mirrors and lensesq
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
divergent lenses
concave
convergent lenses
convex
real image
formed by the converging of reflected light waves
virtual image
reflected light ways do not properly converge, but mirror structure reconstructs light into image based on where it came from
concave mirror focal point
located on same side as the object
convex mirror
located on the opposite side of the object
determining focal point
divide lense radius by 2
thin lens equation
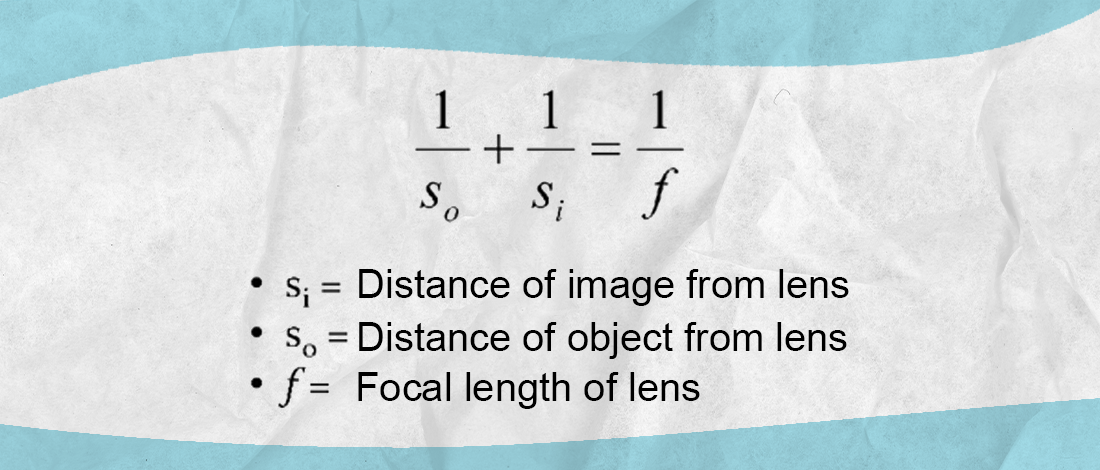
positive image value indicates
the image is realn
egative image value indicates image is
virtual
positive focal point indicates
lens is convex
negative focal point indicates
lens is concave
magnefication
-(1/object distance)
negative magnification value
image is inverted and real
positive magnification value
image is upright and virtual
power
1/focal point
power units
diopters
positive power interpretation
coverging/convex lense
negative power interpretation
diverging/concave lense
spherical abberation
light that hits closer tp center of a spherical lens focuses farther away than a lens that hits closer to the edge, causing multiple focal points