cytoplasm & cytoplasmic organelles
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
what is the function of organelles?
preform metabolic and synthetic, energy requiring and generating, functions in a cell
2
New cards
what are inclusions?
- products of organelles
- have no active role in metabolism
- have no active role in metabolism
3
New cards
what is the cytoplasmic matrix made up of?
soluble proteins and enzymes involved in glycolysis
4
New cards
what are the membranous organelles of the cell?
- Rough and smooth ER
- golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- peroxisomes
- mitochondria
- golgi apparatus
- lysosomes
- peroxisomes
- mitochondria
5
New cards
what are the non-membranous organelles of the cell?
- ribosomes
- microtubules
- actin filaments
- intermediate filaments
- centrioles
- basal bodies
- microtubules
- actin filaments
- intermediate filaments
- centrioles
- basal bodies
6
New cards
what are the inclusions of the cell?
- secretory vesicles
- pigment granules
- neutral fat
- lipid droplets
- glycogen
- stored waste product
- pigment granules
- neutral fat
- lipid droplets
- glycogen
- stored waste product
7
New cards
what do ribosomes look like under light microscope?
- not visible
- basophilic appearance (dark blue/purple) due to the phosphate groups in RNA
- basophilic appearance (dark blue/purple) due to the phosphate groups in RNA
8
New cards
what do ribosomes look like under transmission electron microscope?
- visible
- appear electron dense because they absorb electrons
- appear electron dense because they absorb electrons
9
New cards
what are polyribosomes?
ribosomes clumped together with mRNA and attached to the ER
10
New cards
what produces ribosomes?
rough ER and nucleolus
11
New cards
what are ribosomes composed of?
- 2 subunits with 4 types of rRNA in the nucleus and 80 proteins in the cytoplasm
12
New cards
where is RNA synthesized?
in the nucleus
13
New cards
where do synthesized proteins go?
proteins go from the place of synthesis, cytoplasm, to the nucleus to be attached to rRNA
14
New cards
how do subunits go to cytoplasm?
through nuclear pores
15
New cards
what is the function of ribosomes?
they are the site where amino acid molecules are incorporated into protein molecules
16
New cards
what is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
a network of channels formed by continuous membranes extending to nuclear envelope
17
New cards
where is the rough ER abundant?
in cells specialized with protein secretion (basophilic cells)
18
New cards
explain this picture
- proteins are made by the ribosomes on the surface of ER
- they are then transported into the interior to be modified
- proteins accumulate in vesicles
- vesicles bud off the surface of ER and are transported to GA
- they are then transported into the interior to be modified
- proteins accumulate in vesicles
- vesicles bud off the surface of ER and are transported to GA
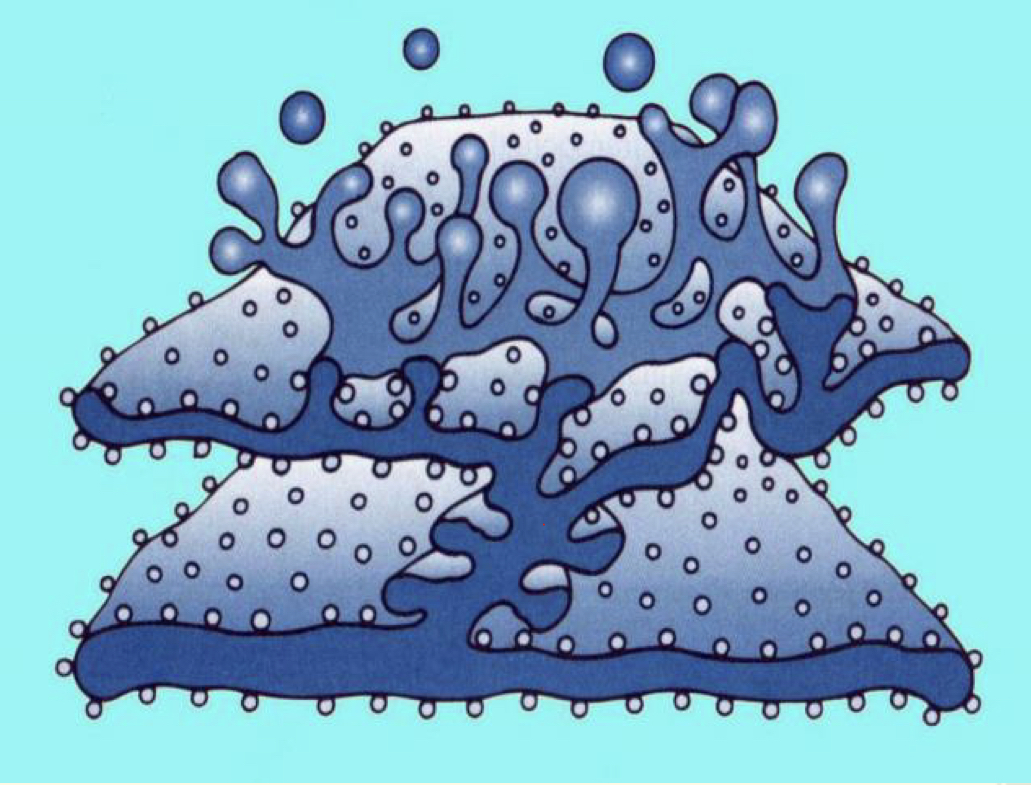
19
New cards
what is the smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
extension of the rough ER which forms networks if membranous tubules
20
New cards
what is the function of smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
transfer proteins to golgi
21
New cards
what is the smooth ER abundant?
- liver cells (detoxifying enzymes)
- muscle cells (break down glycogen)
- cells that produce glycogen, lipids or steroids
- muscle cells (break down glycogen)
- cells that produce glycogen, lipids or steroids
22
New cards
explain this picture
plasma cells which have a lot of rough ER
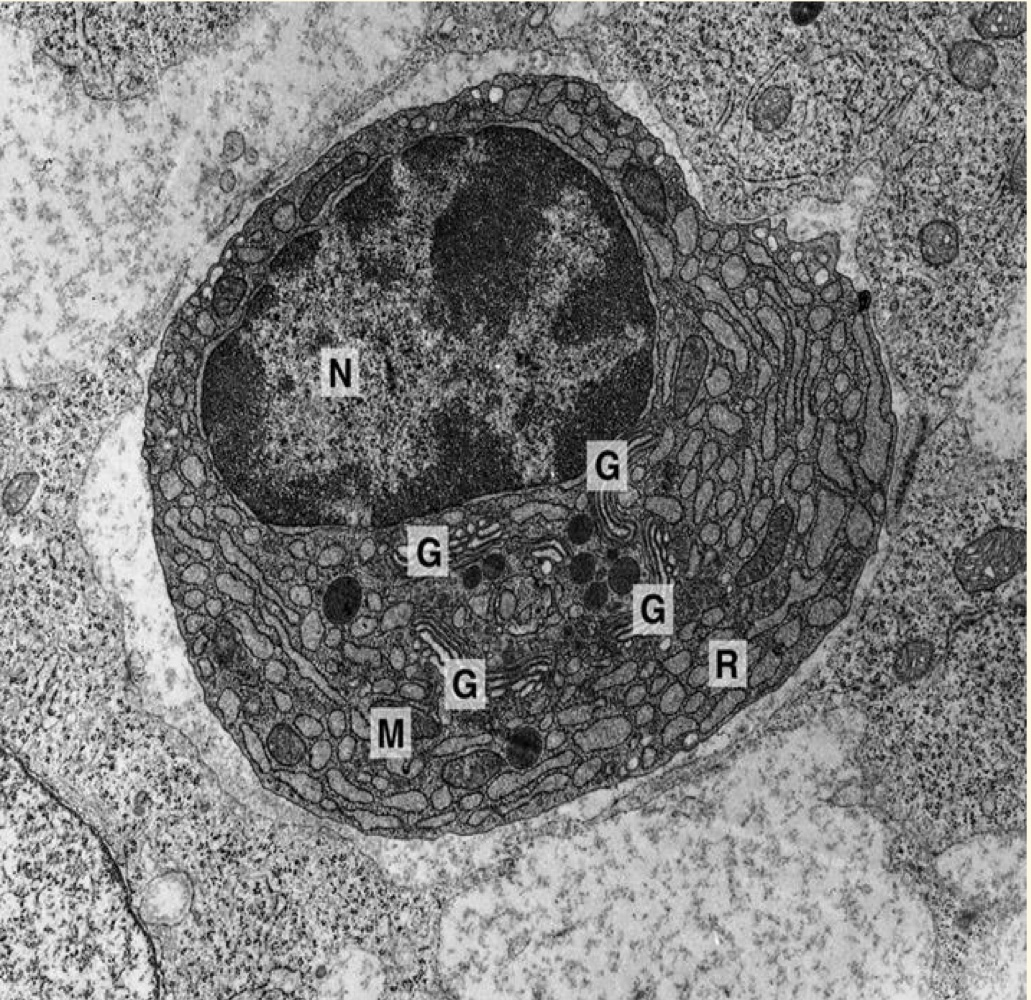
23
New cards
explain this picture
leydig cells found in the reproductive system and have a lot of smooth ER
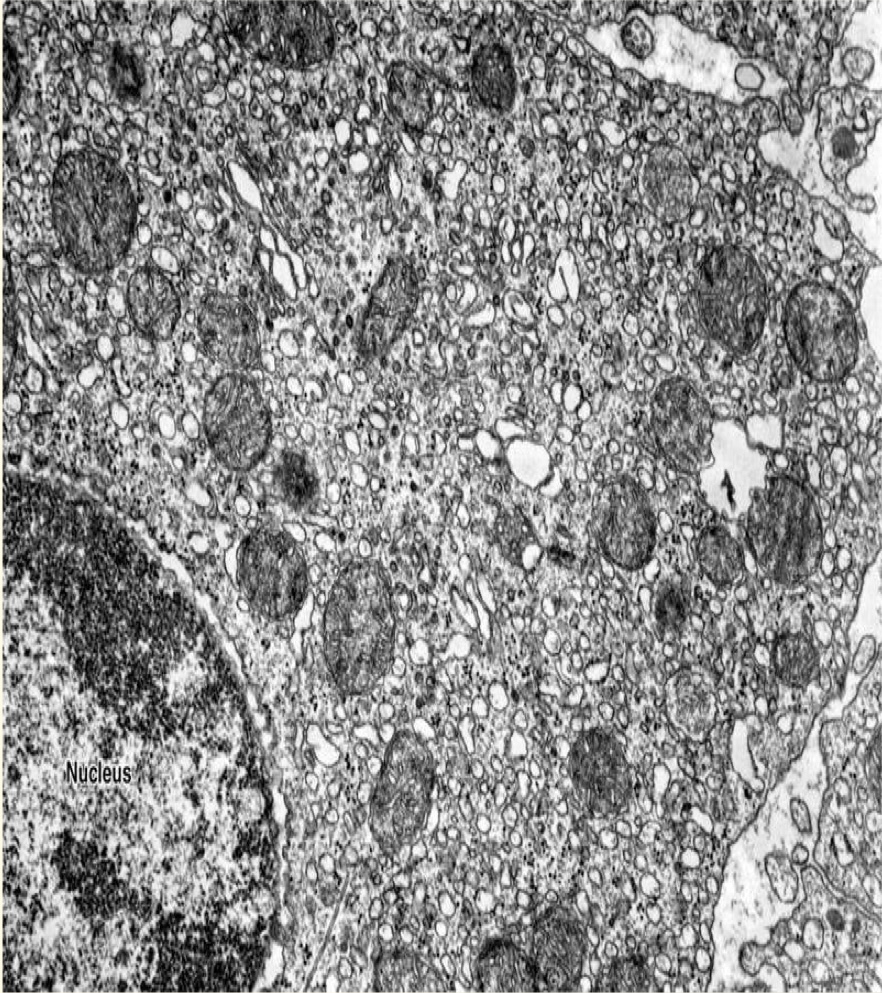
24
New cards
what is the golgi apparatus?
3 - 20 flattened polarized cisternae (membrane sacs)
25
New cards
which face of GA is mature?
the trans face which is concave
26
New cards
which face of GA is immature?
the cis face which is convex
27
New cards
label the picture
1- vesicles that have bud off
2- trans golgi
3- mid golgi
4- cis golgi
5- smooth ER
6- rough ER
7- nucleus
2- trans golgi
3- mid golgi
4- cis golgi
5- smooth ER
6- rough ER
7- nucleus
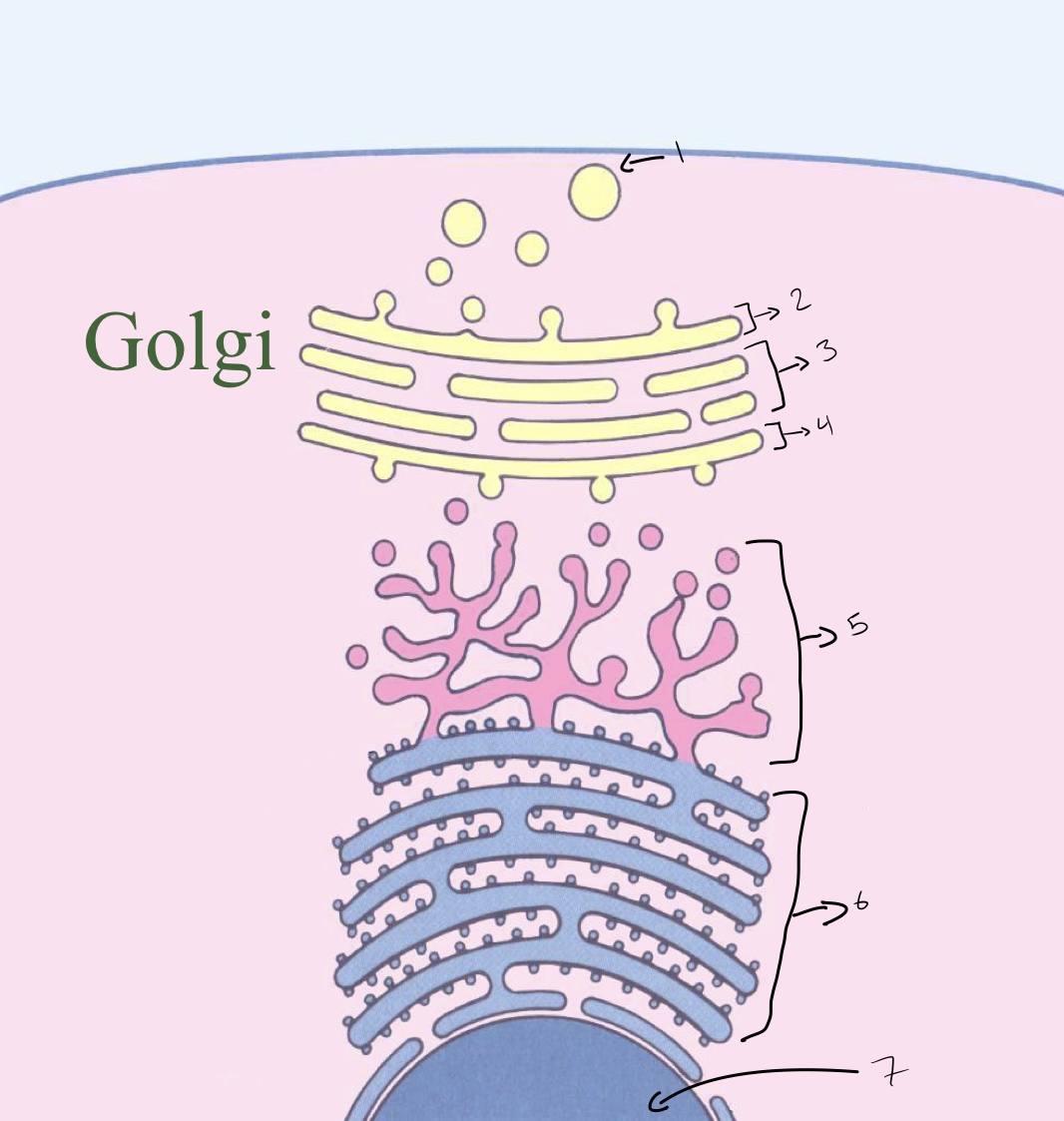
28
New cards
in what direction do proteins travel through the GA?
from cis to trans
29
New cards
functions of GA
- modify proteins by cutting or adding
- removal of amino acids
- glycosylation, sulfating and phosphorylations
- packing vesicles
- sorting and distributing proteins
- repair cell membrane
- formation of lysosomes
- removal of amino acids
- glycosylation, sulfating and phosphorylations
- packing vesicles
- sorting and distributing proteins
- repair cell membrane
- formation of lysosomes
30
New cards
what are lysosomes?
- intracellular digestive organelles
- DOUBLE membrane
- surround hydrolytic enzymes formed in GA
- DOUBLE membrane
- surround hydrolytic enzymes formed in GA
31
New cards
what do lysosomes look like under EM?
- electron dense granules
- take on basophilic colour because lysosomal enzymes work under an acidic environment
- take on basophilic colour because lysosomal enzymes work under an acidic environment
32
New cards
what are the functions of lysosomes?
- autophagy (digestion of old organelles)
- autolysis (destruction of own cell)
- digesting materials taken by endocytosis
- autolysis (destruction of own cell)
- digesting materials taken by endocytosis
33
New cards
explain this picture
- lysosomal enzymes are secreted in the rough ER and transported to golgi
- in the golgi these enzymes are modified (attaching mannose-6-phosphate) and packaged
- lysosome is then formed in the golgi and contains all the hydrolytic enzymes
- a primary lysosome is released
- in the golgi these enzymes are modified (attaching mannose-6-phosphate) and packaged
- lysosome is then formed in the golgi and contains all the hydrolytic enzymes
- a primary lysosome is released
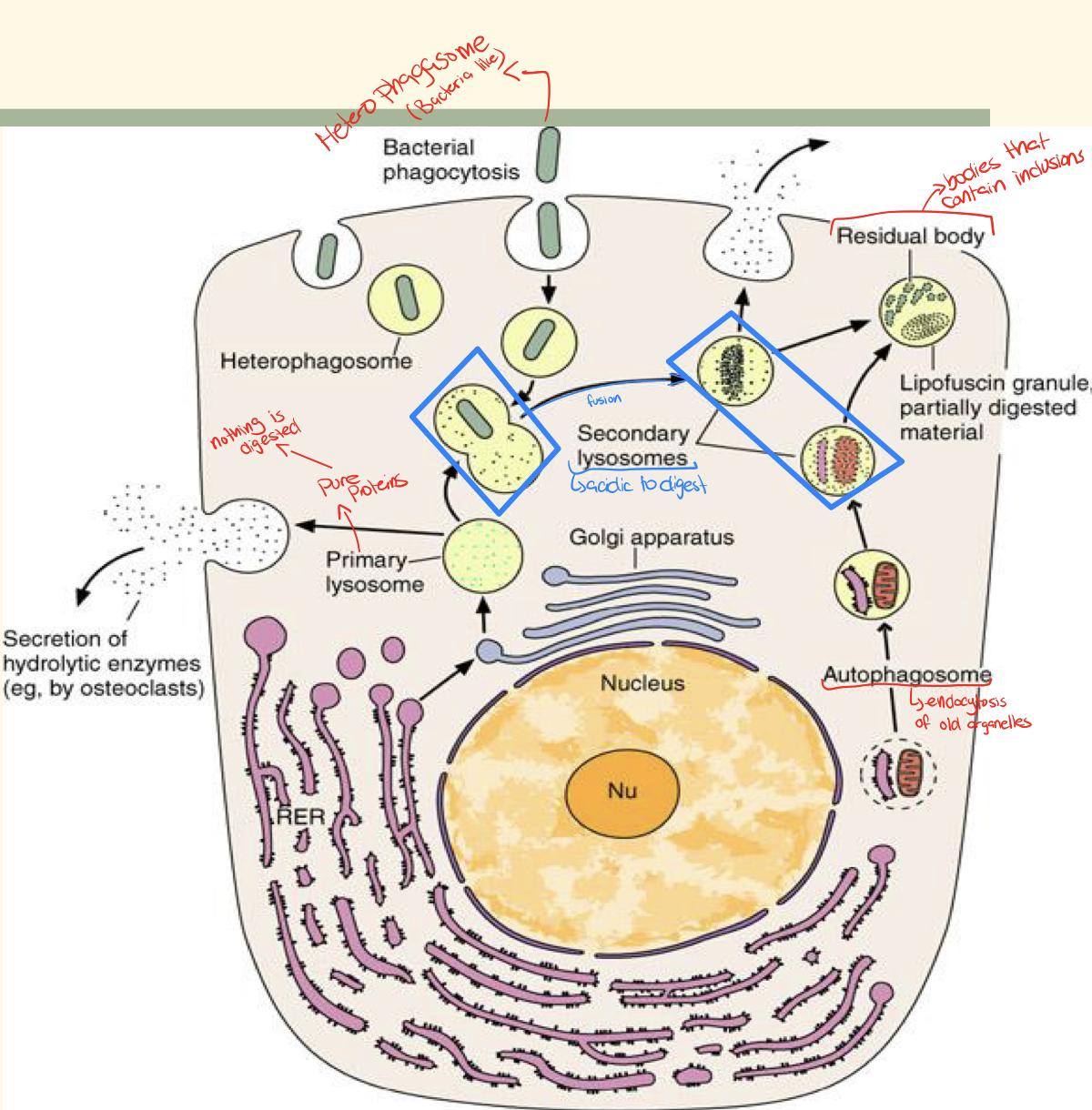
34
New cards
what is on the surface of lysosomal enzymes?
mannose-6-phosphate
35
New cards
what is a primary lysosome?
- pure lysosome freshly bud off of GA
- contains inactive digestive enzymes
- cannot undergo digestion
- can't eliminate content
- contains inactive digestive enzymes
- cannot undergo digestion
- can't eliminate content
36
New cards
what is a secondary lysosome?
- fusion of primary lysosome and endosome
- contains active digestive enzymes
- undergoes digestion
- can eliminate content
- contains active digestive enzymes
- undergoes digestion
- can eliminate content
37
New cards
what are indigestible materials known as?
residual bodies
38
New cards
where do residual bodies accumulate?
- heart cells, muscle cells and neurons
- form intracellular pigments such as lipofuscin or age pigment
- form intracellular pigments such as lipofuscin or age pigment
39
New cards
where are peroxisomes found?
liver
40
New cards
what are peroxisomes?
- single membrane-bound
- self-replicating
- formed in the ER
- associated with free ribosomes
- self-replicating
- formed in the ER
- associated with free ribosomes
41
New cards
function of peroxisomes
detoxification of H2O2 to produce water and oxygen
42
New cards
structure of mitochondria
- outer membrane (limits organelles)
- inner membrane (folded to form cristae)
- matrix
- inner membrane (folded to form cristae)
- matrix
43
New cards
how does the outer membrane prevent diffusion of contents of the mitochondrial matrix?
passive diffusion
44
New cards
how does the inner membrane prevent diffusion of contents of the mitochondrial matrix?
active transport
45
New cards
what does the mitochondrial matrix consist of?
electron dense granules which represent the binding sites of calcium ions and krebs cycle enzymes
46
New cards
why is the mitochondria self-replicating?
the matrix contains DNA, RNA and ribosomes
47
New cards
what is the cytoskeleton?
dynamic 3D structure that fills the the cytoplasm
48
New cards
cytoskeleton function
important for movement and stability of the cell
49
New cards
what are the primary fibers of the cytoskeleton
- microfilaments
- microtubules
- intermediate filaments
- microtubules
- intermediate filaments
50
New cards
what are microfilaments?
- fine filled protein fibers
- composed predominantly of f-actin (thin)
- contains myosin
- composed predominantly of f-actin (thin)
- contains myosin
51
New cards
what are microtubules?
- cylindrical hollow tubes
- composed of 13 subunits of tubulin arranged in a polarized ring
- subunits are termed alpha and beta
- composed of 13 subunits of tubulin arranged in a polarized ring
- subunits are termed alpha and beta
52
New cards
how do microtubules grow?
- via subunit polymerization
- grow from the +ve end
- under control of Ca2+ and MAP
- grow from the +ve end
- under control of Ca2+ and MAP
53
New cards
how do microtubules help build other organelles?
they act as scaffolding by providing tracks for them to move on
54
New cards
what organelles do microtubules help build?
- cilia
- flagella
- centrioles (used in cell division)
- spindle fibers
- flagella
- centrioles (used in cell division)
- spindle fibers
55
New cards
transport by microtubules
- motor proteins like kinesin move along microtubules
- powered by ATP
- transports cellular cargo
- transport is from the center of the cell to the periphery
- powered by ATP
- transports cellular cargo
- transport is from the center of the cell to the periphery
56
New cards
what are intermediate filaments?
- provide tensile strength
- present in keratins (epithelium), desmin (muscle) and neurofilaments (neurons)
- present in keratins (epithelium), desmin (muscle) and neurofilaments (neurons)
57
New cards
where are all 3 fibers found?
cytoskeleton of epithelial cells in the intestine
58
New cards
what are centrioles?
- rod organelles
- found in pairs
- 9 sets of 3 microtubules
- found in pairs
- 9 sets of 3 microtubules
59
New cards
what is this?
inclusions of glycogen in liver cells
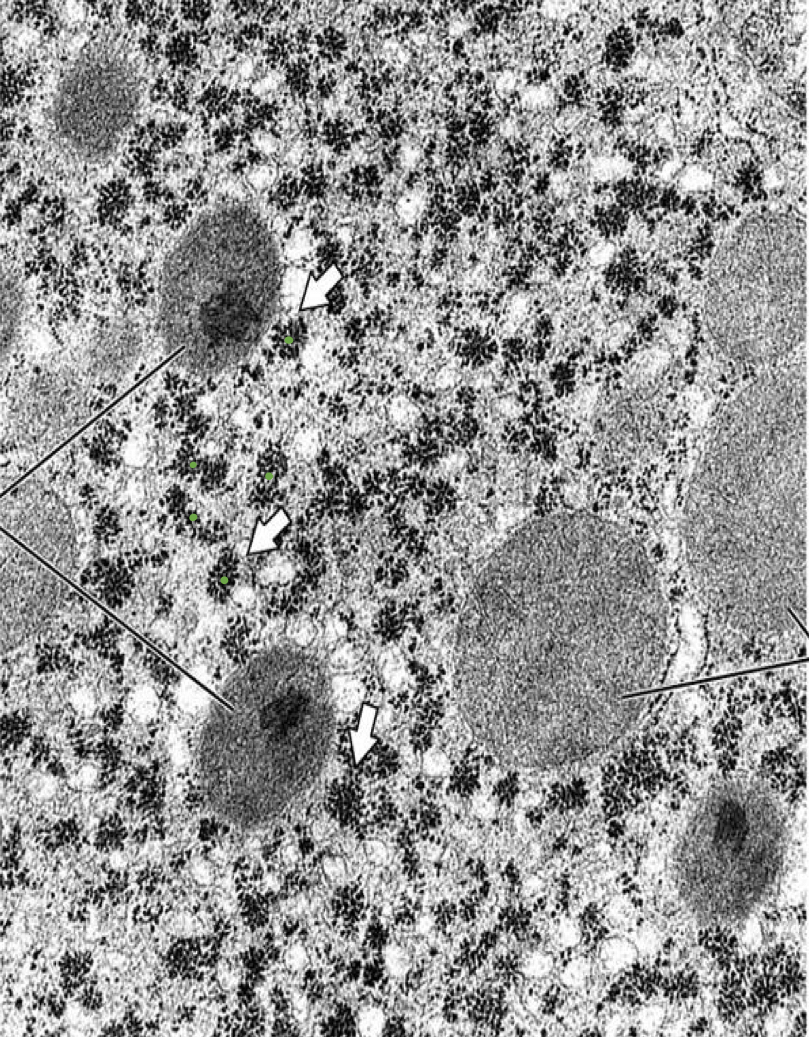
60
New cards
what is this?
inclusions of secretory vesicles in pancreatic cells
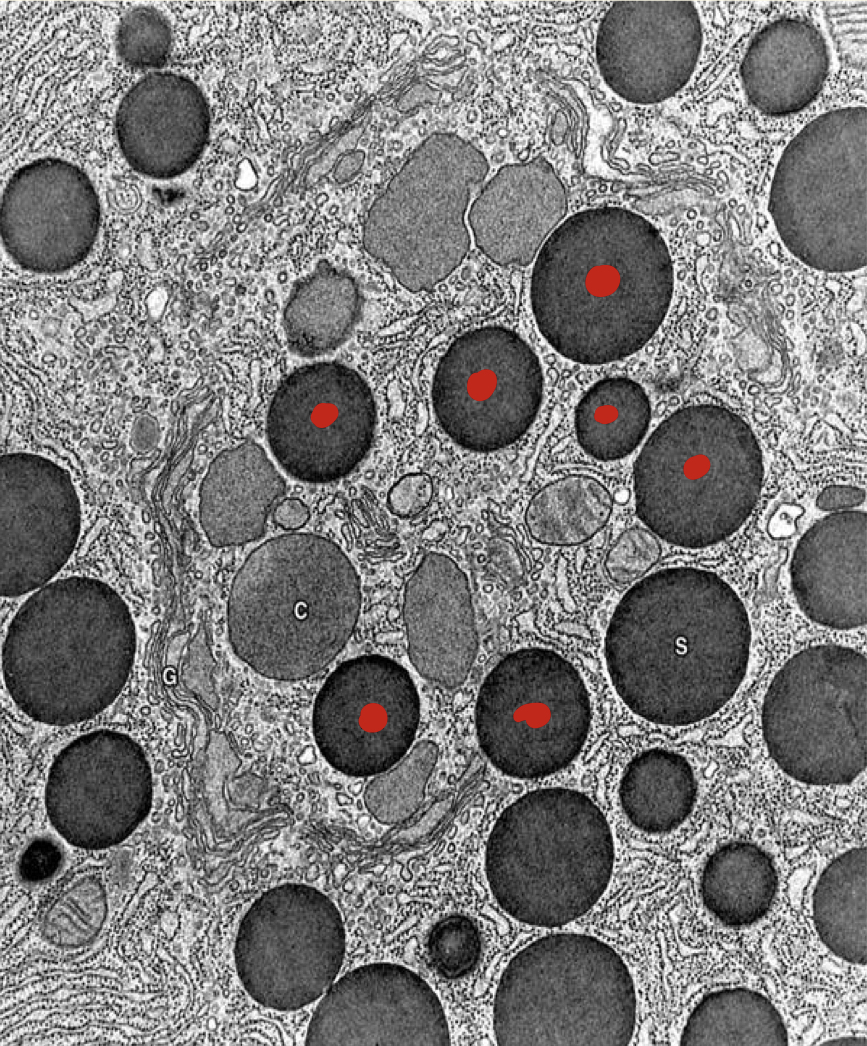
61
New cards
how do lipid droplets look like under LM?
- do not stain
- extracted by organic solvents
- appear to by empty
- extracted by organic solvents
- appear to by empty
62
New cards
how do lipid droplets look like under EM?
- stain electron dense by osmium tetroxide
- not delaminated by phospholipid monolayer
- not delaminated by phospholipid monolayer