BIOL 1113 (General Biology 2) Exam 2 Mary Susan Potts Santone
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Virus
Obligate intracellular parasite composed of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat; cannot reproduce outside living cells; can be culture only inside living cells; cannot move, metabolize or respond to stimuli; evolve as a result of mutation and natural selection; very specific; all are infectious
Capsid
Protein coat of viruses the encloses a genome
Nucleic acid core
DNA or RNA in a virus that is either single or double stranded; linear or circlar
(4) morphological categories
Icosahedral, complex, helical, spherical
Type of nucleic acid, size, shape, and presence of outer envelope
What is the classification of viruses based on?
Bacteriophage
A virus that infect and replicates within a bacterium
Lytic cycle
Attachment, penetration, biosynthesis, maturation/assembly, release; growth cycle of the bacteriophage in which the production and release of new viruses; ultimately leads to cell lysis
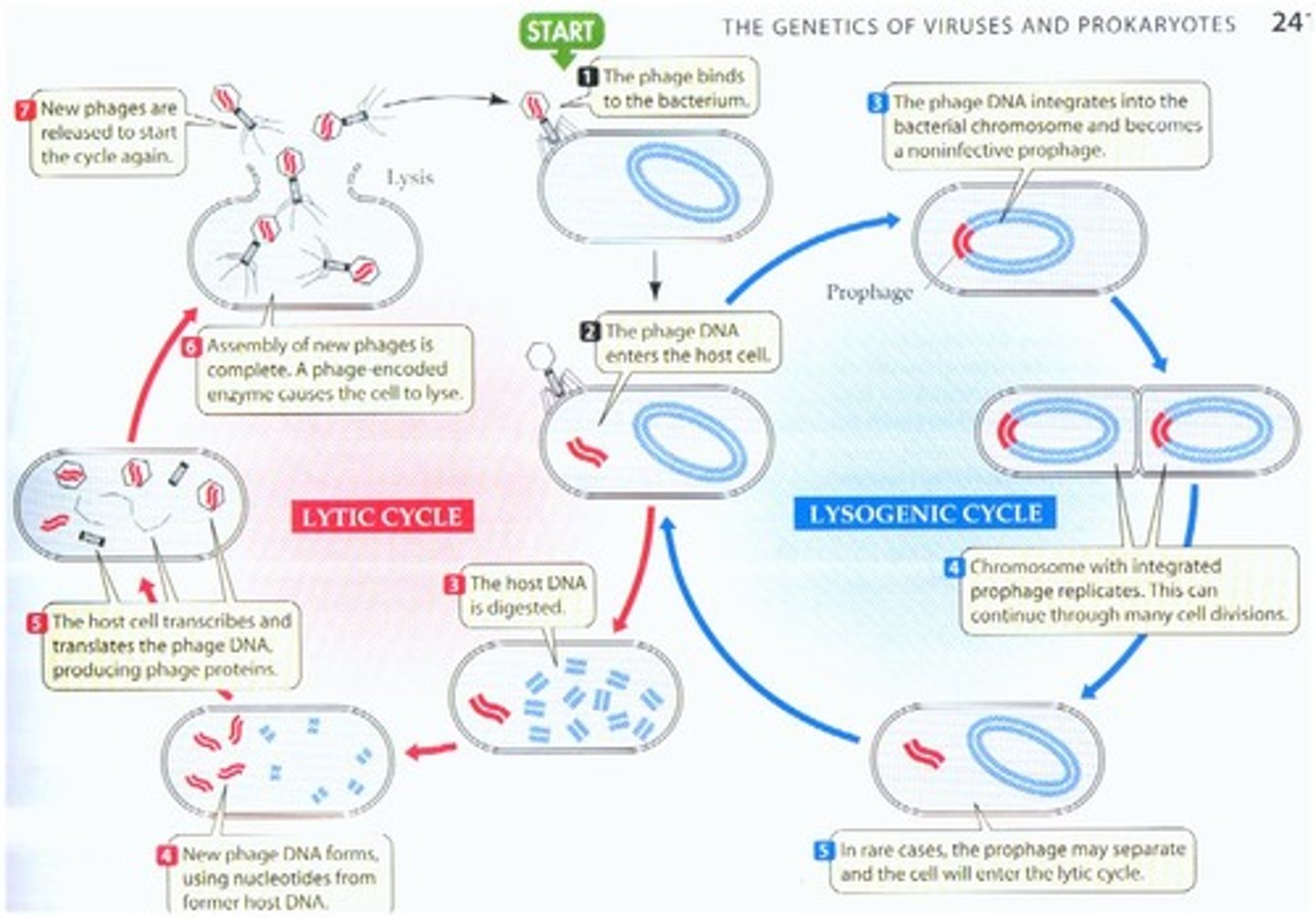
Lysogenic cycle
Growth cycle of a bacteriophage consisting of integration, prophase integration, and excision; new phages are not made and the host cell is not destroyed during this cycle
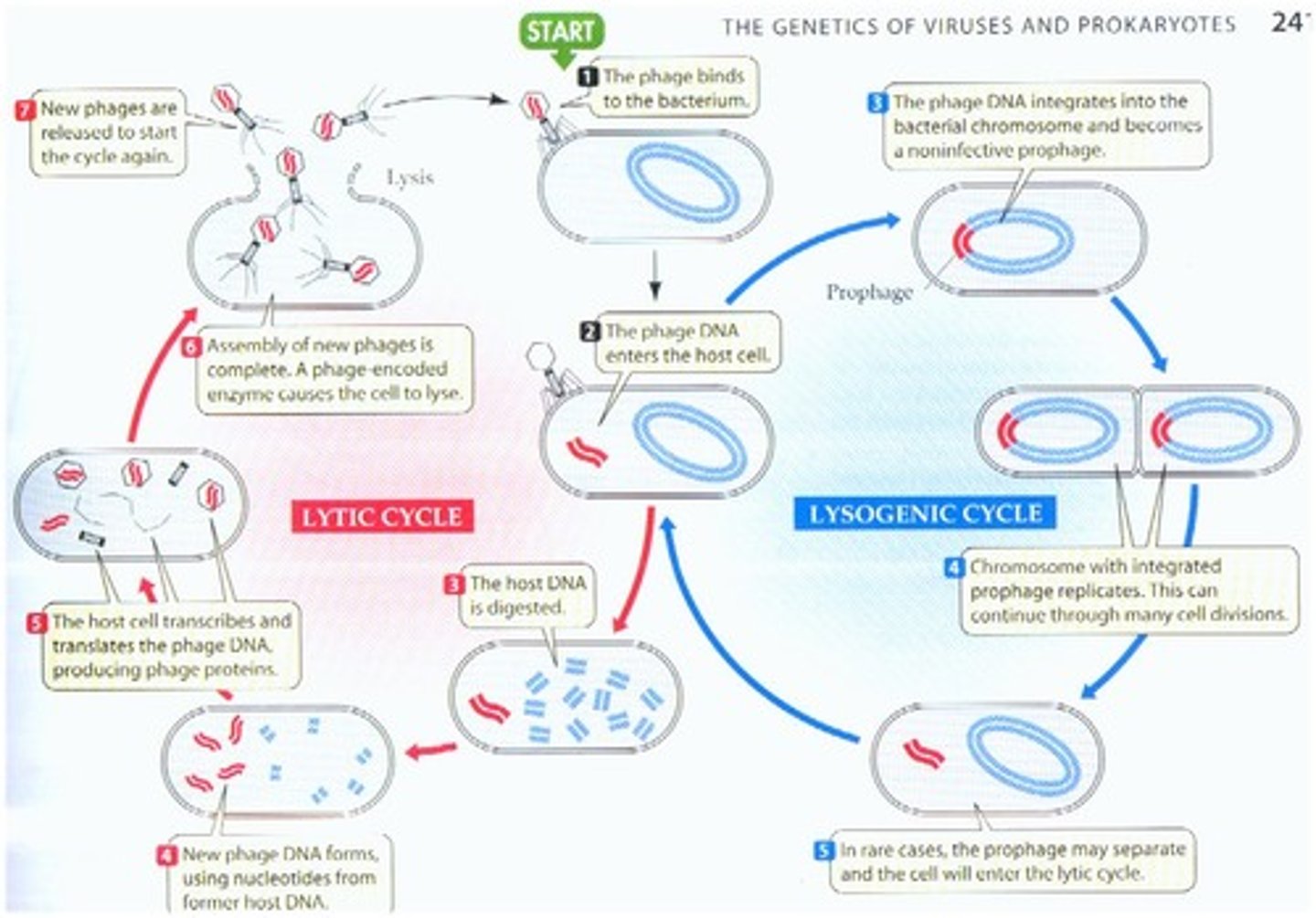
Prophage
The genetic material of a bacteriophage, incorporated into the genome of a bacterium and able to produce phages if specifically activated
Viroid
naked strands of RNA; causes many crop diseases
Prion
Protein molecules with contagious tertiary structure; causes some human and other animal diseases
Emerging disease
Disease that that has appeared in a population for the first time, or that may have existed previously but is rapidly increasing in incidence or geographic range
HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus, is the cause of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome; primarily spread by sexual contact between infected and uninfected individuals.
Zika Virus
Viral illness that causes fever, rash, joint pain, and conjunctivitis; mosquito is vector; spread from Africa to the Americas
Prokaryote
Single-celled organism that has neither a distinct nucleus with a membrane nor other specialized organelles; bacteria and archaea
Bacteria
Domain of prokaryotes; Cell wall contains peptidoglycan; base sequence of rRNA different from archaea; most 1-5 micrometers
Archaea
Domain of prokaryotes; cell walls contain polysaccarides and proteins; base sequence of rRNA different from bacteria; biochemically more like Eukarya than bacteria; better suited for extreme environments
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Movement of one or more genes from one species to another; increases genetic diversity; common among archaea and bacteria
Prokaryote cell surface
Plasma membrane surrounded by cell wall surrounded by glycocalyx
Cilia
An organelle used for cell movement; lines the surface of the cell an beats in rhythmic waves to provide locomotion
Flagellum
A thin, threadlike structure on cells that provides locomotion by whipping back and forth; prokaryotic type spin, propelled by machines composed of a filament, hook, and motor
Binary fission
Asexual reproduction in which the fully grown parent cell splits into two halves, producing two new cells
Budding
Asexual reproduction in which a new organisms develops from a bud due to cell division at one particular site
Conjunction
Sexual reproduction where sex pilus forms between two cells; donor cell passes DNA to recipient through puilus
Transformation
Sexual reproduction that occurs then bacterium picks up free pieces of DNA from other prokaryotes
Transduction
Sexual reproduction when bacteriophages carry portions of bacterial DNA from one cell to another
Plasmid
Small, circular, double stranded, DNA molecule within a cell, separate from chromosomal DNA;
Endospore
Asexual spore that develops inside some bacteria cells; response to unfavorable reproduction conditions of cells
Obligate aerobes
Prokaryotes unable to grow in the absence of free oxygen
Obligate anaerobes
Prokaryotes unable to grow in the presence if free oxygen; these organisms can cause botulism, gangrene, and tetanus
Facultative anaerobes
Prokaryotes able to grow in either the presence or absence of oxygen
Autotroph
An organisms capable of synthesizing its own food from inorganic substances using light or chemical energy
Heterotroph
An organism incapable of manufacturing its own food and instead must obtain food and energy by taking in organic substances
Photoautotroph
An organisms that carries out photosynthesis to synthesize its own food
Chemoautotroph
Organisms that oxidizes inorganic compounds to obtain energy; reduces CO2 to use for organics it needs to synthesize
Saprotroph
Organism that feeds on or derives nourishment from decaying organic matter; decomposers
Symbiosis
A relationship between two or more organisms that live closely together; there are many types such as commensalism, parasitism, or mutualism
Commensalism
Symbiotic relationship where one benefits the other without affecting it
Mutualism
Symbiotic relationship where both organisms benefit
Parasitism
Symbiotic relationship where one organisms lives off and harms the other
Common bacterial diseases
Salmonela, E. coli, anthrax, syphillis, gonorrhea, chlamidya, plague, whooping cough, lyme disease are examples of what?
Antibiotic
A medicine that inhibits the growth of or destroys microorganisms
Gram-positive (bacteria)
Type of bacteria that stains purple, has a thick peptidoglycan layer on outer envelope, and responds most to cillin antibiotics
Gram-negative (bacteria)
Type of bacteria that stains pink, has thin peptioglycan layer covered by a thin lipoplysaccharride layer
Shapes of bacteria
Round, rod, comma, rigid spiral, and flexible spirals are all what?
Pseudopodia
A temporary cytoplasm filled projection of an cell that provides locomotion by extending forward then retracting the body in the direction of movement
Archaea
This domain of organisms are mostly chemoautotrophs found in harsh conditions, sometimes mutualistic or commensalistic, never parasitic or photosynthetic
Extremophile
An organisms that thrives in physically or geochemically extreme conditions.
Methanogen
Archaea that produce methane gas from H2 and CO2; may live in anaerobic marshes or ruminant (herbivorous) gut
Halophile
Archaea that require high salt concentrations to grow; often found in salty lakes
Thermoacidophile
Archaea that reduce sulfides and survive best at temps above 80ºC; plasma membranes contain unusual lipids that allow tolerance to high temps
Protist
Any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal plant or fungi; very diverse: some photoautotophic (many plankton), some heterotrophic, many symbionts, some pathogenic/parasitic; difficult to classify
Eukaryotes
Discoba, Land plants and relatives, Stramenopila, Alveolata, Amoebozoa, Rhizaria, and Opisthokonta are supergroups of what ?
Discoba
Euglenozoa, Kinetoplatids, and Metamonada are a part of what supergroup ?
Euglenoids
Small freshwater unicellular organisms; difficult to classify; have 2 flagellae and an eyespot; have chloroplasts surrounded by 3 rather than 2 membranes
Kinetoplastids and Metamonada
Colorless heterotrophs with unusual mitochondria; most symbiotic and many parasitic; well known for causing carious disease in humans
Kinetoplastids
Trypanosomes (African sleeping sickness) and Leishmania are types of what class of eukarya?
Metamonada
Giardia lamblia (common flagellate in digestive tract) and trichomonas vaginalis (sexually transmitted protist) are types of what class of eukarya?
Land plants and their relatives
Green algae, red algae, haptophytes, and the Kingdom Plantae are a part of which eukaryotic supergroup?
Stramenopila
Brown algae, diatoms, and water molds are a part of which eukaryotic supergroup ?
Alveolata
Ciliophora, Dinozoa, and Apicomplexa are a part of which eukaryotic supergroup?
Amoebozoa
Amoeboids and slime molds are a part of which eukaryotic supergroup?
Rhizaria
Foraminiferans, Radiolarians, and Chlorarachniophyta are a part of which eukarytoic supergroup ?
Opisthokonta
Chanoflagellates and Kingdoms Animalia and Fungi are a part of which euaryotic supergroup ?
Green Algae
Member of the phylum Chlorophyta, this classification of organisms are found in a variety of environments; majority are unicellular, but many are filamentous or colonial; some are multicellular and resemble leaves of lettuce; some symbiotic with fungi, plants, or animals.
Red Algae
Member of the phylum Rhodophyta, this classification of organisms are multicellular, found in marine environments, and are of great economic importance for their use in things such as agar, carrageenan, and sushi
Brown Algae
Member of the supergroup Stramenopila, this classification of organisms often live in cold ocean waters along rocky coasts; never unicellular and can come in small simple form or large forms that may exceed 200m in length; seaweeds, kelp, rockweed, holdfast, stipe, blade, air bladder,
Diatom
Member of the supergroup Stramenopila, this classification of organisms are the most numerous unicellular algae in the oceans; they make up a significant portion of phytoplankton; cell wall constructed of two valves (larger valve acts as lid) and cilia
Dinozoa
Member of the supergroup Alveolata, this classification consists of aquatic and marine unicellular organisms; they have cells bounded by protective cellulose plates and have two flagella;
Ciliophora
Member of the supergroup Alveolata, this classification of organisms are among the most complex of the protozoans: have hundreds of cilia beat in coordination, most are holozoic (swallow food whole), divide in asexual reproduction, have two nuclei of differing types (micronucleus: heredity; macronucleus: metabolism)
Apicomplexans
Member of the supergroup Alveolata, this classification of nonmotile obligate parasites (move around in spore state) contain apical complex of organelles on mesozoites/sporozoites; are parasites and one species causes Malaria, another causes toxoplasmosis
Plankton
Microscopic organisms drifting or floating in the sea of fresh water, consisting chiefly of diatoms, protozoans, small crustaceans, and the eggs and larval stages of larger animals; Many animals are adapted to feed on these organisms.
Amoeboids
Members of the supergroup Amoebozoa, these organisms move and ingest their food with pseudopods; Entamoeba histolytica is a parasite of the human colon; Naegleria fowleri causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis
Foraminiferans and Radiolarians
Members of the supergroup Rhizaria, these two classifications of organisms both have skeleton of either calcite or silica
Choanofagellates
Members of the supergroup Opisthokonta, this classification of microscopic organisms are found in marine and fresh water environments, can be solitary or colonial, attached or free swimming, and have single flagellum surrounded by collar of microvillia
Modes of nutrition
(look in lab book)
Spore
Unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival until finding a suitable habitat to grow
Life cycle of Plasmodium vivax
Asexual reproduction
Type of reproduction by which offspring arise from a single organisms and inherit the genet of that parent only
Sexual reproduction
Type of reproduction by which organisms combine genetic information from two individuals of different sexes
Conjugation
The temporary union of two bacteria or unicellular organisms for the exchange of genetic material
Red tide
Tremendous concentrations of dinoflagellates in the water collumn
Zooxanthellate
Symbiotic dinoflagellates in corals
Paralytic shellfish poisoning
When toxins from dinoflagellates affect organisms higher up the food chain than the filter-feeders that ingest dinoflagellates, especially effects humans who may eat shellfish
Paramecium
Ciliates that partake in conjugation where the macro nucleus will degenerate and the micro nucleus with replicate through meiosis; when the paramecium conjugate, the organisms will swap micro nuclei and one will become the new macronucleus
Haploid life cycle
Life cycle where haploid cells turn into gametes, gametes fuse to form diploid zygote that undergoes meiosis to produce many haploid cells; occurs in organisms like volvox, dinoflagellates, sporozoans, and trypanossomes; organisms that we recognize are in their haploid state
Sporic/alternation of generations (life cycle)
Life cycle where in the course of the cycle we see two multicellular individuals, sporophyte (diploid) and gametophyte (haploid) generations;
a gametophyte gametes fuse into diploid zygote, which becomes a diploid sporophyte that produces a sporangium where meiosis occurs and produces haploid gametophyte spore; green plants, algae, and foraminiferans
Diploid life cycle
Life cycle where we recognize the diploid individual; haploid gametes fuse into diploid zygotes that undergo lots of mitosis; Animals, green algae, diatoms, ciliates
Fungi
Sapotrophic decomposers that include mushrooms, mildew, mold, morels, and yeasts
Osmotrophy
Uptake of dissolved organic compounds by osmosis for nutrition
Thallus
A plant body that is not differentiated into stem and leaves and lacks true roots and a vascular system
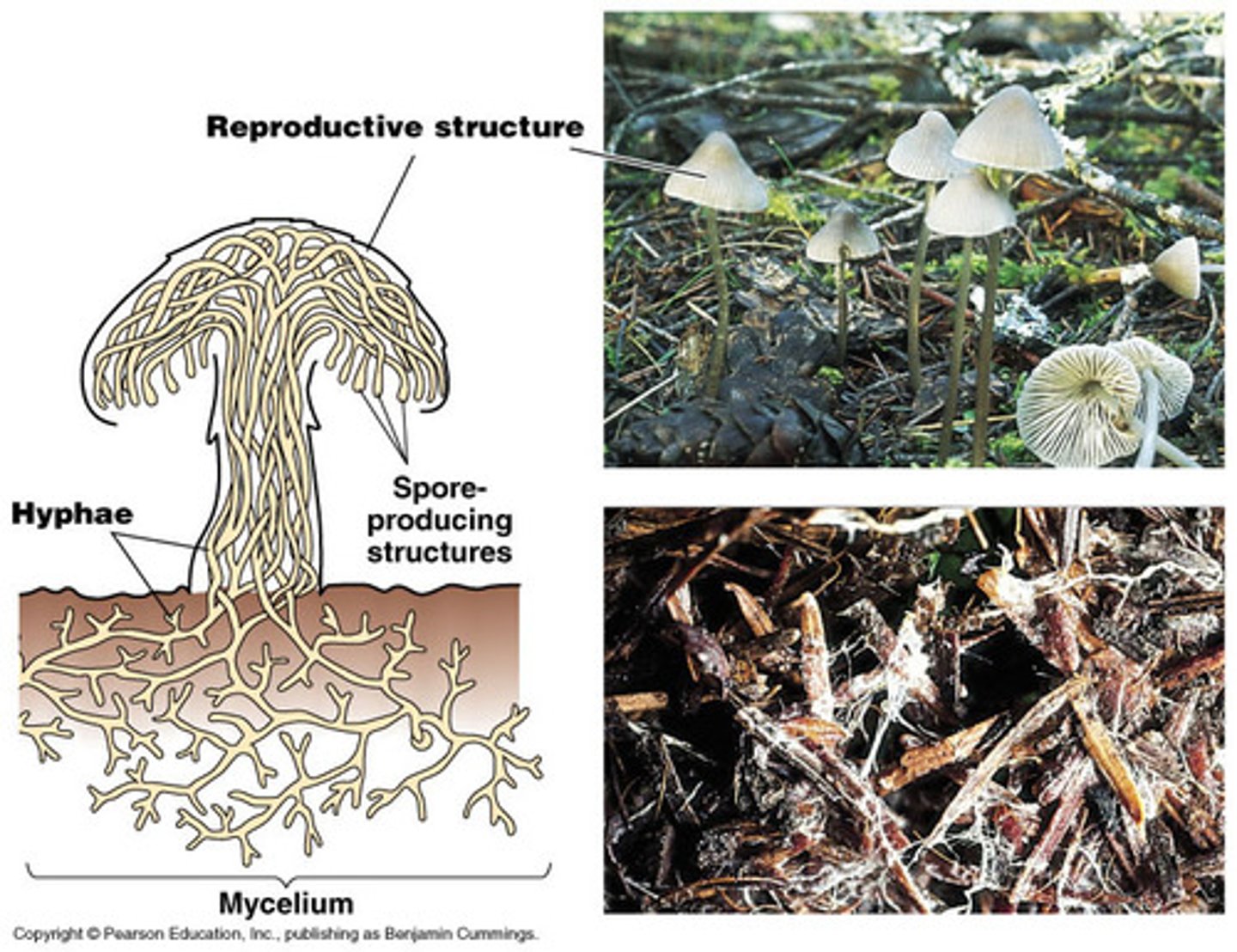
Mycelium
Fungal body composed of vast network of thread-like filaments called hyphae
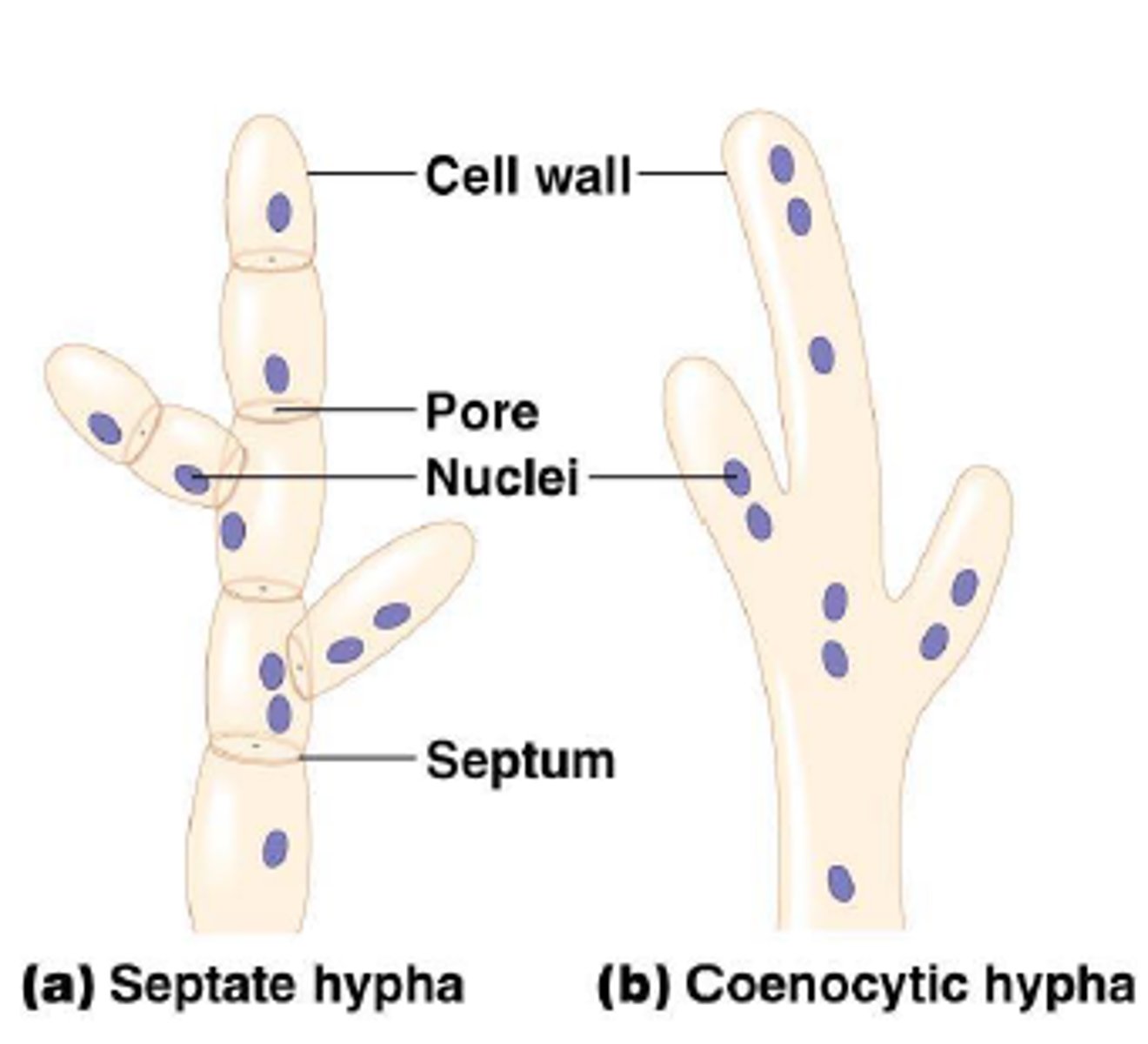
Aseptate fungi
Type of fungi with hyphae that is not partitioned by septa; multinucleated
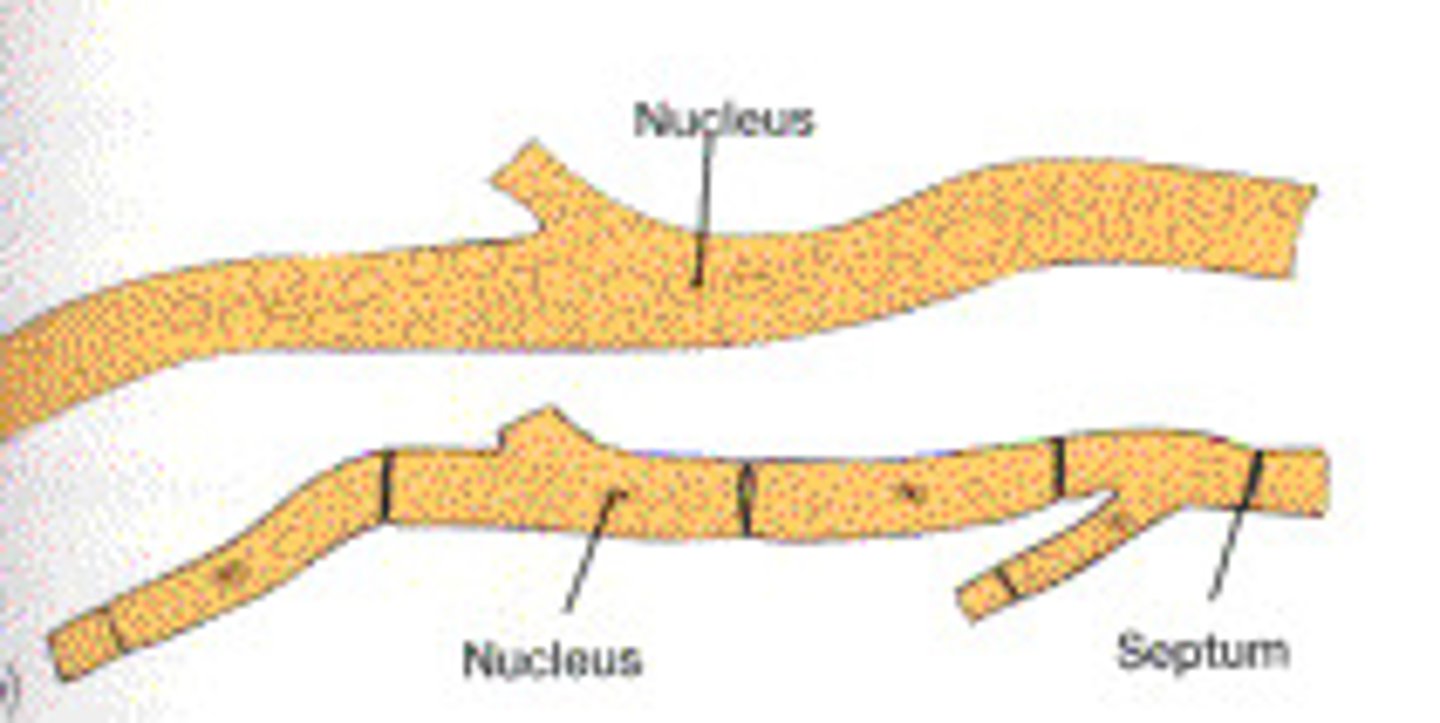
Septate fungi
Type of fungi with hyphae that is partitioned by septa (cross walls); ascomycota (sac fungi) basidiomycota (club)
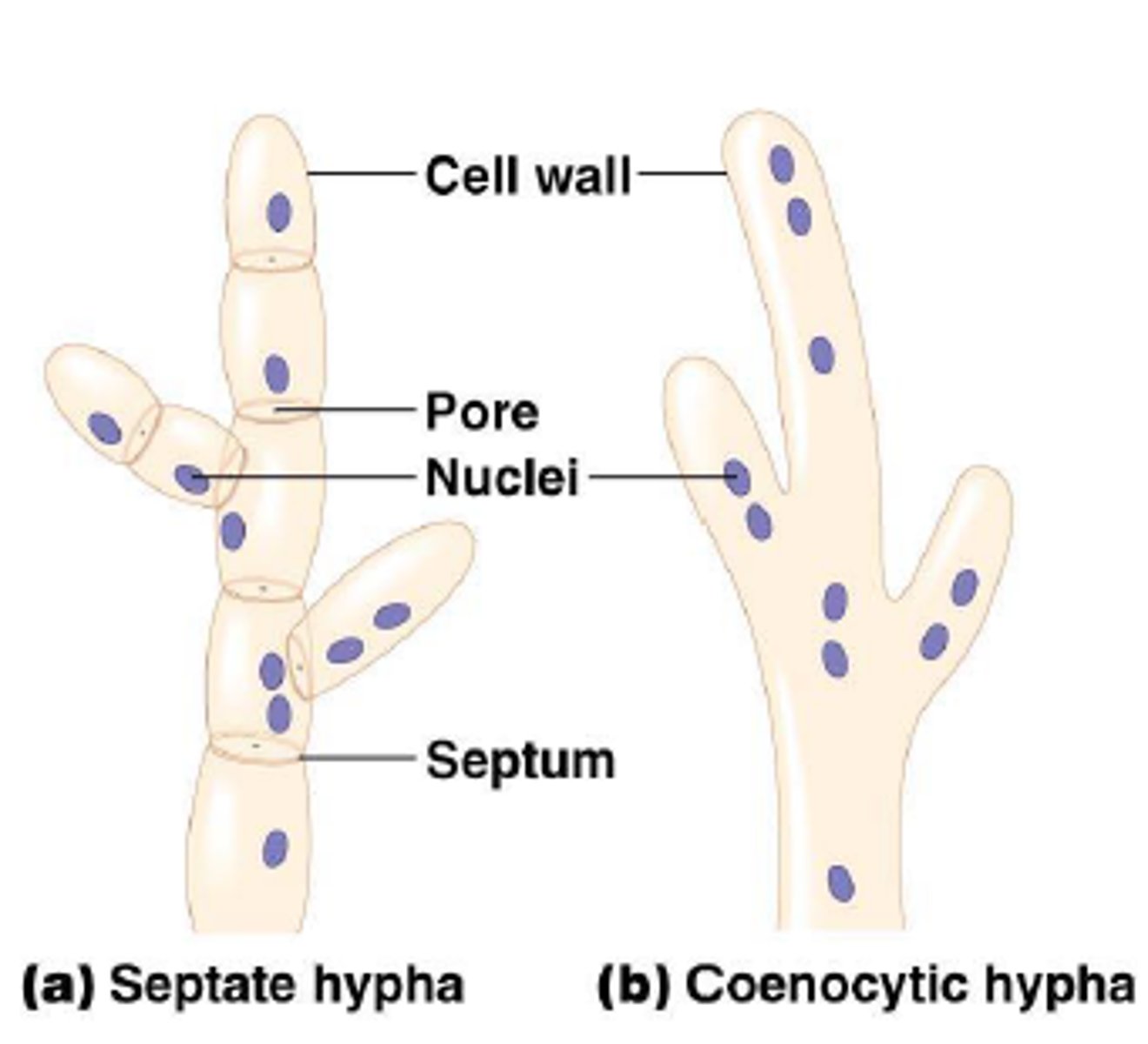
Hyphae
A branching filament that make up the mycelium of a fungus
Chitin
A polysaccharide that makes up the cell walls of fungi
(Fungal) sexual reproduction
Way that fungi reproduce which involves four different stages: haploid hyphae, dikaryotic stage, diploid zygote, spores
(Fungal) asexual reproduction
Way that fungi reproduce that involves sporangium and zygospores
Bread molds (zygospore fungi)
Type of fungi, mainly saprotrophs that decompose animal and plant remains; some parasites of soil protists worms and insects; ie black bread mold
Sac fungi (Ascomycota)
Type of fungi, ascomycetes, mainly saprotrophs that digest resistant materials containing cellulose, lignin, or collagen; septate hyphae; produce asci, ascospores, and ascocarps; produce dikaryotic mycelium with two kinds of nuclei; ie neurospora, morels and truffles, yeasts, penicillin