Geography IGCSE - Plate tectonics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
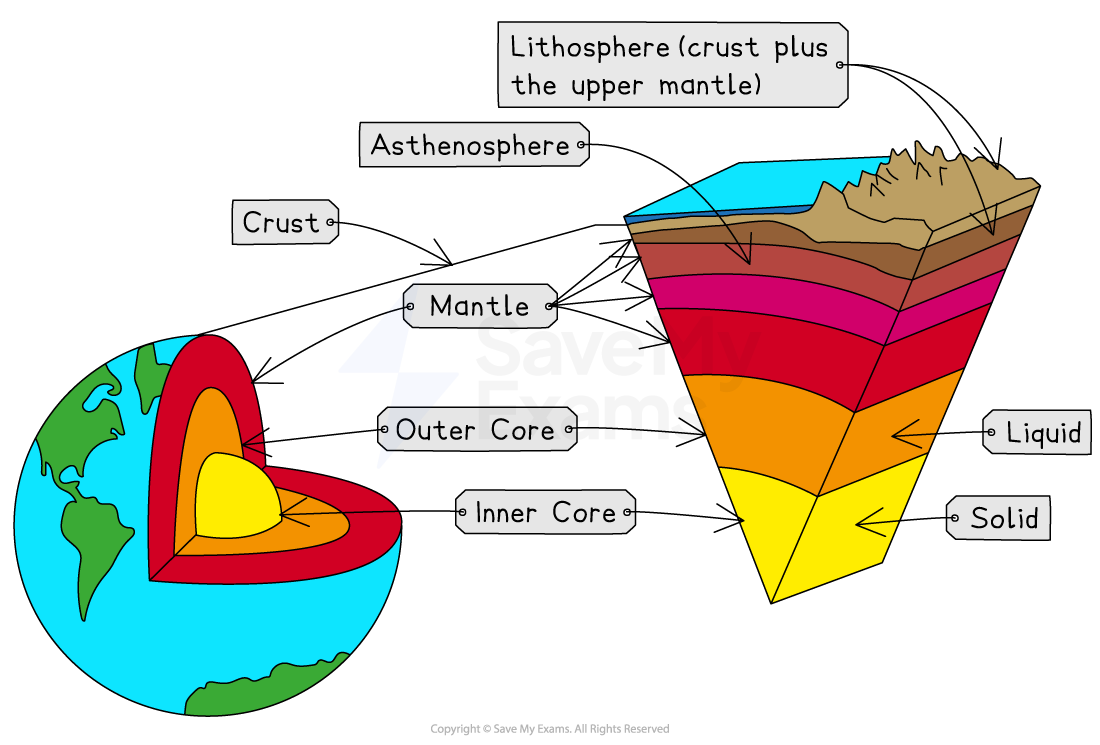
Earth structure
What makes plates move
Magma (semi-molten rock) near outer core is heated → as magma warms → it expands + becomes less dense → less dense magma starts to rise towards crust → as magma nears crust → it begins to cool → cooling magma becomes denser → begins to sink → rising + falling magma creates circular currents within mantle → these currents create friction with crust above → causes crust to move → process known as convection currents
Continental crust VS Oceanic crust
Continental crust | Oceanic crust |
|
|
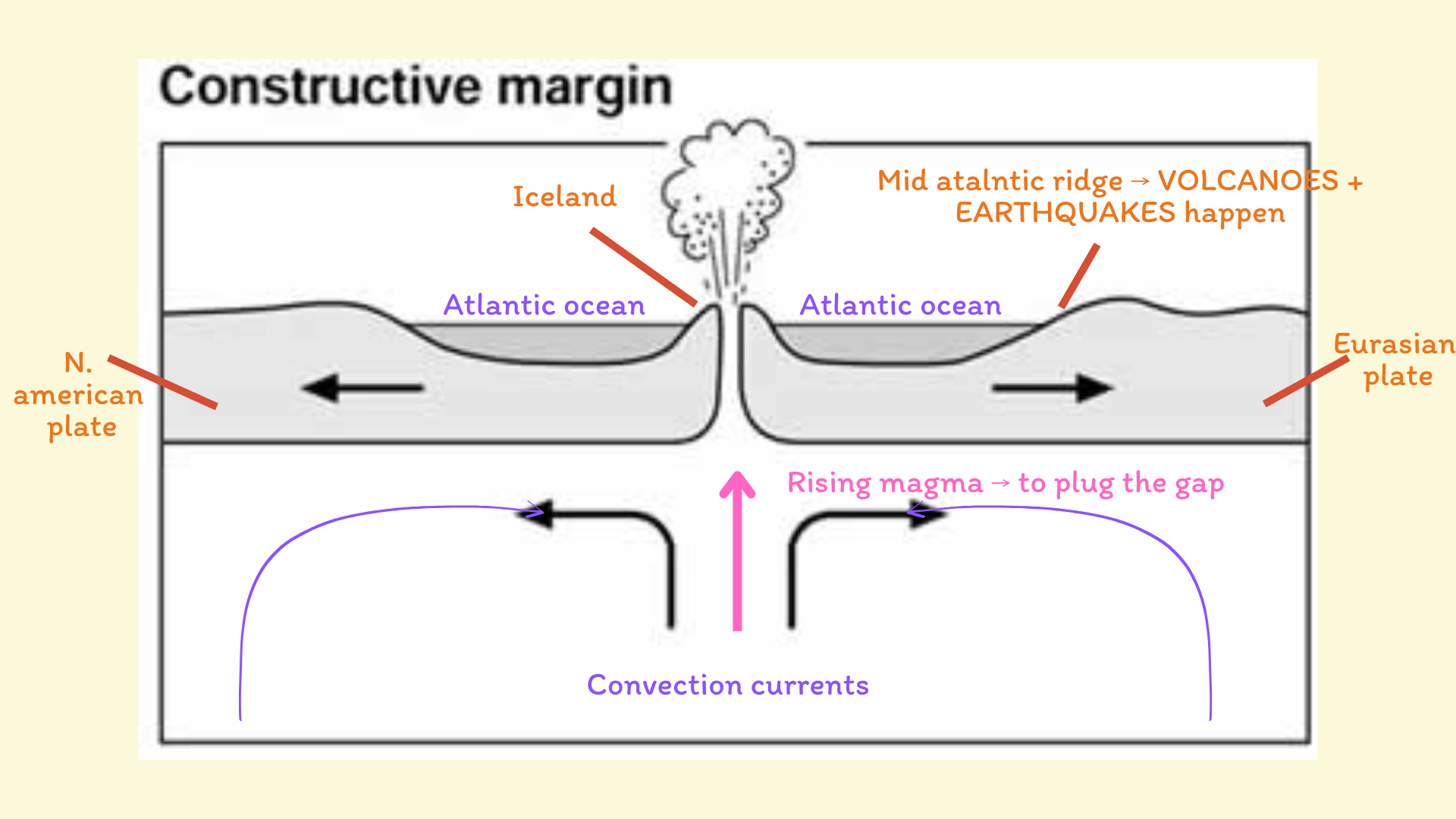
Constructive margin
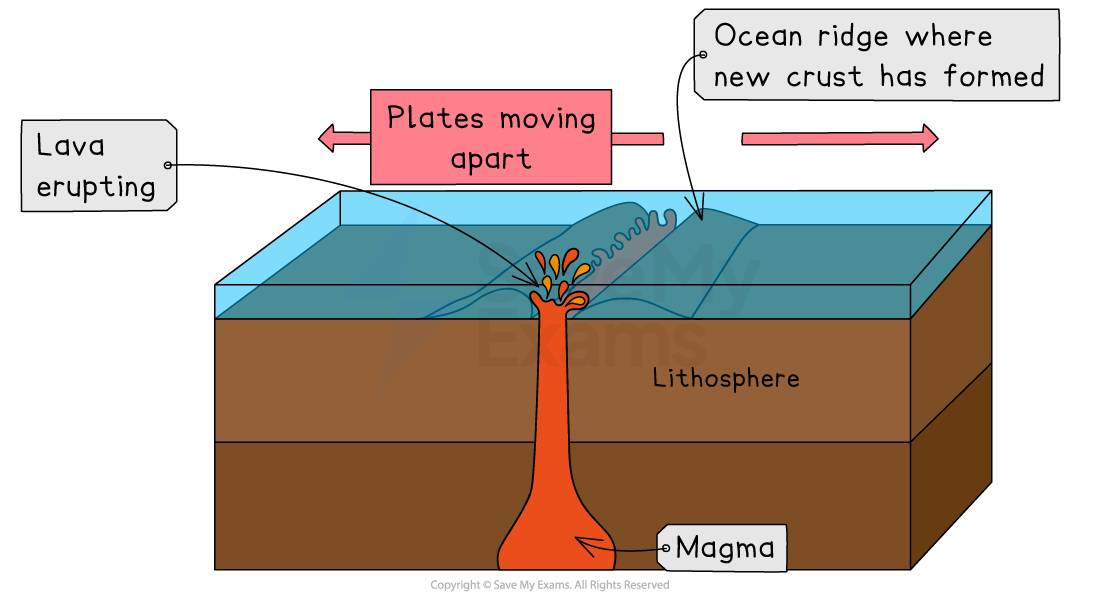
Constructive margin example
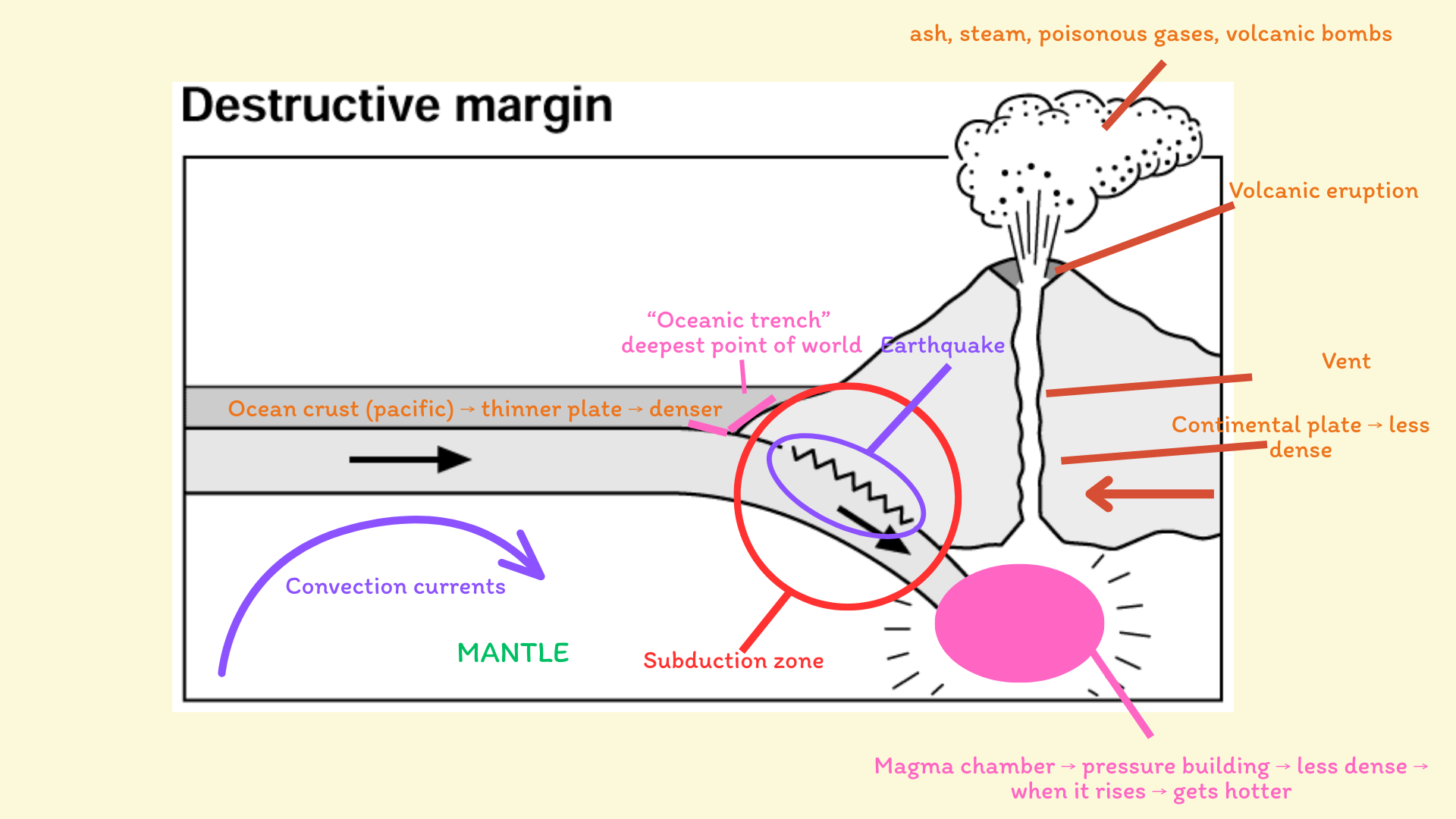
Destructive margin
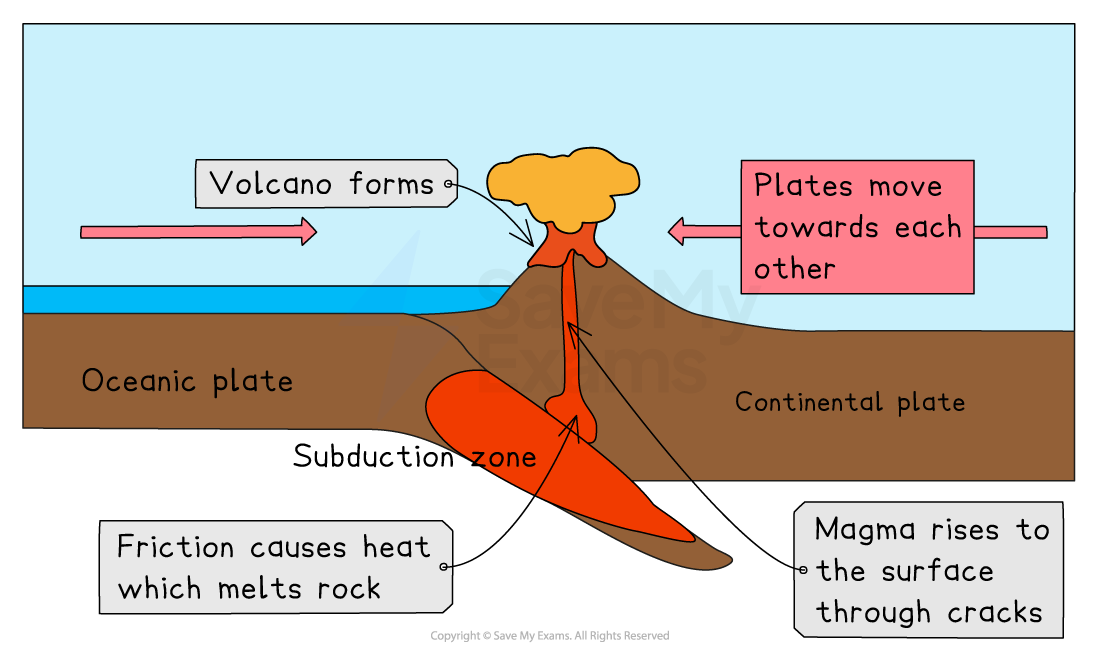
Destructive margin example
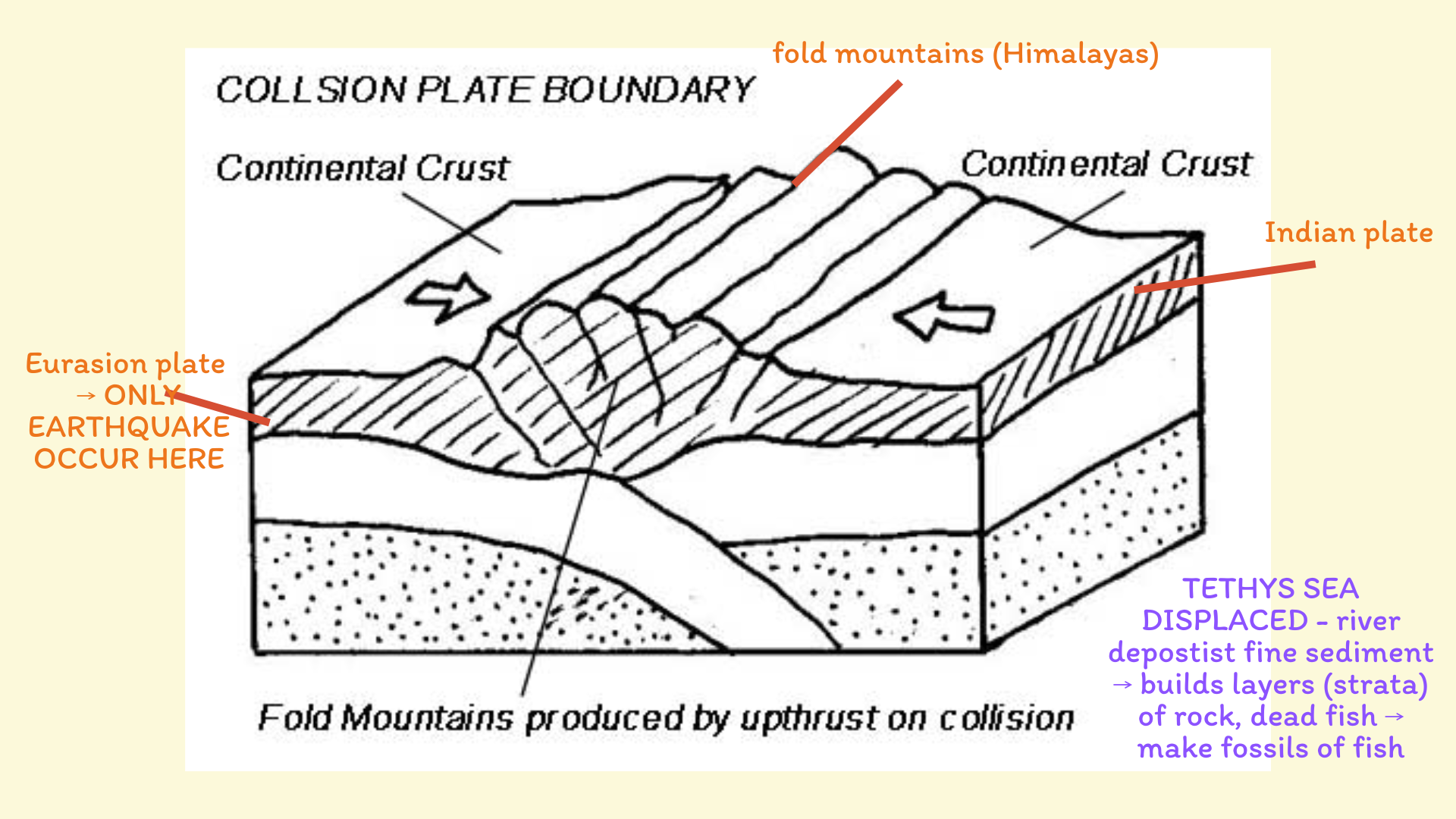
Collision boundary
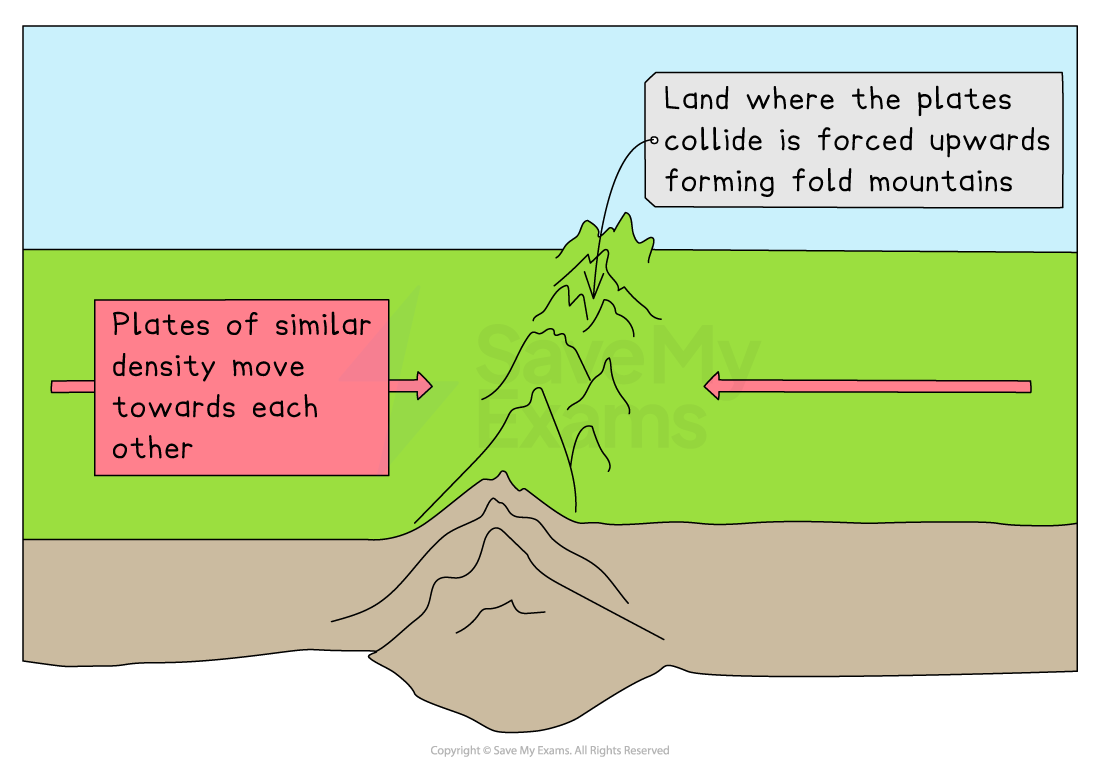
Collision boundary example
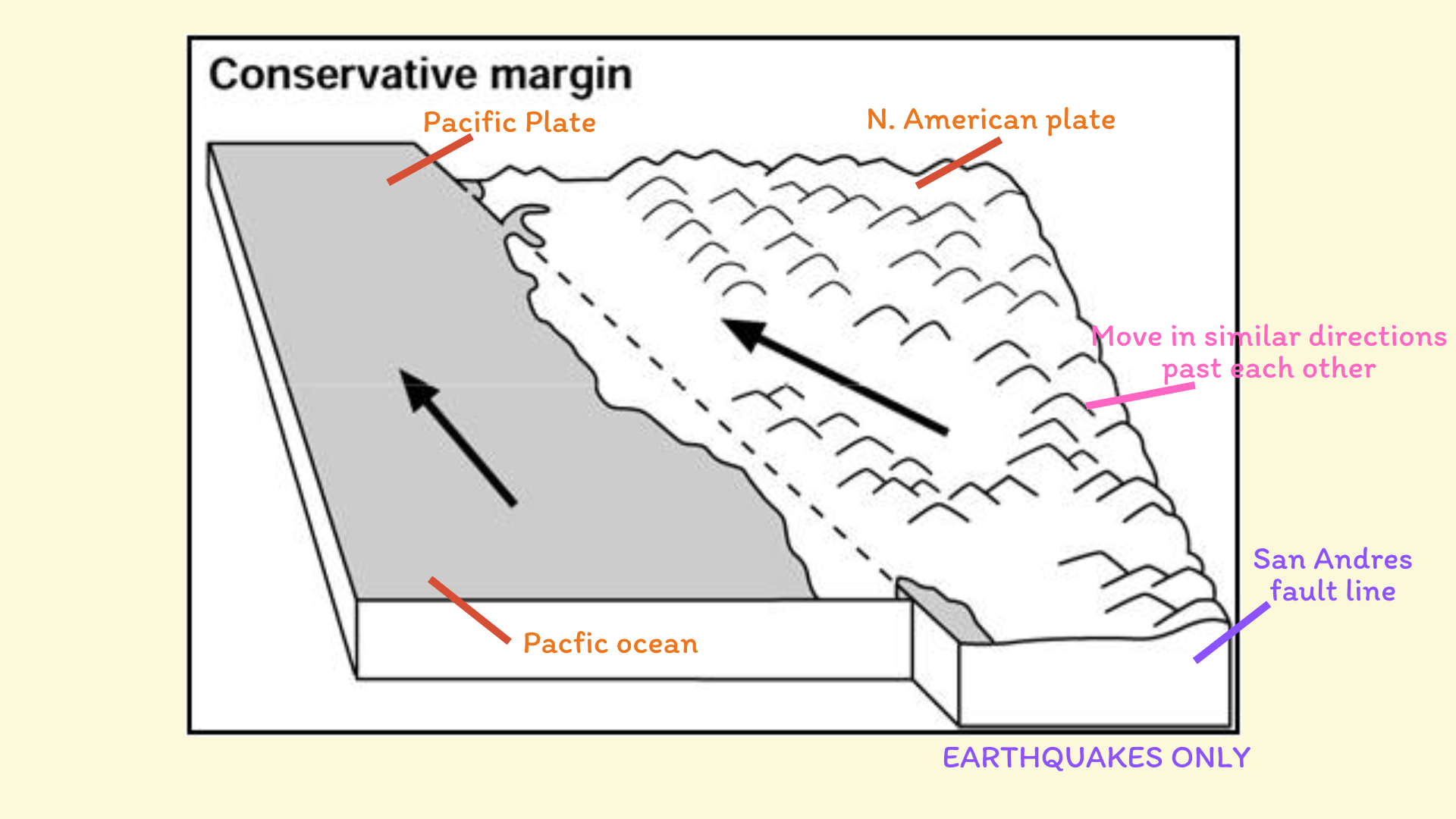
Conservative boundary
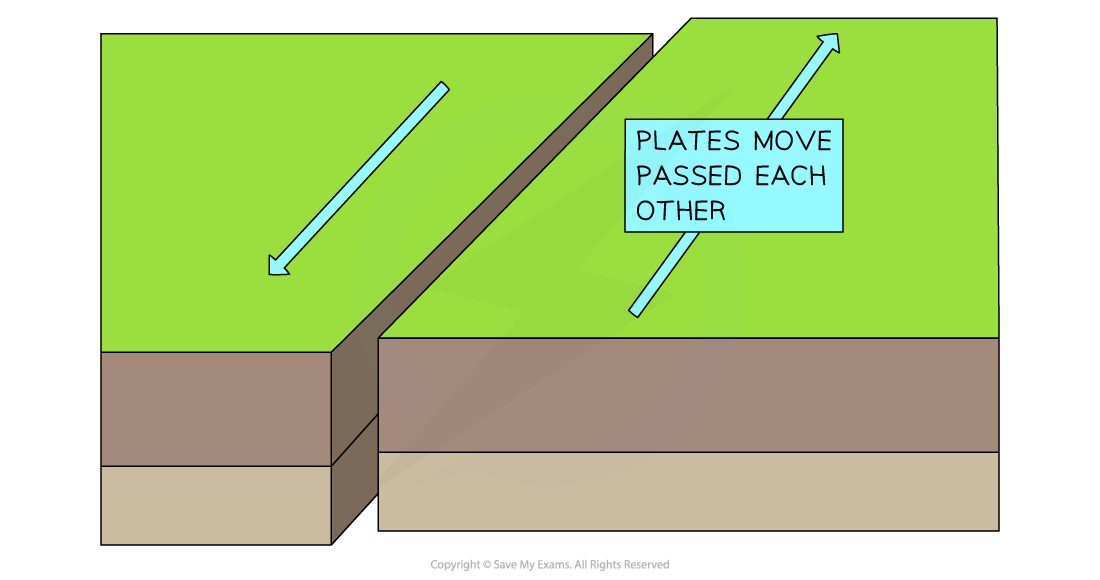
Conservative boundary example
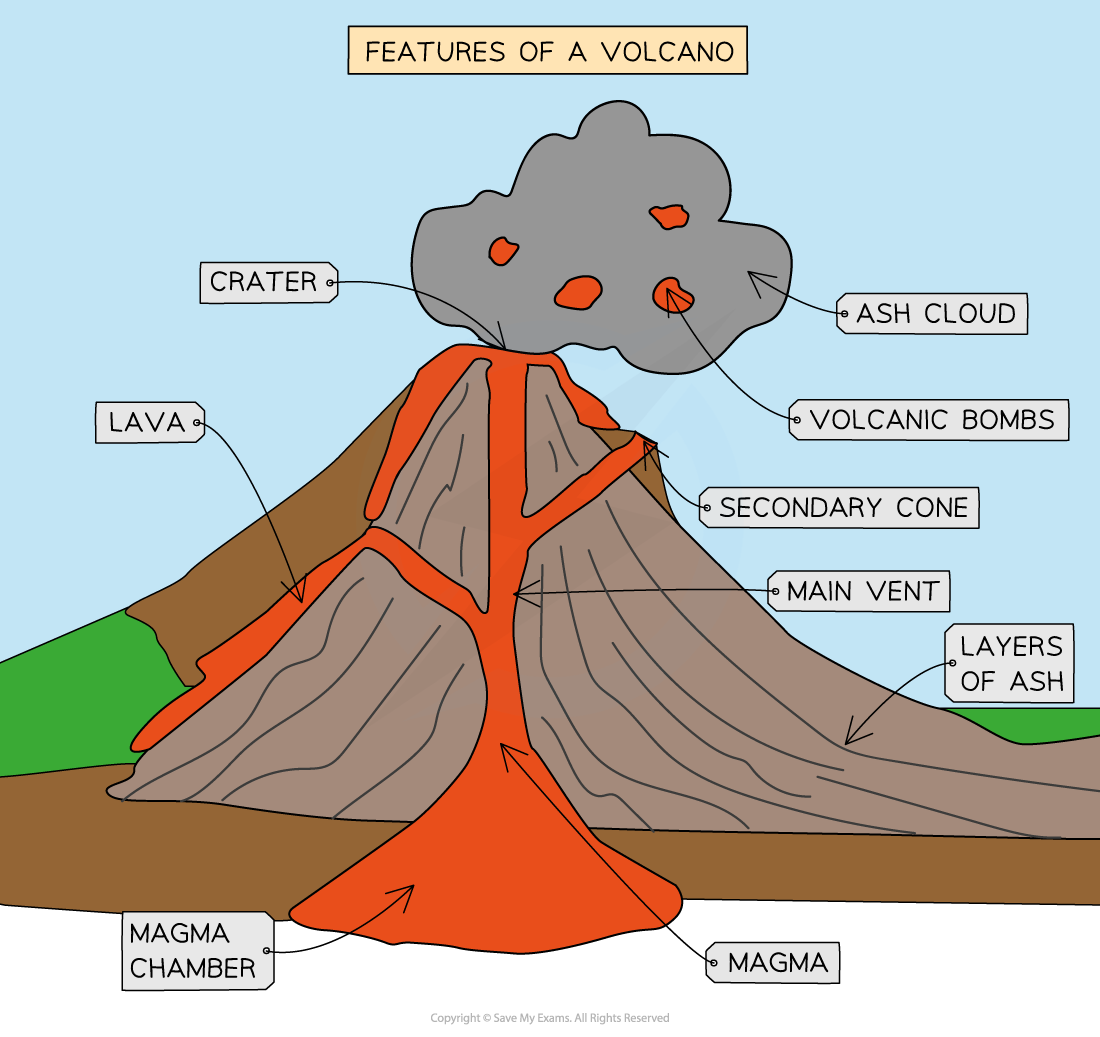
What are volcanoes
An opening in the earth’s crust through which lava, molten rocks and ash are erupted onto land
Where can volcanoes be found
found at edges of tectonic plate boundaries → often formed in long linear patterns → especially along destructive + constructive boundaries → majority occur along coastlines → particularly around Pacific Ocean → Ring of Fire → also found at hotspots → where magma rises through a weak point in crust
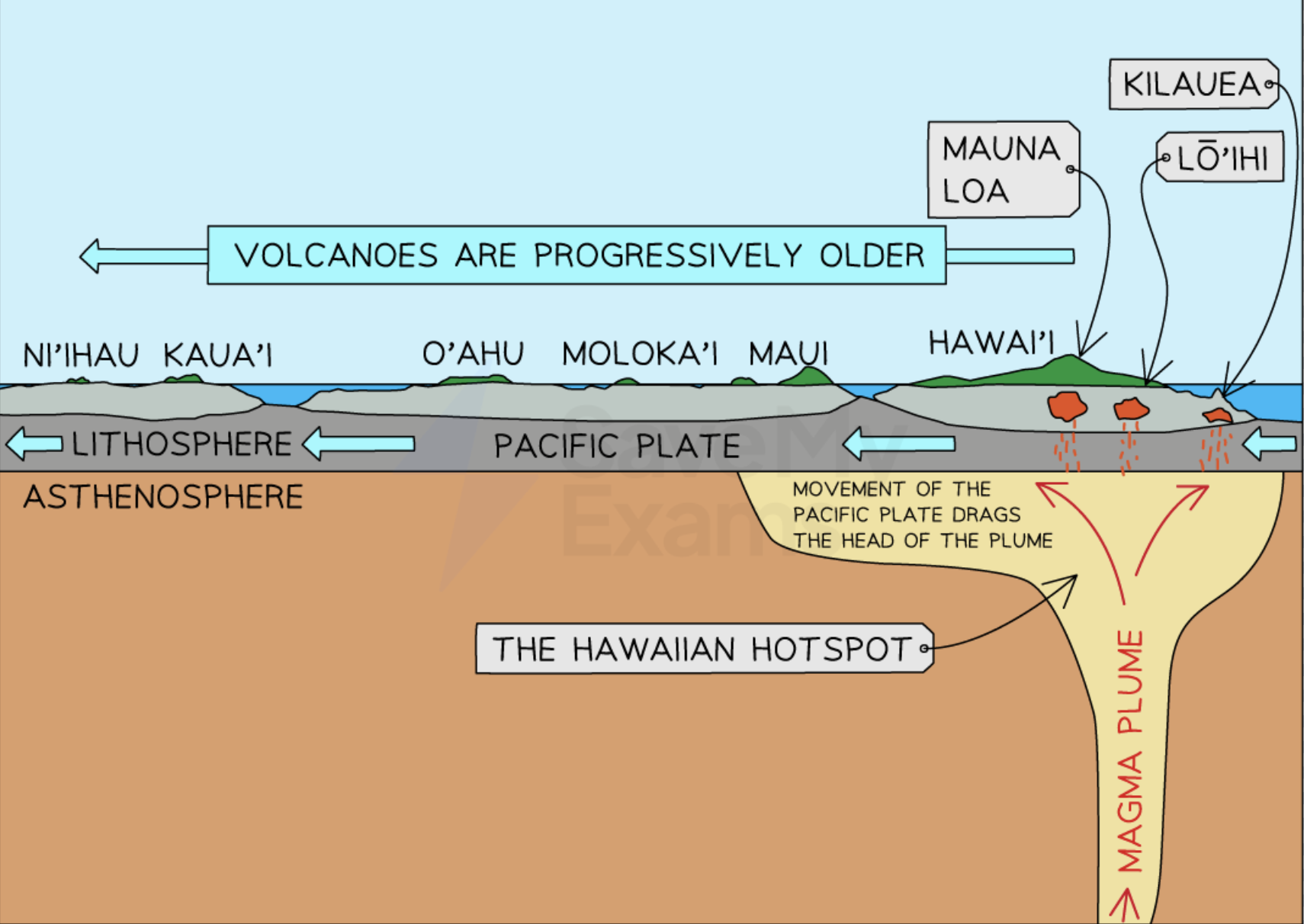
What are hotspots + how do they work
Areas in middle of tectonic plates where heat from mantle → causes fixed magma plume to rise → magma breaks through crust under pressure → forms volcanoes away from plate boundaries → as tectonic plate moves over hotspot → chain of volcanoes forms → e.g. Hawaiian Islands → older islands lie further from active hotspot
What causes volcanoes
Convection currents in mantle drives movement of tectonic plates → at destructive plate boundary → denser oceanic plate subducts beneath less dense continental plate → as it descends → oceanic plate melts due to heat + friction → forms magma → magma is less dense than surrounding rock → magma rises through cracks in crust → eventually, erupts through a vent → forms volcano
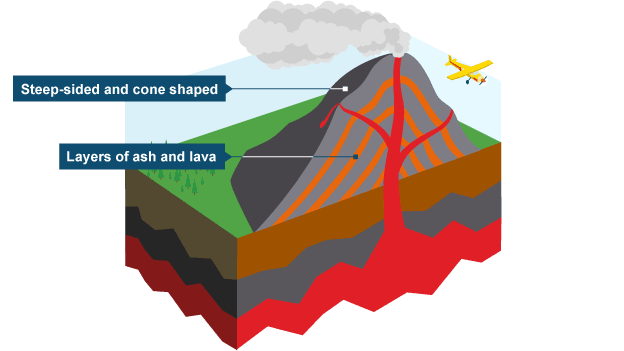
Stratovolcano (shape)
Tall, steep-sided, cone shaped volcanoes
Built in layers of ash + lava → from many eruption
Stratovolcano (location)
Found at destructive plate boundaries → e.g. Andes, Japan, Philippines
Where oceanic plate subducts beneath a continental plate
Stratovolcano (eruption style)
Explosive + violent → due to thick, high viscosity lava → acidic and high in silica →
Lava cools quickly + blocks vents → builds pressure
Often produces pyroclastic flows, ash clouds + lahars
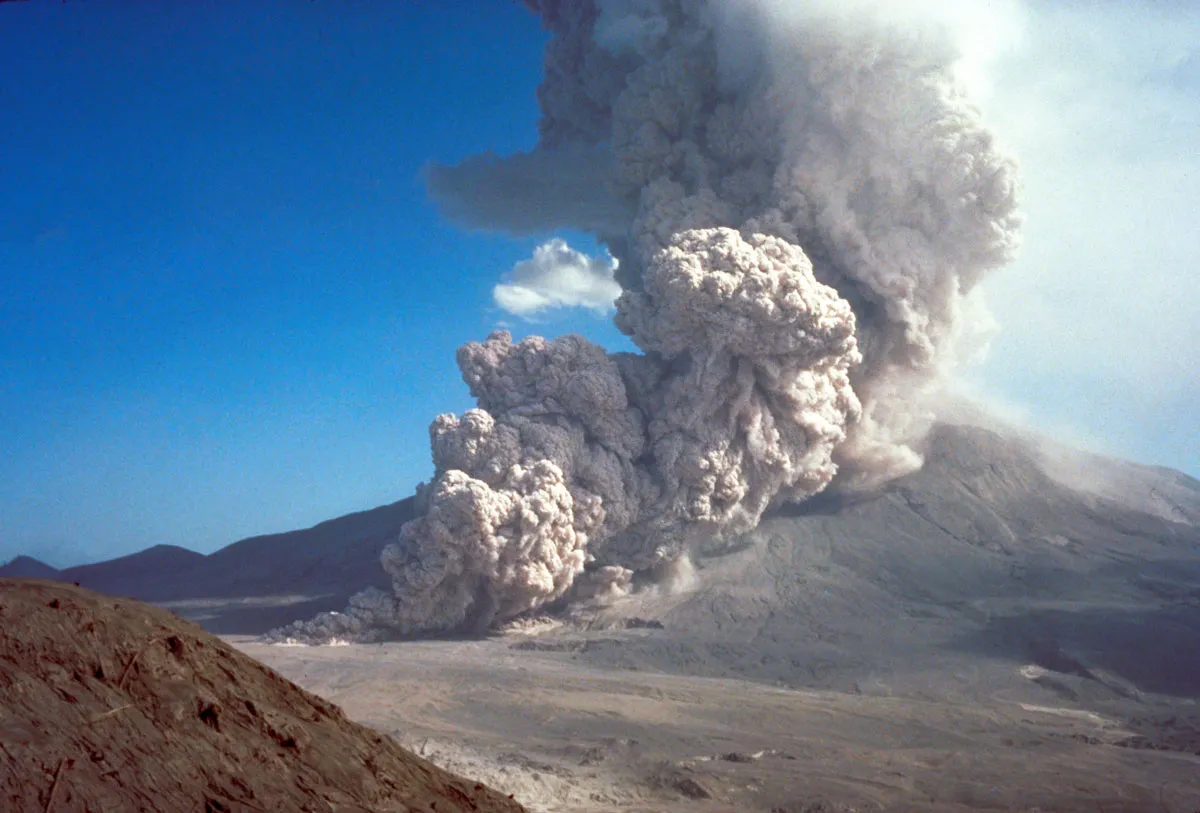
Pyroclastic flows
a fast-moving, hot current of gas + volcanic debris → flows along ground during some volcanic eruptions

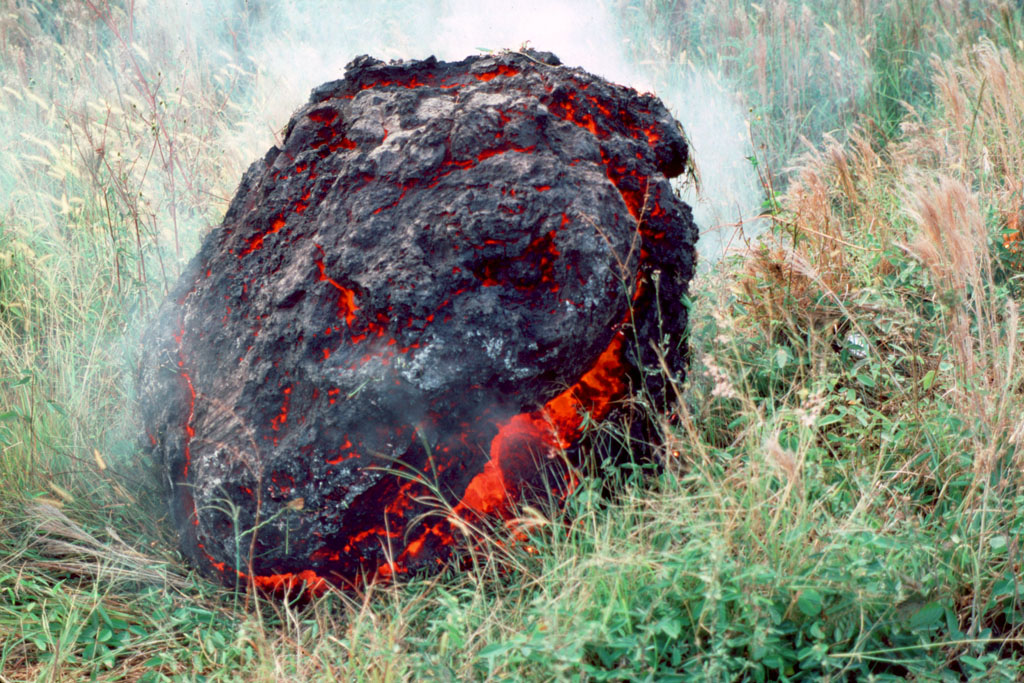
Volcanic bombs
a mass of partially molten rock larger than 64 mm in diameter → formed when volcano ejects viscous fragments of lava during eruption

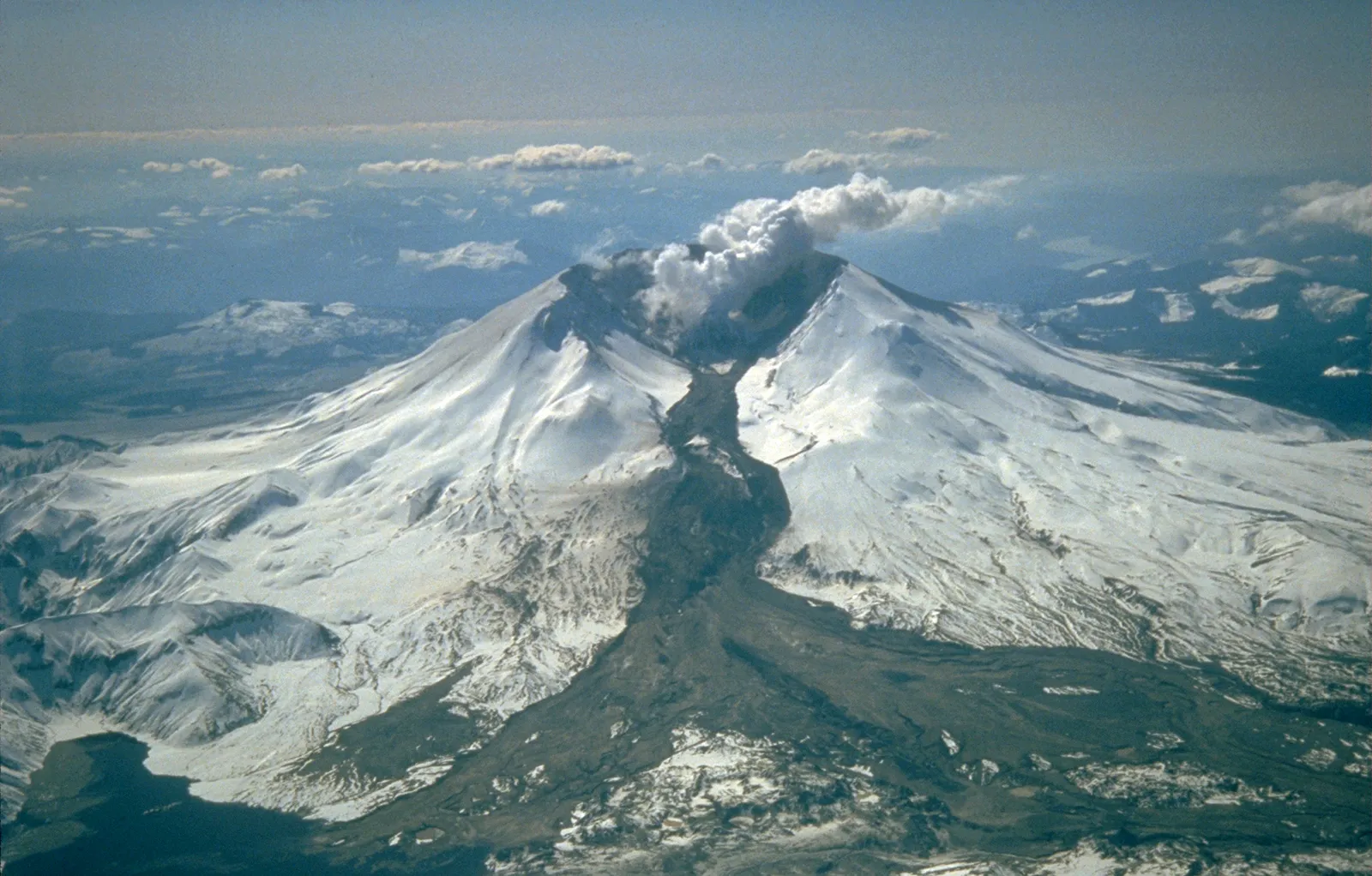
Lahars
mudflows created when water → from rain or meltwater from glaciers → + volcanic ash mix

Shield volcano (shape)
Wide, low, gently sloping sides → like warrior’s shield
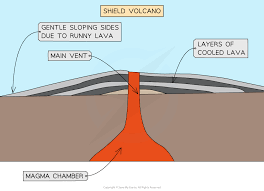
Shield volcano (location)
Found at constructive plate boundaries + hotspots → e.g. Iceland (Mid-Atlantic Ridge) + Hawaii
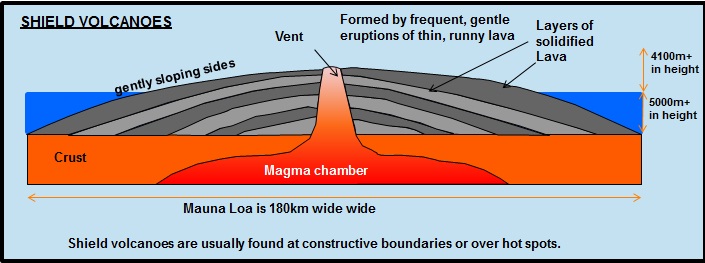
Shield volcano (eruption style)
Frequent but gentle eruption
Less pressure builds → less explosive
Runny (low viscosity) + basaltic lava
Flows easily → spreads over large areas
Lava flows can cover wide areas → but usually slow
Less ash + gas than stratovolcanoes
Volcanic eruption monitoring
Seismometers → detect small earthquakes → caused by rising magma
Gas sensors → measure increases in gases → e.g. sulfur dioxide
Tiltmeters + GPS → detect swelling of volcano → ground deformation
Thermal imaging → spots rising temperatures at surface
Satellite imagery → shows changes in volcano’s shape or heat
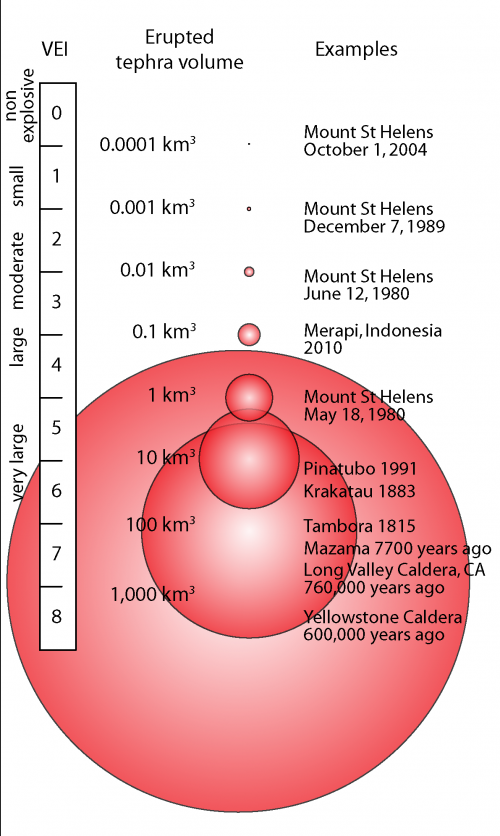
How volcanic eruptions are measured
Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI).
Scale from 0 to 8 → compares eruptions based on:
Height of eruption column
Duration of eruption
Amount of material ejected → ash, lava, rock
Logarithmic scale → each number is 10× stronger than the one before
Effects of volcanic eruptions on people
Death + injury → from pyroclastic flows, lava, ash +
Homes destroyed or buried under ash/lava
Crops and livestock killed → food shortages
Airports closed, roads blocked → transport + trade disrupted
Job loss → in farming, tourism + industry
Respiratory problems from ash inhalation
Evacuations + long-term displacement
Volcanic eruption effects on environment
Forests + habitats → B by lava, ash, or gas
Wildlife killed or displaced
Rivers + lakes polluted → by ash and acidic rain
Soil initially damaged → long-term fertility improves from mineral rich ash
Climate impact → ash clouds can block sunlight → cooling effect (short-term)
Volcano’s opportunities to people
Beauty → beautiful to look at + enjoy
Minerals → possible to mine minerals → e.g. sulphur from volcanoes
Geothermal potential → cheap + clean renewable energy → e.g. Iceland + El Salvador
Tourism → tourists like to view + walk up volcanoes → e.g. Mt Bromo
Tourism → often hot springs near volcanoes → tourists + locals can enjoy → e.g. onsens in Japan
Land around volcanoes very fertile → all minerals → many people choose to farm land
Poverty → people can't afford to live anywhere else apart from marginal land on volcanoes
Complacency or naivety → since volcano has not erupted for a long time
Confidence → be given adequate warning to evacuate
Family home → always lived in area → don't want to leave
Shortage of space + high population density
Volcano’s hazards to people
Pyroclastic flows → fast-moving, superheated gas + ash → can destroy everything quickly
Lava flows → slow but destructive → burn homes, roads + farmland
Ash fall → causes breathing problems, roof collapse + poor visibility
Lahars → mudflows of ash + water → deadly + can bury entire villages
Toxic gases → sulphur dioxide + carbon dioxide → can poison air + water
Earthquakes + landslides → triggered by volcanic activity → damages homes + infrastructure
Fires → caused by lava igniting vegetation or buildings
Evacuation + displacement → people may lose homes, jobs + access to services
How to reduce impacts of volcanic eruptions
Monitoring → use seismometers, gas sensors + satellites to detect signs
Early warning systems → alert people to evacuate in time
Evacuation plans → pre-planned routes + drills to move people to safety
Public education → teach communities what to do before, during + after eruptions
Land-use planning → avoid building in high risk zones
Emergency services → have rescue teams + supplies ready
What are earthquakes
a sudden, violent shaking of the ground caused by tectonic plate movements
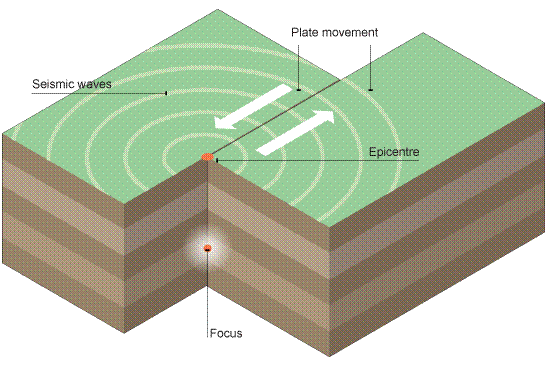
Pattern of earthquakes
Pattern of earthquakes occur along tectonic plate boundaries → in linear patterns → especially the Pacific Ring of Fire + Mid Atlantic Ridge → vast majority of earthquakes occur at or near plate boundaries → where force of tectonic plate movement is most intense
How earthquakes occur
Mostly at plate boundaries → e.g. collision or destructive margins → but can happen in all 4 plate boundaries → heat from the core moves plates → causes pressure + friction where they meet → plates get stuck → builds stress + pressure → when pressure overcomes the friction → fault gives way → releases energy as seismic waves → sudden release causes ground to shake → leads to destructive earthquakes → will occur in primary + secondary waves
Focus
the exact point at which the earthquake has occured (deep in the ground)
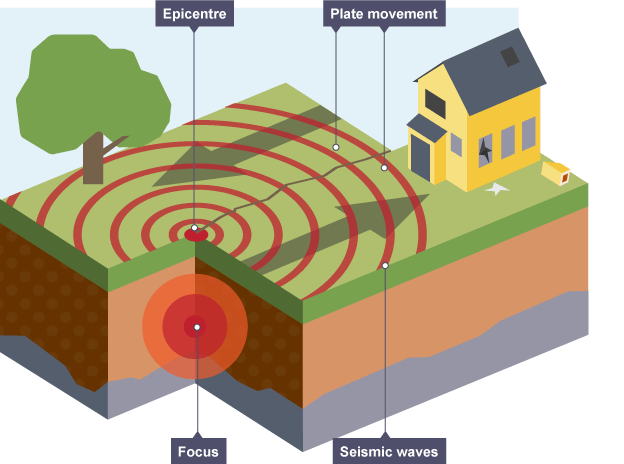
Epicentre
point on surface of the earth directly above the focus
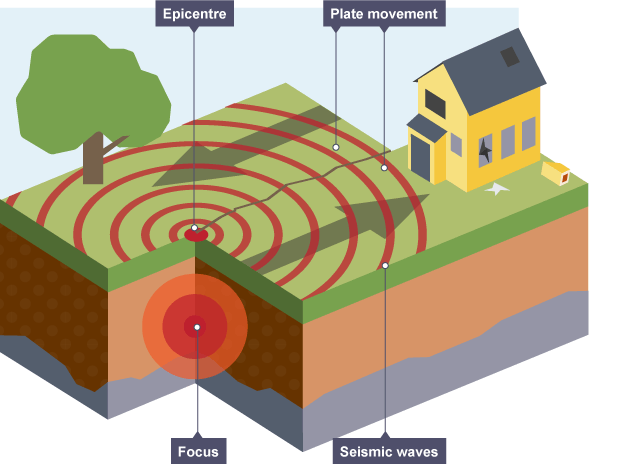
Seismic waves
the shockwaves that move outwards from the focus
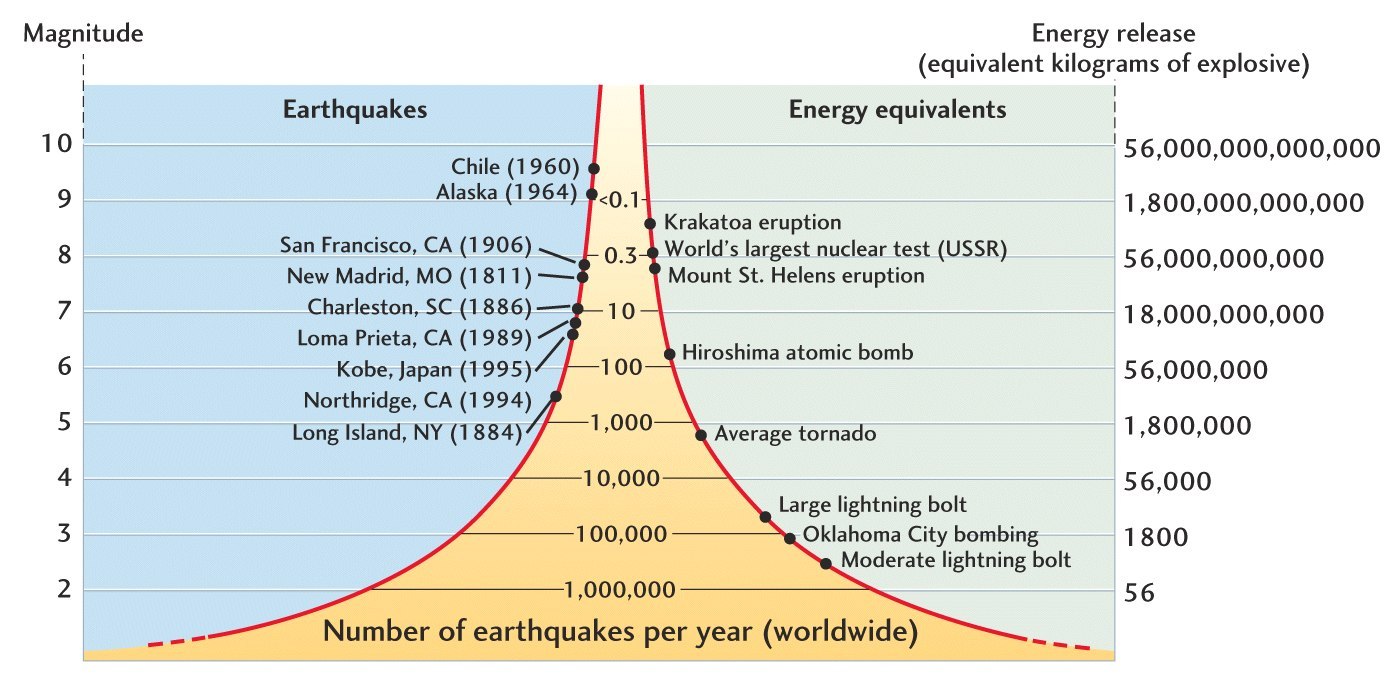
Richter Scale
Measures magnitude → how strong the earthquake is
Logarithmic scale → each number is 10× more powerful than one before
Scale goes from 1 to 10+
Uses a seismometer to record ground shaking
Mercalli scale
Measures impacts + damage caused
Based on observations → what people saw or felt
Scale goes from I (not felt) to XII (total destruction)

Earthquakes effect on people
Deaths + injuries f→ rom falling buildings, collapsing roads + landslides
Homes destroyed → people made homeless or displaced
Water pipes + power lines damaged → lack of clean water + electricity
Hospitals + schools destroyed → reduced access to healthcare + education
Job loss → as shops, factories + offices damaged
Transport disrupted → roads, railways + airports shut down
Emotional trauma + mental health issues → from losing family or property
Earthquakes effect on environment
Landslides + rockfalls → triggered especially in mountainous areas
Ground cracks + surface rupture → damage natural landscapes
Rivers blocked or diverted → can cause flooding
Soil liquefaction → ground behaves like liquid → damages ecosystems
Fires → from ruptured gas lines → spread into forests
Coastal earthquakes → can cause tsunamis → affect marine + coastal habitats
Air + water pollution → from damaged infrastructure → sewage + chemicals
How to reduce impacts of earthquakes
Monitoring → use seismometers to detect tremors → issue early warnings
Emergency plans → practice drills + evacuation routes
Education → teach people what to do before, during + after
Earthquake-resistant buildings → use shock absorbers, deep foundations + flexible materials
Land-use planning → avoid building on fault lines or unstable slopes
Quick emergency response → rescue teams, medical aid + supplies ready to deploy
Features for earthquake resistant buildings
Flexible materials → absorb shaking
Shock absorbers
Cross-bracing → strengthen walls
Deep, strong foundations
Automatic shut-off valves → for gas lines → prevent fires