L5: Cellular Energetics
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Q: What is bioenergetics?
A: how cells produce, store, and use energy based on the laws of thermodynamics.
- capture (respiration, photosynthesis)
- storage (ATP, NADH, proton gradient)
- conversion (light, chemical, kinetic)
Q: What is the first law of thermodynamics?
A: Energy cannot be lost within the Universe; it can only be converted from one form to another.
Q: What is the second law of thermodynamics?
A: Every energy transfer increases the entropy (chaos) of the Universe.
Q: What is Gibbs free energy (G)?
A: The portion of a system's energy that can perform work, with spontaneous processes decreasing G (Δ𝐺<0).
Q: What is the role of ATP in cells?
A: ATP acts as the energy currency, coupling energy-releasing reactions with energy-requiring processes.
Q: How does ATP release energy?
A: By hydrolyzing its outermost phosphate group, forming ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi).
Q: What is chemiosmosis?
A: movement of ions down their electrochemical gradient across a semipermeable membrane
used to produce ATP
Q: What are the stages of cellular respiration?
A: Glycolysis, the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation.
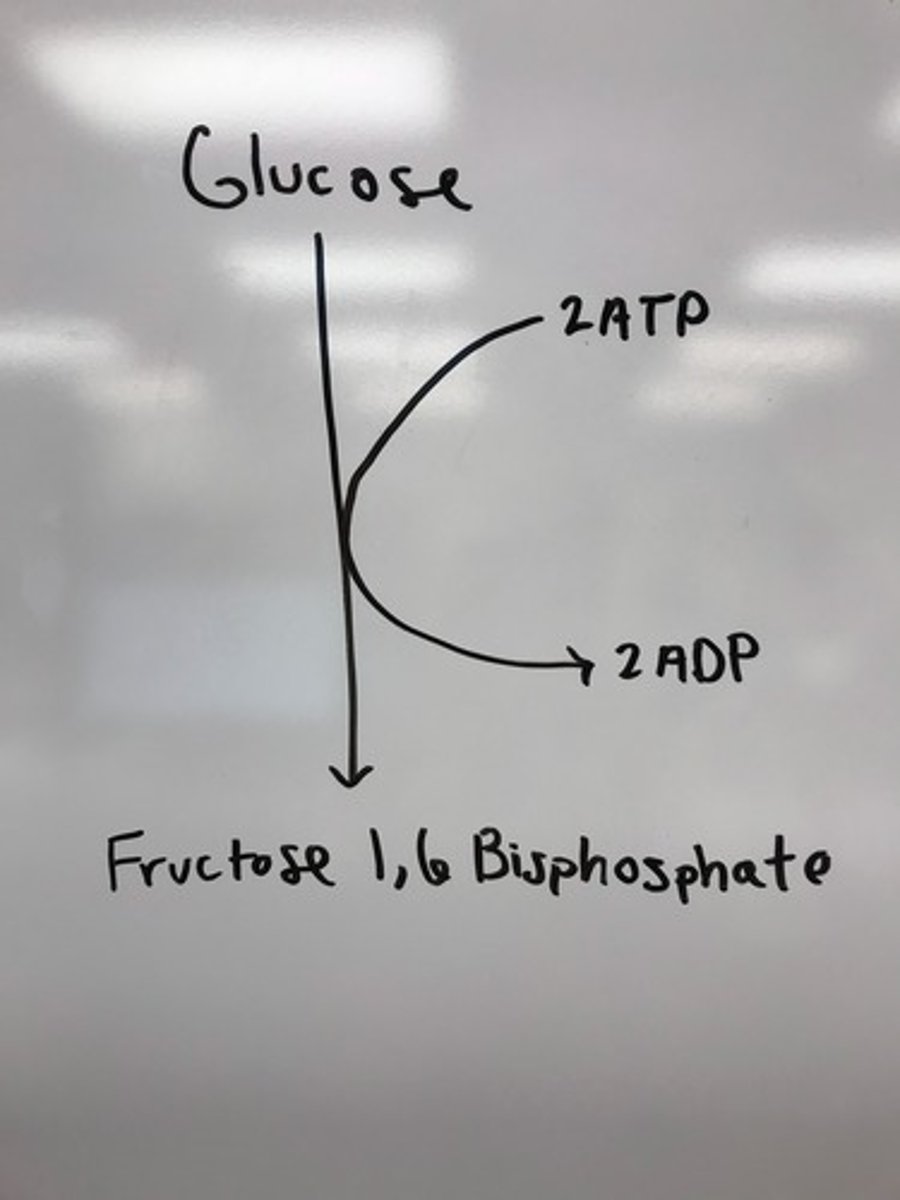
Q: What is glycolysis?
A: A process that breaks down glucose (6-carbon) into two pyruvate molecules (3-carbon) while producing 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
Q: What are the key steps of glycolysis?
Step 1: ATP phosphorylates glucose (enzyme: kinase).
Step 4: Glucose splits into two 3-carbon molecules (enzyme: lyase).
Step 6: NADH is produced (enzyme: dehydrogenase).
Step 10: ATP is produced from substrate-level phosphorylation (enzyme: kinase).
Q: What is the role of the citric acid cycle?
A: To oxidize Acetyl-CoA into CO₂ while producing 3 NADH, 1 FADH₂, and 1 ATP per cycle.
Q: What happens in the link reaction?
A: Pyruvate is converted into Acetyl-CoA, producing 1 NADH and releasing CO₂ per pyruvate.
Q: What is the electron transport chain (ETC)?
A: A series of protein complexes in the inner mitochondrial membrane that transfer electrons to oxygen, forming water.
Q: What is the proton gradient in chemiosmosis?
A: A high concentration of H⁺ ions in the intermembrane space that flows back through ATP synthase, driving ATP production.
Q: How much ATP is produced by oxidative phosphorylation?
A: Approximately 30-32 ATP per glucose molecule.
Q: What is fermentation?
A: An anaerobic process that regenerates NAD⁺ and produces 2 ATP per glucose through glycolysis.
Q: What is NAD⁺ and NADH's role in cellular respiration?
A: NAD⁺ captures electrons in redox reactions to form NADH, which donates electrons to the ETC.
Q: What is the overall reaction for cellular respiration?
A: 𝐶6𝐻12𝑂6 + 6𝑂2 → 6𝐶𝑂2 + 6𝐻2𝑂, with Δ𝐺= −2870kJ/mol
Q: Why is oxidative phosphorylation more efficient than fermentation?
A: It uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor, enabling the production of up to 32 ATP per glucose versus 2 ATP in fermentation.
Q: What is the role of enzymes in metabolism?
A: Enzymes catalyze reactions by lowering activation energy, regulate pathways via feedback, and are controlled by gene expression or modification.
Q: What is the importance of redox potential in respiration?
A: Electrons are transferred from molecules with lower to higher electronegativity (e.g., sugars to oxygen), releasing energy used for ATP production.
Q: What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
A: The direct transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from a phosphorylated substrate to form ATP.
Q: What is the significance of the proton gradient in ATP synthesis?
A: The gradient provides energy for ATP synthase to convert ADP and Pi into ATP during chemiosmosis.
Not all forms of energy can be converted into biologically relevant work (e.g. movement/growth) -
An organism loses some of its energy to the environment (typically heat)
An organism fixes some of its energy irreversibly (e.g. animal growing hair)
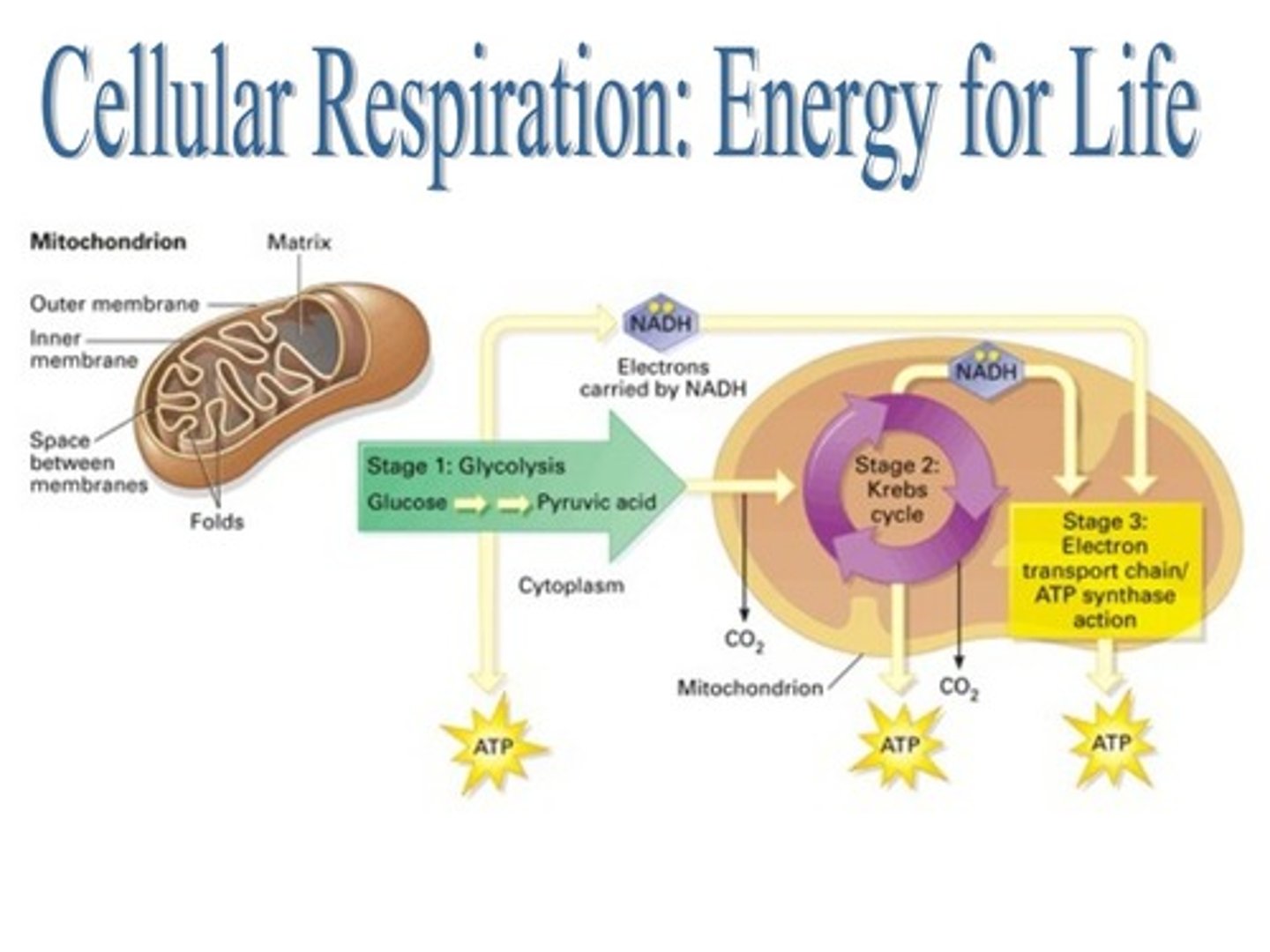
Cellular respiration:
metabolic process with which an organism obtains energy by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products
Metabolism =
totality of organism’s chemical reactions via anabolic and catabolic pathways
Anabolism:
use energy to build complex molecules
e.g. protein synthesis from amino acids
Catabolism:
release energy through molecule breakdown
e.g. breakdown of glucose in glycolysis
Gibbs Free Energy Rule:
A reaction/transport process only occurs spontaneously if it decreases G (if ΔG is negative).
Gibbs Free Energy Equation
ΔG = ΔH - T ΔS

endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings: +ΔG
Does not occur spontaneously

enzymes lower a_________ e________(Ea) required to kickstart a reaction
activation energy
Enzyme negative feedback loop
enzymes are usually inhibited by the end product
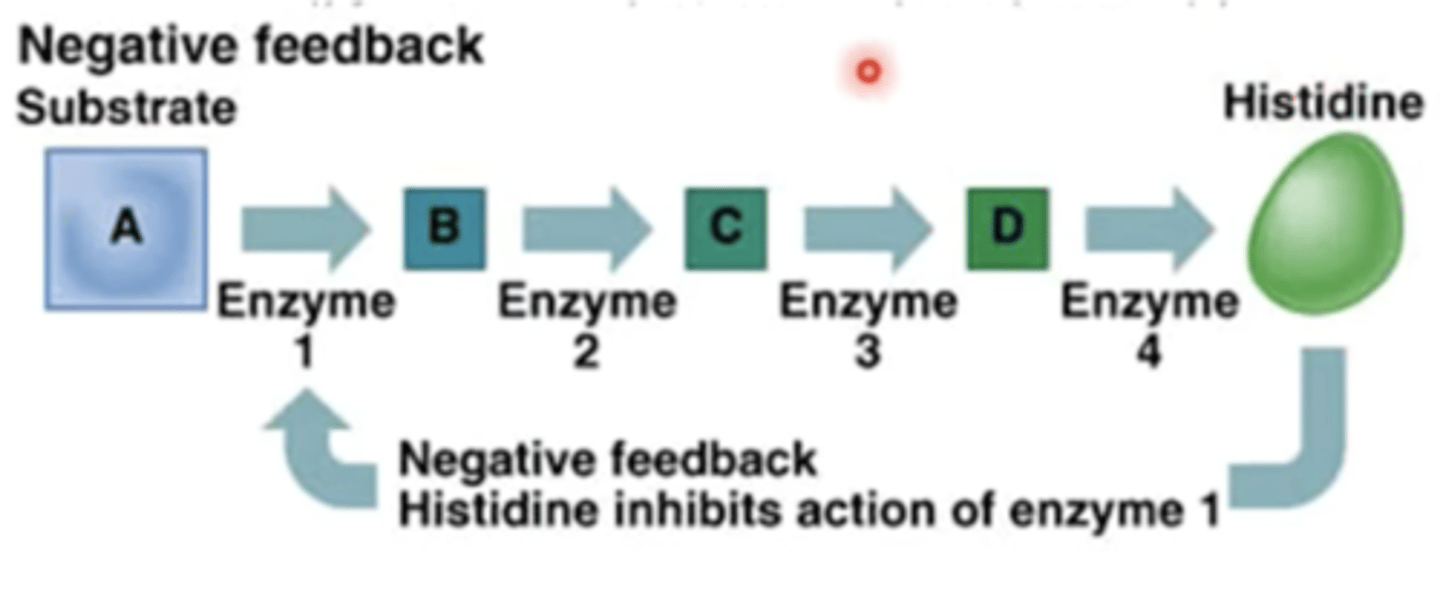
enzymes are regulated by:
- pH
- gene expression and protein modification (e.g. phosphorylation )
why is chemical energy stored in the outermost Pi group?
negative charges repel each other
how is ATP formed?
1. Substrate-level phosphorylation
(transfer of phosphate group)
e.g. glycolysis: phosphoglycerokinase
2. Oxidative phosphorylation (Chemiosmosis)
e.g. ATP synthase in inner mitochondrial membrane
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP

redox potential
storage of energy - the tendency of a molecule to acquire electrons
electronegativity
affinity of an atom to uptake or release e- from outer shell
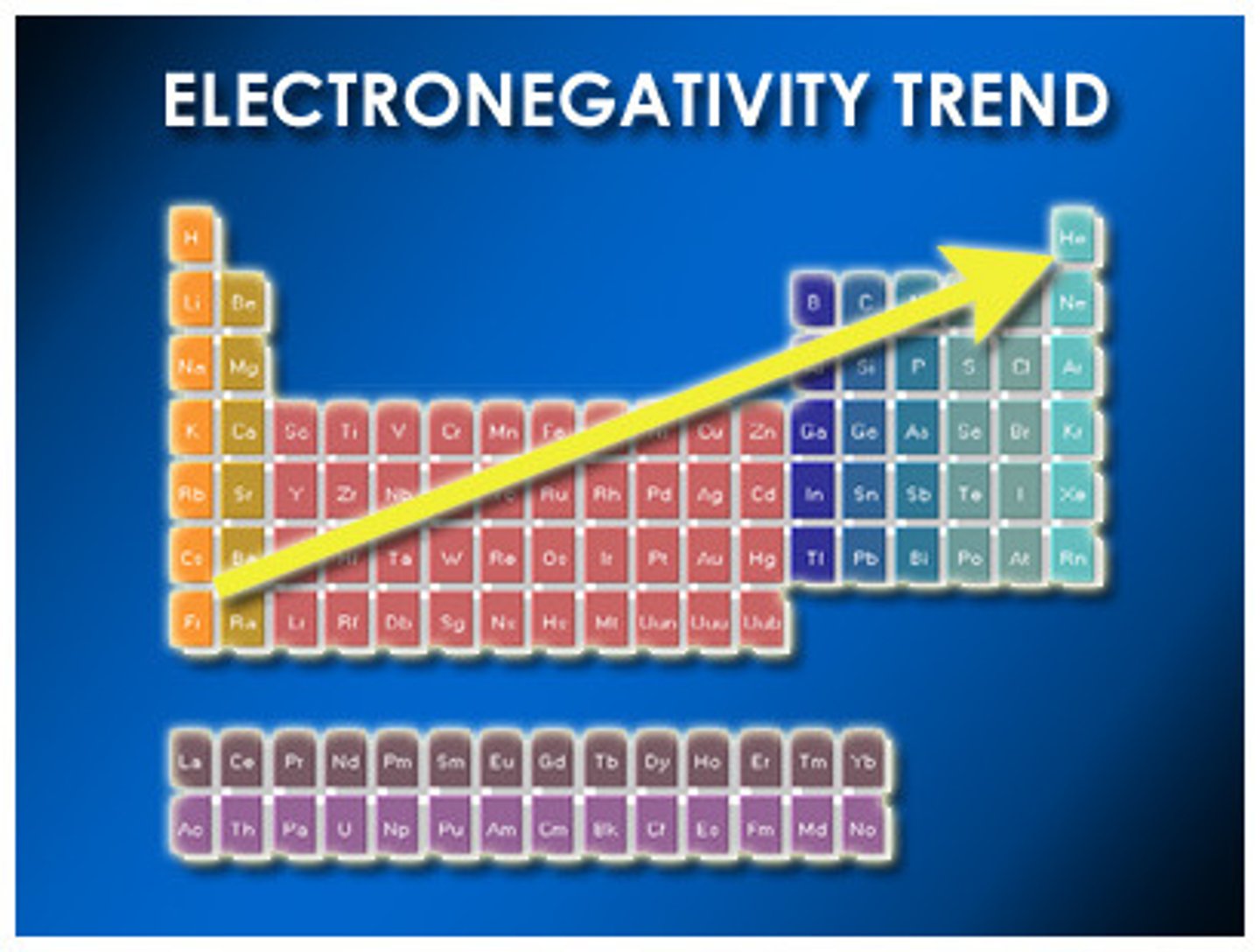
what does relocating e- from sugars (weakly electronegative) to oxygen (strongly electronegative) do?
releases energy
obtains electron
reduced
loses electron
oxidised
oxidative phosphorylation
production of ATP using energy from redox reactions of electron transport chain
third major stage of cellular respiration
energy investment phase
Initial phase of glycolysis consuming ATP - uses 2 ATP
ATP is formed by s____- l______ and o_____ p_______ of ADP and acts as an e_____ c_______
substrate-level
oxidative phosphorylation
energy currency
NAD+ captures e______ from r_____ reactions and in the form of N___ delivers them to the electron transport chain
electrons
redox
NADH
1. The electron transport chain establishes a p____ g______ across the inner membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts
2. H+ flow back through membrane-bound A__ s______ which produce ATP
3. The trans-membrane H+ gradient acts as a ‘h__- e____’ i______ between redox potential and ATP synthesis
proton gradient
ATP synthases
high energy intermediate
Cellular respiration can be divided into three stages:
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
Cellular respiration produces approximately ? ATP per glucose
30-32 ATP
Under anaerobic conditions, glucose is fermented and only produces ? ATP per glucose
2 ATP