Chapter 5 - The Economy & Income Security
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Economic Growth
The increase in the market value of the goods and services produced by an economy.
Measures of Economic Success
Economic growth, employment rate, inflation, and balance of trade.
Causes of Economic Growth
Increases in productivity due to new physical resources like oil, water, and minerals, and increased human resources like education and technology
Measures of Economic Growth
Real GDP (adjusted for inflation), and the growth ratio of the GDP to the population (per capita/per income)
Top 5 Areas of US Spending
Health insurance, social security, defense, economic security programs, and benefits for veterans and federal retirees.
Recession
period of reduced economic activity and negative growth rate
Sustainable v.s. Unsustainable Growth
Sustainable growth can be maintained over time without causing major problems, while unsustainable growth occurs too quickly and can lead to economic issues.
Sustainable v.s. Unsustainable Growth Examples
Investing in clean energy and infrastructure that can be maintained overtime without drastic issues v.s. the US housing boom in the 2000s that was driven by easy credit and speculation
Unemployment
The employment rate is a ratio that measures the proportion of the working-age population that is employed; heavily dependent on economic growth, varies by educational attainment and race, when in growth jobs open, when in recession jobs close
Full Employment
4-5% unemployment.
Inflation
The purchasing power of money, where high inflation means things cost more and low inflation means they cost less
Causes of Inflation
Demand-pull (demand outweigh supply), cost-push (costs for raw materials increase), excessive money supply, or global events affecting supply, when there are too few goods and services in the market and prices rise
Export
A good or service produced in one country and sold to buyers in another country, increases national income, creates jobs, improves trade balance, risk - over-reliance on exports make economies vulnerable to global downturns
Import Trade Deficit
When a nation imports more products than it exports, leading to a negative trade balance, Trump's tariff war is tumultuous
Positive Trade Balance
When the value of exports exceeds the value of imports over a specific time period, citizens believe it is better to be a net exporter
What does laissez-faire mean?
A hands-off approach where the government does not interfere in the free market; not setting wages, avoiding price regulation, not bailing up companies, markets determined only by supply and demand
Classical
A laissez-faire model where the economy regulates itself through supply and demand, advocating for austerity during recessions; failures will correct over time, use austerity in recession, spend when you have money and the economy recovers
Keynesian Approach
Deficit spending in a recession to stimulate the economy; the government should spend more to curb recessions as they will get money back in tax revenue when people start spending again/going back to work because the government is investing more heavily in the market to make the recession end faster - FDRs New Deal
Monetary Policy
Managing the supply of money in the economy, typically done by the Federal Reserve; selected by President approved by Senate, they wield power quietly and control discount rates over the banks and therefore the interest rates given to consumers
Regulation
government intervention in the decisions that firms make or in market outcomes
Price Setting
the government establishing a price ceiling or floor on an industry with limited competition; a good can only cost X amount, the US government and states set prices for Medicaid services to help control spending
Entry Restrictions
only specified firms may participate (they meet some criteria), like how you need a barbers license to cut hair
Service Obligations
minimum standards of operations for firms; attorneys must provide a set amount of pro bono work
Fiscal Policy
Taxing and spending policy enacted by the President and Congress.
Taxes
a collective action problem: society wants specific programs, but individuals may not be willing to pay for them, collected through percentages of earnings from individuals and legal entities; looking for a tax scheme that will allow for economic growth, job security, and also still provide enough revenue for government programs to operate optimally
Tax Deductions/Expenditures
people who buy a house can take deductions for interest payments for example, expenditures is basically just the government paying you money back if you meet certain criteria
Proportional (flat) Tax System
A tax system where everyone pays the same fraction of their income in taxes - Russia, Saudi Arabia, Ukraine, Estonia
Regressive Tax System
A tax system where poorer earners pay a higher fraction of their income in taxes than higher-income earners; sales taxes and sin taxes
Progressive Tax System
A tax system where lower-income earners pay a lower fraction of their income in taxes than higher-income earners.
Tax Incidence
Who pays the tax; often split between employers and employees
Laffer Curve
A hypothetical curve showing the relationship between taxation and economic activity, illustrating the optimal tax rate.
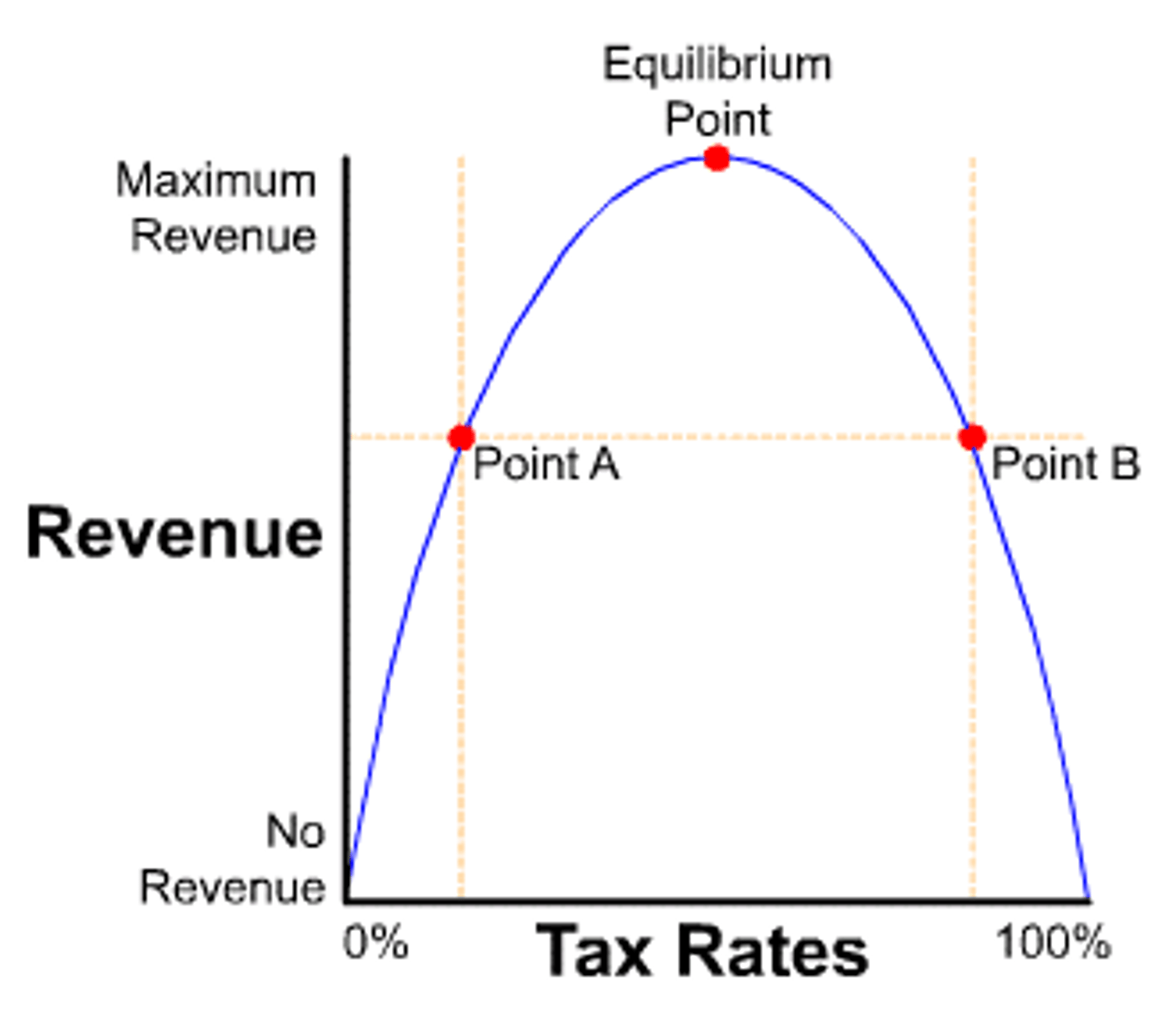
Income Inequality
The distribution of income across a population, with high inequality indicating wealth is concentrated among a small group.
Causes of Income Inequality
wage inequality due to shifts in labor demands (automation/technology), globalization (trade/tech in the international market), institutional changes (economic deregulation), education
What is the 'Veil of Ignorance' concept?
Making decisions without knowing one's future economic position to ensure fairness in policy - what do you want the system to look like if you do not know whether or not you will be rich or poor in the future or your current position, idea that we need a floor
Utilitarianism
The principle that the best policy produces the greatest good for the greatest number of people; not concerned about fairness, highest average benefit is most important
Redistribution
aking from those who have more and giving to those who have less, generally seen as less favorable by the public as compared to social security and unemployment insurance
Predistribution
Preventing inequality through measures like increasing the minimum wage and government involvement in labor markets and educational development
Collective Action Problem
The challenge of individuals being unwilling to pay for social welfare without coercion.
Social Insurance
a system of compulsory contribution to provide government assistance in sickness, unemployment, etc. - receiving benefits is conditional on payment into social insurance programs, generally viewed somewhat positively
Social Security
OASDI, 1935 act established by FDR, benefits to retired people and those who are unemployed or disabled (retirement, disability, medicare), funded by the young for the old and disabled, employers and employees pay 6.2% of wages towards this
Unemployment Insurance
1935 Social Security Act, pay for 40-50% of income for workers that lose jobs due to no fault of their own, temporary income support, generally paid by state governments, funded primarily by state and federal payroll taxes levied against employers, last 6 months
TANF
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, a program providing aid to families below the poverty line; redistributive, means-tested program, allowed 60 months in lifetime, must find a job within 24 months of enrollment, feds give money to states who have lots of say in who gets what, services include cash, child care, work/education programs
EITC
Earned Income Tax Credit, a negative income tax that provides payments to low-income individuals; you calculate taxes and then the EITC is subtracted from what you owe and if the EITC is larger than the owed taxes, you get a refund check, giving an incentive to low income people to work by taking away the de-incentivizing burden of taxes
Minimum Wage
Fair Labor Standards Act of 1937, currently $7.25, provides a baseline income for workers, critics say that it decreases an employers' willingness to employ additional people and thus leads to higher unemployment
Card and Kruger
increases in minimum wage do not increase unemployment and in fact found increases in employment in some cases
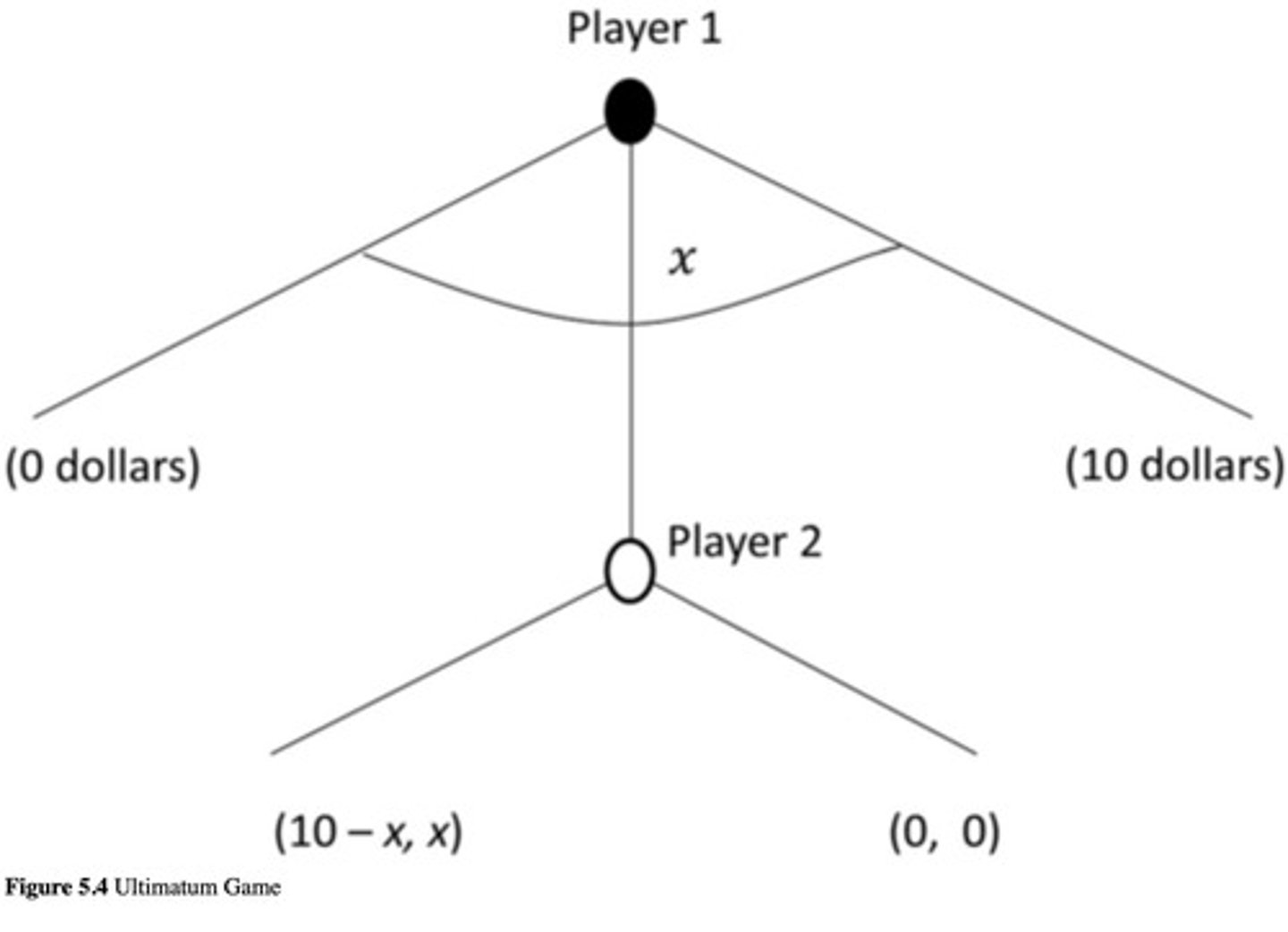
What is the Ultimatum Game in economics?
A game where one player offers a portion of money to another, who can accept or reject the offer; average is $5 given even though NE is $1, $9
What is the Dictator Game?
A game where one player decides how much money to share with another player who has no say; average is still $5 given even though $0, $10 is most ideal
Concerns with Unemployment Insurance
Adverse selection and moral hazard, where higher-risk individuals may seek benefits more often - certain industries are more likely to have unemployed workers, and people may take more risks or delay coming back to work because they are protected in part from consequences