integumentary system
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is the integumentary system
your bodies outer layer
what is included in the integumentary system
skin, hair, nails and associated glands
what are the two main skin layers
epidermis (outer) and dermis (inner)
what is the main role of the epidermis
protection, keratinised barrier against injury, water loss and pathogens
what is the main role of the dermis
strength, elasticity, sensation, it also contains nerves, glands, blood vessels and follicles
what is the function of the skin
protection, sensation, temperature regulation, vitamin D production
what are the four key skin cells
keratinocytes, melanocytes, intraepidermal macrophages and tactile cells
what are keratinocytes
cells that produce keratin, which provides structure and waterproofing
what are melanocytes
cells that produce melanin, protect against UV radiation
what are intraepidermal macrophages
cells that are part of the immune defence in the skin
what are tactile cells
cells the detect touch and pressure
what is the main cause of aging skin
reduced collagen and elastic fibreswh
what is the result of aging skin
wrinkles, thinner skins, less sweat/oil and slower healing
what are some key skin cancer warning signs
moles changing shape, size, colour, bleeding, irregular boarders
what is necrotising fasciitis
rapid, severe bacterial infection causing tissue death
what is the main risk from burns
infection and severe fluid losswh
whare are three burn zones
coagulation (dead tissue), stasis (at risk) and hyperaemia (recovers)
what is the impact of systemic burn effects
fluid loss → hypovolaemic shock + inflammatory response → distributive shock
what is a 1st degree burn
red, painful, epidermis only
what is a 2nd degree burn
blistering, very painful, epidermis and dermis
what is a 3rd degree burn
white/black, painless centre (nerve distruction)
what is a 4th degree burn
extended into the muscle/bone, usually life threatening
what does burn severity depend on
depth, percentage of body covered, location, age, inhalation injury and other comorbidities.
what are the key dangerous burn locations
face, airway, hands, genitalia and major joints
what are high risk groups for burn injuries
very young, elderly and immunocompromised
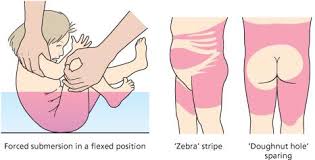
what are signs of burn abuse
symmetrical burns, no splash marks, patterned burns, doughnut sign
what are the key rules for burn management
cool for 20 mins, dont use ice, cover with cling film to reduce fluid loss and infection, fluids (use JRCALC), watch for hypothermia and inhalation injury