AP Bio Midterm S1
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Units 2, 3, 5, 6, 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Element
substance that cannot be broken down by a chemical reaction
compound
2 elements mixed in a fixed ratio
4 elements that make up 96% of all living matter
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON)
Calculate the number of NEUTRONS:
Atomic mass - Atomic #
calculate the ATOMIC MASS
protons + neutrons
isotope
Has different # of neutrons and mass
Periodic table
rows = Number of Shells
columns = Number of Valence Electrons
Which shell has the most potential energy?
(3rd shell) farthest from the nucleus
Van der Waals IMF
attraction/repulsion btwn particles caused by uneven electron distribution
happens when particles are close together
Strongest to weakest bonds
ionic
covalent
hydrogen
van der waals
Dynamic Equilibrium
Concentrations stabilize and the ratios remain the same
Rate of forward = Rate of reverse
cohesion
sticking to itself
adhesion
sticks to something else
Why can someone walk on water?
Water’s high surface tension due to cohesion + hydrogen bonds
Bonding due to polarity (asymmetry of water)
How does hydrogen bonding contribute to water’s specific heat?
Water needs a lot of heat energy to break hydrogen bonds
Why does ice float?
Ice has a lower density than water
Ice forms crystalline lattice that takes up more volume but has the same amount of particles —> higher density than H20
solvent
substance that does the dissolving
solute
substance being dissolved
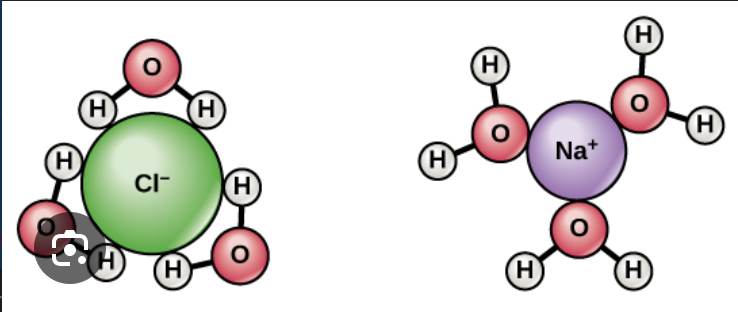
Why is water a good solvent?
Water is polar and surrounds other atoms
ex: NaCl dissociates in H20
hydrophobic
water fearing, dissolves in OIL BASED substances
hydrophilic
water loving, dissolved in H20
Why does water not dissolve oil?
LIKE DISSOLVES LIKE
H20 — Hydrogen Bonding
Oil — Van der Waals
Acidic
pH < 7, more H+ ions
Basic
pH > 7, more OH-
4 Macromolecules
Carbs, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids
Polymer
long molecule with identical building blocks linked by COVALENT bonds
Dehydration Reaction
Bonds are created by removing water
Each reactant provides hydroxyl group (OH- and H+ to make H20)
Hydrolysis
Water is added to break bonds
Is glucose a monomer or polymer?
monomer
What is the monomer of all carbs?
monosaccharides
Monosaccharide ratio
1 - 2 - 1
CH2O
Ex: Glucose
Isomer
same chemical formula, different structure
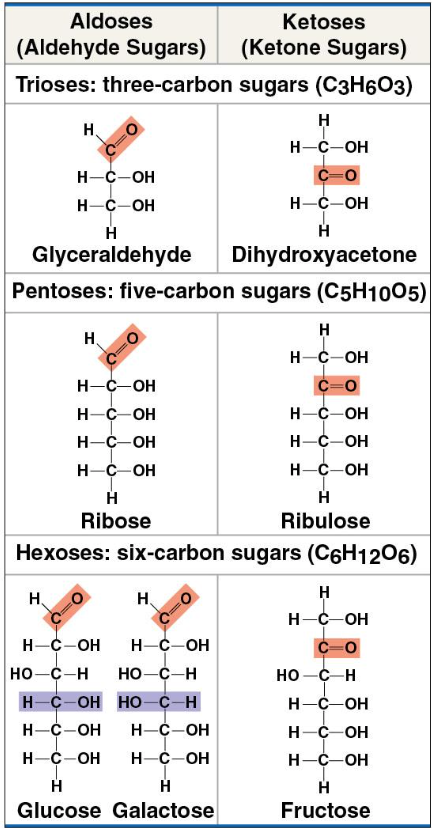
What is an example of a hexose sugar?
Glucose
Carbon chain forms ring
unlabeled corners = carbon
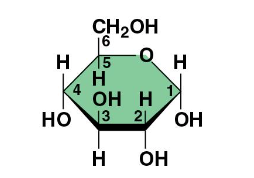
Glycosidic Linkage
covalent bond formed between 2 monosaccharides = polymer via dehydration
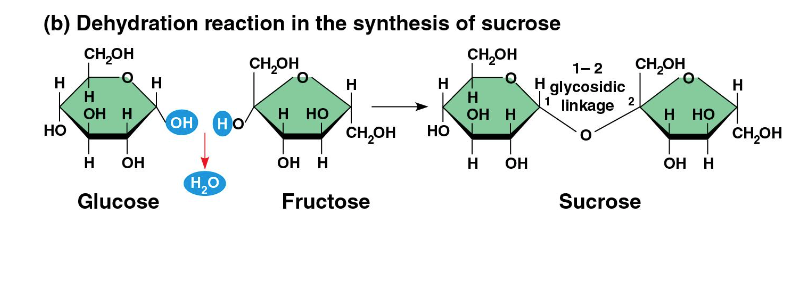
What are the 2 functions of a polysaccharide?
storage and structural support
Storage Polysaccharide
plants/animals store sugars for later
starch (monomer = glucose) and glycogen (muscle and liver)
Structural Polysaccharide
plants/animals build strong materials
cellulose supports the plant wall
Why can humans not digest cellulose
we lack the enzymes
What structural polysaccharide gives cockroaches their “crunch”?
chitlin
Which polysaccharide has 1-4B glucose linkages
cellulose
What characteristic do all lipids share?
all lipids are hydrophobic
What is a fat composed of?
Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acids
C-H makes fats hydrophobic
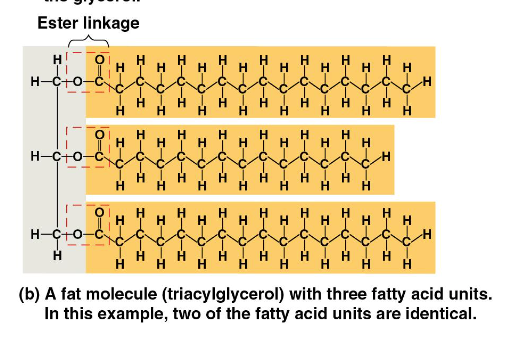
How are fats assembled?
dehydration reactions
What is an ester linkage (in fats)?
hydroxyl (OH) + carboxyl (C)
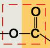
to form a fat, how many water molecules are removed?
3 (b/c there are 3 fatty acids that bond to glycerol)
Saturated Fats
Animal Fats, NO double bonds
solid at room temp
ex: lard

Unsaturated Fats
Plant Fats, double bonded and less flexible to condense/harden
Liquid at room temp
ex: oils

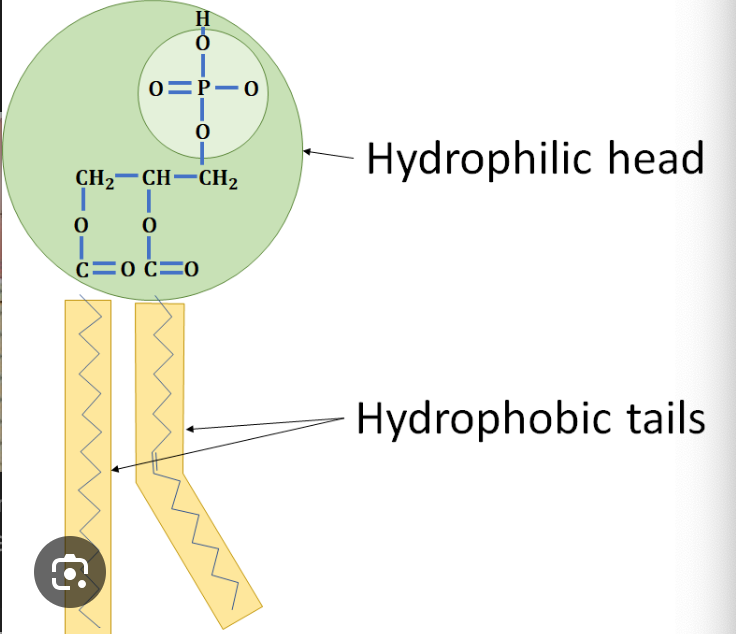
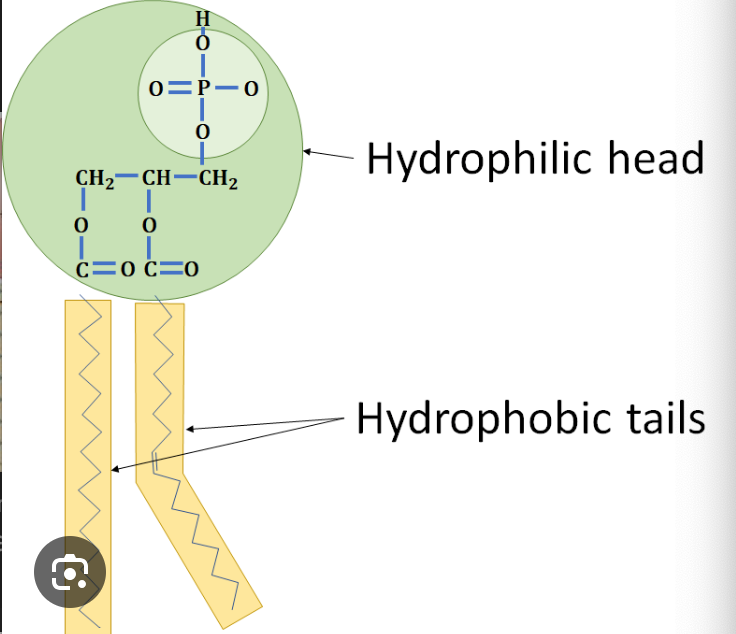
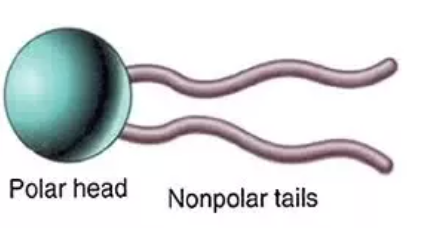
What is the charge of a phospholipid head and tail?
head = negative (hydrophilic)
tail = neutral (hydrophobic)
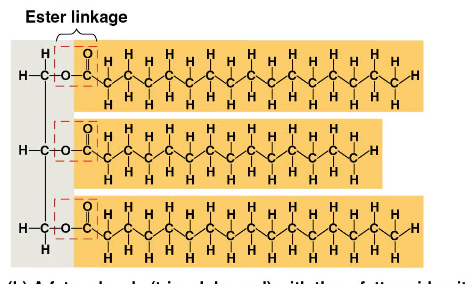
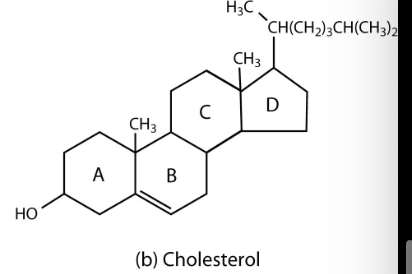
What does cholesterol (steroid) look like?
steroid = sex hormones, anabolic steroid
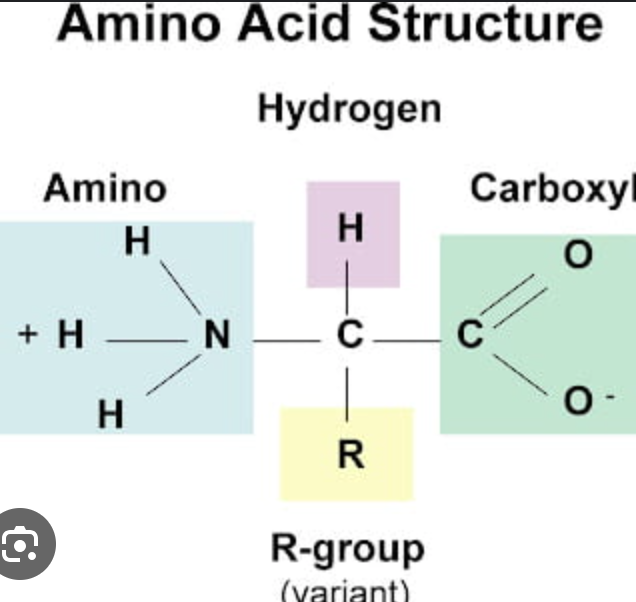
What are amino acids made of?
R-Group, Amino Group, carboxyl group (C—O)
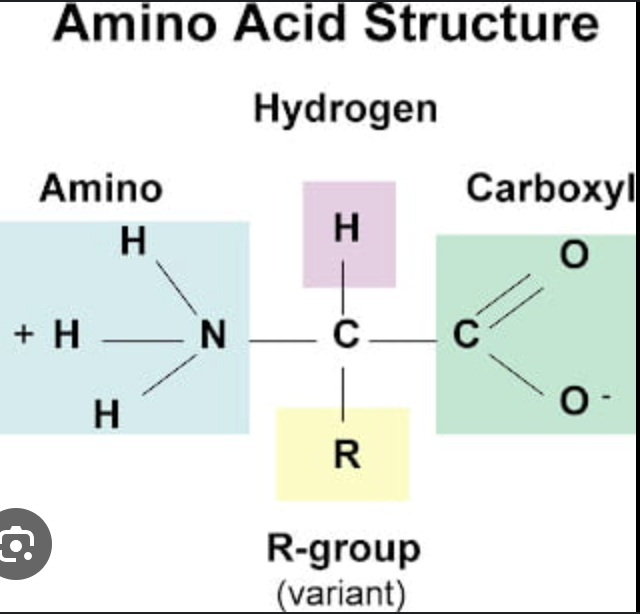
What varies in amino acids?
the R-Group
peptide bond
bond between amino acids
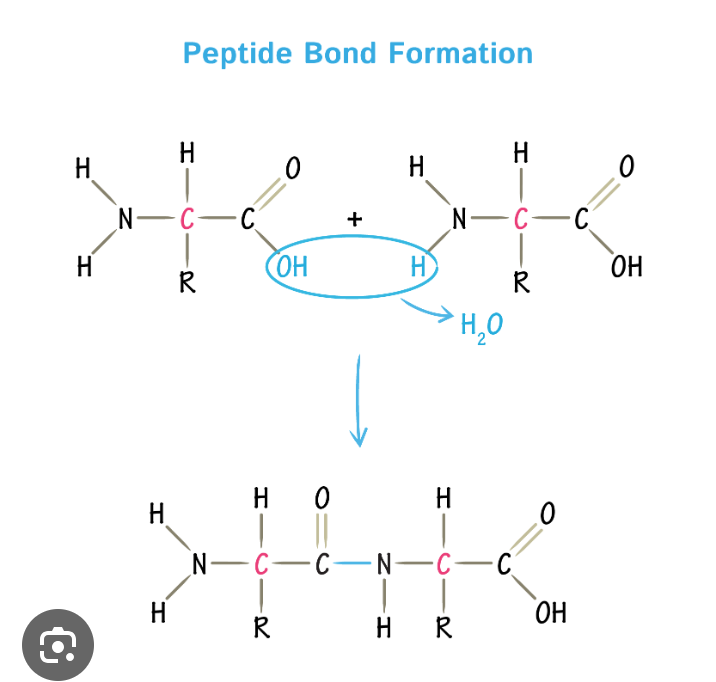
polypeptide
polymer created by amino acids
Primary protein structure
Primary Protein Structure
Linear amino acid chain (composed of multiple polypeptide chains)
each has 127 amino acids (20 types)

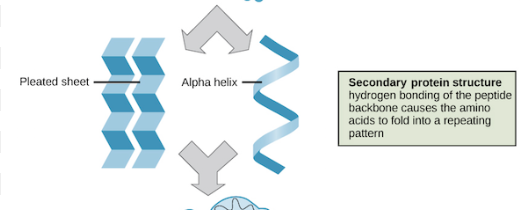
Secondary Protein structure
Hydrogen bonds stabilize atoms on the polypeptide backbone
alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
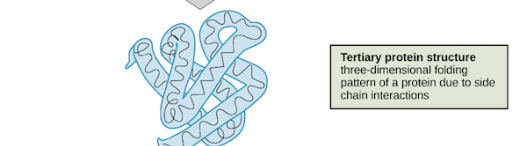
Tertiary Protein Structure
amino acid R-group interactions —> 3d folding
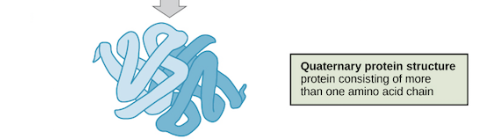
Quaternary Protein structure
polypeptide subunits are combined to protein
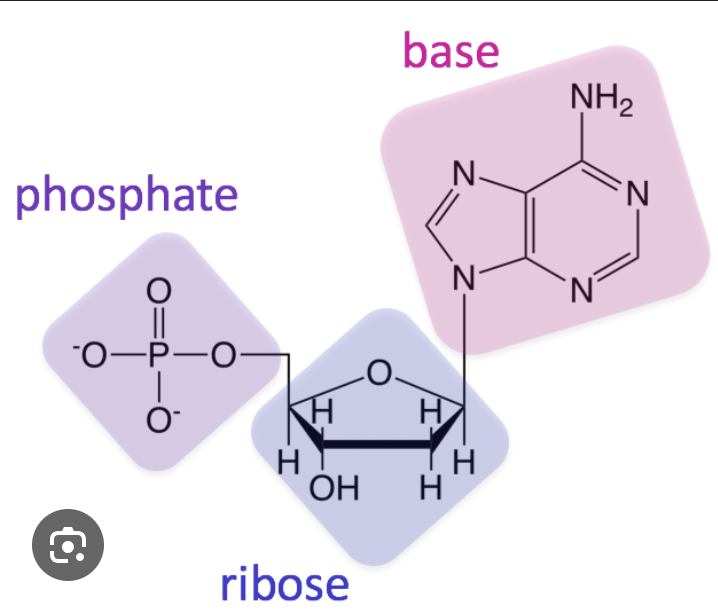
Which 2 molecules make up the “uprights” of DNA?
phosphate + sugar
What is a nucleic acid made of?
phosphate group, nitrogenous base, sugar (RIBOSE)
What is the smallest organelle broken up during cell fractionation?
ribosomes
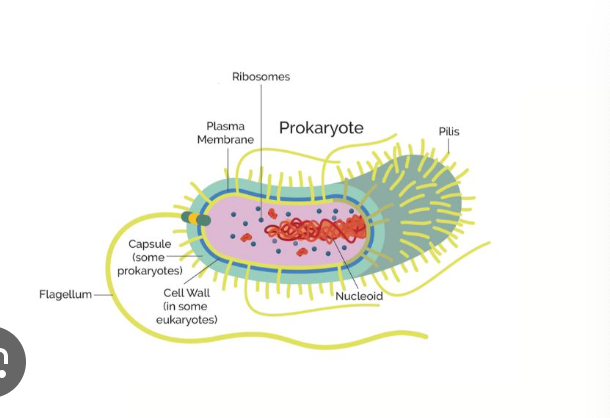
Which 2 domains consist of prokaryotic cells?
bacteria and archea
Which cell type has a membrane bounded nucleus
eukaryotic
Parts of a prokaryotic cells
cell wall
plasma membrane
bacterial chromosome
nucleotide
cytoplasm
flagella
Relationship between cell size and SA: Volume ratio
inversely proportional: as cells increase in size, SA: Volume decreases
What connects the layers of the nuclear envelope?
pore complexes
nuclear lamina
protein networks that maintain shape of nucleus by supporting envelop
nuclear matrix
framework of protein fibers w/in nucleus
What are ribosomes composed of?
rRNA + Protein
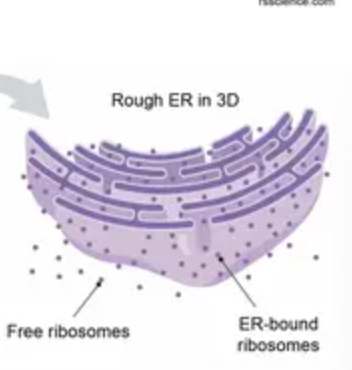
Free ribosomes
suspended in cytosol
ex: enzymes
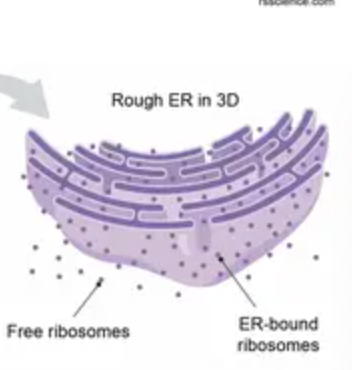
Bound ribosomes
attached to the outside of the rough ER
ex: lysosomes
Smooth ER
no ribosomes
synthesizes lipids
detoxifies
stores Ca2+
Rough ER
“membrane factory”, has ribosomes
synthesizes PROTEINS (glycoproteins)
distributes vesicles
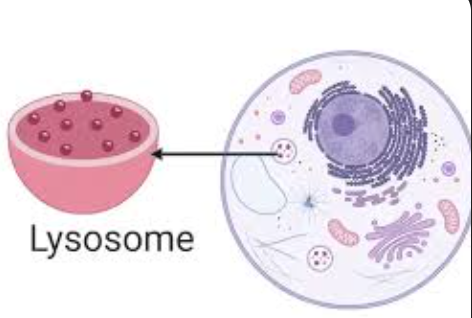
lysosome
membrane-bound sac of hydrolytic enzymes that digests macromolecules
phagocytosis
food is digested when food vacuole fuses with lysosome (INTRACELLULAR DIGESTION)
Difference between rough ER’s cisface and transface
transface - ships vesicles
cisface - receives vesicles
Contractile vacuole
pumps excess H20 out of cell
maintains ion Equilibrium
central vacuoles in plants
responsible for plant waste and growth
cytoskeleton
fiber network that supports cell and enables motility (of motor proteins)
microtubules
shape and supports cell, makes up tubulin
centrosomes
located by nucleus, organizes microtubule assembly in plants
Cilia V. Flagella
Cillia - more abundant, shorter
Flagella - singular, longer
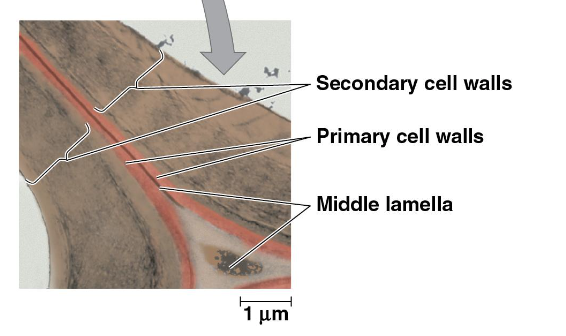
3 parts of a cell wall
middle lamella
primary cell walls
secondary cell walls
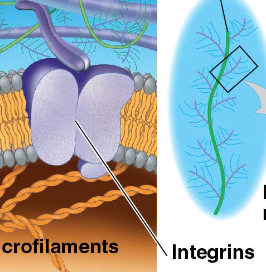
Integrin Proteins
transmembrane linkers that enables the cells to grip the matrix
How does cholesterol act at high temps?
temp restrains phospholipid movement —> hardens
How does cholesterol act at low temps?
low temp = buffer, fluidity is difficult to reach
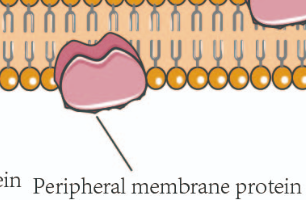
peripheral proteins
loosely bound to membrane surface (NAME TAG + ID)
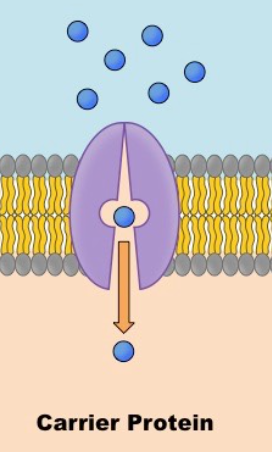
carrier proteins
Molecule must be a specific size to fix
channel proteins
hydroPHILIC channel used by ions/molecules
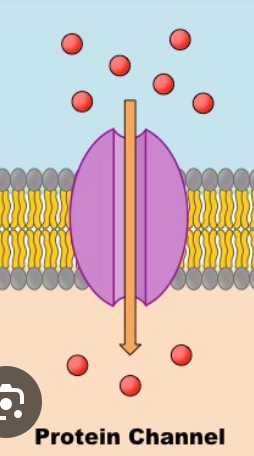
How do non-polar molecules travel through the membrane?
non-polar molecules are attracted to polar heads —> passive diffusion
how do polar molecules travel through the membrane?
polar molecules are repelled by polar heads —> facilitated diffusion
Active Transport
facilitated diffusion that requires energy (carrier proteins NOT channel proteins)
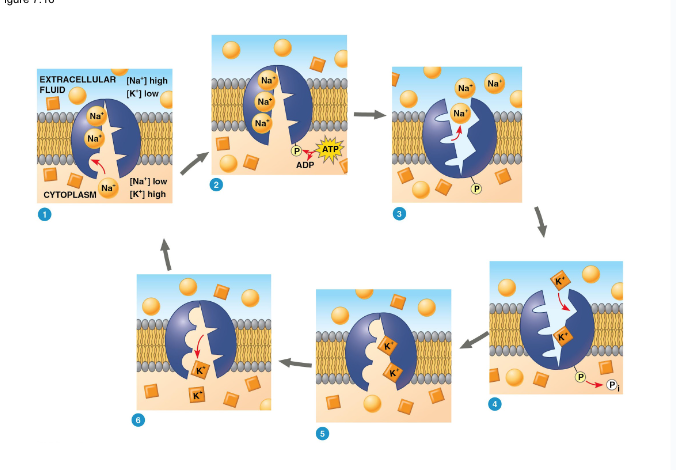
Sodium Potassium Pump
3 Na+ bind to pump
Phosphorylation occurs (ATP is created)
Protein shape is changed
3 Na+ leave, 2 K+ enter
What are 2 forces that drive the diffusion of ions across the membrane?
chemical (concentration gradient) + electrical (membrane potential) = electrochemical gradient
endocytosis
macromolecules are taken into the cell in vesicles
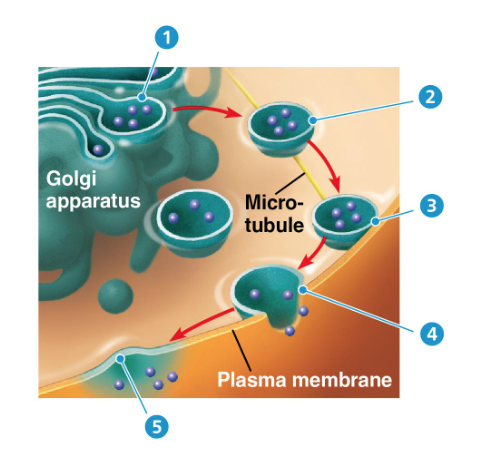
exocytosis
vesicles fuse with the membrane and release their contents outside the cell
ex: insulin
cotransport
downhill diffusion drives uphill diffusion
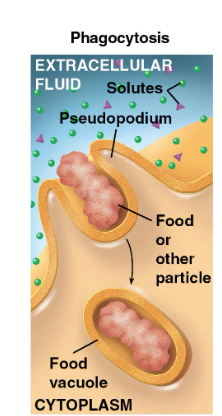
phagocytosis
“cellular eating” - cell engulfs another food/particle
food digestion
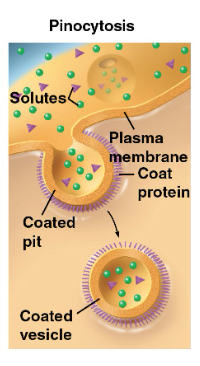
pinocytosis
“cellular drinking” - cell “gulps” fluid into vesicles
not selective!