Week 9: Microscopic Anatomy of the GI System
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, serosa
four layers of the GI Wall
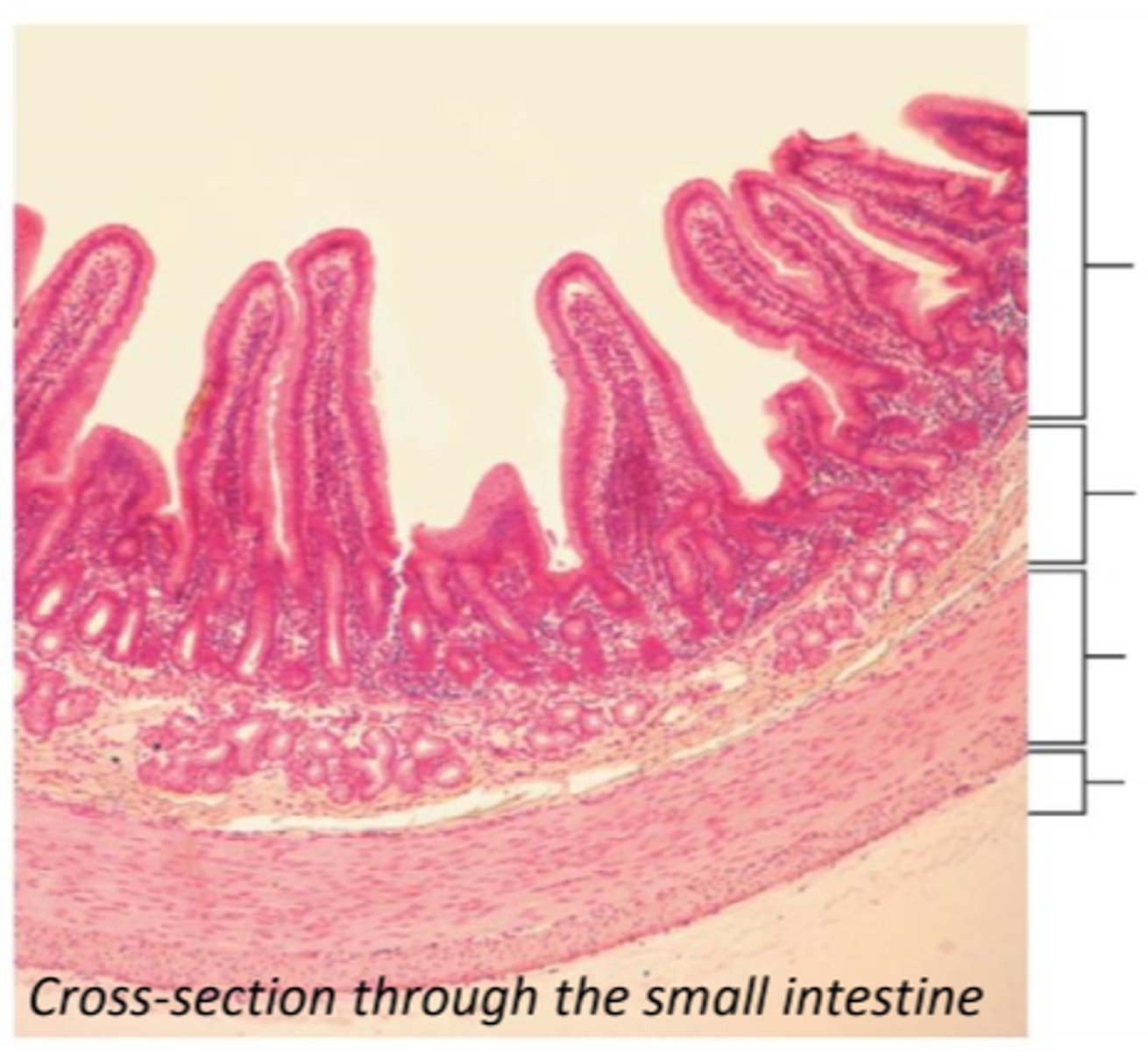
mucosa
comprises the innermost layer of the GI tract; contains many glands
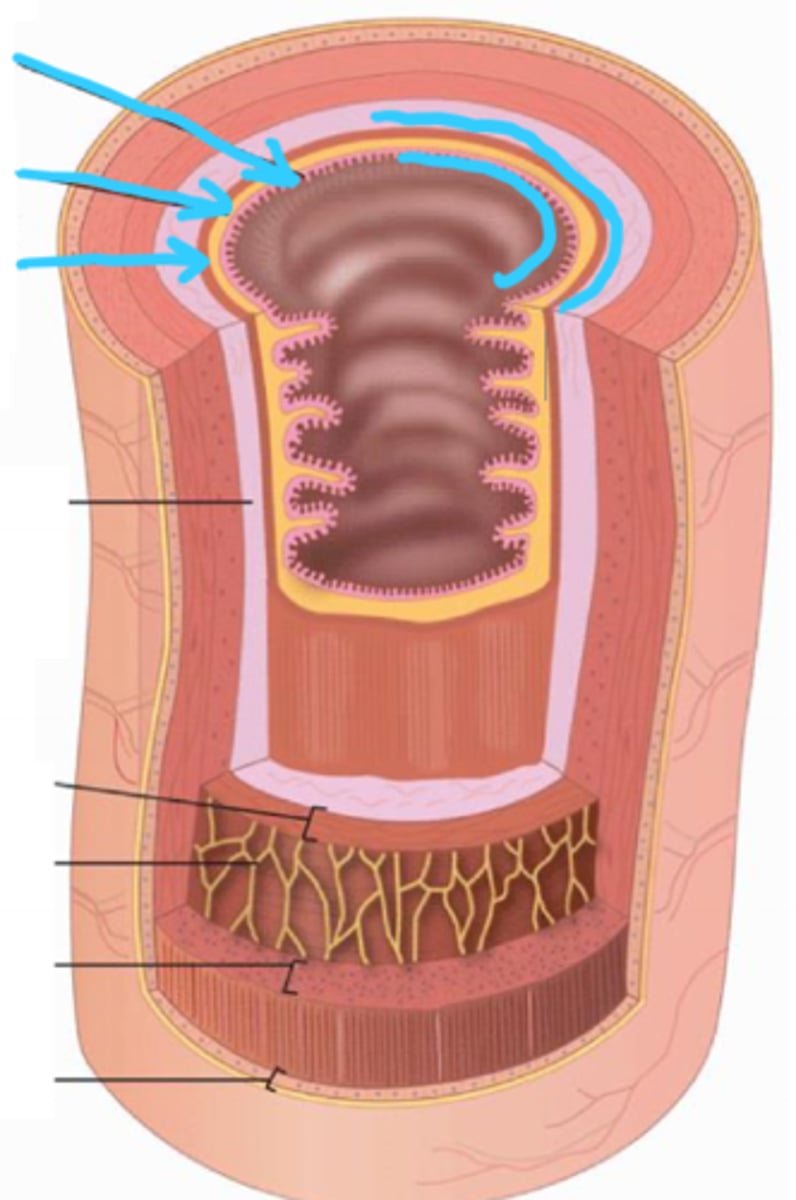
epithelium
lines the lumen of the mucosa in the GI tract
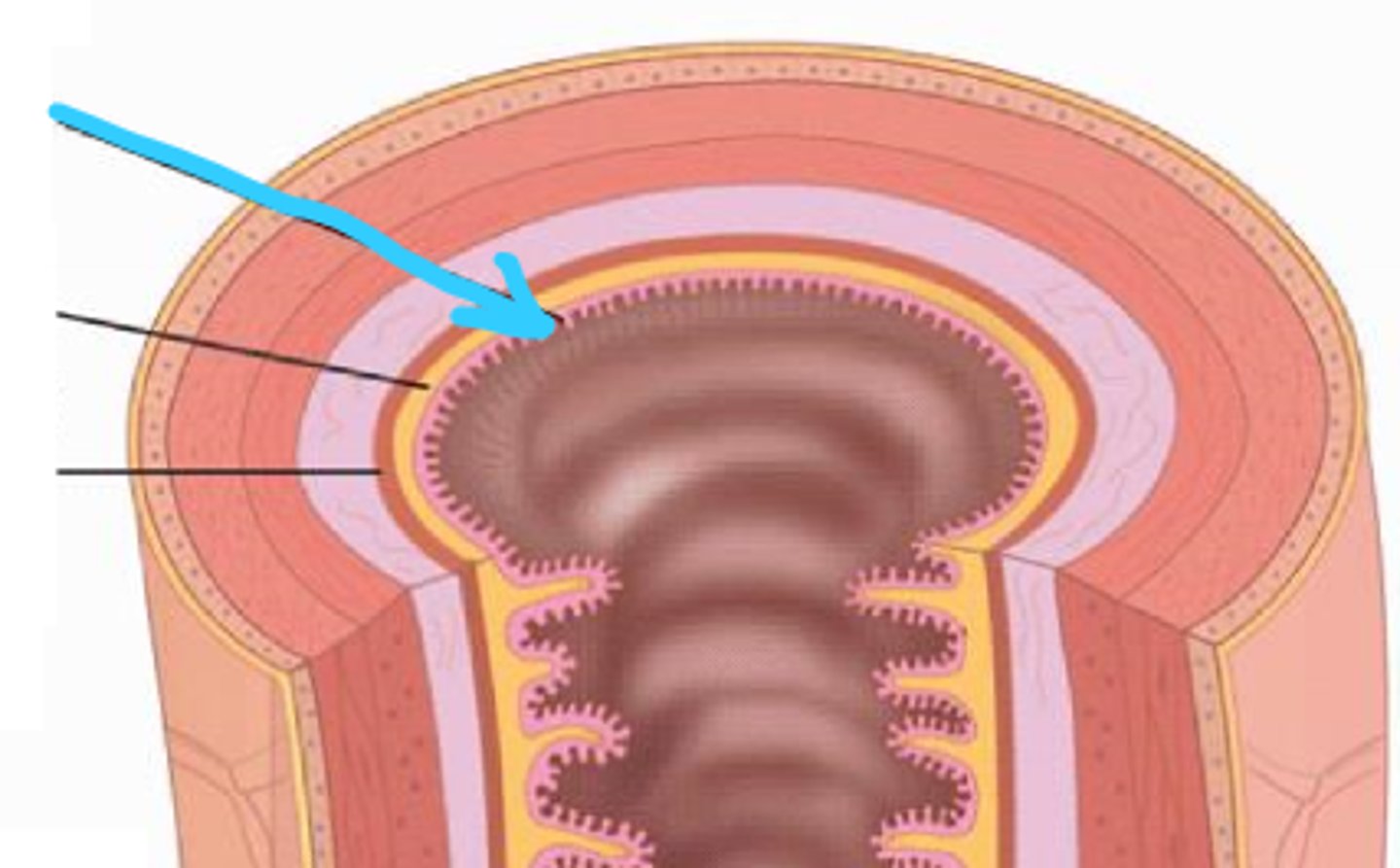
lamina propria
mucosa connective tissue supporting the epithelium; contains lymphatic tissue (MALT)
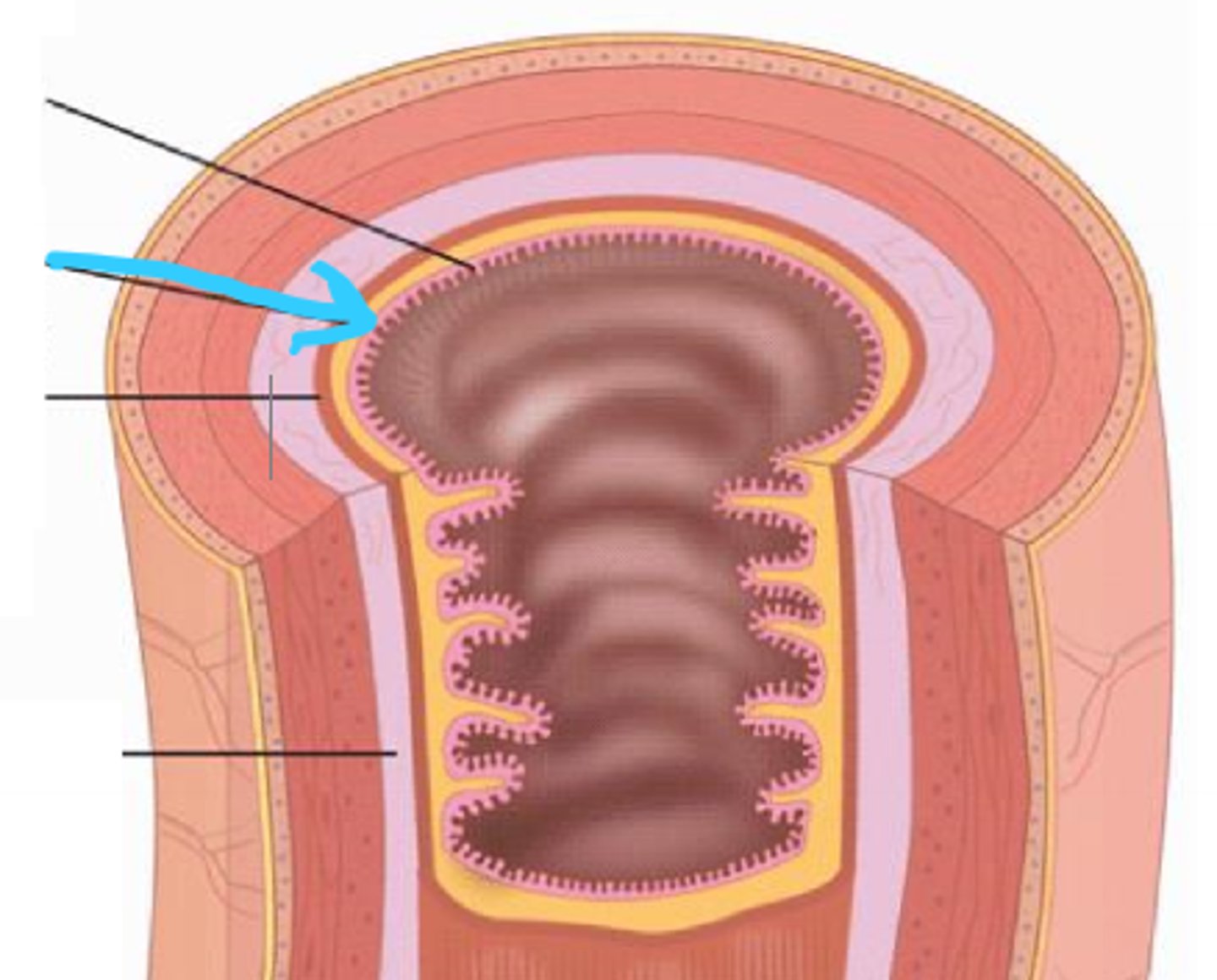
muscularis mucosae
part of the mucosa that is composed of a thin layer of smooth muscle in the GI tract
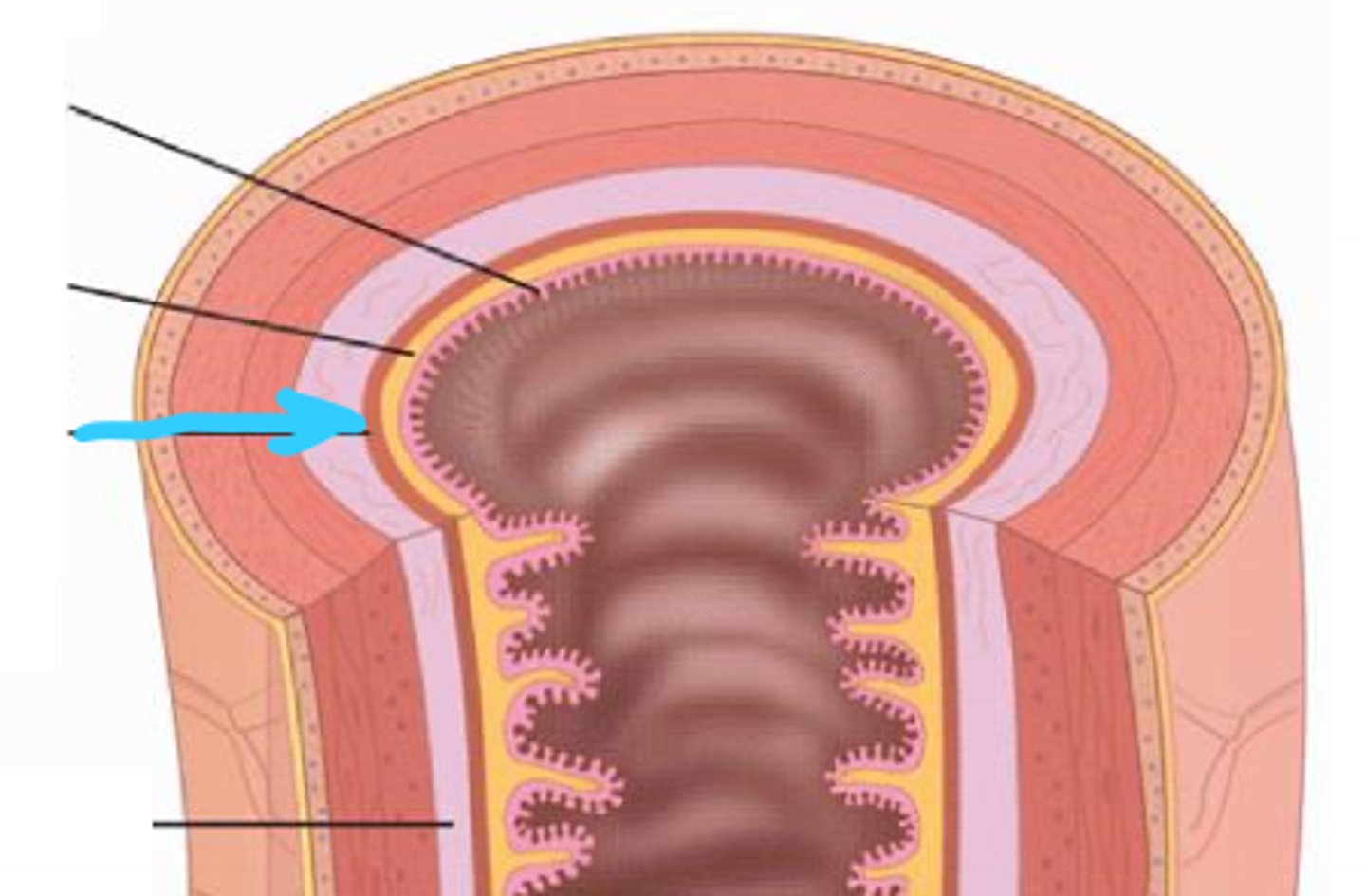
submucosa
connective tissue layer external to the mucosa; contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatics; may contain glands (found within the esophagus and duodenum only)
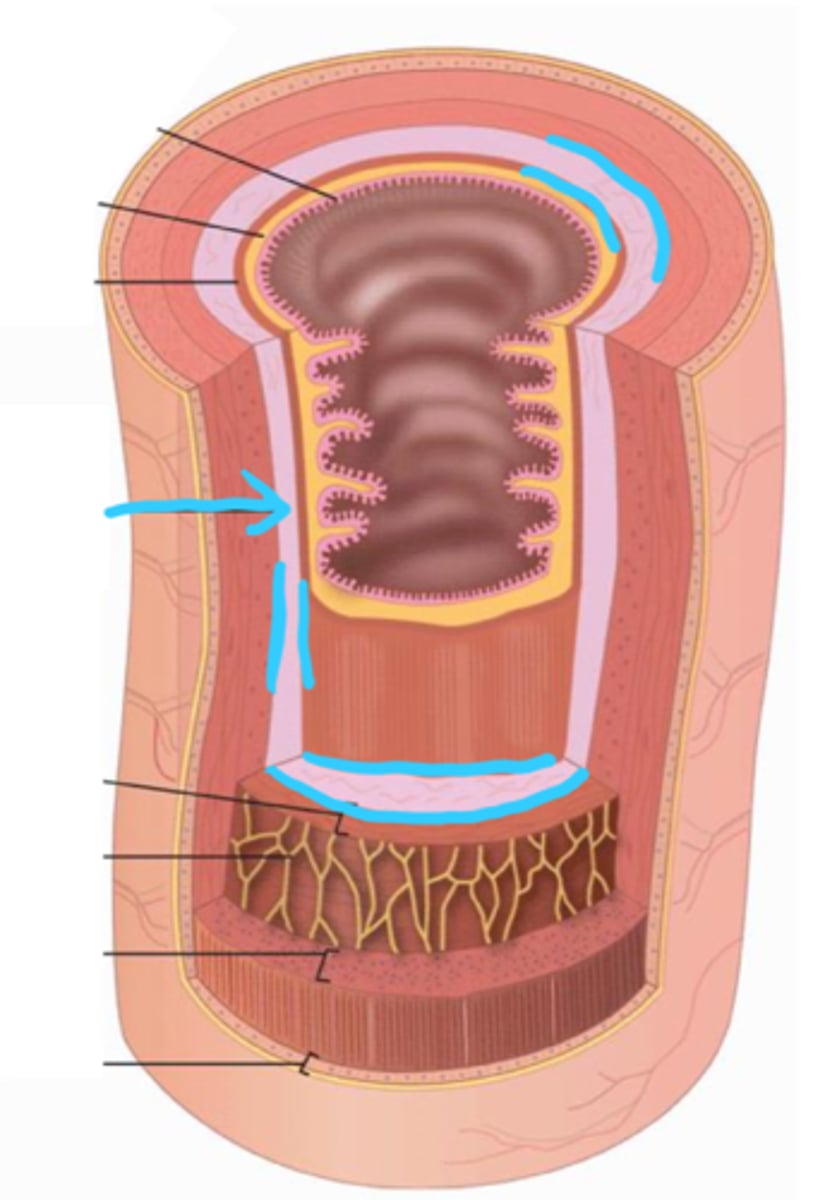
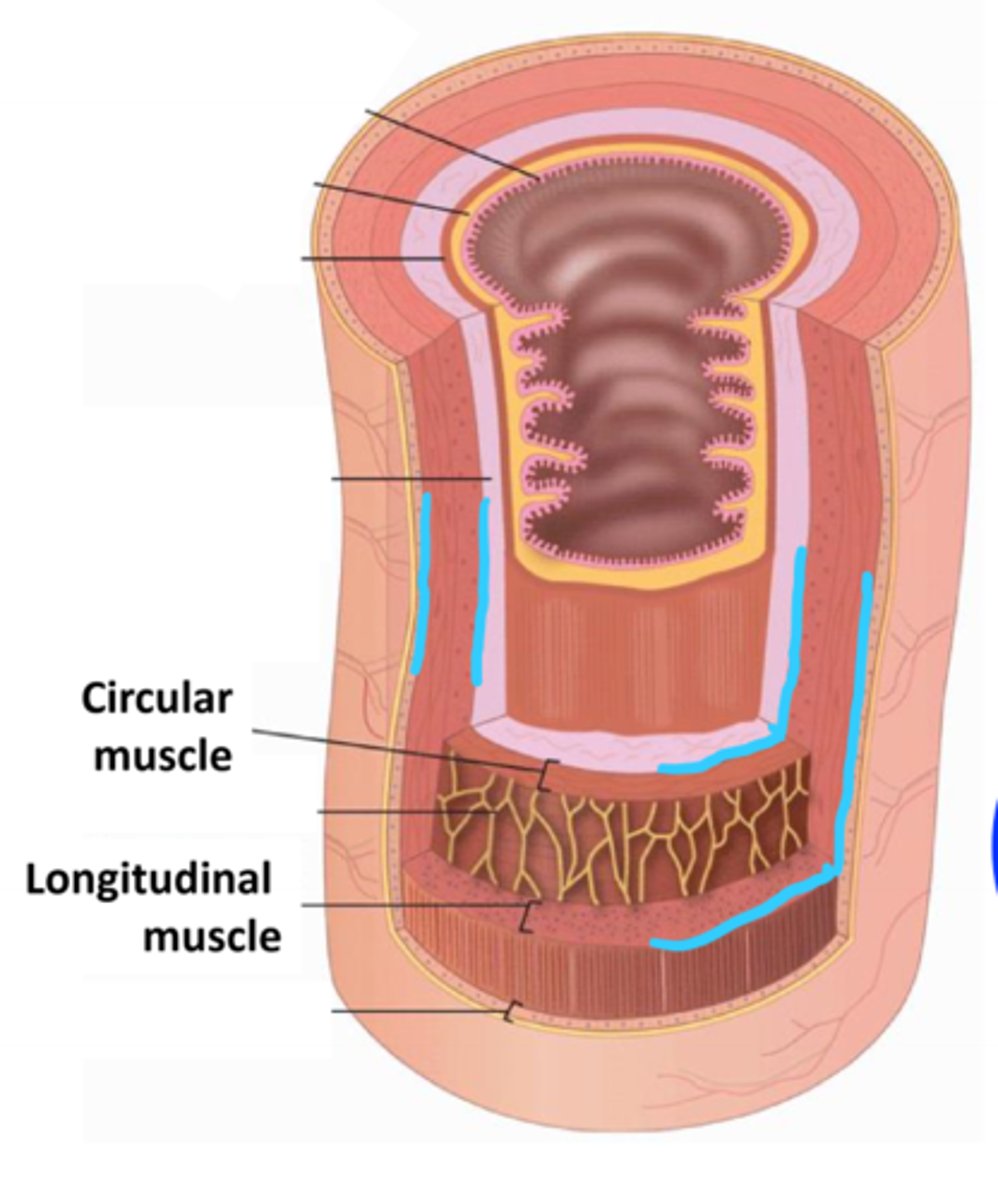
muscularis externa
layer of smooth muscle external to the submucosa; consists of a circular, longitudinal, and oblique layer (in stomach only)
serosa
connective tissue and simple squamous epithelium (mesothelium) that covers intraperitoneal organs
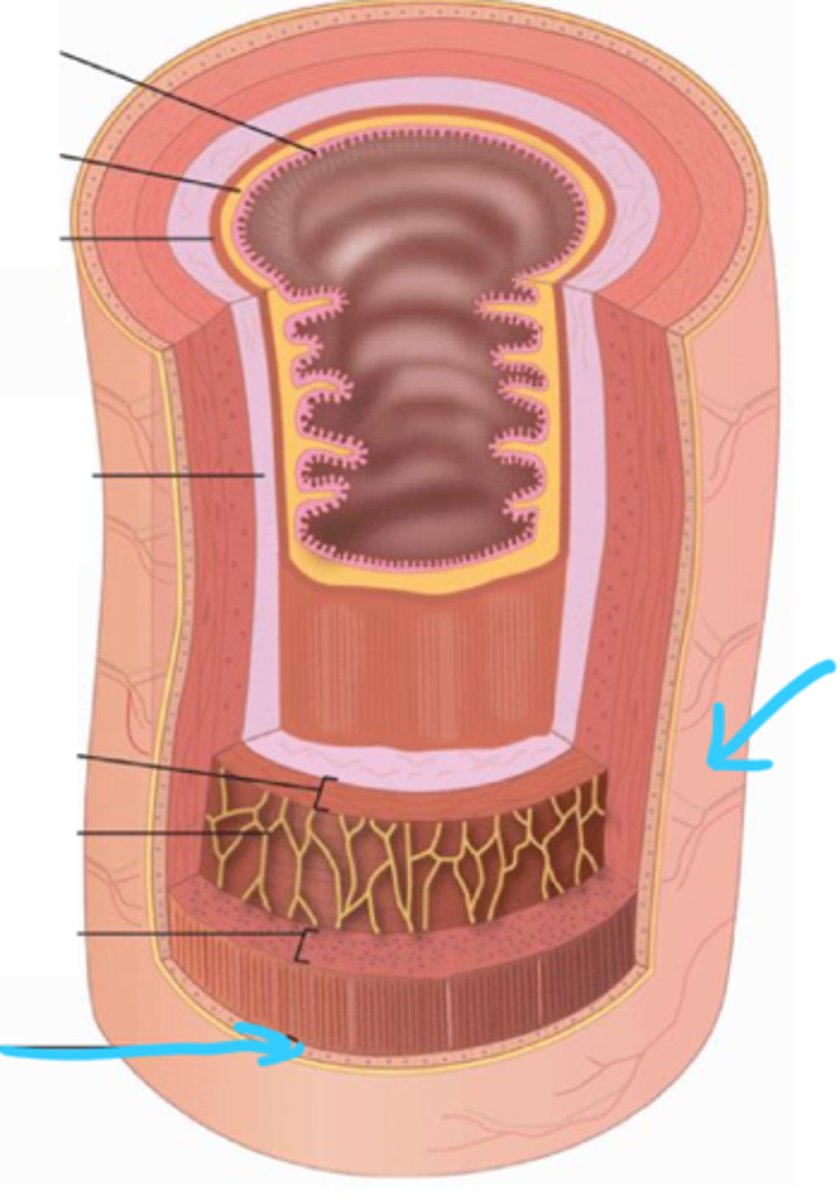
adventitia
connective tissue outer layer that covers retroperitoneal organs
oral cavity
function: ingestion, moisture production, and enzyme production
-recieves saliva from salivary glands
-lined by nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium
esophagus
function: conducts a food bolus from the oral cavity to the stomach
-mucosa with nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium and goblet cells
-submucosa has mucus secreting glands
-covered externally by adventitia
goblet cells
mucus secreting cells in the esophagus
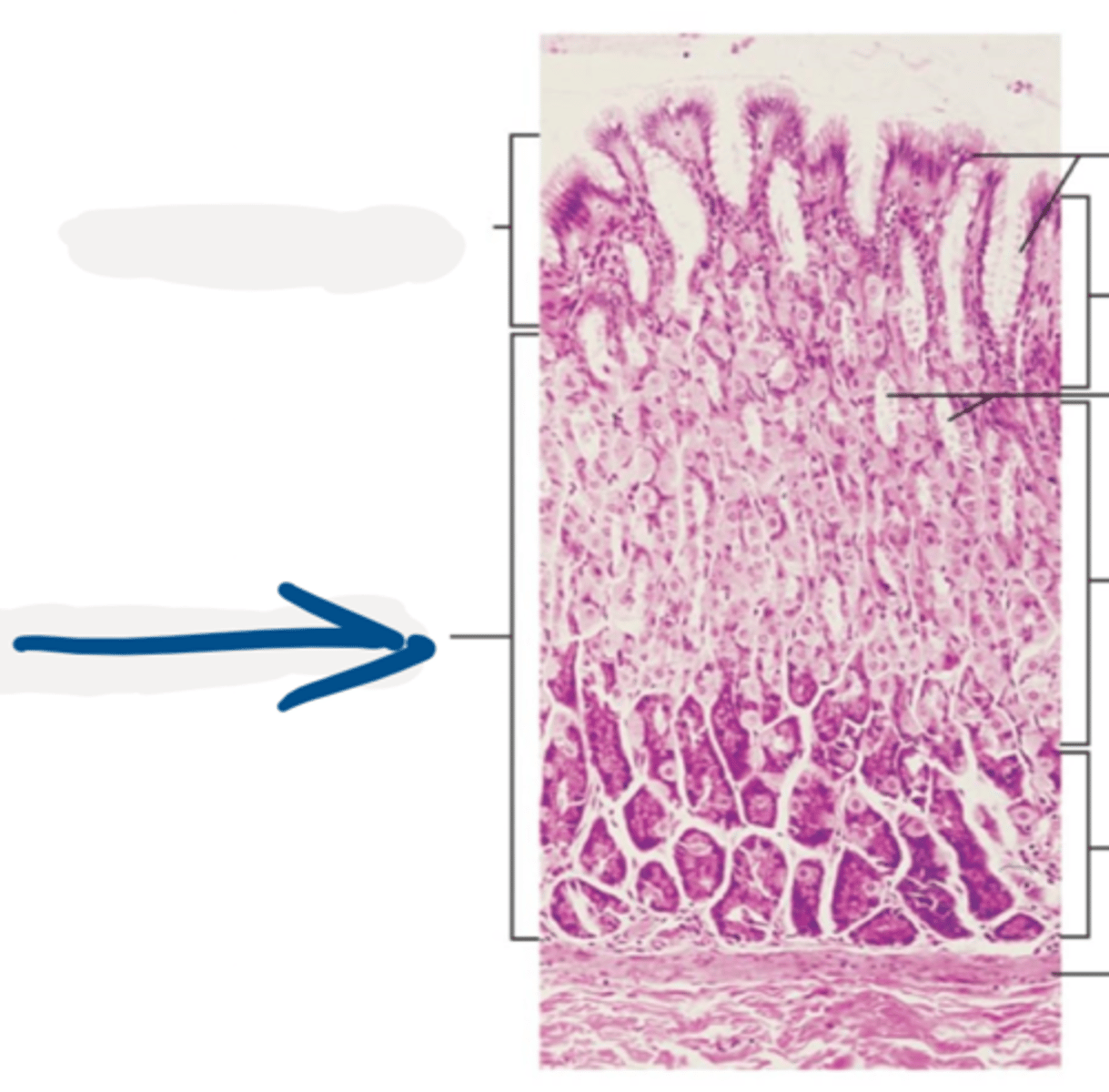
stomach
function: mechanical and enzymatic breakdown of food
-muscularis externa has an oblique layer in addition to circular and longitudinal layers
-epithelium secretes enzymes
-mucosa folded into rugae
rugae
the folds in the mucosa lining the stomach
oblique layer
the muscularis externa of the stomach has an _____________________ in addition to the circular and longitudinal layers
simple columnar
stomach mucosa is lined by _______________________ epithelium
gastric pits
form depressions in the stomach
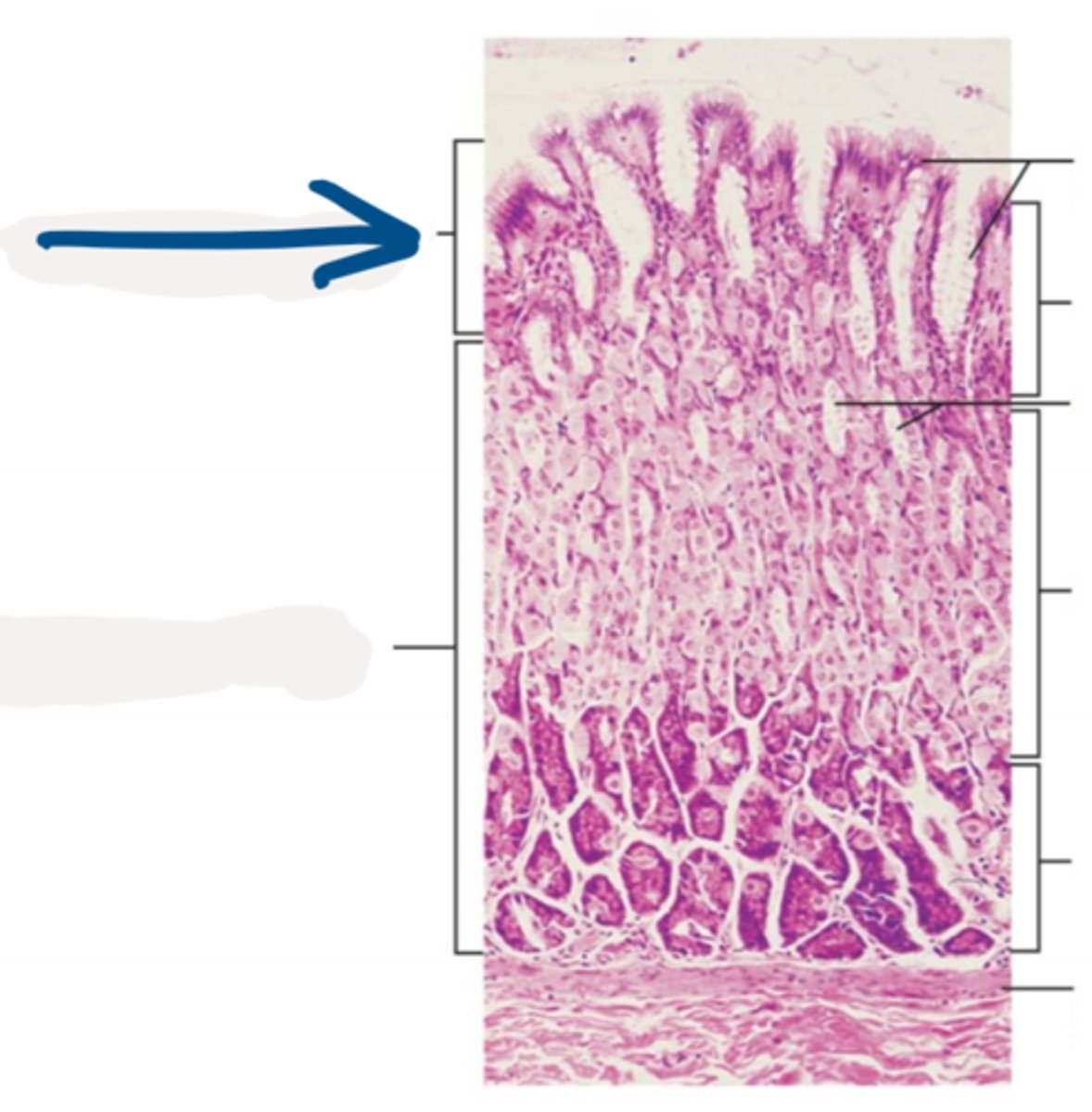
gastric glands
____________ in the lamina propria of the stomach mucosa secrete pepsinogen, hydrochloric acid, and mucus
small intestine
function: enzymatic digestion and nutrient absorption
three component: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
villi
projections of mucosa increasing small intestine surface area; contain blood vessels and lymph channels (lacteals) - glands are located in between
lacteals
Specialized lymphatic capillaries in the small intestine
microvilli
small projections of villi from epithelial cells (enterocytes)
simple columnar
the mucosa of the small intestine is lined by __________________ epithelium
enterocytes
major absorptive cells of the epithelium which have microvilli
duodenum
the first portion of the small intestine; receives bile and pancreatic enzymes; has long leaf-like villi
brunner glands
within the submucosa of the duodenum; secrete bicarbonate to neutralize stomach contents
jejunum
the second portion of the small intestine responsible for nutrient absorption; epithelium is mostly composed of enterocytes; contains long, finger-like villi are present
ileum
the third portion of the small intestine; contains many goblet cells and Peyer patches (lymphoid tissue); contains short, broad villi
colon
function: water and electrolyte absorption
lined by simple columnar epithelium; enterocytes absorb water and electrolytes; goblet cells secrete mucus
simple columnar
the colon is lined with __________________ epithelium
long, short, no
the duodenum and jejunum contain __________ villi
the ileum contain __________ villi
the colon contains _________ villi