Astrophysics and cosmology
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
What is a nebulae?
A cloud of dust and gas (mainly of hydrogen) often hundreds of times larger than the Solar System
Describe how a star is formed?
A large cloud of gas (mainly hydrogen) and dust in space is formed (Nebula). The gas and dust experience gravitational attraction, pulling particles together.
As particles move closer, gravitational potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, heating the material.
The collapsing cloud forms a protostar
The temperature and pressure in the core increase as particles collide.
The protostar continues to condense and heat up, when the core temperature reaches about 10 million K, hydrogen nuclei start to fuse into helium.
This releases a huge amount of energy (E=mc²), creating outward radiation pressure.
A balance (equilibrium) is reached between: Gravitational pressure inwards and Radiation and gas pressure outwards from fusion
The star enters the main sequence phase, where it spends most of its life, steadily fusing hydrogen into helium.
What is a protostar?
A very hot and very dense condensing sphere of dust and gas that is the stage before becoming a main sequence star
What is a main sequence star?
Stars that are in the stable phase of their lives, where it fuses hydrogen into helium at a steady rate
What is the difference between a main sequence star and a protostar?
Nuclear Fusion hasn’t occurred yet in the protostar
What conditions are required for nuclear fusion to occur and explain why these conditions are required?
High pressures and temperatures inside the core are required to overcome the electrostatic repulsion between the hydrogen nuclei to fuse them into helium nuclei
Describe the balance of forces in a main sequence star?
Include a diagram
Balanced between the Gravitational pressure inwards and Radiation and gas pressure outwards from fusion (They are in equilibrium)

What determines how long a star remains as a main sequence star?
Depends on the star’s size and mass of the star's core
(Larger stars produce helium much quicker)
Describe a planetary satellite?
An object in an orbit around a planet
e.g. moons and man-made satellites
List the 4 characteristics of a planet?
It has no fusion reactions
It has a mass large enough for its own gravity to give it a round shape
It has cleared its orbit of most other objects
It orbits a star
Describe a comet?
An irregular shaped body made of ice, dust and small rock
They have highly elliptical orbits, taking them close to the Sun and far out into the solar system.
When near the Sun, the heat causes the ice to sublimate (turn directly into gas)
What is a solar system?
A sun with all the objects (planets, comets etc.) that orbit around it
What is a galaxy?
A collection of stars, interstellar dust and gas
Contains 100 billion stars on average
What is an asteriod?
An object too small and uneven to be a planet, in near circular orbit around a Sun without the presence of ice
What is a dwarf planet?
Similar to a planet, but they have not cleared their orbits of other objects
What is a Universe?
Contains all the galaxies and intergalactic space
Contains all the EM radiation, energy and matter
What mass is determined to be a “low mass star”? (In Solar masses)
0.5 - 10 Solar masses
Produce a flow diagram for the stages in the life cycle of a low mass star?

Explain why a star with a low mass remains on the main sequence for a longer time than a more massive star?
The core of the stars with a low mass is cooler than that of a more massive star
They remain stable for much longer, burning fuel at a slower rate
Describe how a red giant is formed?
Eventually, the hydrogen in the core in a main sequence star is used up.
Fusion slows down, so outward radiation pressure decreases.
Gravity causes the core to contract → The core contracts and heats up.
Hydrogen around the core (in a shell) starts fusing again. (Shell burning)
This creates more energy, causing the outer layers to expand.
The star expands massively and cools at the surface (gives the red colour)
The core is hot and dense, mostly helium, but not yet hot enough for helium fusion (in lower mass stars).
What are the properties of a red giant?
Inert Core
Fusion no longer takes place in the core
Fusion occurs in the shells around the core
What are the properties of a white dwarf?
Very dense, often with a mass of our Sun, but with a volume of the Earth
No fusion takes place
It emits energy only because it leaks photons created in its earlier evolution
The collapse is stopped by electron degeneracy pressure
What is electron degeneracy pressure?
When electrons are squeezed together when the core of the stars begins to collapse under gravity → It creates a pressure that prevents the core from further collapse
What is the Chandrasekhar limit?
Electron degeneracy pressure is only sufficient to prevent gravitational collapse if the core has a mass less than 1.44 Solar masses (maximum mass a white dwarf can have before it collapses under its own gravity)
What mass is determined to be a “high mass star”? (In Solar masses)
>10 Solar masses
Produce a flow diagram for the stages in the life cycle of a high mass star?

Describe the formation and structure of a red super giant?
Include a diagram
Once hydrogen in the core runs out, fusion stops there.
The core contracts under gravity, becoming hotter and denser.
Hydrogen fusion begins in a shell around the core.
The core temperature rises enough to fuse helium into heavier elements, like carbon, oxygen, and others (depending on mass).
The outer layers expand and cool, making the star much larger and redder.
The star becomes a red supergiant

Iron is created in the core (cannot fuse any further)
Why does a supernova occur once a red supergiant has formed an iron core?
A supernova occurs when a red supergiant forms an iron core because iron cannot undergo fusion to release energy. Once the core is made of iron, fusion stops, and there’s no longer enough pressure to counteract gravity. This causes the core to collapse, triggering a massive implosion of the outer layers
What condition is required for a neutron star to be formed after a supernova?
If the mass of the core is greater than the Chandrasekhar limit, the gravitational collapse continues, forming a neutron star
Greater than 1.44 Solar masses, but less than 3 Solar masses
Describe a neutron star?
Stars made up almost entirely in neutrons, very small and has a typical mass of 2M
Supported by neutron degeneracy pressure
What condition is required for a black hole to be formed after a supernova?
If the core has a mass greater than about 3M, the gravitational collapse continues to compress the core
Describe a black hole?
A gravitational field so strong an object will need a speed greater than the speed of light to escape
Describe how both heavy and light elements are produced in the life cycle of a star and how they are distributed throughout the universe?
Heavy elements above iron in the periodic table are created by supernova - Supernova also helps distribute heavier elements throughout the universe
Lighter elements (Up to Iron) are created in Red-Super giants through fusion of those elements
What is the Hertzsprung-Russel Diagram? (Label the axis and which direction does temperature increase)
A graph of stars in our galaxy showing the relationship between their luminosity and average surface temperature
Luminosity (Y-axis) and average Surface temperature (X-axis)
Temperature increases from right to left
Define the luminosity of a star?
The total radiant power output of a star
Luminosity is related to brightness
Produce diagram of Hertzsprung-Russel diagram?

Show directions of the life cycle of high mass and low mass stars on the Hertzsprung-Russel diagram?

(X → Y shows high mass stars)
Describe what is meant by an energy level?
When electrons are bound to their atoms in a gas, they can only exist in one of a discrete set of energies
Explain why all energy levels have negative values?
External energy is required to remove an electron from the atom
Negative values indicate that the electrons are trapped in the atom
What is the energy level of an electron which is free from the atom
Electron with 0 energy
What is the ground state?
The energy level with the most negative value
What does it mean if an electron in an atom or molecule is excited?
When an electron moves from a lower to a higher energy level in an atom
How can an atom be excited?
It requires external energy e.g. from an electric field
Draw a diagram to show a photon being emitted as an electron moves from a higher to a lower energy level, also explain the process in terms of the conservation of energy?
When an electron makes a transition from a higher to a lower energy level, a photon is emitted to conserve the energy
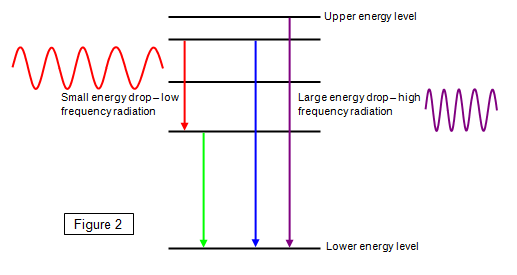
State the equation to calculate the energy of an emitted photon during de-excitation?
Define all terms
ΔE = hf
Change in energy = Planck Constant X Frequency
Describe emission line spectra. How are emission line spectra produced?
Include a diagram showing electron transition
If the atoms in a hot, low density gas are excited, →then when the electrons drop back into a lower energy level, they emit photons with a set of discrete frequencies specific to that element

Describe a continuous spectra, and how are continuous spectra produced?
All visible frequencies or wavelengths are present, the atoms of a heated solid metal will produce this type of spectrum e.g. filament lamp

Describe absorption line spectra. How are absorption line spectra produced?
Include a diagram showing electron transition
Series of dark spectral lines against the background of a continuous spectrum- Dark lines have exactly the same wavelengths as bright emission spectral lines for the same gas atoms
Light from a hot, dense source passes through a cold gas, some photons pass through the gas, and some are absorbed by the gas atoms, raising electrons up into higher energy levels- exciting the atoms → only photons with energy exactly equal to the difference between the different energy levels are absorbed (specific wavelengths absorbed)

Describe how absorption spectra are used to identify the elements present in a star?
Some wavelengths of light are missing- photons have been absorbed by atoms of cooler gas in the outer layers of the star → compare with line emission spectrum of a particular elements we know to analyse
What is a diffraction grating?
Optical component with regularly spaced slits or lines that diffract and split light into beams of different colour, travelling in different directions
Explain what happens when a white light passes through a diffraction grating?
It splits into component colours, because the direction of these beams depends on the wavelength of light
Explain how a diffraction pattern is formed when monochromatic light passes through a diffraction grating?
Include a diagram
Light is diffracted at each slit, the interference pattern is the result of the superposition of the diffracted waves in the space beyond the gratings

What is the path difference and phase difference for the light arriving at the first order maxima?
Path difference = λ (1 wavelength)
Phase difference = 2π (360 degrees)
State the general condition for constructive interference?
The path difference between 2 interfering waves must be an integer multiple of the wavelength
State the general condition for destructive interference?
The path difference between the two waves must be an odd multiple of half a wavelength. they cancel each other out, creating a reduced/ zero amplitude
State the diffraction grating equation?
d = n λ / sin θ
grating spacing = number order X wavelength / angle of diffraction
How can the number of slits per metre on the grating be calculated?
N = 1/ d
d = grating spacing
N= number of slits/ m
Describe an experiment that can be performed to determine the wavelength of light using a diffracting grating?
Measure the angle between several maxima and the central maxima and then plot a graph of sinθ against n → produces a straight line through the origin with the gradient as λ/d
Grating spacing(d) = 1/ lines per metre
How many lines would a grating with 600 lines per mm, have in metres and what would be its grating spacing?
600,000 lines (Grating has 600 lines per mm, There are 1000 mm in 1 metre → 600 X 1000)
(1×10-3 / 600) = 1.67×10-6 → grating spacing
What is a black body?
An object that absorbs all EM radiation that shines onto it, and when in thermal equilibrium, emits a characteristic distribution of wavelengths at a specific temperature
Sketch a graph to show the characteristic distribution of wavelengths that are emitted at a specific temperature by a black body?
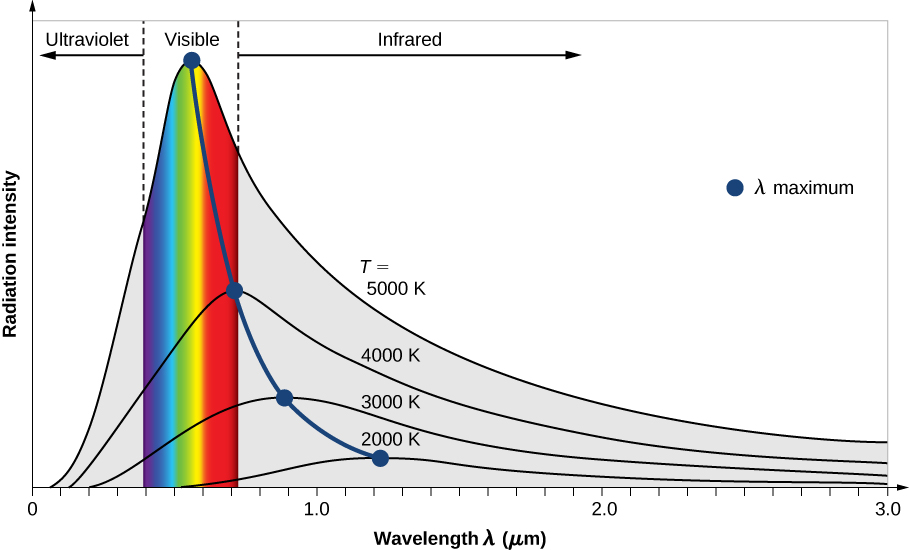
Describe how the wavelengths emitted by a black body change with temperature, and how does the graph change?
Shorter wavelengths as the temperature increases
Peak of the graph becomes sharper
State Wein’s displacement law in words?
The wavelength at which a black body emits radiation most intensity (max wavelength) is inversely proportional to its absolute temperature
State the equation for Wein’s displacement?
λmax= b / T
b- Wein’s constant
T - absolute temperature of black body
State Stefan’s law?
Total power radiated per unit surface area of a black body is directly proportional to the 4th power of the absolute temperature of the black body
State the equation for the luminosity of a star?
L = 4πr²σT^4
L = luminosity
σ= Stefan–Boltzmann constant
T^4 -Surface temperature in Kelvin
What is the luminosity of a star?
The total power radiated by a star
How can Wein’s displacement law and Stefan’s law be used together to estimate the radius of a star?
λmax X T = constant
L = 4πr²σT^4 can be used to show r = √ L / 4πσT^4
Define the astronomical unit (AU)?
Average distance from the Earth to the Sun (150 million km)
Define the light year?
Distance travelled by light in a vacuum in a time of one year
Show that 1ly is approximately 9.5×10^15 m?
d = s X t
3.00 ×10^8 X (365 X 24 X 60 X 60) = 9.46 X 10^15
What is an arc minute and an arc second?
There are 60 arc minutes in 1°
There are 60 arc seconds in each arc minute, therefore 1 arc second is equal to (1 / 3600)°
Define the parsec and include a diagram?
The distance at which a radius of one AU subtends an angle of one arc second
1AU / 1pc = 1 arc second X tan
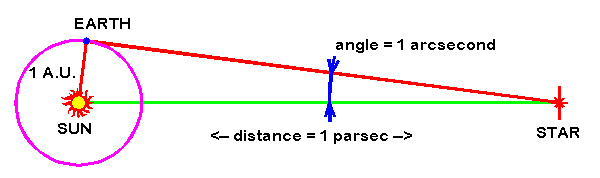
Show that 1 parsec is approx. 3.1 ×10^16 m?
tan 1AU/1pc
1pc = 1.50×10^11 / tan (1/3600) - 3.1×10^16
Explain how the small angle approximation can be used to determine a simple relationship between the distance in pc and the angle subtended in arcseconds?
If point S is at a distance of 2pc, the angle subtended by the radius will be ½ arc seconds
If point S is at a distance of 3pc, then the radius subtended will be 1/3 arc seconds, and so forth
1/d arcsecond = angle subtended
What is meant by Stellar parallax?
A technique used to determine the distance to stars that are relatively close to the Earth at distances less than 100pc
Describe how stellar parallax can be used to determine the distance to stars that are relatively close to the Earth?
Include a diagram?
Parallax is the apparent shift in position of a relatively close star against the backdrop of much more distant stars as the Earth orbits the Sun
d = 1/p (d= distance to a star in parsecs (pc) p = parallax angle in arc seconds)

What is the limitation of the stellar parallax technique?
It is only limited to stars less than 100pc from the Earth, because as distance to a star (d) increases, the parallax angle (p) decreases becoming too small to measure
Use a diagram to explain the Doppler effect?

What happens to the observed wavelength if the wave source is moving away from the observer?
The observed wavelength increases, as they appear more stretched out
What happens to the observed wavelength if the wave source is moving towards the observer?
The observed wavelength decreases, as they appear more compressed
If a galaxy is moving away from the Earth, what happens to the absorption lines of the spectrum for the galaxy?
Lines will be Red Shifted - moves towards the red end of the spectrum, wavelength appears more stretched
If a galaxy is moving towards the Earth, what happens to the absorption lines of the spectrum for the galaxy?
Lines will be Blue Shifted - moves towards the blue end of the spectrum, wavelength appears more compressed
What is the Doppler effect for electromagnetic waves and what it the limitation of this equation?
∆λ / λ (source) ≈ ∆f / f(source) ≈ v / c(speed of light)
The equation can only be used for galaxies with a speed less than the speed of light
Explain how Doppler shift in starlight can be used to determine the relative velocity of a distant galaxy?
The faster the source moves, the greater the observed change in wavelength and frequency
What measurement did Edwin Hubble make?
H(o) - Hubble Constant
What are the 2 key observations from Hubble’s measurements?
Light from the vast majority of galaxies was red shifted- relative velocity away from the Earth
The further away the galaxy, the greater the observed red-shift, and the faster the galaxy was moving
State Hubble’s law in words and in the form of an equation?
The recessional speed, v of a galaxy is almost directly proportional to its distance, d from the Earth
What is Hubble’s law in equation form?
v=H(0)d
recessional speed = Hubble constant X distance to the galaxy
What is the value of Hubble’s constant?
2.2×10-18 s^-1
Covert 1km s^-1 Mpc^-1 into s^-1?
1kms^-1Mpc^-1 = 1.0×10^3 / 10^6 X 3.1 ×10^16 = 3.2×10-20 s^-1
Sketch a graph of recessional speed against distances for galaxies?
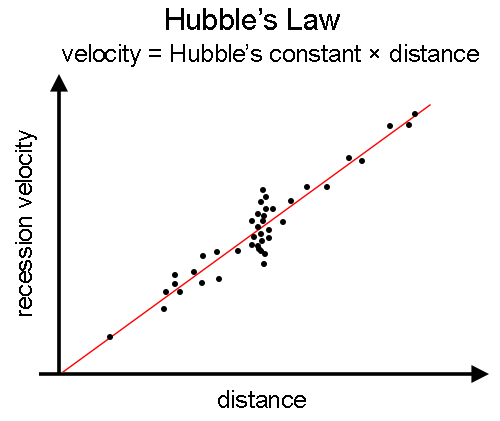
What is the big bang theory?
Some moment in the past, all the matter in the Universe was once contained at a single point- beginning of the Universe
Explain why Hubble’s law is key evidence for the big bang theory?
The observation if light from nearly all the galaxies is red shifted, Space is expanding in all directions
→ explains why more distant galaxies are red-shifted
The cosmological principle, states the universe is homogeneous and isotropic, and the laws of physics are universal. What do these terms mean?
homogeneous- Matter is distributed uniformly across the Universe, for a large volume, the density of the Universe is uniform - structures such as galaxies are seen everywhere
isotropic- Universe looks the same in all directions to every observer- there is no centre/ edge
laws of physics- Can be applied the same throughout the whole Universe
Hubble’s law is a main piece of evidence for the Big Bang, what is the other evidence?
Microwave Background Radiation
Explain what is microwave background radiation?
High energy gamma photons from the Big Bang that have now been stretched over time (stretch of wavelength)
What is the black body radiation temperature of microwave background radiation?
2.7K
How does microwave background radiation support the Big Bang theory?
CMBR is almost the same in all directions, suggesting the universe began from a hot, dense state and expanded uniformly.
Originally this light was high-energy (visible or UV), but due to expansion, it got stretched into the microwave part of the spectrum — showing the universe has expanded over time.
How can Hubble’s law be used to estimate the age of the Universe?
Time = distance / velocity
since velocity = H(0)d (Hubble’s law)
d / v = 1 / H(0)
So the age of the Universe is approx:
t≈ 1/ H(0)
t = 1 / 2.2×10-18 → 14 billion years (age of Universe)