DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Unit
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hard unit uh oh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
What is the function of DNA?
Contains genetic material that controls the production or synthesis of proteins.
Genes are regions in the DNA that contain the instructions for the formation of protein.
Location of DNA in cells?
Eukaryotic - In nucleus
Prokaryotic - In cytoplasm
What did scientists Watson and Crick do for DNA discovery?
They built a model of DNA and published a paper in April, 1953.
What did scientists Wilkins and Franklin do for DNA discovery?
Used X-ray crystallography to study the structure of DNA; famous photograph took by Franklin called ‘Photo 51’
What did scientist Avery do for DNA discovery?
Discovered in the mid-1940’s that DNA carries genetic information
What did scientist Chargaff do for DNA discovery?
Discovered in 1950 that the amount of adenine equals the amount of thymine and the amount of cytosine equals the amount of guanine.
Chargaff’s Rule
Base-pairing rule that states Adenine binds with Thymine, and Cytosine binds with Guanine.
Mnemonics:
For Adenine and Thymine: Apples in a Tree
For Cytosine and Guanine: Cars in a Garage
How do you do a Chargaff’s rule percentage problem?
You would first be given a percentage of one of the nitrogen bases.
You would then need to find the nitrogen bond that binds with their complementary bond and equals the same as each other according to Chargaff’s rule; ex. Cytosine is 30%, so Guanine is 30% as well.
Then for the remaining number of percentages, divided them by two and make into the other two nitrogen bases; ex. If Cytosine and Guanine is 60% total, then Adenine and Thymine will each have 20%, that total to 40%, since they’re equal amounts
Results: Cytosine - 30% Guanine - 30% Adenine - 20% Thymine - 20% (Make sure they equal 100%)

What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What biomolecule and monomer is DNA?
DNA is a type of nucleic acid; they are made up of nucleotides
Parts of a nucleotide of DNA?
Phosphate group
Deoxyribose sugar
Nitrogen Base
What are the four types of nitrogen bases found in DNA called?
Adenine (A)
Thymine (T)
Cytosine (C)
Guanine (G)
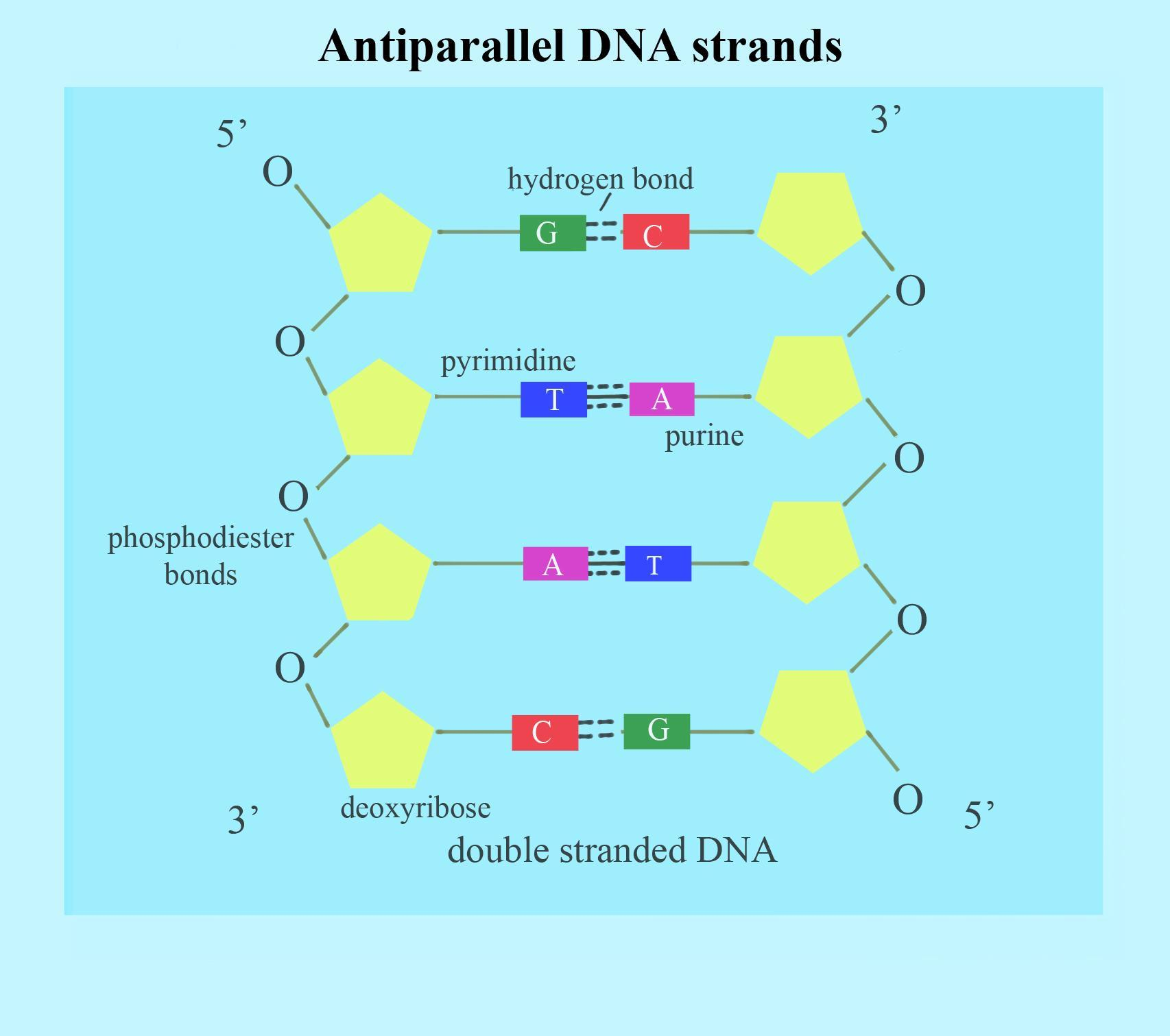
What are the sides of DNA made of? What are the ‘rungs’ or steps of the DNA made of?
Sides: Repeating Phosphate and Sugar
Rungs/Steps: Nitrogen bases
What is the DNA’s shape called?
Double helix
What are bases held together by and why are they weak?
They’re held together by weak hydrogen bonds. They’re weak because so that way they could separate for DNA replication and transcription.
What way does two strands of nucleotides run in?
Antiparallel
What are purines?
A type of nitrogen base with two rings of carbon and nitrogen; ex. Adenine and Guanine
Mnemonic: AnGels are so pure they have two halos (rings)
What are pyrimidines?
A type of nitrogen base with a single ring of carbon and nitrogen; ex. cytosine and thymine
Mnemonic: Py-rates have 1 eye patch (ring) and Uncover Treasure Chests
Why does DNA replication happen?
To ensure that the daughter cell produced during cell division each have an exact copy of all protein recipes.
Where does DNA replication happen in Eukaryotic cells? Prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic - In the nucleus
Prokaryotic - In the cytoplasm
When does DNA replication occur?
Before cell division (Mitosis/Meiosis)
Process of DNA Replication?
An enzyme called DNA Helicase unwinds the DNA and breaks the hydrogen bonds in between the nitrogen bases.
The two strands of DNA separate.
Another enzyme called DNA polymerase binds free-floating nucleotides to complementary bases on each strand.
Two EXACT DNA molecules are formed.
What is semi-conservative replication?
A process in which each DNA molecule produced after DNA replication has one old strand and one new strand.
What is the function of RNA?
The genetic material that helps carry instructions from the DNA to build proteins.
What does RNA stand for?
Ribonucleic acid
What biomolecule is RNA and what is its monomer?
It is a nucleic acid; made up of nucleotides
What is the sugar in RNA called?
Ribose sugar
What are the four nitrogen bases found in RNA?
Adenine
Uracil
Cytosine
Guanine
How many strands is RNA made of?
A single strand
Where is the location of RNA in Eukaryotes? What about Prokaryotes?
Eukaryote - In the nucleus
Prokaryote - In the cytoplasm
What could RNA do that DNA could not?
RNA can leave the nucleus, while DNA cannot.
Types of RNA?
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Codon
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
- Anticodon
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
What is messenger RNA (mRNA)?
The recipe card that carries the message containing directions for making on protein.
What is condon on mRNA?
Three nitrogen bases on mRNA that codes for a specific amino acid (protein monomer).
What is transfer RNA (tRNA)?
Acts like a delivery truck that carries amino acids (protein monomer) to the ribosome.
What is anticodon?
Three nitrogen bases on tRNA.
What is ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
What ribosomes are made of.
Two steps of protein synthesis?
Transcription - Copying down the protein recipe
Translation - Creating the protein
Analogy for DNA, genes, and mRNA?
DNA is like a recipe book with all the recipes the cell needs to create proteins.
A gene is one protein recipe
mRNA is a copy of a protein recipe that is sent to the kitchen to be cooked
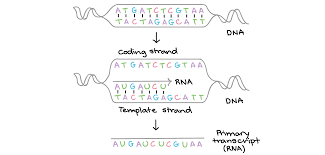
What is transcription?
The process of copying a gene from DNA and mRNA. Occurs inside nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells.
Process of Transcription?
The enzyme DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between the DNA base pairs to unwind the double helix.
RNA polymerase reads the template strand
mRNA is built.
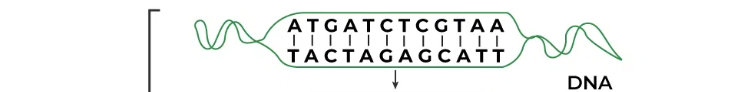
What bases in DNA binds with template DNA during transcription?
Adenine binds with Thymine
Thymine binds with Adenine
Cytosine binds with Guanine
Guanine binds with Cytosine
What bases in DNA bind with RNA during transcription?
Adenine binds with Uracil
Thymine binds with Adenine
Cytosine binds with Guanine
Guanine binds with Cytosine

What bases in mRNA bind with tRNA during translation?
Adenine binds with Uracil
Uracil binds with Adenine
Cytosine binds with Guanine
Guanine binds with Cytosine
What is translation?
The process in which ribosomes produce proteins based on the genetic code (protein instructions) of the mRNA.
Process of translation?
mRNA leaves the nucleus and hooks onto a ribosome. tRNA grabs the amino acid that matches the codon and delivers to the ribosome.
The tRNA delivers the ribosome that matches the codon and delivers it to the ribosome. More and more amino acids are added that are held together by peptide bonds (which are broken).
End when ribosomes encounter a stop codon, completing translation and creating a protein.

How does a ribosome know the sequence of amino acids to build
By translating a mRNA protein sequence.
How to read a codon chart?
Find the first letter in the horizontal row
Find the second letter in the vertical column
Find the third letter in a box within the horizontal and vertical
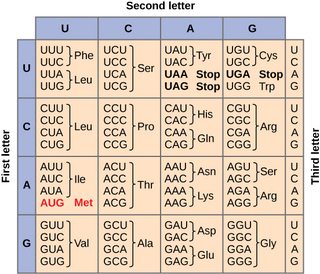
What if you were given something like this?
DNA: CGA CTT CCA GTC TCT
DNA (template):
mRNA (condons which requires codon chart):
tRNA (anticondons)
Amino acid:
DNA: CGA CTT CCA GTC TCT
First convert the DNA into the template strand according to Chargaff’s rule
DNA (template): (GCT GAA GGT CAG AGA)
Then, convert according to transcription. Adenine converts to Uracil this time, but Thymine still remains and converts and Adenine.
mRNA (condons which requires codon chart):
(CGA CUU CCA GUC UCU)
tRNA (anticondons): (GCU GAA GGU CAG AGA)
Thirdly, convert the condons from the mRNA into amino acids, using the condon chart (the dashes are the peptide bonds)
Amino acid: (arg - leu - pro - val - ser)
Finally, use translation rules to convert mRNA into tRNA. Thymine is completely gone and replaced with Uracil, so now Adenine binds Uracil.
What are some things you need to watch out for when converting mRNA to protein/amino acid?
It always has to start with the condon ‘met’, if not, then a protein synthesis cannot happen.
If there is a stop codon, ‘drop your pencil’ and stop listing it down.
If there is any condons in front of ‘met’ then that is removed.
Similarities and differences of DNA v. RNA?
Similarities:
Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids.
Both are made up of nucleotides.
Both contain genetic information.
Differences:
DNA is deoxyribose sugar, while RNA is ribose sugar.
DNA bases are Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine, while RNA bases are Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, and Guanine.
DNA is double stranded while RNA is single stranded.
DNA is located inside of nucleus while RNA can leave the nucleus to go into the ribosome.
Do all cells in a organism have the same DNA? What is gene expression?
Yes, they do; Gene expression is when certain parts of the DNA are ‘turned on’ or ‘turned off’ in regards to creating protein. Key component to cell differentiation.
What is mutation and mutagens?
Mutation - Any change in the sequence of nitrogen bases in DNA
Mutagens - Something that causes mutations
Factors that cause mutations?
Random mistakes during replication, transcription, etc.
Radiation
Chemicals (Tar)
Viruses (HPV)
Inheritable vs not inheritable mutations in DNA?
Inheritable: Reproductive cell mutations become part of future offspring’s and are inherited, called germ cell mutations.
Not inheritable: Body cell mutations are not passed on to offspring, but can cause problems for the individual who has a body cell mutation, called somatic cell mutations.
Types of Mutations
Point mutations: When one nitrogen base is substituted for a different nitrogen base.
Frameshift mutations: Caused by insertion of an extra nitrogen base or a deletion of a nitrogen base. Shifts the ‘reading frame’.
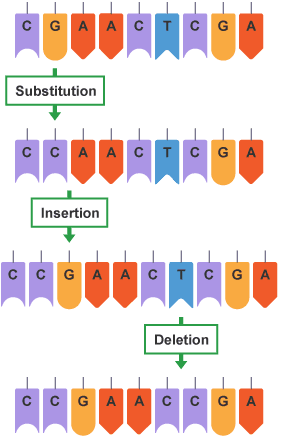
Types of substitution mutations?
Missense mutation - When the substitution changes the amino acid
Silent mutation - When the substitution does not change the amino acid
Nonsense mutation - When the substitution changes the amino acid to a ‘stop’ prematurely
Types of mutations of chromosomes?
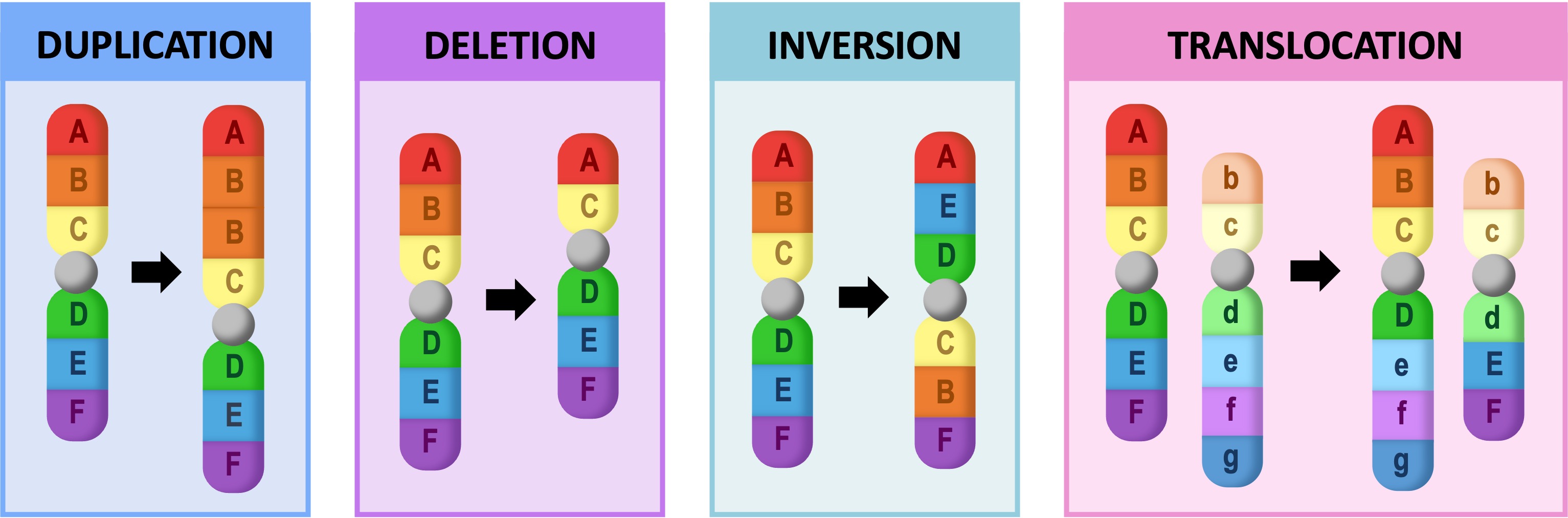
Deletion: A portion of the chromosome is missing or deleted
Duplication: A portion of the chromosome is duplicated, resulting in extra genetic material
Translocation: A portion of one chromosome is transferred to another chromosome.
Inversion: A portion of chromosome has broken off, turning upside down and reattached.