13. respiratory pathology III
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what are consequences of disruption of air conduction in the larynx?
dyspnea
excessive breathing noise
stertor (low pitched)
stridor (high pitched)
choking
aspiration pneumonia
voice change
exercise intolerance
what is the cause of laryngeal hemiplegia in horses?
damage to vagus nerve or recurrent laryngeal nerve (often left)
cause: idiopathic or secondary to direct nerve damage
what are the consequences of laryngeal hemiplegia? what clinical sign is observed?
paralysis and eventual atrophy of cricoarytenoid muscles (dorsal and lateral)
→ inability to adduct and abduct arytenoid cartilages
“roaring”
what causes laryngitis in calves? (infectious; environmental)
infectious agents
IBR (BHV-1)
causes initial damage → allows secondary infection
fusobacterium necrophorum (“calf diphtheria”)
environmental
contact ulcers
what animals are most commonly affected by tracheal collapse?
toy breed dogs
ponies
describe the pathology of tracheal collapse. what regions of the trachea are affected? what clinical sign is associated?
defect in tracheal rings → dorsoventral collapse of trachea with trachealis stretching
may be segmental (cervical or thoracic) or diffuse
clinical sign: dry, honking cough
causes of tracheitis in cattle
IBR (BHV-1)
(malignant catarrhal fever - MCF)
chemical burn from drench
causes of tracheitis in horses
equine influenza
EHV-1
causes of tracheitis in dogs/cats
dogs
canine infectious tracheobronchitis (“kennel cough”)
many agents may be involved → mainly, bordetella bronchiseptica
(canine parainfluenza, canine adenovirus-2, others)
canine distemper (uncommon)
cats
FHV-1
secondary bacterial infection (ex. pasteurella multocida)
causes of tracheal stenosis
chronic tracheitis or trauma with scarring & fibrosis
ex. over-inflated ET tube cuff
neoplasia (extraluminal or intraluminal) → rare
what is the difference between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disease?
obstructive → increased resistance to or blockage of airflow
restrictive → characterized by limited lung inflation/expansion due to lung or thoracic cavity abnormalities
microscopically → anything that thickens alveolar septae
or
macroscopically, outside of lungs (ex. mass, fluid) that restricts inflation
what are examples of obstructive respiratory diseases?
bronchitis / bronchiolitis
asthma
alveolar emphysema
other airway obstruction
what are examples of restrictive respiratory diseases? (lung abnormalities & thoracic abnormalities)
lung abnormalities
pulmonary fibrosis
interstitial edema / pneumonia / emphysema
thoracic (non-pulmonary) abnormalities
thoracic deformities (e.g. pectus excavatum)
pleural effusion
pleuritis
intrathoracic masses
bronchitis / bronchiolitis pathology
bronchitis and tracheitis often concurrent
exudate in lumen can obstruct airways
submucosal inflammation may narrow airway lumen
reflex bronchoconstriction also reduces diameter
what is the result of bronchitis and bronchiolitis?
↑ resistance and ↓ alveolar ventilation
what general categories of infectious agents can cause bronchitis/bronchiolitis?
viral
bacterial
parasitic
what are viral causes of bronchitis / bronchiolitis? describe pathology
often same causes as tracheitis
cattle: BHV-1
cats: FHV-1
usually necrotizing lesions, loss of epithelial cells + cilia → secondary bacterial infection
what bacteria is associated with bronchitis/bronchiolitis? what is its associated pathology?
mycoplasma sp.: organisms associate with cilia
m. bovis, dispar (cattle)
(m. hyopneumoniae - pigs)
continued neutrophil infiltration and submucosal lymphocyte proliferation
what causes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) aka “heaves” in horses?
environmental antigens: fungal spores, hay dust
what are clinical signs of “heaves”?
exercise intolerance
coughing
expiratory dyspnea
external abdominal oblique hypertrophy (heave line)
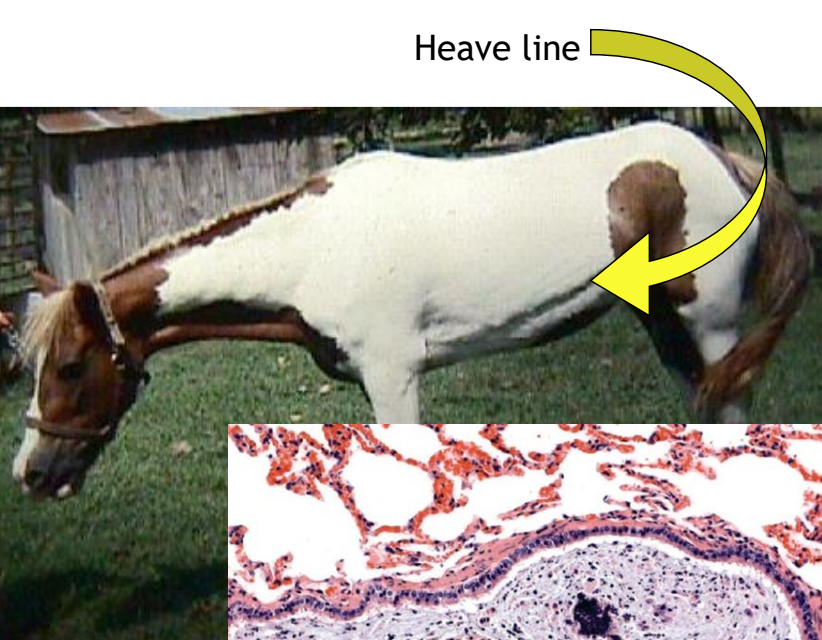
gross pathologic findings of “heaves”
lack of lung collapse when opening thorax
mucus in bronchioles
peribronchiolar fibrosis
what are potential outcomes of chronic bronchitis/bronchiolitis?
bronchiolitis obliterans
bronchiectasis
what is bronchiolitis obliterans?
obstruction of bronchiolar lumen by connective tissue following severe damage to bronchioles and alveoli
healing by fibrosis
blocks airflow to alveoli, reduces vital capacity
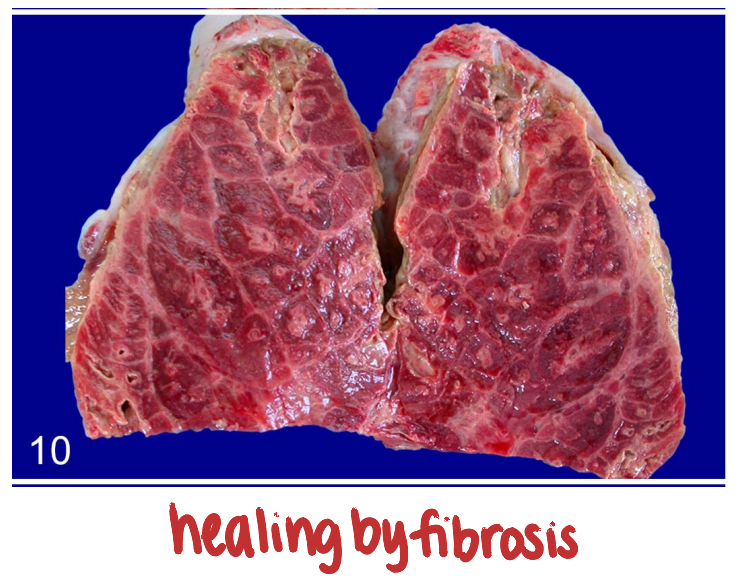
bronchiolitis obliterans sequence of events (pathogenesis?)
necrosis of epithelium with ulceration, delayed repair
exudate rich in fibrin and chemotaxins
macrophages, fibroblasts, endothelial cells proliferate
organization of exudate by granulation tissue
forms obstructive plug
what is bronchiectasis? what is it associated with?
dilation of bronchi beyond normal diameter due to wall destruction
inflammatory cell-mediated damage to wall
associated with chronic bacterial bronchitis
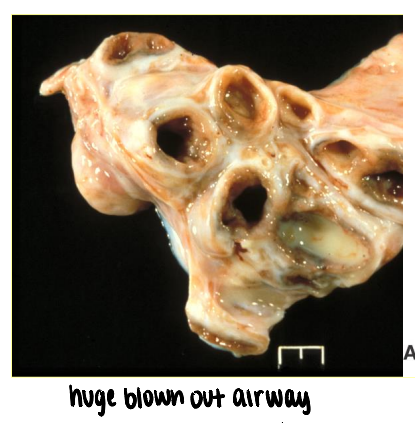
what are consequences of bronchiectasis?
results in increased turbulence of airflow →
increased resistance
impaired mucociliary clearance
deeper penetration of lung by infectious agents
can develop deeper pneumonia