What is the structure of actin filaments?
Twisted chain of globular actin monomers pointing in the same direction
How do actin filaments polymerize?
monomers can be added at either end
Which end of the actin filament would cause faster polymerization if monomers were being added?
(+) end
What are free monomers bounds to?
ATP
What happens to ATP when it’s monomer gets added to a growing filament?
ATP is hydrolyzed
What promotes depolymerization?
ADP in the actin filaments
Growth of the (+) end:
monomers are added faster than ATP hydrolysis
Disassembly at the (-) end:
ATP is hydrolyzed faster than new monomers can be added
What is actin treadmilling?
Monomers moving through the filament from the plus end to the minus end
Cell crawling:
polymerization of cytoplasmic monomers at the leading edge creates protrusions
They make attachments to the substratum
The myosin motor draws the body forward
Actin binding proteins:
regulate structure and organization of actin filaments. Can nucleate to add more monomers, can sequester to prevent unwanted polymerization.
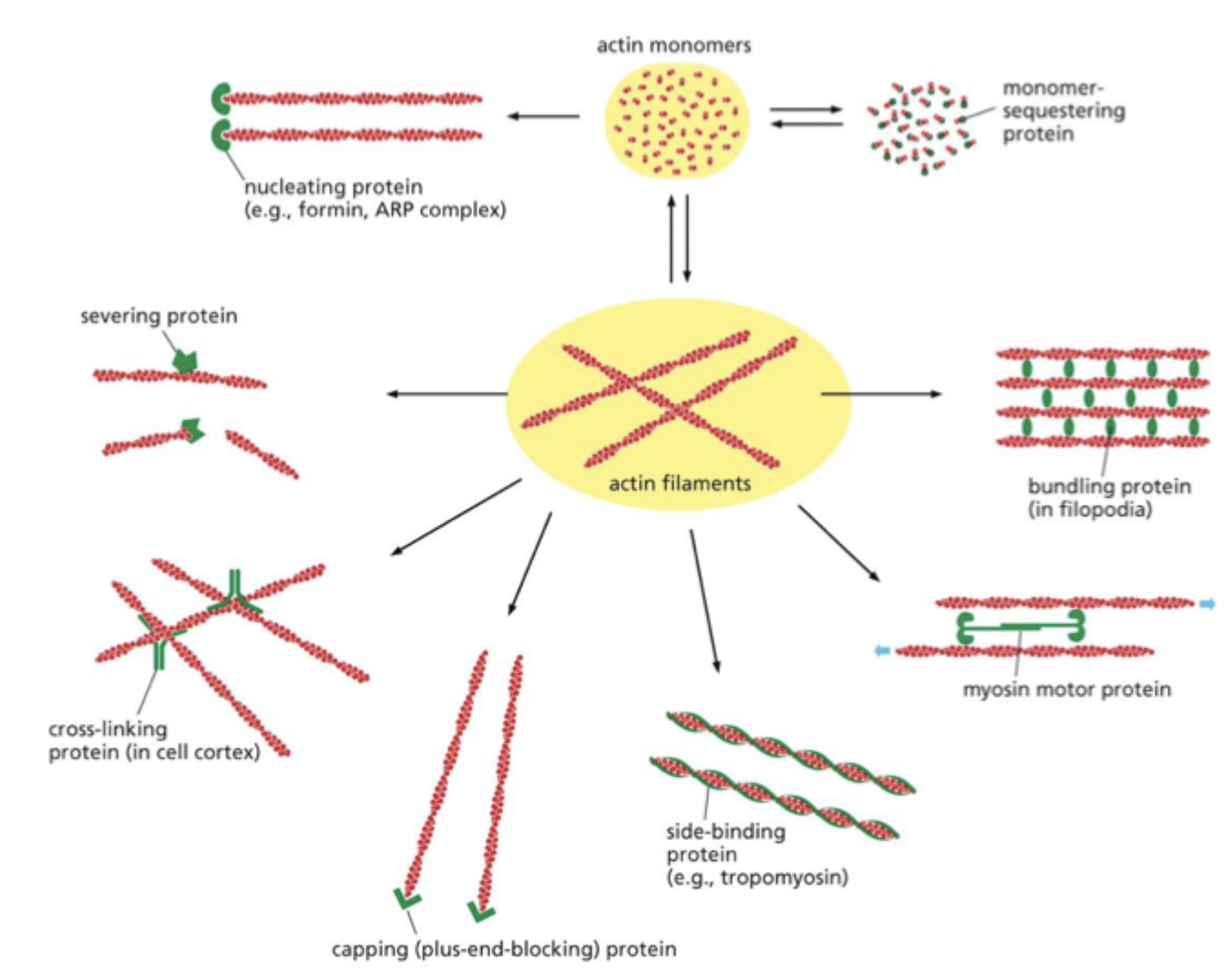
What are binding proteins regulated by?
Extracellular signals → triggers the activation of Rho GTPases → trigger the bundling of actin filaments and activation of formin proteins
What is myosin?
motor protein for actin; uses ATP hydrolysis
Most abundant sub families of myosin:
Myosin-I and Myosin-II
Myosin-I:
Has a singular globular head that attaches to an actin filament and a tail that attaches to another molecule or organelle within the cell, allowing it to move them relative to an actin filament
Myosin-II:
Clusters with each other to form Myosin filaments. It can slide two actin filaments of opposite orientation past each other. Can be seen in muscle contraction and as the contractile ring in cell division.
Skeletal muscle fibers:
Multinucleated cells formed by the fusion of many smaller cells
Sarcomere:
Contractile units of myofibrils containing actin and mysin-II filaments
(+) end are anchored to:
Z disc
(-) ends overlap:
the ends of the myosin filaments
Muscle contraction
-Myosin heads walk along the actin filament in repeated cycles of attachment at detachment
-In each cycle, the myosin head binds to and hydrolyzes one molecule of ATP
-ATP hydrolysis results in a conformational change in myosin, propelling the myosin molecule unidirectionally along the actin filaments
Tropomyosin binds to:
actin helix, blocking myosin heads from attaching to actin filaments
Sarcoplasmic reticulum:
Releases Ca2+ in response to an electrical signal resulting in an increased concentration of cytosolic Ca2+. Increased Ca2+ causes Ca2+ binding to troponin, causing a shape change. This change shifts tropomyosin allowing myosin heads to bind to a tin, initiating muscle contraction