Chapter 5: Reflexes & Reaction Times
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
neuron
nerve cell, single cell that specializes in communication via electrical impulses
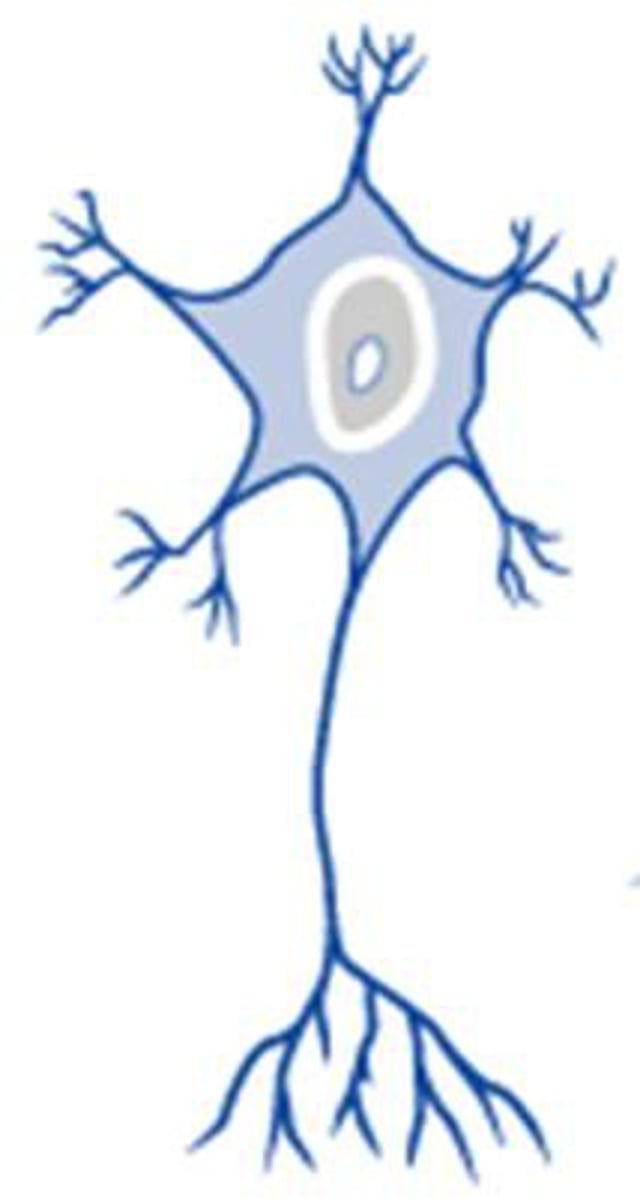
soma
cell body; large part of neuron containing the nucleus and organelles
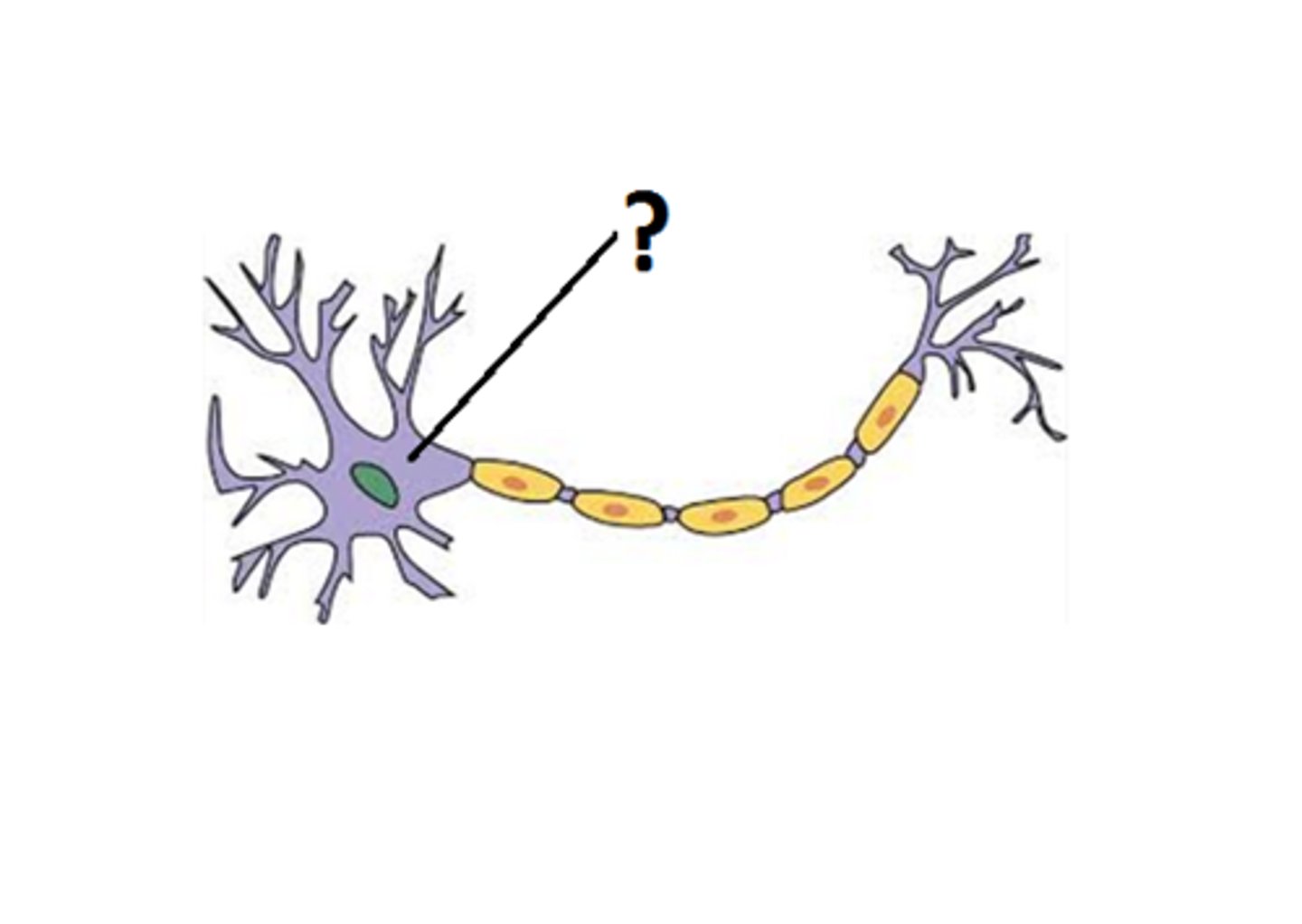
axon
single long projection responsible for transmitting information from the cell body to the next cell
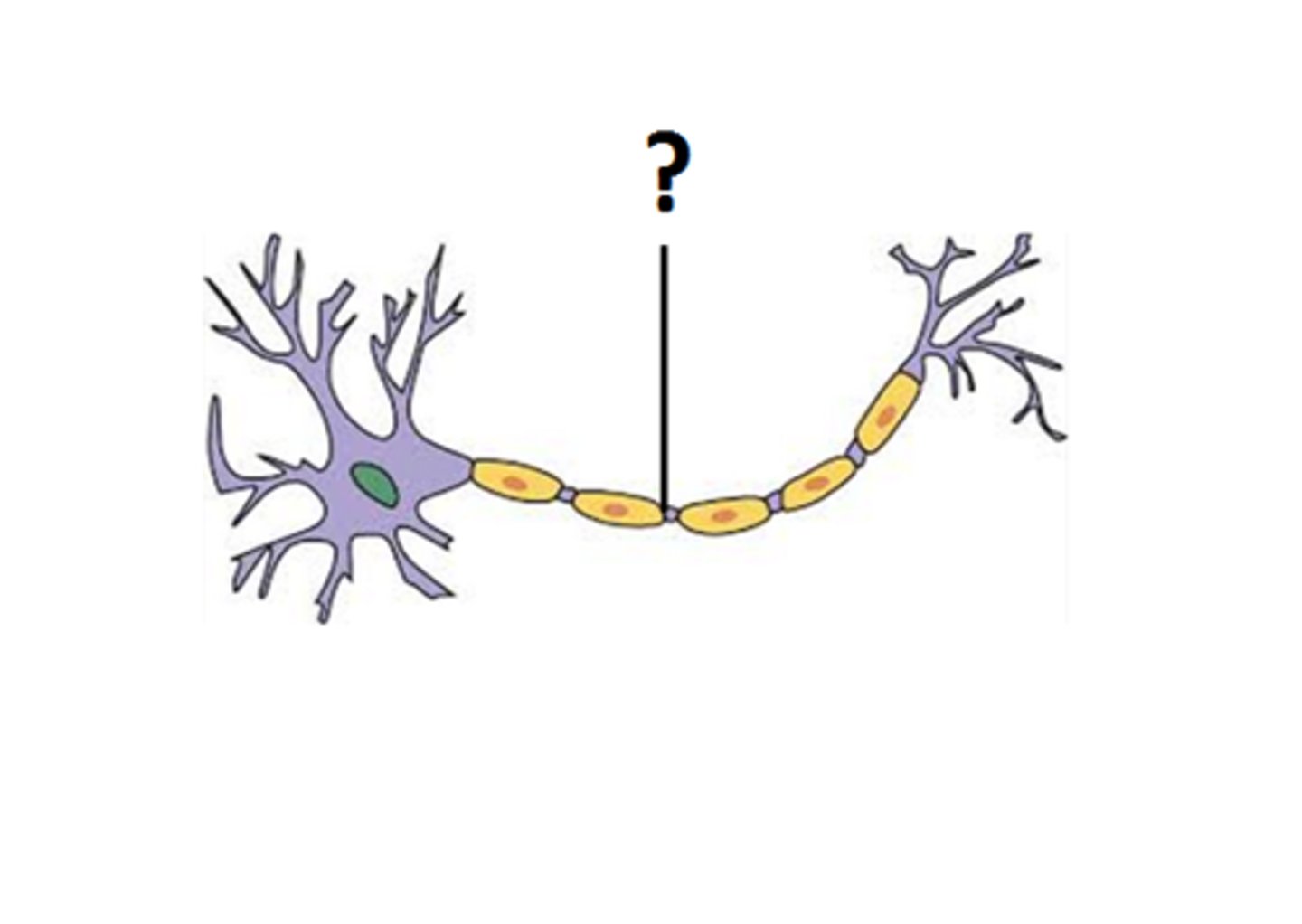
axon hillock
portion of axon connecting the cell body; swollen
- site of action potential generation
axon terminals
end of an axon will branch slightly--responsible for converting the electrical impulse to a chemical signal and passing information to the next cell in line
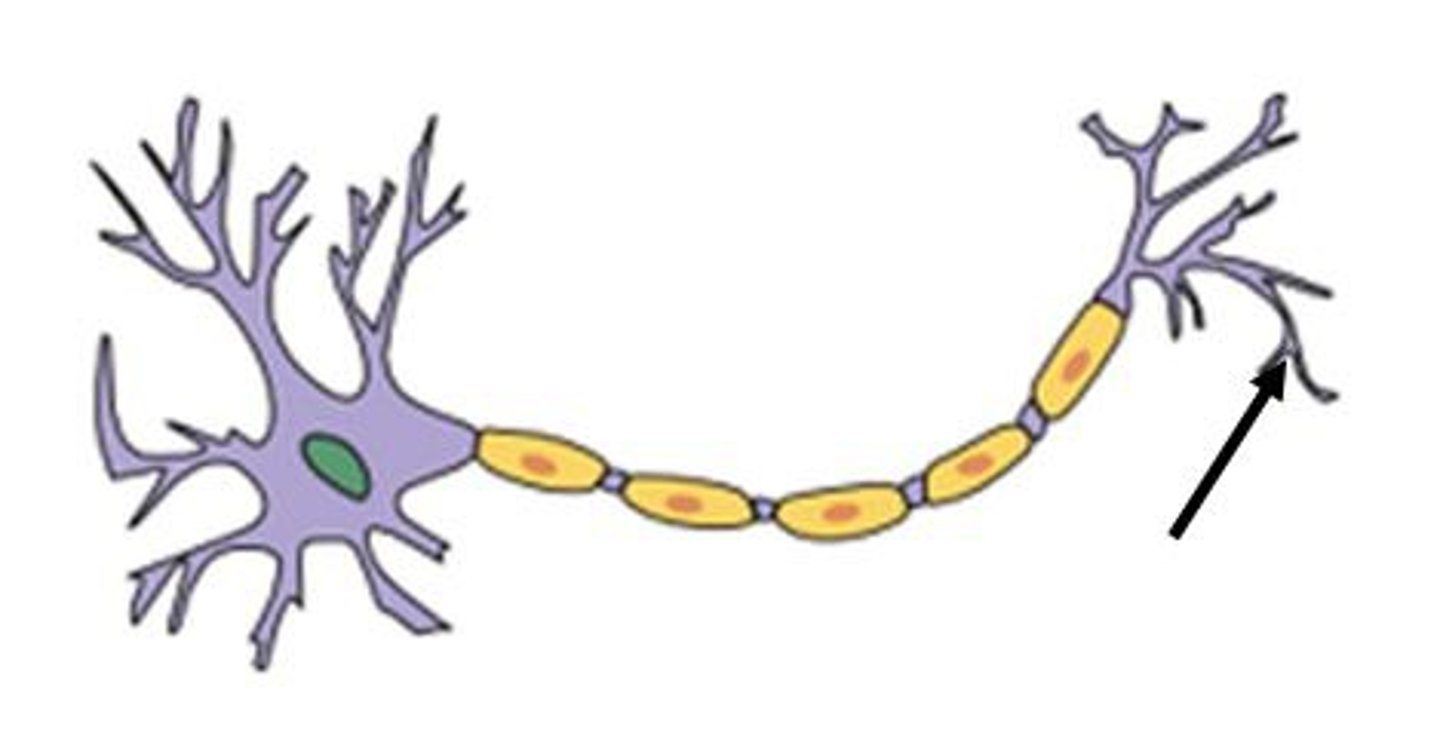
synapse
junction between two nerve cells
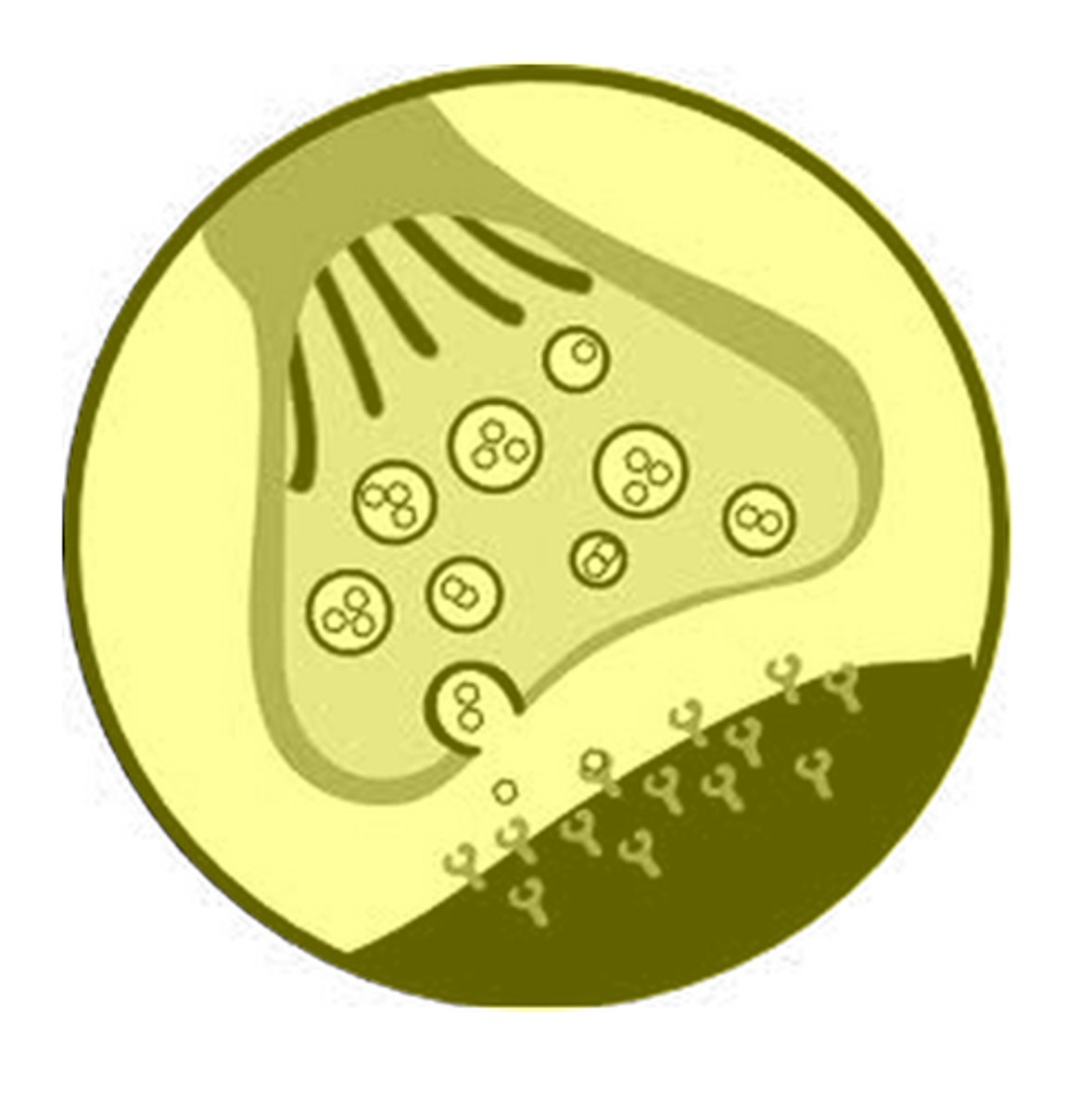
pre-synaptic neuron
neuron that sends signal
post-synaptic neuron
neuron receiving the signal
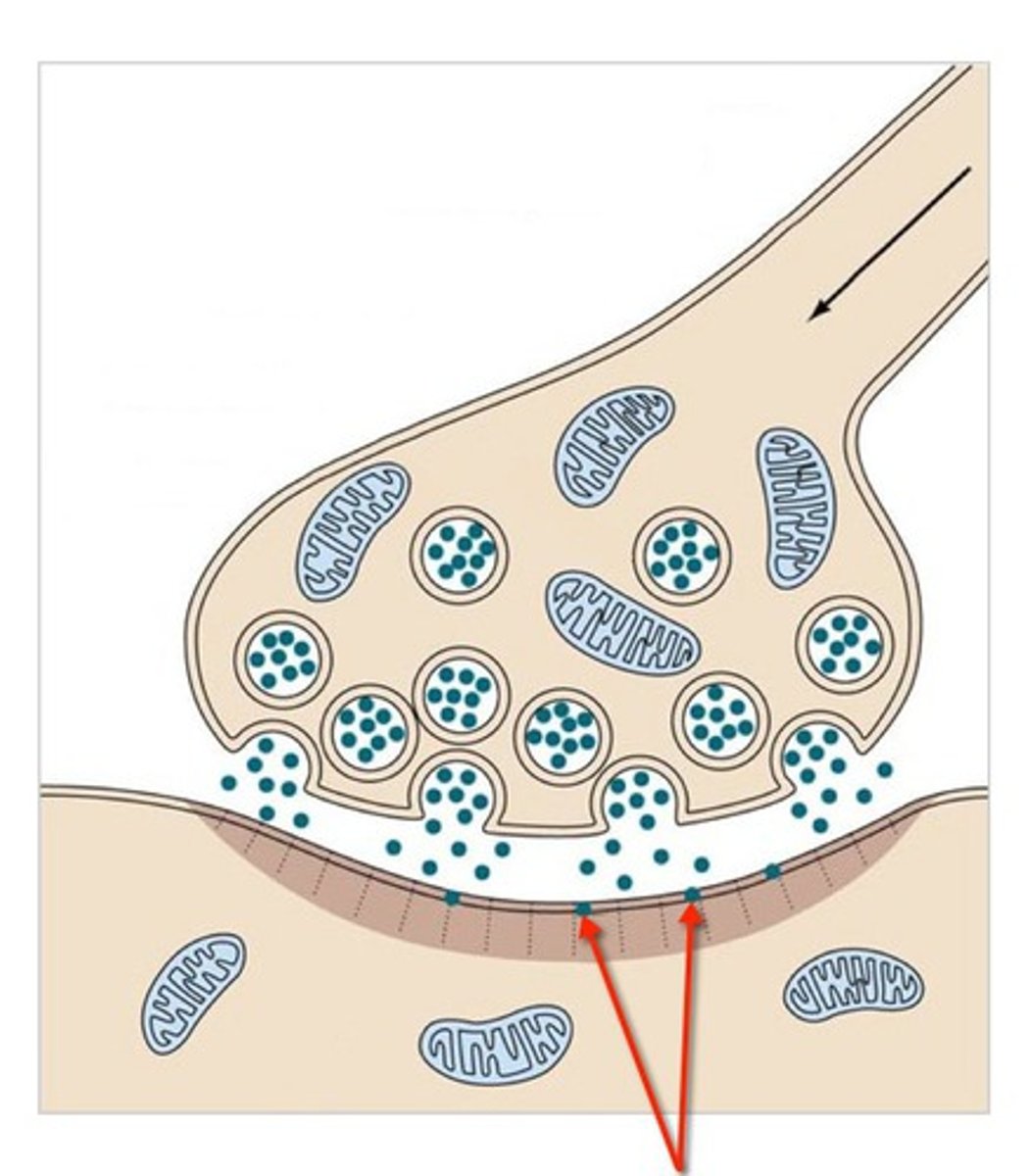
action potential
electrical impulse that travels down the axon of a neuron
neurotransmitter
a chemical that is used to communicate between neurons
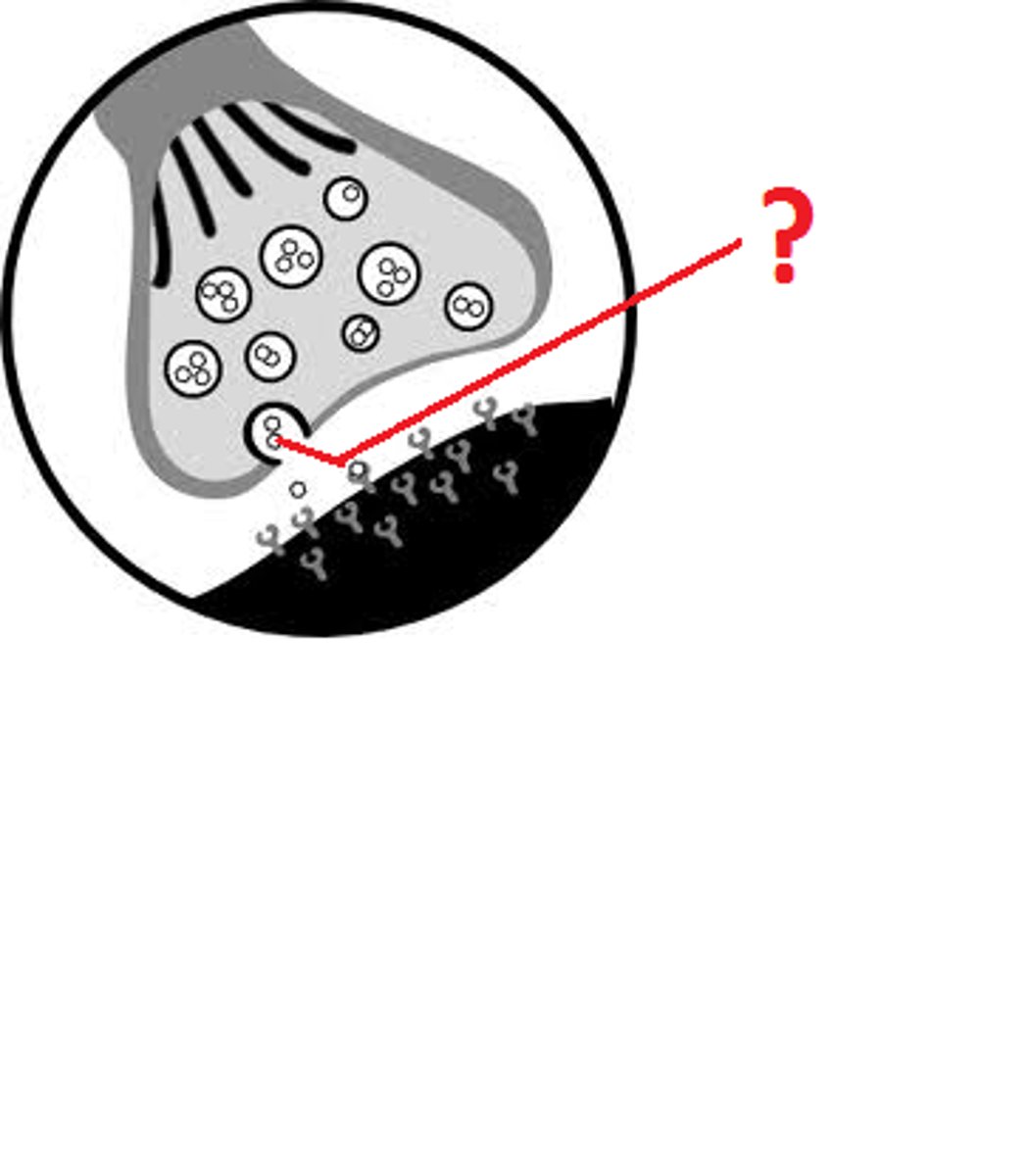
local potential
a small electrical impulse that fades over a distance
excitatory
causes next neuron to initiate an action potential in its axon
inhibitory
less likely to initiate an action potential in next neuron
afferent (sensory) neurons
convey impulses towards the central nervous system from sensory receptors found throughout the body
efferent (motor) neurons
convey impulses away from the central nervous system to a target---muscle or gland
interneurons
found within the central nervous system; connect afferent and efferent neurons and integrate sensory and motor input
reflex
a very fast, involuntary response to a stimulus
latency
a reflex refers to the amount of time that passes between the initial stimulus and the response
in what direction does the action potential travel in the sensory neuron?
to the spinal cord
in what direction does the action potential travel in the motor neuron?
away from spinal cord
Where is the cell body of the afferent neuron located?
dorsal root ganglion
Where does the axon of the afferent neuron enter the spinal cord?
through the dorsal root
Where are the cell bodies of efferent neurons located?
ventral horn
where does the axon of the efferent neuron exit the spinal cord?
ventral root
What is the difference between a reflex and a voluntary reaction?
reflex: involuntary, rapid response to stimulus--only travels to spinal cord
voluntary: take longer---needs to travel to the brain
factors that could increase or decrease reaction time
fatigue & injury
compare the amplitude & latency of a knee-jerk response without and with the Jendrassik maneuver
Latency: doesn't change
- should be the same because reflexes go through same maneuver
Amplitude: higher, less inhibition in movement--kick higher because not focused on it
Two volunteers, Liam (6ft tall), Jackie (5 ft tall)-- which volunteer will have the faster knee-jerk response and why?
Jackie--shorter, less distance for signal to travel
Latency difference between visual and auditory cues?
longer for auditory because it takes longer to hear than to see