CHAPTER 29-32
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Ventilation
-the body's ability to move air in and out of the chest and lung tissue
Oxygenation
-the process of delivering oxygen to the blood by diffusion from the alveoli following inhalation into the lungs
lower
diaphragm
•The chest (thoracic cage) extends from the ____ end of the neck to the _____ .
neurovascular
pleura
•The ____ bundle lies closely along the lowest margin of each rib.
•The _____ covers each lung and the thoracic cavity.
-A small amount of pleural fluid between the parietal and visceral pleura allows the lungs to move freely against the inner chest wall during respiration.
mediastinum
diaphragm
•The _____ contains the heart, great vessels, esophagus, and trachea.
-A thoracic aortic dissection can develop in this area of the chest.
•The ______ is a muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity.
C5
C3
•Patients with a spinal injury below ____ can still breathe from the diaphragm.
Patients with a spinal injury above ___ may lose the ability to breathe
Minute ventilation (minute volume)
-Amount of air moved through the lungs in 1 minute
-Normal tidal volume × respiratory rate
-Patients with a decreased tidal volume will have an increased respiratory rate.
contusion
•Closed chest injury
-Can cause significant cardiac and pulmonary _____
-If the heart is damaged, it may not be able to refill with blood or blood may not be pumped with enough force out of the heart.
-Lung tissue bruising can result in exponential loss of surface area.
-Rib fractures may cause further damage.
Blunt
•______ trauma to the chest may cause:
-Rib, sternum, and chest wall fractures
-Bruising of the lungs and heart
-Damage to the aorta
-Vital organs to be torn from their attachment in the chest cavity
open
•In an ____ chest injury, an object penetrates the chest wall itself.
-Knife, bullet, piece of metal, or broken end of a fractured rib
-Do not attempt to move or remove the object.
Crepitus
Dys
Hemoptysis
Low
injuries of the chest
-Pain at the site of injury
-Localized pain that is aggravated or increased with breathing
-Bruising to the chest wall
-______ with palpation of the chest
-Penetrating injury to the chest
-____pnea
-____ (cough blood)
-Failure of one or both sides of the chest to expand normally with inspiration
-Rapid, weak pulse
-___(low/high) blood pressure
-Cyanosis around the lips or fingernails
Deadly Dozen
Lethal Six
1. airway obstruction
2. tension pneumothorax
3. cardiac tamponade
4. open pneumothorax
5. massive hemothorax
6. flail chest
Hidden Six
7. thoracic aortic disruption
8. tracheobronchial disruption
9. myocardial contusion
10. traumatic diaphragmatic tear
11. esophageal disruption
12. pulmonary contusion
Pneumothorax
___
•Commonly called a collapsed lung
•Accumulation of air in the pleural space
-Blood passing through the collapsed portion of the lung is not oxygenated.
-You may hear diminished, absent, or abnormal breath sounds.
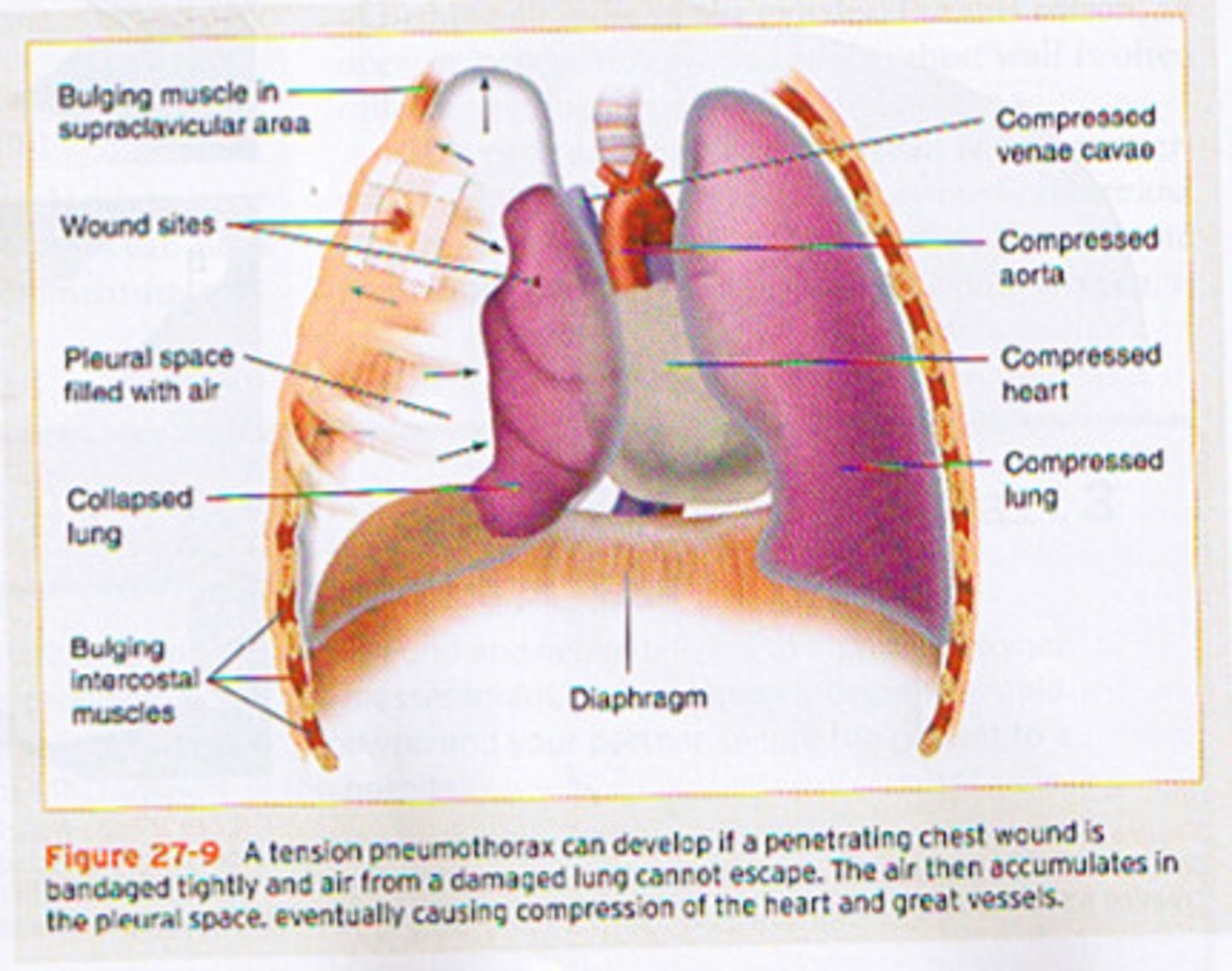
collapsed lung
pleural
oxygenated
Pneumothorax
•Commonly called a ___ ___
•Accumulation of air in the ___ space
-Blood passing through the collapsed portion of the lung is not ________.
-You may hear diminished, absent, or abnormal breath sounds.
open pneumothorax
•Open chest wound
-___ ____ or a sucking chest wound
-Rapidly seal the wound with an occlusive dressing.
-A flutter valve is a one-way valve.
-Carefully monitor the patient for tension pneumothorax.
Simple pneumothorax
•___ ____
-Does not result in major changes in the patient's cardiac physiology
-Commonly due to blunt trauma that results in fractured ribs
-Can often worsen, deteriorate into tension pneumothorax, or develop complications
blunt
ribs
tension pneumothorax
Simple pneumothorax
-Does not result in major changes in the patient's cardiac physiology
-Commonly due to ___ trauma that results in fractured ___
-Can often worsen, deteriorate into ___ ___ , or develop complications
sucking chest
occlusive
flutter valve
tension pneumothorax
•Open chest wound
-open pneumothorax or a ___ ___ wound
-Rapidly seal the wound with an ______ dressing.
-A ___ ___ is a one-way valve.(allows air to leave the chest cavity but not return)
-Carefully monitor the patient for ___ ___ .
Tension pneumothorax
___ ___
-Results from ongoing air accumulation in the pleural space
-Increased pressure in the chest.
-Commonly caused by a blunt injury where a fractured rib lacerates a lung or bronchus
pleural
Increased
blunt
rib
Tension pneumothorax
-Results from ongoing air accumulation in the ____ space
-___ (inc/dec) pressure in the chest.
-Commonly caused by a ____ injury where a fractured ___ lacerates a lung or bronchus
hemothorax
hemopneumothorax
____
•Blood collects in the pleural space from bleeding around the rib cage or from a lung or great vessel.
•Prehospital treatment
-EMT cannot control this kind of bleeding.
-Provide rapid transport.
The presence of air and blood in the pleural space is a _____
great vessel
hemothorax
•Blood collects in the pleural space from bleeding around the rib cage or from a lung or ___ __.
•Prehospital treatment
-EMT cannot control this kind of bleeding.
-Provide rapid transport.
The presence of air and blood in the pleural space is a hemopneumothorax
Cardiac Tamponade
___ ___
•The protective membrane (pericardium) around the heart fills with blood or fluid.
•The heart cannot adequately pump the blood.
•Prehospital treatment
-Support ventilation.
-Provide rapid transport.
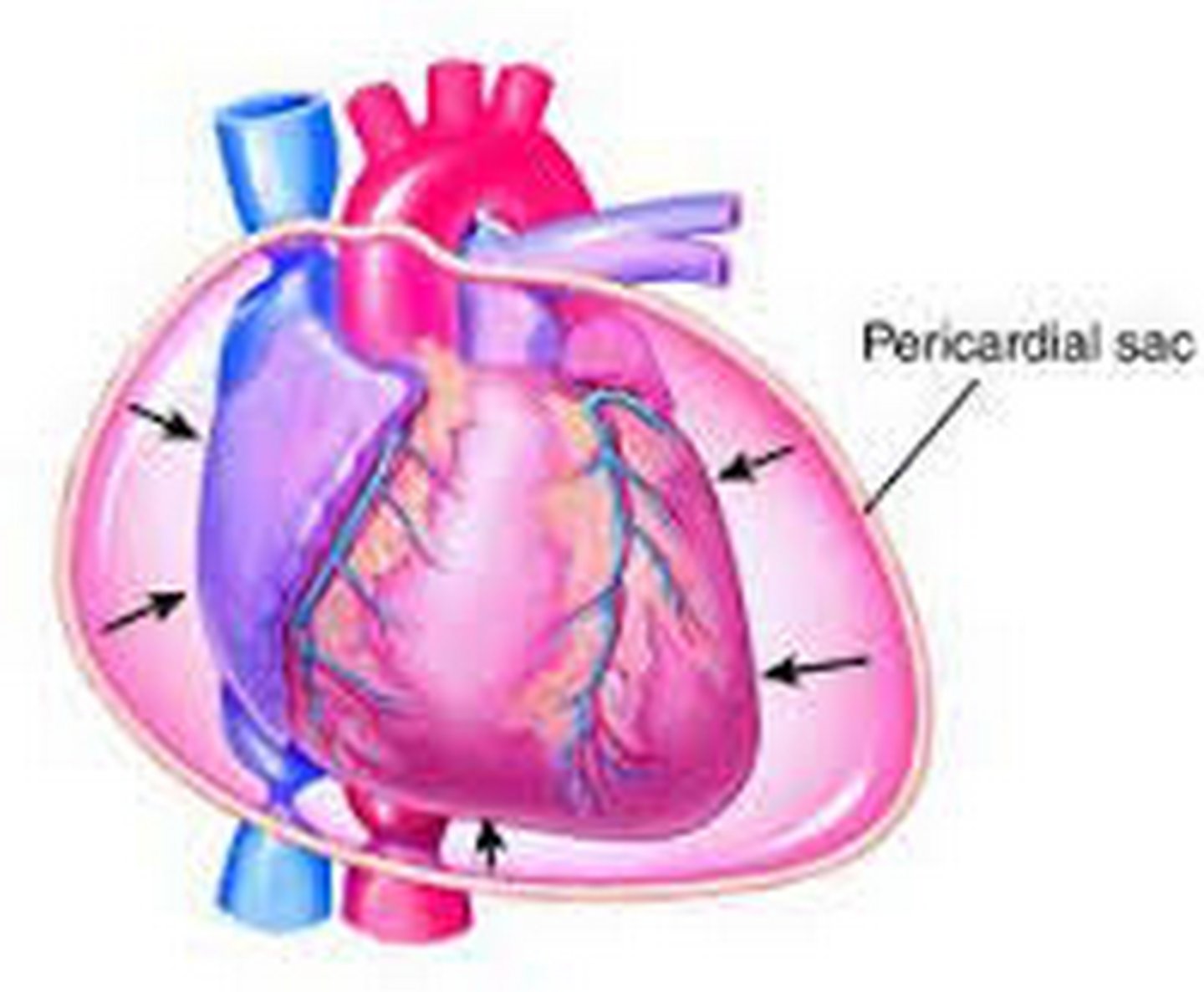
pericardium
Cardiac Tamponade
•The protective membrane (_____) around the heart fills with blood or fluid.
•The heart cannot adequately pump the blood.
•Prehospital treatment
-Support ventilation.
-Provide rapid transport.
4
rib fractures
•Common, particularly in older people
•A fracture of one of the upper ___ ribs is a sign of a very substantial MOI.
•A fractured rib may cause a pneumothorax, a hemothorax, or a hemopneumothorax.
•Give supplemental oxygen.
flail chest
___ ___
•Segment of the chest wall becomes detached from the rest of the thoracic cage
•Detached portion moves opposite of normal
•Prehospital treatment
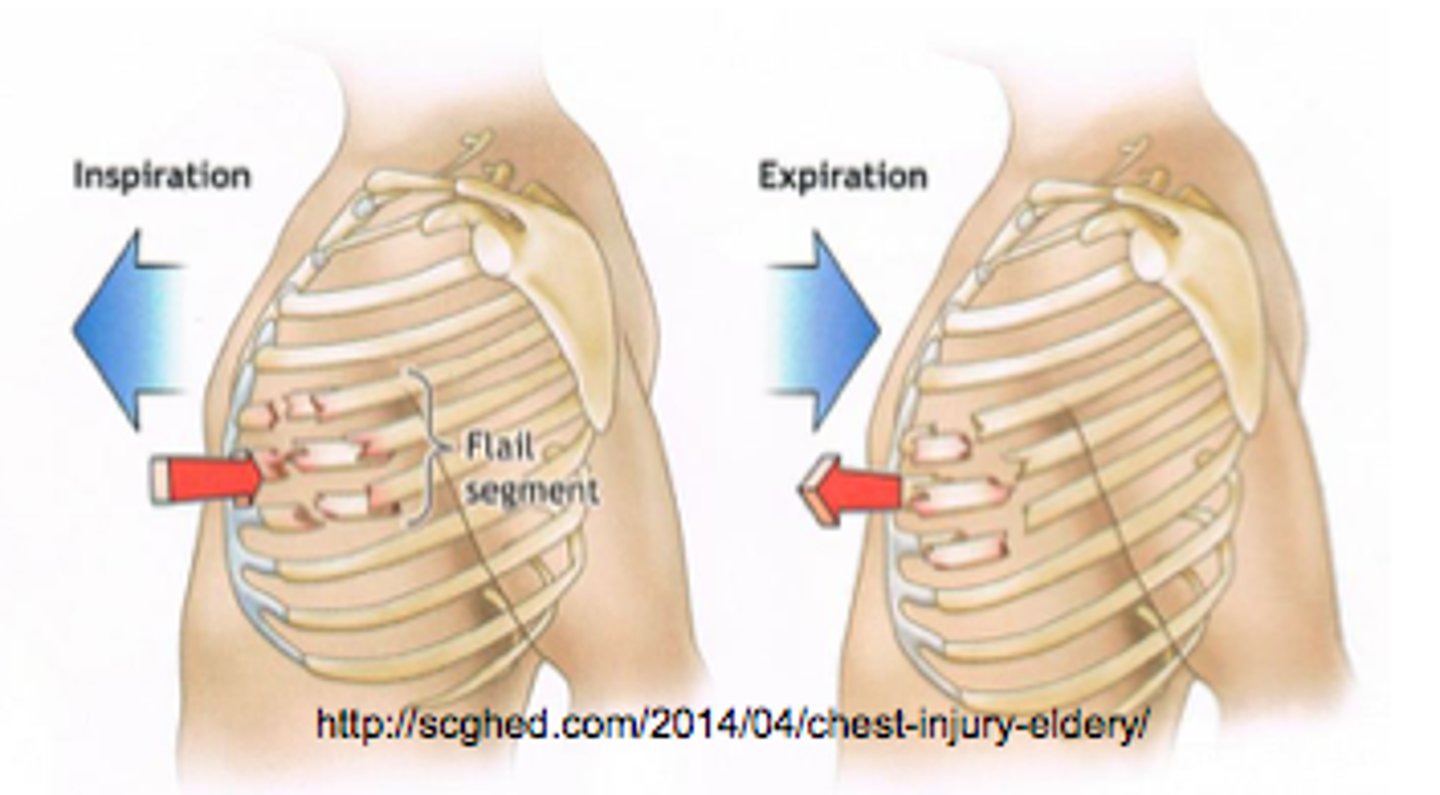
detached
flail chest
•Segment of the chest wall becomes ___ from the rest of the thoracic cage
•Detached portion moves opposite of normal
•Prehospital treatment
Pulmonary contusion
___ ___
-Suspect in a patient with a flail chest
-Pulmonary alveoli become filled with blood, leading to hypoxia
-Provide oxygen and positive-pressure ventilation.
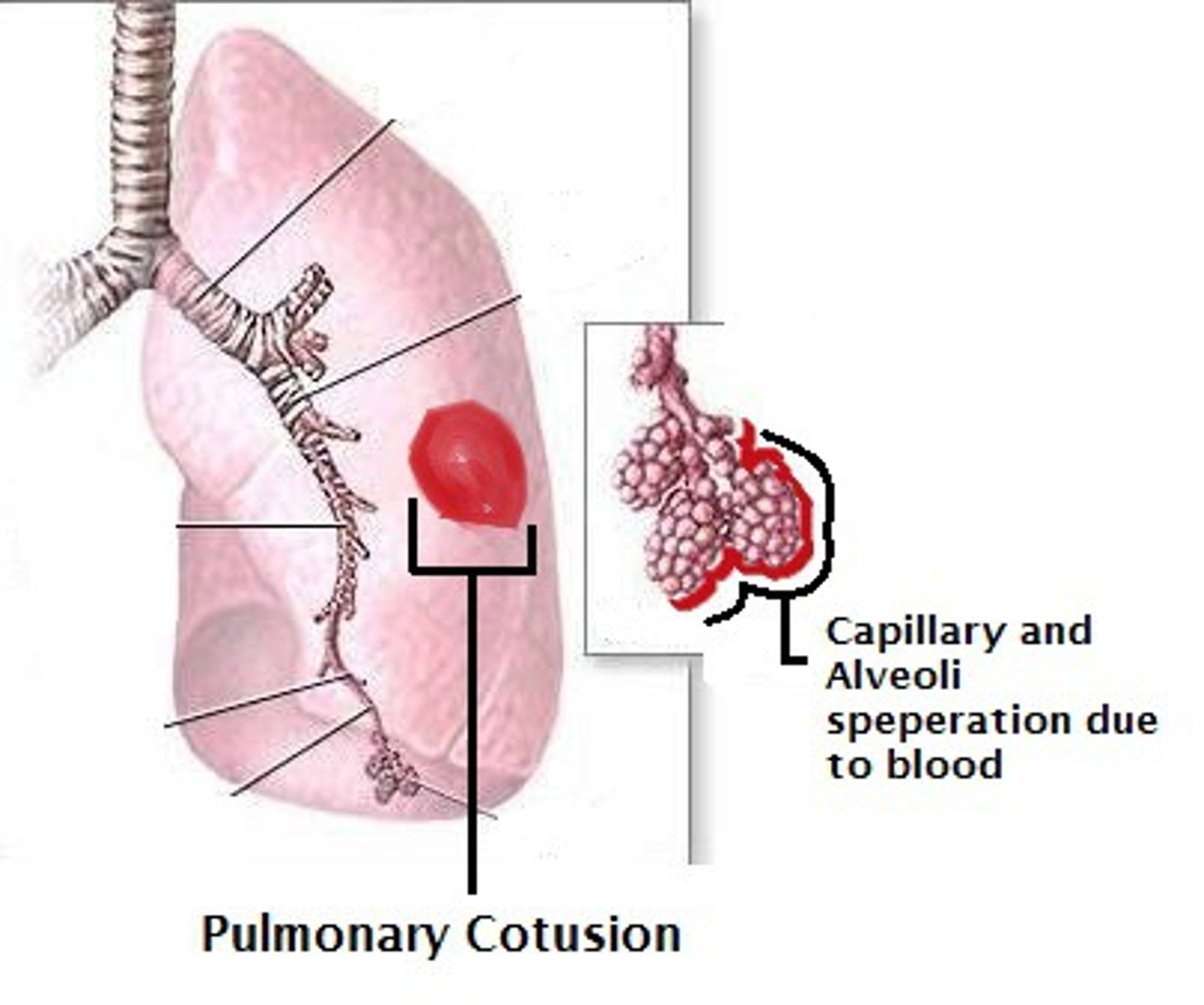
flail chest
alveoli
hypoxia
pulmonary contusion
-Suspect in a patient with a ___ ___
-Pulmonary ___ become filled with blood, leading to _____
-Provide oxygen and positive-pressure ventilation.
Sternal
Clavicle
•Other chest fractures
-____ fractures
•Increased index of suspicion for organ injury
-____ fractures
•Possible damage to neurovascular bundle
•Suspect upper rib fractures in medial clavicle fractures.
•Be alert to pneumothorax development.
Traumatic asphyxia
___ ____
- Sudden, severe compression of the chest, which produces a rapid increase in pressure within the chest
-Suggests an underlying injury to the heart and possibly a pulmonary contusion
-Provide ventilatory support with oxygen, and monitor vital signs during immediate transport.
-Characterized by distended neck veins, cyanosis in the face and neck, and hemorrhage in the sclera of the eye
increase
pulmonary contusion
distended
cyanosis
hemorrhage
Traumatic asphyxia
- Sudden, severe compression of the chest, which produces a rapid ___ (inc/dec) in pressure within the chest
-Suggests an underlying injury to the heart and possibly a ___ ___
-Provide ventilatory support with oxygen, and monitor vital signs during immediate transport.
-Characterized by ___ neck veins, ____ in the face and neck, and ____ in the sclera of the eye
blunt myocardial
___ ___ injury
-Bruising of the heart muscle
-The heart may be unable to maintain adequate blood pressure.
-Suspect in all cases of severe blunt injury to the chest
-Monitor pulse and blood pressure, provide oxygen, and transport immediately.
heart
BP
blunt myocardial
-Bruising of the ___ muscle
-The heart may be unable to maintain adequate____ (abrv)
-Suspect in all cases of severe blunt injury to the chest
-Monitor pulse and blood pressure, provide oxygen, and transport immediately.
Commotio cordis
___ ___
-Injury caused by a sudden, direct blow to the chest during a critical portion of the heartbeat
-May result in immediate cardiac arrest
-Ventricular fibrillation responds positively to defibrillation within the first 2 minutes of the injury.
cardiac arrest
Commotio cordis
-Injury caused by a sudden, direct blow to the chest during a critical portion of the heartbeat
-May result in immediate ___ ___
-Ventricular fibrillation responds positively to defibrillation within the first 2 minutes of the injury.
great vessels
•Laceration of the ___ ___
-May result in rapidly fatal hemorrhage
-Prehospital treatment:
•Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
•Ventilatory support and oxygen
•Immediate transport
•Monitor for shock and changes in vital signs.
B
1.When the chest impacts the steering wheel during a motor vehicle crash with rapid deceleration, the resulting injury, which often kills patients, usually within seconds, is:
A.a hemothorax.
B.aortic shearing.
C.a pneumothorax.
D.a ruptured myocardium.
B
2.Signs and symptoms of a chest injury include all of the following, EXCEPT:
A.hemoptysis.
B.hematemesis.
C.asymmetrical chest movement.
D.increased pain with breathing.
D
3.During your assessment of a patient who was stabbed, you see an open wound to the left anterior chest. Your MOST immediate action should be to:
A.position the patient on the affected side.
B.transport immediately.
C.assess the patient for a tension pneumothorax.
D.cover the wound with an occlusive dressing.
C
4.When caring for a patient with signs of a pneumothorax, your MOST immediate concern should be:
A.hypovolemia.
B.intrathoracic bleeding.
C.ventilatory inadequacy.
D.associated myocardial injury.
B
5.What purpose does a one-way "flutter valve" serve when used on a patient with an open pneumothorax?
A.It prevents air escape from within the chest cavity.
B.It allows a release of air trapped in the pleural space.
C.It only prevents air from entering an open chest wound.
D.It allows air to freely move in and out of the chest cavity.
C
6.Signs of a cardiac tamponade include all of the following, EXCEPT:
A.muffled heart tones.
B.a weak, rapid pulse.
C.collapsed jugular veins.
D.narrowing pulse pressure.
B
7.A patient experienced a severe compression to the chest when trapped between a vehicle and a brick wall. You suspect traumatic asphyxia due to the hemorrhage into the sclera of his eyes and which other sign?
A.Flat neck veins
B.Cyanosis in the face and neck
C.Asymmetrical chest movement
D.Irregular heart rate
C
8.A 14-year-old baseball player was hit in the chest with a line drive. He is in cardiac arrest. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
A.Myocardial contusion
B.Traumatic asphyxia
C.Commotio cordis
D.Hemothorax
A
9.Paradoxical chest movement is typically seen in patients with:
A.a flail chest.
B.a pneumothorax.
C.isolated rib fractures.
D.a ruptured diaphragm.
A
10.A 40-year-old man, who was the unrestrained driver of a car that hit a tree at a high rate of speed, struck the steering wheel with his chest. He has a large bruise over the sternum and an irregular pulse rate of 120 beats/min. You should be MOST concerned that he:
A.has injured his myocardium.
B.has a collapsed lung and severe hypoxia.
C.has extensive bleeding into the pericardial sac.
D.is at extremely high risk for ventricular fibrillation.
digestive
urinary
genitourinary
•The abdomen is a major body cavity extending from the diaphragm to the pelvis
-Contains organs that make up the (3systems) systems.
•Significant trauma to the abdomen can occur from blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, or both.
RL
____Q is a common location for swelling and inflammation.
Hollow
peritoneal
peritonitis
•____ organs
-Stomach, intestines, ureters, bladder
-Most contain digested food, urine, or bile.
-When ruptured or lacerated, contents spill into ____ cavity.
•Can cause intense inflammatory reaction and infection, such as in the case of _______
mesentery
peritoneal
-Intestinal blood supply comes from ____.
•Connects the small intestine to the abdominal wall
•Patients with injuries to the *** can bleed into the _____ cavity.
Solid
rich
•__ organs
-Liver, spleen, pancreas, kidneys
•Perform chemical work of the body: enzyme production, blood cleansing, energy production
•Because of ____ blood supply, hemorrhage can be severe.
Compression
Deceleration
•Blunt trauma to abdomen without breaking the skin
-______
•Poorly placed lap belt
•Being run over by a vehicle
- clasp knife injury
-______
•Fast-moving vehicle strikes an immoveable object.
-pain can be deceiving
•Often diffuse in nature
•May be referred to another body location
-Blood in peritoneal cavity produces acute pain in entire abdomen.
P
shoulder
Liver and spleen injuries refer pain to the ____.
guarding
____: Conscious or unintentional stiffening of the muscles of the surface of the abdomen to avoid further pain
- difficult to locate location of pain
___ ____ or swelling between the xiphoid process and the groin is often the result of free fluid, blood, or organ contents spilling into the peritoneal cavity.
- Additional signs of abdominal injury are bruising and discoloration.
- Closed abdominal injuries may initially appear as abrasions.
penetrating
____ injury
•Foreign object enters abdomen and opens the peritoneal cavity to the outside
low
___ velocity injuries
•Knives, other edged weapons
medium
___ velocity injuries
•Smaller caliber handguns and shotguns
high
___ velocity injuries
•High-powered rifles and handguns
cavitation
•High- and medium-velocity injuries
-Have temporary wound channels
-Caused by ______ (cavity forms as the pressure wave from the projectile is transferred to the tissues)
- Causes microscopic tears to the blood vessels and nerves
xiphoid
•Low-velocity injuries
-Internal injury may not be apparent.
-Injury at or below ____ process may affect thoracic and peritoneal cavities.
Evisceration
• _______: bowel protrudes from peritoneum
-Can be painful and visually shocking
-Do not push down on abdomen.
-Only perform visual assessment.
-Cut clothing close to wound.
-Never pull on clothing stuck to or in the wound channel.
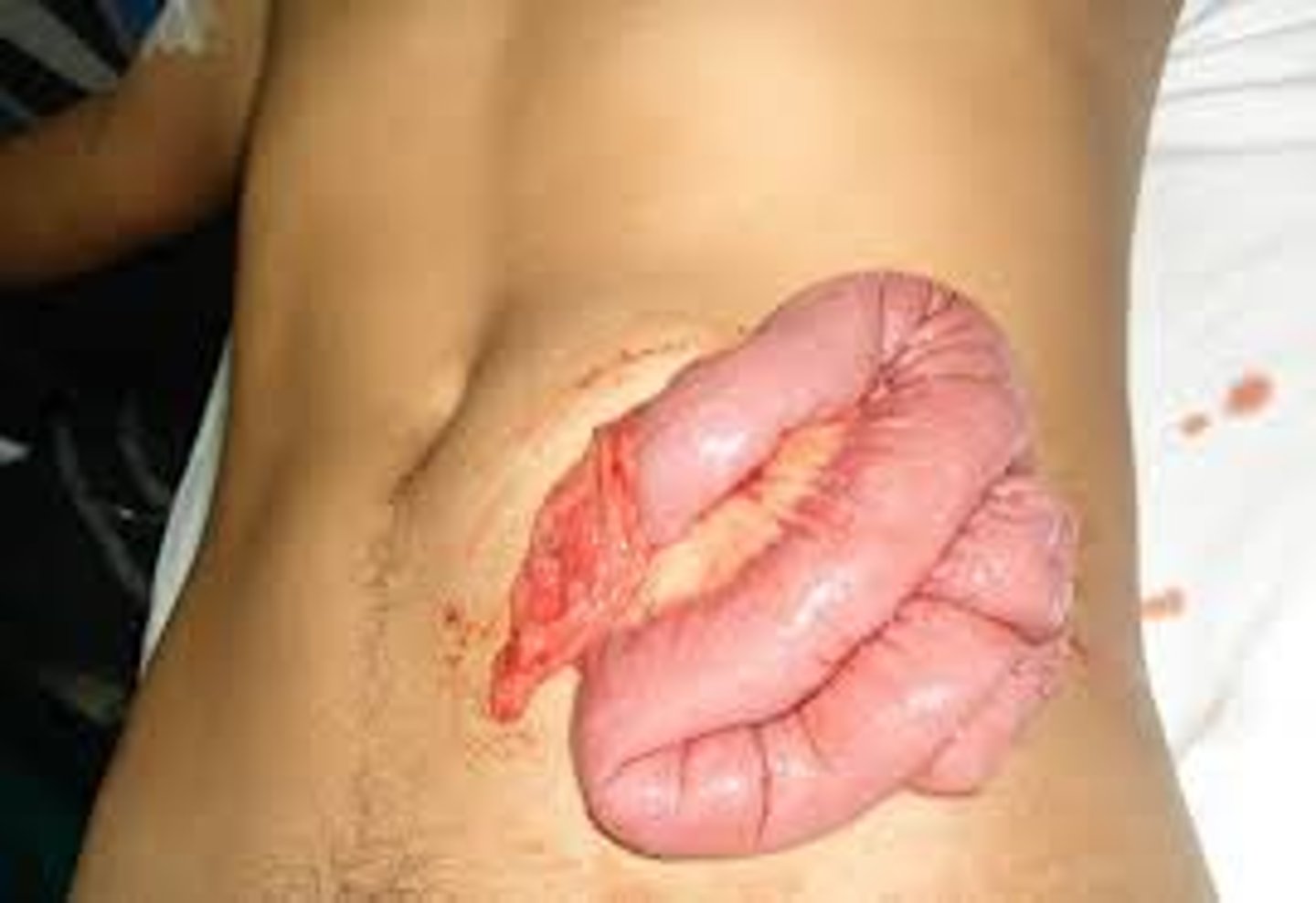
Tachy
increase
shock
open abdomen injuries
-___cardia
•Heart (inc/dec) pumping action to compensate for blood loss
-Later signs include:
•Evidence of ____
•Changes in mental status
•Distended abdomen
Infection
Hollow organ injuries
•Often have delayed signs and symptoms
•Spill contents into abdomen
-____ develops, which can take hours or days.
-Stomach and intestines can leak highly toxic and acidic liquids into peritoneal cavity.
Blunt
Penetrating
infection
septic
•Both blunt and penetrating trauma can cause hollow organ injuries.
-___ trauma causes organ to "pop."
-_____ trauma causes direct injury.
•Air in peritoneal cavity causes pain.
Severe ___ and ____ shock may develop
liver
hypo
LR
•The ___ is the largest organ in the abdomen.
-Very vascular and can lead to ____perfusion
•Often injured by fractured (abrv) rib or penetrating trauma
bowels
dys
•Diaphragm
-When penetrated or ruptured, loops of ____ invade thoracic cavity.
•Patient may exhibit ___pnea.
urine
urinary meatus
•Kidneys
-Can cause significant blood loss
-Common finding is blood in ____
-Blood visible on ___ ____ indicates significant trauma to genitourinary system.
far
kidney
-Palpate quadrant (far/close) away from quadrant exhibiting signs of injury and pain.
-Perform full-body scan to identify injuries.
•If you find life threat, stop and treat it.
-Inspect and palpate ___ area for tenderness, bruising, swelling, or other trauma signs.
log roll
-Patient with blunt abdominal injury should be ___ ___ to a supine position on a backboard.
-Protect the spine.
-Monitor vital signs.
-Patients with penetrating injuries
•Maintain high index of suspicion for unseen blood loss
-Inspect patient's back and sides for exit wounds.
-Apply dry, sterile dressing to all open wounds.
-If penetrating object is still in place, apply stabilizing bandage around it.
evisceration
-Never try to replace a protruding organ.
-Keep the organs moist and warm.
-Cover with moistened, sterile dressings.
-Secure dressing with bandage.
-Secure bandage with tape.
genitourinary
___ system
•Controls reproductive functions and waste discharge
-Genitourinary organs are located in the abdomen
•Kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
-Male genitalia lie outside pelvic cavity.
-Female genitalia lie within pelvic cavity.
kidney
•Suspect ____ damage if patient has a evidence of any of the following:
-Abrasion, laceration, contusion on the flank
-Penetrating wound in region of flank or upper abdomen
-Fractures on either side of lower rib cage or of lower thoracic or upper lumbar vertebrae
-A hematoma in the flank region
soft tissue
•External male genitalia injuries
-___ ____ wounds
-Painful and of great concern for patient
•Rarely life threatening
•Should not be given priority over more severe wounds unless there is severe bleeding
pregnant
•Female genitalia injuries
-Internal female genitalia
•Uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes are rarely damaged.
•Exception is ___ uterus
-Uterus enlarges substantially and rises out of pelvis
-Injuries can be serious.
-Also keep the fetus in mind.
rich
-External female genitalia
•Vulva, clitoris, major and minor labia
•Very(rich/poor) nerve supply
•Consider sexual assault and pregnancy.
•If external bleeding, a sterile absorbent sanitary pad may be applied to the labia.
•Do not insert anything into the vagina.
Tachy
tachy
low
weak
•___cardia; ____pnea; ___ blood pressure; ____ pulse; and cool, moist, pale skin indicate hypoperfusion.
blood loss
connective
-Amputation of penile shaft
•Managing___ ___ is top priority.
-If ____ tissue surrounding erectile tissue is damaged, shaft can be fractured or angled.
•Associated with intense pain, bleeding, and fear
rectal bleeding
___ ___
-Common complaint
-Possible causes include sexual assault, rectal foreign bodies, hemorrhoids, colitis, ulcers, or hemorrhoid surgery.
D
1.Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the:
A.liver.
B.spleen.
C.kidney.
D.stomach.
●
A
2.Which of the following organs would be the MOST likely to bleed profusely if severely injured?
A.Liver
B.Kidney
C.Stomach
D.Gallbladder
●
C
3.Which of the following statements regarding intra-abdominal bleeding is FALSE?
A.Intra-abdominal bleeding often causes abdominal distention.
B.Intra-abdominal bleeding is common following blunt force trauma.
C.The absence of pain and tenderness rules out intra-abdominal bleeding.
D.Bruising may not occur immediately following blunt abdominal trauma.
C
4.Even when seatbelts are worn properly and the airbags deploy, injury may occur to the:
A.chest.
B.extremities.
C.iliac crests.
D.lower ribcage.
●
A
5.While inspecting the interior of a wrecked automobile, you should be MOST suspicious that the driver experienced an abdominal injury if you find:
A.a deformed steering wheel.
B.that the airbags deployed.
C.a crushed instrument panel.
D.damage to the lower dashboard.
●
D
6.Other than applying a moist, sterile dressing covered with a dry dressing to treat an abdominal evisceration, an alternative form of management may include:
A.placing dry towels over the open wound.
B.cleaning the exposed bowel with sterile saline.
C.applying the PASG to stop the associated bleeding.
D.applying an occlusive dressing, secured by trauma dressings.
B
7.You are transporting a patient with possible peritonitis following trauma to the abdomen. Which position will he MOST likely prefer to assume?
A.Sitting up
B.Legs drawn up
C.Legs outstretched
D.On his right side
●
C
8.A 16-year-old boy was playing football and was struck in the left flank during a tackle. His vital signs are stable; however, he is in severe pain. You should be MOST concerned that he has injured his:
A.liver.
B.spleen.
C.kidney.
D.bladder.
●
B
9.The term "hematuria" is defined as:
A.blood in the stool.
B.blood in the urine.
C.vomiting up blood.
D.urinary bladder rupture.
A
10.When caring for a female with trauma to the external genitalia, the EMT should:
A.use local pressure to control bleeding.
B.carefully pack the vagina to reduce bleeding.
C.remove any impaled objects from the vagina.
D.cover any open wounds with moist, sterile dressings.
●
skeletal
___ •muscle attaches to the bones and usually crosses at least one joint.
-Called voluntary muscle because it is under direct voluntary control of the brain
-Makes up the largest portion of the body's muscle mass
tendons
•All skeletal muscles are supplied with arteries, veins, and nerves.
Skeletal muscle tissue is directly attached to the bone by ____
Protects
move
blood cells
206
the skeleton
•Gives us recognizable form
•____ vital organs
•Allows us to ____
•Produces ___ ____
•Made up of approximately ____ bones
skull
•The ___ protects the brain.
thoracic cage
•The ___ ____ protects the heart, lungs, and great vessels.
pectoral girdle
•The ___ ___ consists of two scapulae and two clavicles.
humerus
radius
ulna
•Upper extremity extends from the shoulder to the fingertips
-Composed of the upper arm (______), elbow, and forearm (____ and ____)
carpals
metacarpals
phalanges
•The hand contains three sets of bones:
-Wrist bones (____)
-Hand bones (____)
-Finger bones (____)
pelvis
•The _____ supports the body weight and protects the structures within the pelvis.
•The lower extremity consists of the bones of the thigh, leg, and foot.
-Femur, tibia, fibula, patella