The Urogenital System - The Reproductive Organs
1/104
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 309
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
105 Terms
list the male reproductive organs
gonads (paired)
gonadal duct system (paired)
accessory glands
urethra
penis
what are the singular and plural forms of gonads?
singular — testis, testicle
plural — testes, testicles
function of gonadal duct system?
convey the sperm and seminal fluid of the testes to the urethra
two structures within the gonadal duct system?
epididymis
ductus deferens
what male reproductive organ contributes to the bulk of semen?
accessory glands
name the accessory glands
prostate gland
vesicular glands
ampullary glands
blubourethral glands
placement of urethra…
extends from the bladder to the free extremity of the penis
function of urethra?
serves for the passage of both urine and semen
function of penis?
deposits the semen within the reproductive tract of the female
what are the skin structures associated with the penis and testicles?
prepuce
scrotum
the testis ranges in ______, ______ and ________ depending on species
size, shape, and orientation
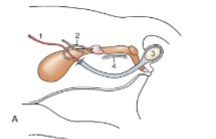
shape of testis in cats and swine
tilted toward the anus
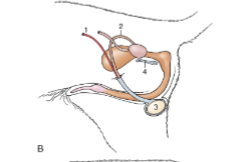
shape of testis in horses and dogs
horizontally oriented between the hindlimbs
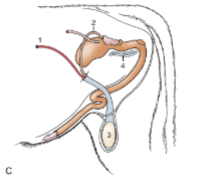
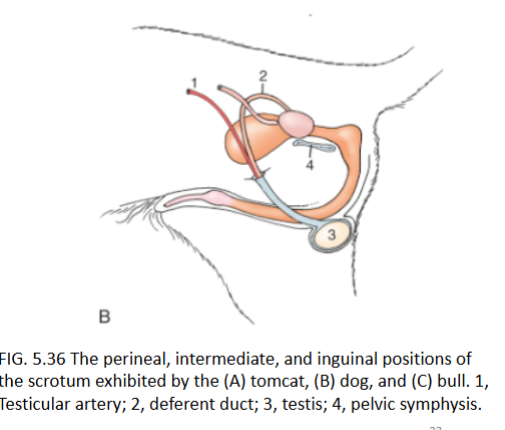
shape of testis in ruminants
vertically oriented and pendulous between thighs
describe the testis
solid encapsulated ellipsoidal organ outside of the body cavity which is suspended within the scrotum by a spermatic cord
what does the testis produce?
testosterone
sperm, spermatozoa
what is the tough, outer layer of connective tissue that surrounds the testis?
Tunica Albuginea
the soft, yellowish or brownish testicular parenchyma consists of ________ _________
seminiferous tubules
where does spermatogenesis occur?
in seminiferous tubules
what are the 2 cell types that line seminiferous tubules?
Sertoli cells
support and nourish sperm cells
spermatogenic cells
produce sperm cells
the seminiferous tubules are surrounded by interstitial cells known as…
Cells of Leydig
function of Cells of Leydig?
secrete Testosterone
where do seminiferous tubules gather at?
the mediastinum of the testicle
the seminiferous tubules gather at the mediastinum and pierce the capsule to join the …
head of the epididymis
the epididymis is attached to the testicle from end to end and is responsible for…
for storing sperm cells
describe the epididymis
a firm organ attached to the testicle that is for numerous convolutions duct
the epididymis is divided into three parts. what are they?
head, body, tail
the tail of the epididymis continues to become the …
Ductus Deferens
the ductus deferens runs ______ to the epididymis
medial
the ductus deferens heads toward the testicular vessels that form…
the bulkier components of the spermatic cord
the constituents of the spermatic cord remain together as they pass through the _______ ________ but disperse at the _______ ______
inguinal canal; vaginal ring
the ductus deferens penetrates the ________ before finally entering the urethra
prostate
the testicle and spermatic cord are enclosed within a pocket of Peritoneum from the abdomen through the Inguinal Canal called the ________ _______
vaginal tunic
what is spermatic fascia and what does it surround?
it’s a continuation of abdominal and transversalis fascia, and surrounds the structures emerging from the superficial inguinal ring (this includes the vaginal tunic (spermatic cord) and cremaster muscle)
what are the 2 parts of the vaginal tunic?
parietal vaginal tunic
visceral vaginal tunic
parietal vaginal tunic
the outer layer of this diverticulum in the male and extends to the bottom of the scrotum
visceral vaginal tunic
closely fused to the testis and epididymis and surrounds the ductus deferens
what are the 2 parts of the spermatic cord?
ductus deferens
testicular artery and vein
the bulk of the spermatic cord consists of…
testicular arteries and veins
the testicular artery branches from…
the abdominal aorta
the testicular veins constitute the close-meshed ___________ ________
Pampiniform Plexus
what’s involved in the Pampiniform Plexus?
contortions of the testicular artery are involved
where does the pampiniform plexus branch from?
the caudal vena cava
function of accessory sex glands?
produce seminal plasma which nourishes, transports and activates sperm
seminal plasma
liquid noncellular portion of semen
ampullary gland
widening or enlargement of the wall of the distal portion of the ductus deferens
what animals have ampullary glands?
ruminants, horses and dogs
absent in cats and poorly developed in boars
vesicular glands
paired glands that are dorsocranial to the pelvic urethra and empty directly into the urethra
what animals have vesicular glands
some form in horses, ruminants, swine
absent in dog and cat
the vesicular glands are often referred to as what in horses? why?
referred to as seminal vesicles because they are sac-like with a lumen
prostate gland
lies near the junction between the bladder and pelvic urethra
great species variation regarding shape and location
bulbourethral glands
paired glands on either side of the pelvic urethra near the ischial arch
usually small and ovoid and are characterized by being quite dense due to the high degree of fibrous connective tissue within them
location of the penis
suspended below the trunk and is partly contained between the thighs, where it is anchored to the floor of the pelvis by a suspensory ligament in the large species
describe the penis in a quiescent (dormant) state
the free extremity is concealed within an invagination of the abdominal skin (the Prepuce) which opens at a variable site behind the umbilicus
describe the scrotum
a pouch divided by an external raphe and an internal median septum into 2 cavities, each of which is occupied by a testis, an epididymis, and the distal part of the spermatic cord
the lower part of the scrotum is molded on the testes and adjusts as…
as their position varies with the ambient temperature
the scrotal skin adheres to a tough fibromuscular layer called the…
Tunica Dartos
the Tunica Dartos also extends as a…
septum between the compartments that separately lodge the testes
the cremaster muscle adheres to the…
spermatic cord
what 2 structures aid in the cooling and warming the testicles depending on ambient temperature?
Tunica Dartos and Cremaster Mucle
what is a traditional castration (neuter) procedure?
removal of the testicles
what are alternative castration procedures to removing the testicle?
vasectomy — ligation of ductus deferens
what are common surgical complications in castrations?
internal/external bleeding — testicular artery/vein
dehiscence of surgery site
scrotal swelling
list the female reproductive organs
gonads (paired)
oviducts (paired)
uterus
vagina
vestibule
function of oviducts
capture the ova on their release from the ovaries and convey them to the uterus
function of uterus
where the fertilized ova are retained and nourished until prenatal development is complete
function of vagina
serves as both copulatory organ and birth canal
function of vestibule
continues the vagina to open externally at the vulva and doubles as a urinary passage
what do the ovaries produce?
ova and hormones (estrogen)
describe the ovaries
solid, ellipsoidal body, although it’s commonly made irregular by the projection from the surface of large follicles and corpora lutea
each ovary is suspended within the…
cranial part of the broad ligament
the parenchymatous zone (cortex) is bounded by a tunica and is strewn with _______ in various stages of development and regression
follicles
as follicles fill with more fluid in the ovary, what hormone increases in the body?
estrogen
each follicle in the ovaries contain a single ______
ovum
what is ovulation?
the follicle selected for maturity will rapidly fill with fluid until it ruptures
the cavity within the ruptured follicle will initially fill with a blood clot and then transition into what?
a solid body known as the Corpus Luteum
corpus luteal cells are the source of __________
progesterone
when corpus lutea regress, they are replaced by what?
by connective tissue scars called corpora albicans (white bodies)
what is the oviduct?
the small convoluted ducts that transport ova and sperm (aka Fallopian Tubes or uterine tubes)
the oviduct consists of:
infundibulum
ampulla
isthmus
infundibulum
the terminal end of the oviduct and consists of a funnel-shaped opening which forms a pocket that “captures” the newly ovulated oocyte
what does the infundibulum lead directly into?
ampulla
describe the ampulla
makes up a majority of the oviductal length and merges with the isthmus of the oviduct; it is also the site of fertilization between the ovulated oocyte and spermatozoa
describe the isthmus
smaller in diameter than the ampulla; it’s connected directly to the uterus
what is the point of juncture between the isthmus and uterus called?
uterotubal junction
describe the uterus
“the womb”, the enlarged part of the tract in which embryos arrive to establish a means of physiologic exchange with the mother’s bloodstream
what constitutes the basis for classification of mammalian uteri?
the degree to which the uterine horns are developed
what are the 3 anatomical types of uteri?
duplex uterus
2 cervical canals leading to 2 separate uterine horns
bicornuate uterus
2 uterine horns and uterine body
simplex uterus
uterine body only
in all domestic mammals, the median part of the uterus has 2 segments. what are they?
cervix and lumen of the cervix
function of cervix
provides a sphincter controlling access to and from the vagina
function of the lumen of the cervix
(aka cervical canal) is constricted and often almost occluded by mucosal folds
how is the extent of the cervix easily discoverable on rectal palpation?
on the basis of its firmness in comparison with the adjacent parts
the horns (cornua) of the uterus vary greatly in length based on _________
species
describe the look of the uterine horns in different mammals.
round in ruminants
straight and divergent in mares and bitches
intestine-like loops in sows
what are the layers of the uterus’ wall?
serosal (perimetrium)
muscular (myometrium)
mucosal layer (endometrium)
describe the vagina
a long thin-walled tube that occupies the middle of the pelvic cavity
the cranial part of the vagina is purely ____________ _________ that runs from the cervix to the urethral orfice
reproductive passage
the caudal part of the vagina is called the _________, and extends from the urethral orifice to the vulva
vestible
what are the 2 arteries that supply blood to the female repro tract?
ovarian artery
uterine artery
the ovarian artery supplies blood to what organs?
supplies the ovary and branches in varying patterns to the uterine tube and cranial part of the horn of the uterus