Radiology: Medical Imaging of the GI Tract
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards summarizing key concepts and methodologies in radiology specific to imaging the gastrointestinal tract.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is fluoroscopy used for in medical imaging?
Fluoroscopy is used to view peristalsis in real-time, primarily for imaging hollow organs like the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
What is the primary advantage of ultrasound in medical imaging?
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves and has no ionizing radiation, making it safe and cost-effective compared to other modalities.
What are the contraindications for MRI?
Patients with heart pacemakers, metallic implants, or foreign bodies in the eye cannot undergo MRI.
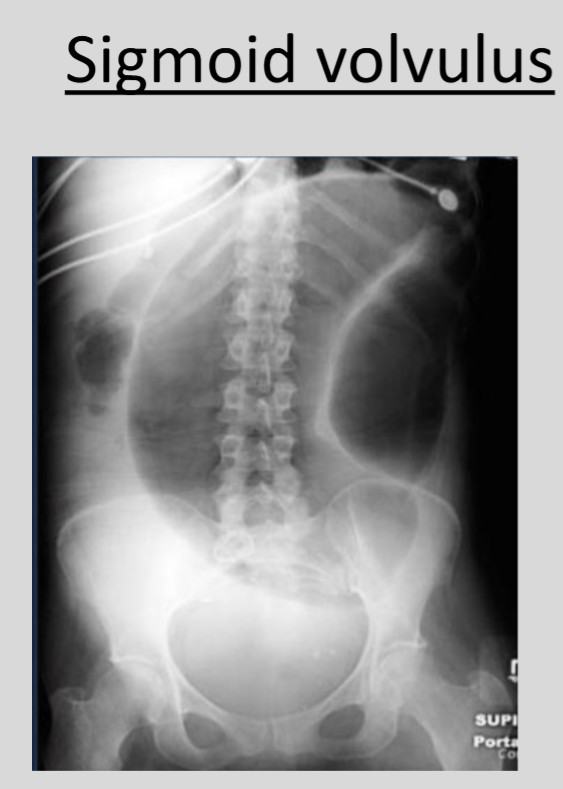
What is the significance of the 'coffee bean sign' in medical imaging?
The 'coffee bean sign' is indicative of sigmoid volvulus, a condition in which the sigmoid colon twists on itself.
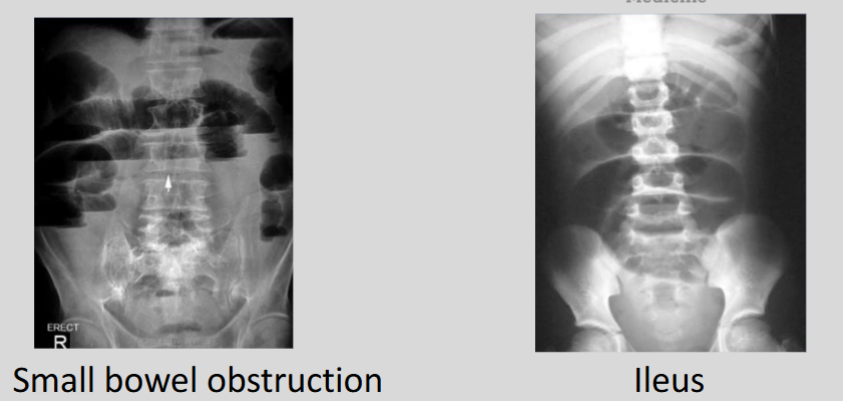
Explain the difference between small bowel obstruction and ileus as seen on imaging.
A small bowel obstruction shows dilated small bowel > colon with a possible transition point, while ileus appears as equal dilation of small bowel and colon.
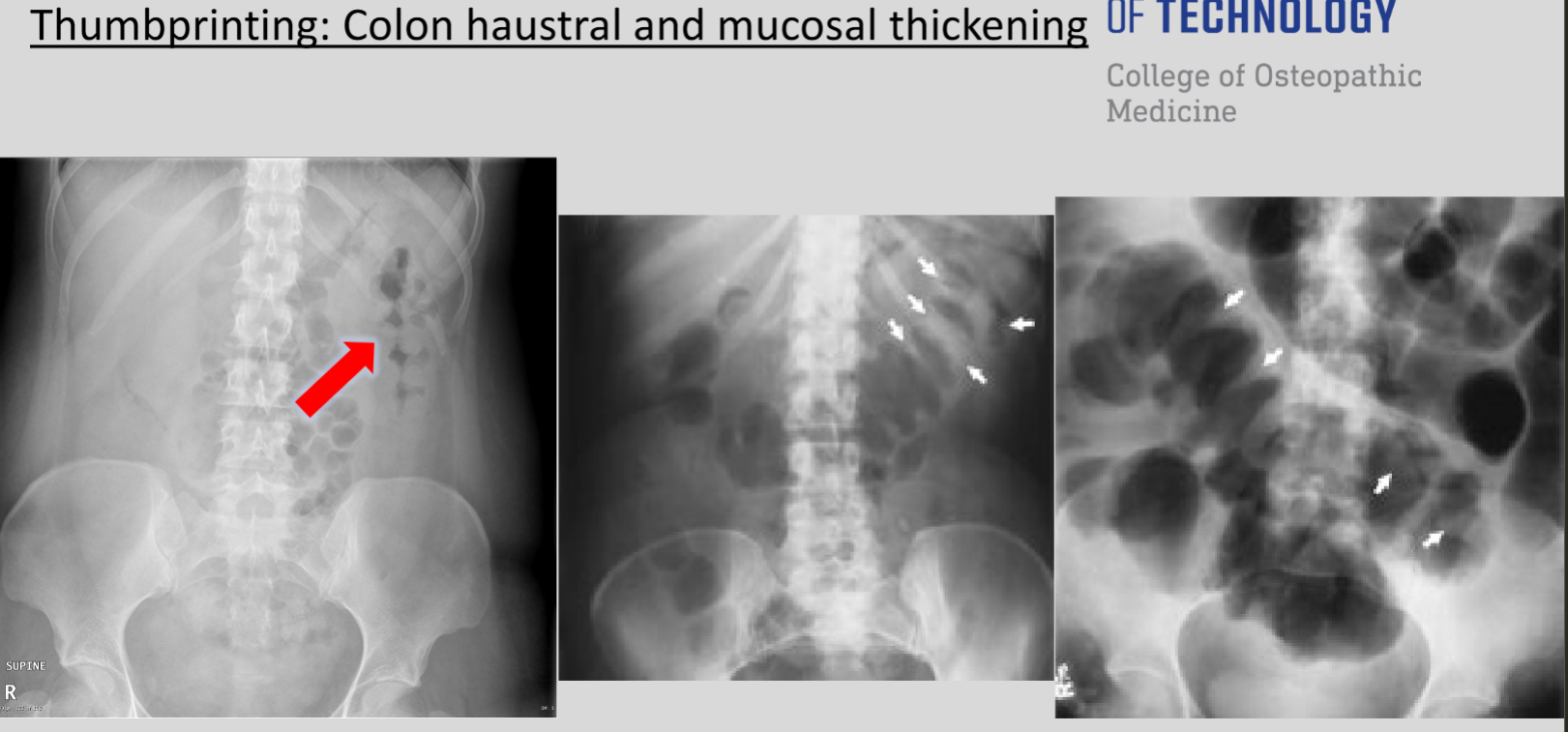
What is 'thumbprinting' and in which conditions can it be observed?
Thumbprinting refers to thickened large bowel wall and can occur in ischemia, C. difficile infections, hemorrhage, and chronic conditions like inflammatory bowel disease.
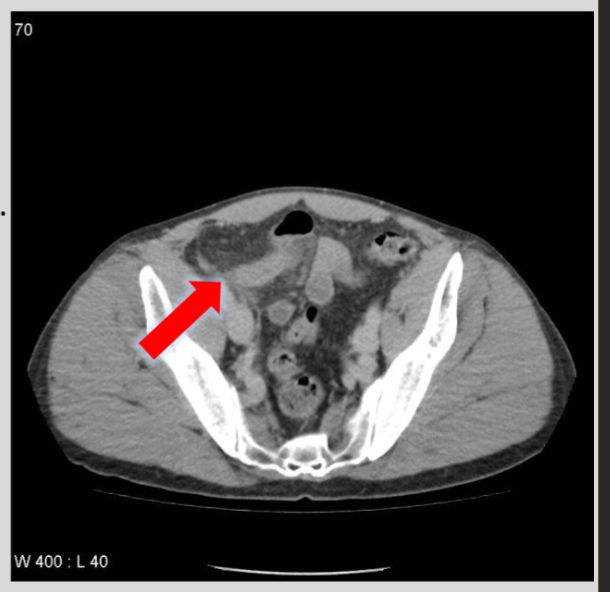
What is the role of CT in diagnosing appendicitis?
CT is the modality of choice for appendicitis, identifying a fluid-filled appendix > 6 mm in diameter with thickened walls, mucosal hyperenhancement, and surrounding inflammation changes
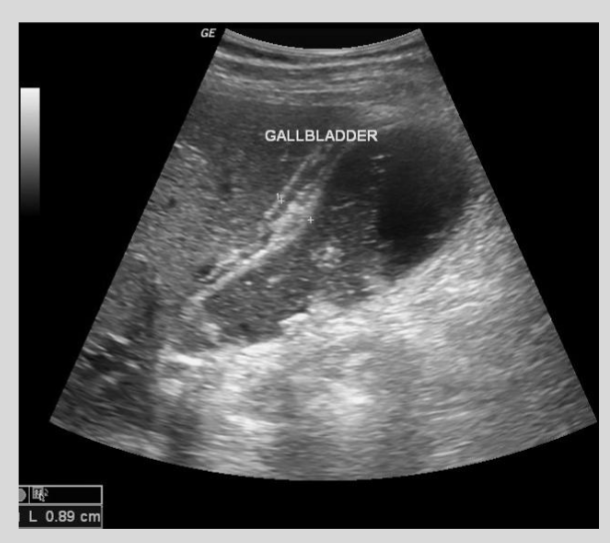
Describe the preferred radiologic approach to detect gallstones and acute cholecystitis
Ultrasound is the first choice modality to detect gallstones and diagnose acute cholecystitis, showing echogenic stones and gallbladder wall thickening
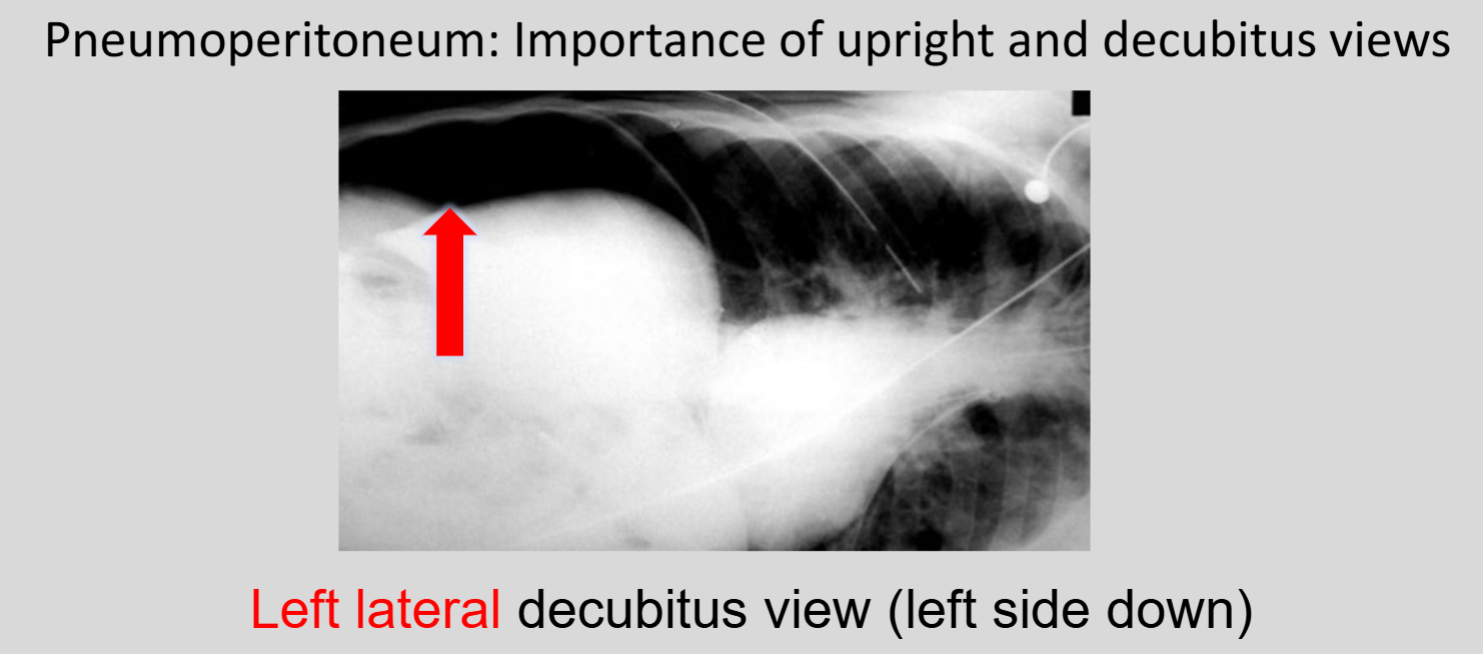
What imaging method is most sensitive for detecting pneumoperitoneum?
CT is much more sensitive than abdominal radiography for detecting pneumoperitoneum
What is fluoroscopy used for in medical imaging?
Fluoroscopy is used to view peristalsis in real-time, primarily for imaging hollow organs like the esophagus, stomach, and intestines.
What is the primary advantage of ultrasound in medical imaging?
Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves and has no ionizing radiation, making it safe and cost-effective compared to other modalities
How does computed tomography (CT) create images of the body?
CT uses X-rays and a computer to create cross-sectional images of the body/organs, which are extremely sensitive compared to plain X-ray—>
note** there are 3 planes: axial, coronal, and sagittal imaging
What are the contraindications for MRI?
Patients with heart pacemakers, metallic implants, or foreign bodies in the eye cannot undergo MRI.
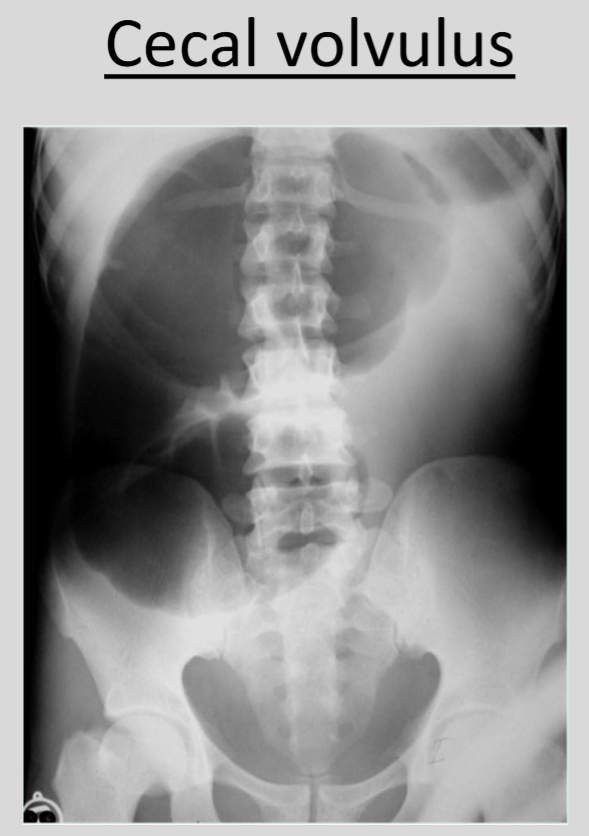
What is the significance of the 'C sign' in medical imaging?
The 'c sign’ is a cecal volvulus, a condition in which the cecum twists around itself or its mesentery
What is the 'lead-pipe sign' and what condition does it typically represent?
The 'lead-pipe sign' refers to a featureless, narrow colon lacking haustral markings, characteristically seen in chronic ulcerative colitis.
Which imaging modality is considered the gold standard for detecting renal stones?
Non-contrast CT (often referred to as CT KUB) is the gold standard for diagnosing renal stones due to its high sensitivity for calcifications.
What are the hallmark findings of a small bowel obstruction on an upright abdominal X-ray?
Hallmarks include dilated small bowel loops (> 3 \text{ cm}) and the presence of multiple air-fluid levels.
How is 'toxic megacolon' identified on a radiograph?
Toxic megacolon is identified by extreme colonic dilation (> 6 \text{ cm}) combined with clinical signs of systemic toxicity, often complicating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
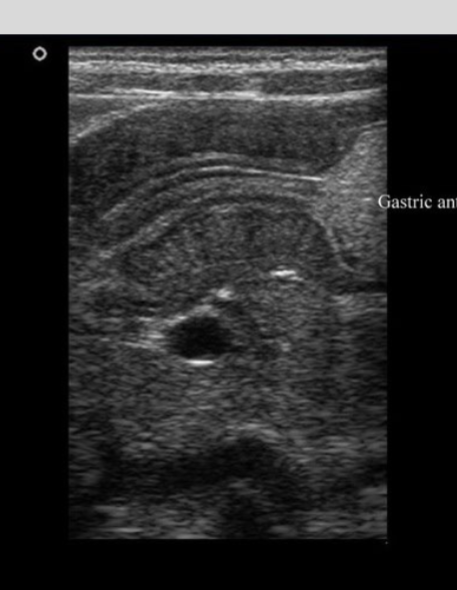
Describe the 'string sign' and its common clinical associations.
The 'string sign' describes severe narrowing of the bowel lumen that resembles a string; it is commonly associated with Crohn\'s disease or hypertrophic pyloric stenosis.
What is the preferred imaging modality for assessing suspected acute pancreatitis?
Contrast-enhanced CT is the preferred modality to evaluate the severity, necrosis, and potential complications of acute pancreatitis.
What are the common CT findings for acute diverticulitis?
CT findings usually include focal colonic wall thickening, pericolic fat stranding, and the presence of diverticula.
What does a positive 'sonographic Murphy sign' indicate?
A positive sonographic Murphy sign is maximal tenderness elicited by the ultrasound probe directly over the gallbladder, indicating acute cholecystitis.
What imaging findings are suggestive of mesenteric ischemia?
Findings include bowel wall thickening, abnormal bowel wall enhancement, and in advanced cases, pneumatosis intestinalis (air within the bowel wall).