Mental illnesses
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of 100 flashcards covering key concepts from neuroscience and mental health, designed to aid in the understanding and retention of critical information.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Neurology
The branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of nervous system disorders.
Psychiatry
The branch of medicine focused on the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders.
Mental Illness
A diagnosable disorder of thought, mood, or behavior that causes distress or impaired functioning.
Mood Disorders
Psychiatric disorders characterized by disturbances in mood, such as depression and bipolar disorder.
Freud’s theory
mental illness, unconscious and conscious elements of psyche come into conflict
treatment: unearthing hidden secrets of unconscious
Skinner’s theory
a behaviorist approach where mental illness arises from learned behaviors, and treatment focuses on modifying those behaviors through reinforcement.
treatment: unlearning through behavior modification
psychotherapy
a therapeutic approach to mental health that involves communication between a trained therapist and a patient to explore thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, aiming to improve emotional well-being.
former major disorder
general paresis of the insane
symptoms: mania, cognitive deterioration
cause: infection w treponema pallidum (syphilis)
paul ehrlich discovered penicillin as treatment
this showed that there is a biological basis for these illnesses (vitamin B deficiency, HIV in brain, autoimmune response)
pathophysiology
the study of the functional changes associated with or resulting from disease or injury.
IPSCs are induced pluripotent stem cells that can differentiate into various cell types, offering potential for regenerative medicine.
molecular medicine in psychiatry
human psychiatric disease → gene discovery → mouse disease model → disease pathophysiology → target identification and drug development → human clinical trials → new medicine → human psychiatric disease
Anxiety Disorders
caused by inappropriate expression of fear or worry.
Fear: adaptive response to threatening situations, innate and species specific fears, learned fears
biological bases: genetic predisposition
treatments: Psychotherapy, Anxiolytic meds (GABA, benzodiazepines, SSRIs), new drugs target CRH receptors (blocking could alleviate stress)
Panic Disorder
An anxiety disorder characterized by recurrent panic attacks and intense fear.
2% of population , more in women, 50% are usually depressed
generalized anxiety disorder: excessive, uncontrollable worry about various aspects of life.
specific phobias (social phobia: intense fear of social situations Engaging in social interactions, often leading to avoidance)
Agoraphobia
An anxiety disorder involving the fear of places or situations from which escape might be difficult.
PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder, a condition that occurs after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, characterized by flashbacks, nightmares, and severe anxiety.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
A mental disorder characterized by obsessions (recurrent thoughts) and compulsions (repetitive behaviors).
Obsessions: recurrent, intrusive thoughts, images, ideas, impulses
compulsions: repetitive behaviors to reduce anxiety
HPA Axis
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal axis; a complex set of interactions between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands involving stress responses.
Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone (CRH)
A hormone involved in the stress response and regulation of the HPA axis.
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol, playing a key role in the body's stress response.
humoral response
CRH → ACTH → cortisol
Amygdala
A brain structure involved in emotion regulation, particularly fear and anxiety.
regulate CRH neurons
Hippocampus
A brain region important for memory formation and regulation of the HPA axis.
regulate CRH neurons
Push-pull regulation
amygdala →+ HPA - ← hippocampus
HPA → cortisol → + hippocampus
if amygdala is overstimulated, high cortisol will overexcite hippocampal cells so they’ll die out, leading it to have less of a negative effect on HPA and leading to excessive cortisol production.
Learned fear
is an acquired emotional response to a specific stimulus, often resulting from negative experiences and mediated by the amygdala.
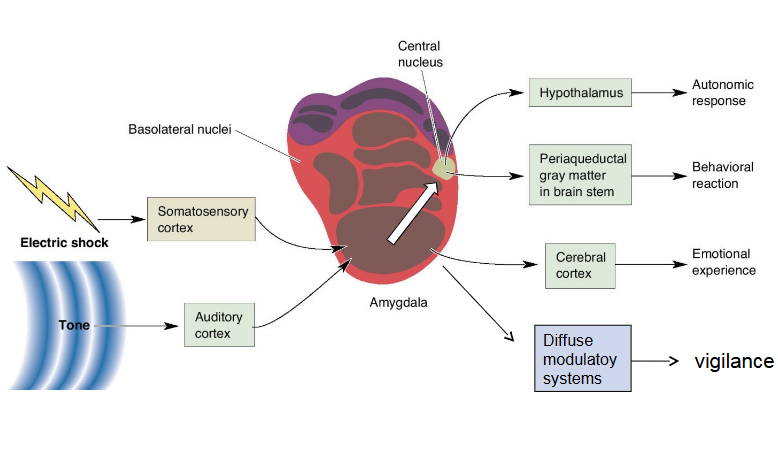
Affective disorders
are mental health conditions characterized by significant changes in moods, such as depression and bipolar disorder, affecting emotions and behavior.
untreated, lasts 4-12 months, 38,000 suicide/yr
depression: major depression, dysthymia: lower level
Diathesis-stress hypothesis
is a psychological theory that suggests that mental disorders develop from a combination of genetic predisposition (diathesis) and environmental stressors. This model emphasizes the role of both hereditary factors and life experiences in the onset of mental illnesses.
role of HPA axis: overactivity can cause depression because of low glucocorticoid receptors in hippocampus
impact of injected CRh
HPA function becomes hyperactive
child neglects leads to low glucocorticoids receptors in hippocampus and leads to poor negatie feedback on HPA
Anterior cingulate cortex dysfunction
refers to impaired functioning of a brain region involved in emotional regulation, decision-making, and impulse control, which can be associated with various mental disorders, including depression and anxiety.
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
A treatment for severe depression involving electrical stimulation of the brain.
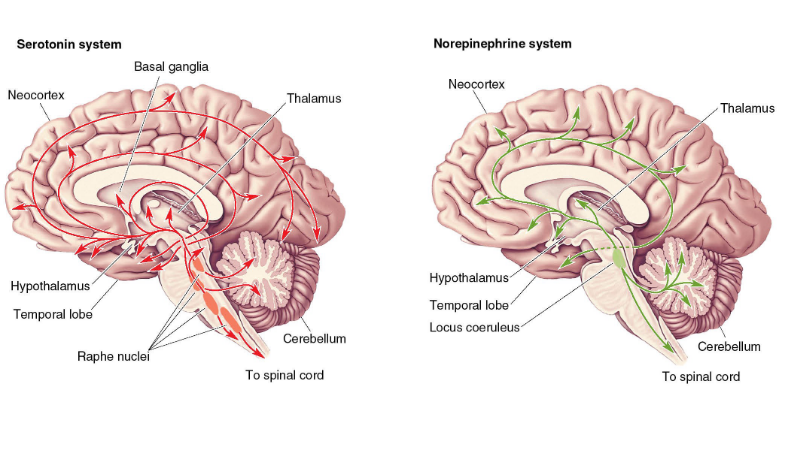
Monamine Hypothesis
A theory suggesting that depression is linked to a deficiency in certain neurotransmitters, particularly norepinephrine and serotonin. (deficit in diffuse modulatory systems)
reserpine: reduces Bp and mood, MAO inhibitors: kills Tb and elevates mood, Imipramine reuptake inhibitor
inhibition leads to inc in NA and DA
Bipolar Disorder
A mood disorder characterized by alternating periods of depression and mania.
Type 1: mania, Type 2: hypomania
tricyclic antidepressants
A class of medications used to treat depression by increasing levels of neurotransmitters in the brain, primarily norepinephrine and serotonin, by inhibiting their reuptake.
Tardive Dyskinesia
A potential side effect of antipsychotic medications characterized by involuntary movements.
Dopamine Hypothesis
A theory that suggests that schizophrenia results from an overactivity of dopamine pathways in the brain.
Glutamate Hypothesis
A theory that suggests schizophrenia may be linked to the dysfunction of glutamate receptors.
Lithium treatment for bipolar disorder
A mood stabilizer that helps reduce the frequency and severity of mood swings in individuals with bipolar disorder. Li-urate from manic patients injected in guinea pigs calmed them
MAO inhibitors
A class of antidepressant medications that work by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine oxidase, which breaks down neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain.
SSRI (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor)
A class of antidepressants that increase serotonin levels in the brain.
SSRIs take weeks to work because they promote neurogenesis in the hippocampus and they produce an upregulation of glucocorticoid receptors
Deep brain stimulation
A neurosurgical procedure that involves implanting electrodes in specific brain areas to alleviate symptoms of mood disorders, such as depression or obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
A psychological treatment that addresses faulty thoughts and maladaptive behaviors.
Penicillin
An antibiotic discovered to be effective in treating general paresis of the insane.
Affect Regulation
The ability to manage and respond to emotional experiences.
Impulse Control Disorders
Disorders characterized by the inability to resist a temptation or urge.
Pharmacotherapy
The use of medications to treat mental health disorders.
Biofeedback
A technique that teaches control over physiological functions by providing real-time feedback.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
A non-invasive procedure that uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain.
Behavioral Activation
A treatment that encourages patients to engage in activities that are emotionally rewarding.
Psychopathology
The study of psychological disorders and abnormal behavior.
schizophrenia stuff